All about the black cotoneaster
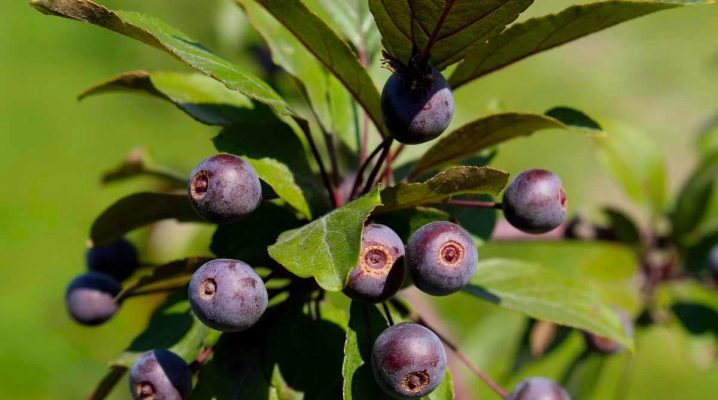

Black cotoneaster is an unpretentious shrub that has the ability to perfectly tolerate frost and heat. Thanks to this, the plant is successfully grown almost throughout the territory of Russia.
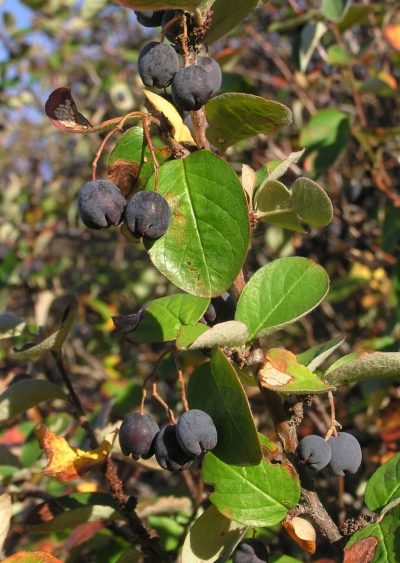

Description
Black cotoneaster (in Latin Cotoneaster melanocarpus) is a plant of the genus of thornless shrubs of the Pink family. There are several other names for this shrub among the people: champolnik, tarsum, kouroslep.
An adult plant can reach 2 meters in height (under favorable conditions and higher), while the crown of the shrub has the ability to spread up to one and a half meters in diameter.
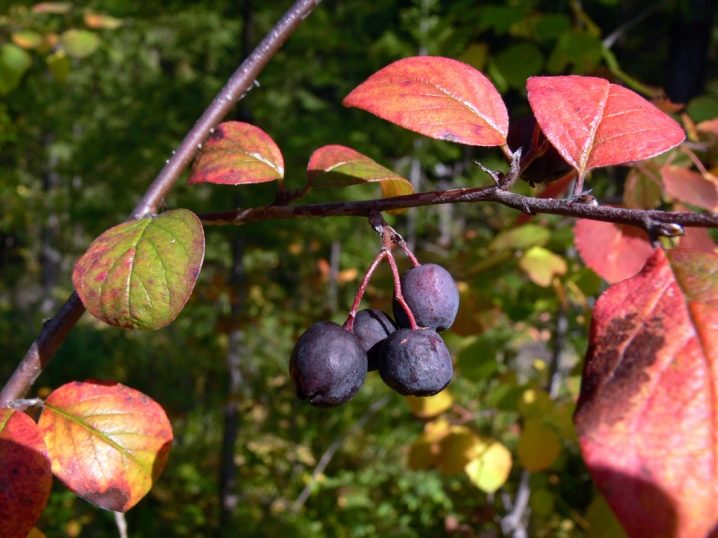

Black cotoneaster is a frost-resistant shrub that is completely undemanding to the soil. It grows well even in infertile soils. It can also thrive in shaded areas. The bush lives up to 50-60 years.
The area of growth of the black-fruited cotoneaster is very extensive, it can often be found in the territory from the Himalayas to the Caucasian foothills, in the Far East, in central Russia, Eastern and Western Siberia. Loves sandy, mountainous, calcareous soils. The shrub grows on rocky slopes, in mixed forests, on limestone ledges.
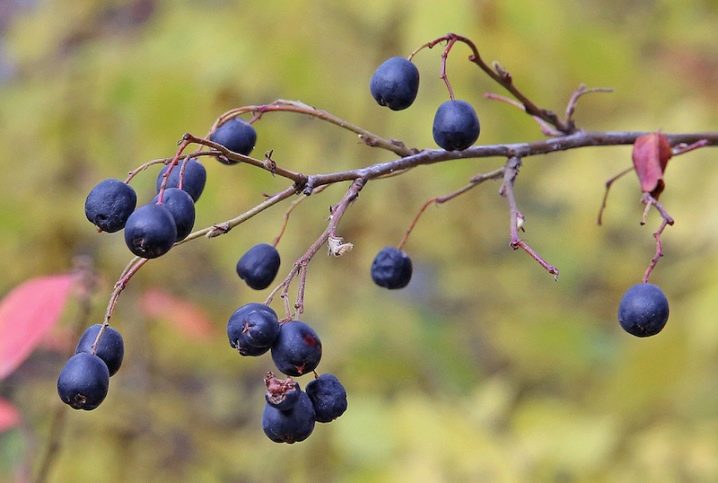

It is limestone that has a very beneficial effect on the development of the cotoneaster. Therefore, during cultural cultivation, they try to add lime to the soil mixture.
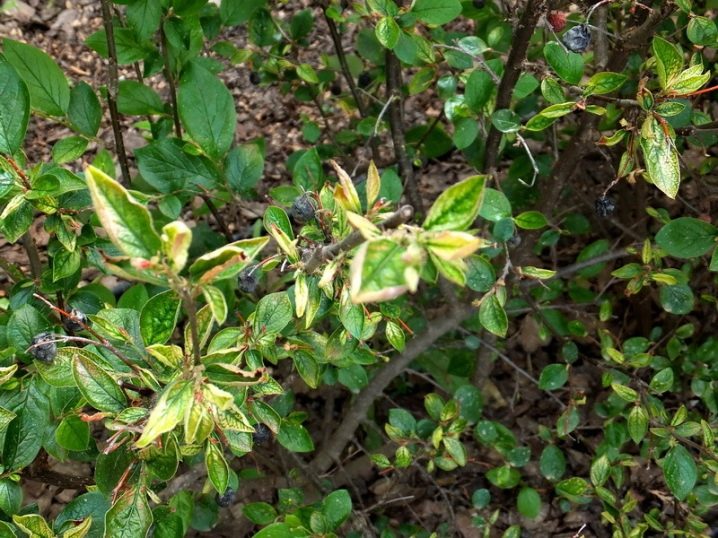
The bush has ovoid leaves with clear veins. The leaves have a flat front side, without depressions and protrusions, and a rough surface on the back side. The size of the sheet is approximately 4 centimeters. During the summer, the leaves are dark green in color, and in the fall they change color, becoming bright purple. Thanks to this, the cotoneaster looks very attractive and elegant.
In the spring, oblong, conical buds form on the branches. Their length reaches 6-7 millimeters. The buds are hairy, scaly.

The flowering shrub begins at the end of May and lasts about 4 weeks. Small-sized white-pink flowers are collected in 5-12 corymbose inflorescences. After flowering, fruit ovaries of the bush are formed. The flower formula coincides with the formulas of other plant species of the cotoneaster genus.
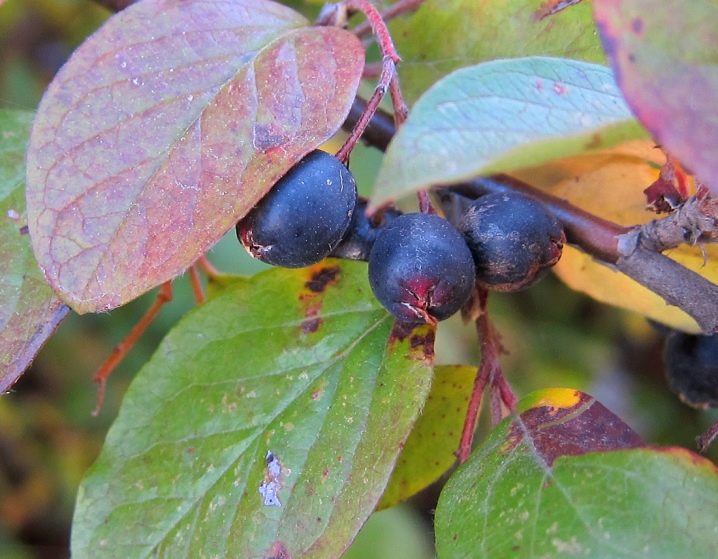
Berries are formed only 5 years after the plant is planted. But in subsequent years, even if the weather conditions are not very favorable, the shrub blooms profusely and bears fruit well. Unripe, rounded fruits are brown in color. When they ripen, they become bluish-black in color.
Ripe fruits can be harvested in late October or November. Quite often, the berries winter right on the branches of the bush. Therefore, in winter, the black cotoneaster looks very decorative.

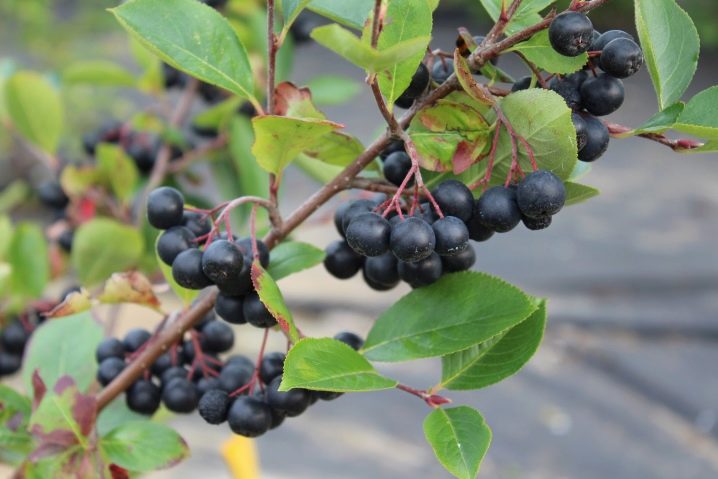
Despite the fact that cotoneaster berries are edible, they are rarely eaten. This is due to the taste, which is very bland. But in terms of the content of nutrients, trace elements and vitamins, this is a very valuable fruit. Therefore, ripe fruits are dried and a powder is prepared from them, which is added to starch or flour during the preparation of various baked goods. And also can be used in the manufacture of sweets, cakes, marshmallows, pies and more. It is dry berries that acquire an unusual taste.
Cotoneaster fruits are added to tea, using its beneficial properties. For this purpose, fresh, frozen or dried berries can be used.Sometimes homemade alcoholic drinks are stained with a cotoneaster.

Black cotoneaster is actively used in traditional medicine recipes. In this case, all parts of the shrub, except for its root, are considered healing. The young bark of the plant, its leaves, buds, flowers have good antibacterial properties. Black fruits are rich in acids useful for humans: phenolcarboxylic, ascorbic and others. They are also used as an astringent to help with dysentery and indigestion. In addition, cotoneaster berries are very effective in disrupting the functioning of the intestines, manifestations of flatulence.
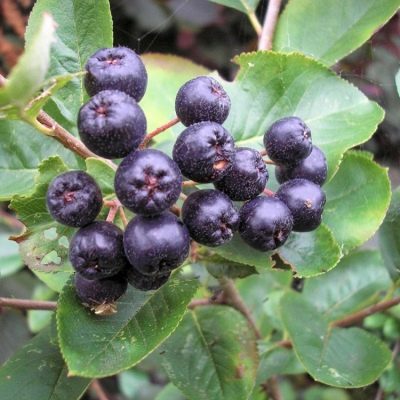

The leaves contain flavonoids, vitamin C and glycoside, they are usually used with young shoots of a shrub. Residents of the Far North from the leaves with twigs get resin, which is used to treat various skin diseases.
Landing
The black cotoneaster can be propagated by seed or cuttings. You can plant one- or two-year-old seedlings.
In the area where the planting will take place, groundwater should not be too close to the surface. And also in the pit it is necessary to form a drainage layer. If you plan to create a hedge, then it is more advisable to use a moat instead of several holes.
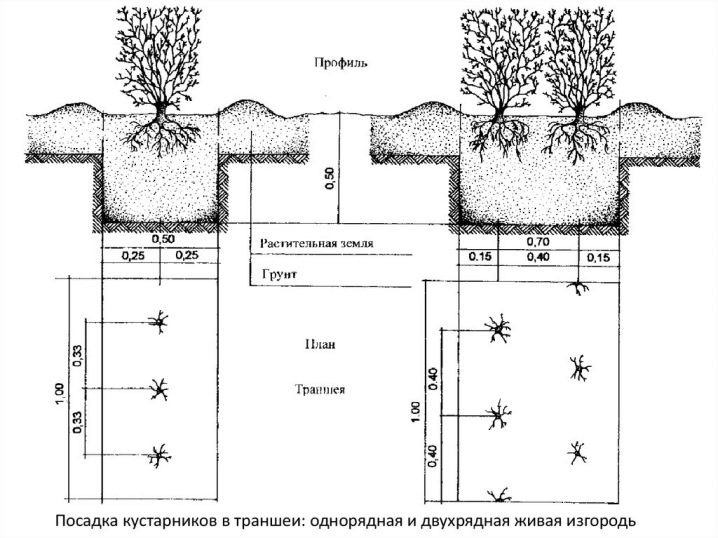
Seed viability is approximately 80%. In the case of planting with seeds, they initially need to be mixed with peat and clean sand, placed in a prepared box and moistened. The layer thickness of the seed mixture should be approximately 30-40 centimeters. The seeds should be in this box for 1-2 months at a temperature of about zero degrees. Sulfuric acid can be used to reduce the time required for stratification. For this, the seeds are processed for 5-20 minutes.

Another option for seed propagation is to soak them in water. Further, when sowing, the seeds are immersed in the ground to a depth of 0.5-1 centimeters (that is, in the immediate vicinity of the surface). Next, the soil is covered with another 1 centimeter thick layer of sand. Seeds need to be moistened from time to time, watering should be as careful as possible. Young seedlings require protection from too cold air and direct sunlight.
Cuttings are usually poorly rooted. Therefore, this method of breeding cotoneaster is not used very often.

The plant is easily transplanted without harm to growth and general condition. When planting, it is worth adhering to a distance of at least one meter between individual plants.
Care
The cotoneaster is very unpretentious, so caring for it will not be difficult even for a novice gardener. The bush must be fed, pruned and watered sparingly.
Black cotoneaster perfectly tolerates drought, so it does not require abundant watering. In order for the plant to feel comfortable, it is enough to water it once every two weeks, even in hot summer without rain. Watering is carried out at the rate of one bucket of water per one bush. If it rains periodically, then the plant can be watered less frequently (once a month) or not watered at all if rainy weather is observed frequently.

You need to feed the black cotoneaster at least once a season. The best time for this procedure is spring. You can prepare a solution consisting of 25 grams of urea and 10 liters of water. It is applied to the root zone of the plant. Before flowering, you can feed the bush with potassium fertilizer. Peat mulching can be done in autumn.
The shrub tolerates seasonal pruning without problems. In order to prevent uncontrolled growth of young shoots, they are shortened 1-2 times during the summer season. Pruning can be of two types: formative and sanitary. With annual formative pruning, branches that are too long are removed to make the shrub look neat. Sanitary pruning involves the removal of damaged and diseased shoots.
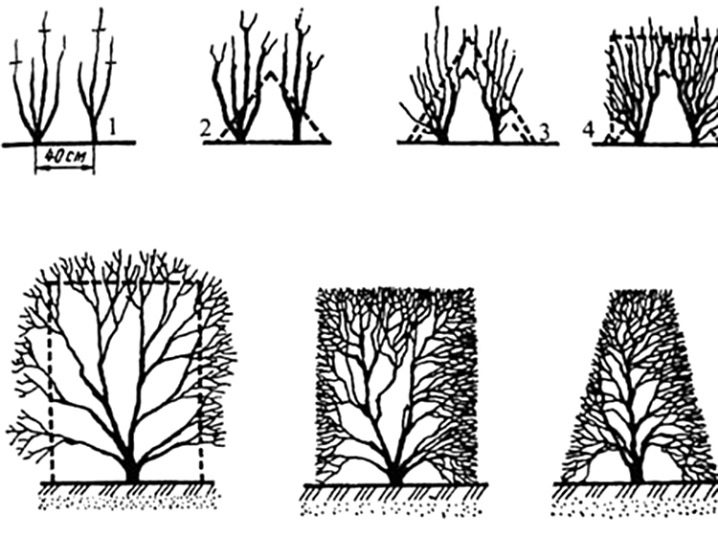
The plant is quite resistant to diseases and pests. Due to the high humidity, the cotoneaster can undergo fusarium, which is a fungal disease. Of the pests, the most dangerous are spider mites, aphids, and scale insects. Timely processing helps to easily deal with this problem. In some cases, as a preventive measure, healthy shrubs can be treated with a solution of laundry soap or ash.

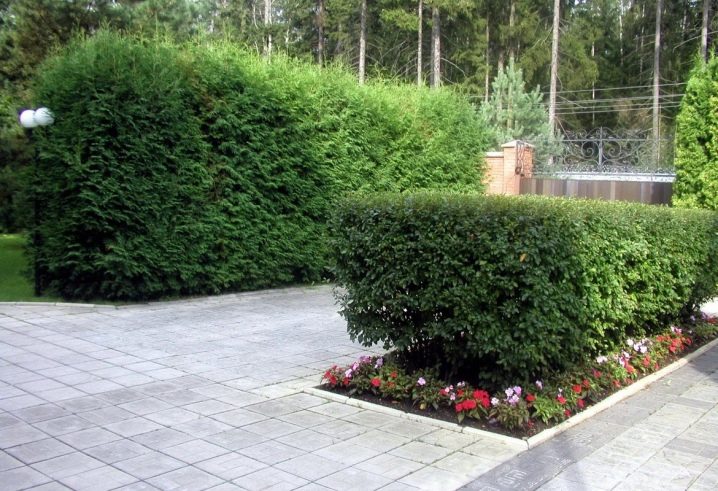
Application in landscape design
This plant has been cultivated since 1829. Since the black cotoneaster is very decorative, it is often used as a hedge, in some cases it can be seen in group or single compositions.
With proper pruning, figures of various shapes and sizes can be formed from the crown of the plant. Such figures are a great decoration for any site.

The black cotoneaster looks especially decorative and attractive when the berries turn black and the leaves turn bright purple hues. The berries are located very close to each other, which gives the impression of large beads strung on flexible threads.
The cotoneaster gets along well next to other plantings, but still the best option is low conifers.

Growing a cotoneaster is beneficial and aesthetic pleasure. It looks great on the backyard, decorating the landscape, and can be used as a medicine and a means of supporting human immunity.


































































The comment was sent successfully.