The subtleties of calculating bricks at home

The popularity of brick buildings is explained by a number of positive characteristics of this building material. Durability comes first. Brick houses, if laid correctly, will last for centuries. And there is evidence of this. Today you can see the strong buildings, erected several centuries ago.
Dense brick perfectly withstands the "attacks" of bad weather. It does not collapse under rain streams, does not crack from temperature changes and can withstand both severe frosts and searing heat. The brick is immune to the sun's rays.
Atmospheric phenomena can damage the masonry, but this will take more than a decade.
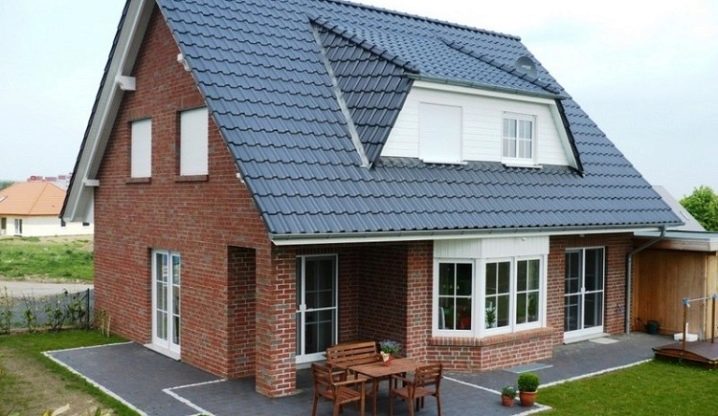

The resistance to biological destruction speaks in favor of the brick. In addition, the brick is fireproof. Even after prolonged exposure to open fire, the walls do not collapse. Architects love this building material because it allows them to bring interesting architectural solutions to life.
Nowadays, not only white silicate and red bricks are produced, but also multi-colored, which makes it possible to create original colored facades. Brick houses look solid, reliable, like a real fortress from a famous saying.


What does it depend on?
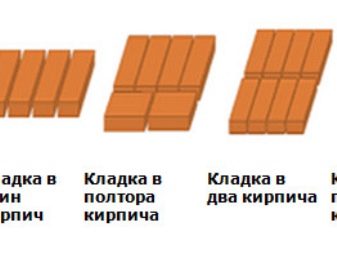
First of all, the need for brick for building a house depends on the dimensions of the walls, more precisely, on their thickness. The thicker the walls, the more building material they will need. The thickness of the walls is determined by the type of masonry. Their variety is limited.
Depending on the number and location of bricks, masonry is distinguished in:
- half a brick (masonry is used for partitions, since capital structures are not built in half a brick);
- one (masonry is used for partitions, sometimes for garden houses where there is no heating);


- one and a half (suitable for the construction of buildings in warm climates);
- two (suitable for the construction of buildings in central Russia, Ukraine, Belarus);
- two and a half (most often used in the construction of private houses and cottages in regions of the II climatic zone);
- three (now practically not used, but it is found in buildings of the past, before last and earlier centuries).

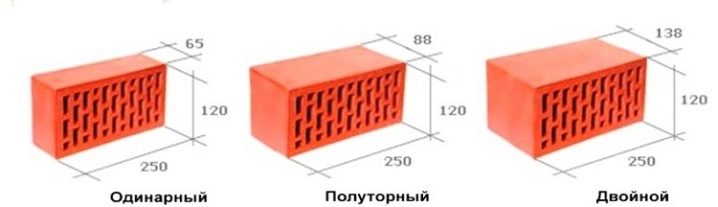
The bricks themselves differ in size. According to existing standards, all manufacturers produce building material with identical dimensions only in length and width. The first parameter (length) is 25 cm, the second (width) - 12 cm.The differences are in the thickness.
The following thickness measurements are taken:
- single - 6.5 cm;
- one and a half - 8.8 cm;
- double - 13.8 cm.
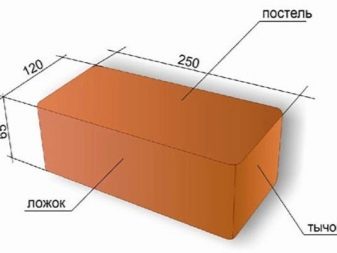
Bricks of the same or different types can be used in masonry. If, after building, it is not planned to cover the facade with plaster, a single brick will become the most preferable, as it looks great.
Often, a single view is used for cladding, and the inside of the masonry is made up of thickened (one-and-a-half) or double bricks. The combined use of the two types usually takes place if you need to save money. After all, a double brick in terms of volume is much cheaper than a single or one and a half.

When determining the amount of building material, it is necessary to focus on two parameters: the type of masonry and the type of bricks.
Peculiarities
In order to correctly calculate the need for a brick for building a house, you need to know its dimensions. Usually, newcomers to construction make mistakes and receive significantly more building material than they actually need.
The mistake is that mortar joints are not taken into account. Meanwhile, the layer of mortar between the bricks is a considerable volume. If you omit the volume of the seams, the result will differ by at least 20 percent.

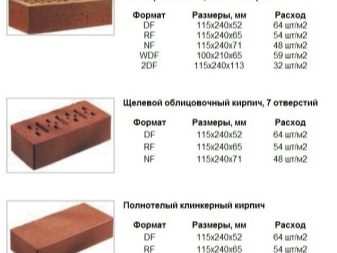
As a rule, the seams are at least 5 mm and not more than 10 mm thick. Knowing the dimensions of the main material, it is easy to calculate that in one cubic meter of masonry, from 20 to 30 percent of the volume is occupied by masonry mortar. An example for different types of bricks and the average thickness of the mortar joint. Practice shows that for one cubic meter of masonry there are 512 single bricks, 378 thickened or 242 double bricks.
Taking into account the solution, the amount decreases significantly: single bricks are required 23% less, that is, only 394 pieces, one and a half, respectively, 302, and double - 200 pieces. The calculation of the required number of bricks for building a house can be done in two ways.

In the first case, a brick can be taken not of a standard size, but with allowances equal to the thickness of the mortar joint. The second method, in which the average consumption of building material per square meter of masonry is taken into account, is more preferable. The problem is solved faster, and the result is quite accurate.
The deviation in one direction or another is no more than three percent. Agree that such a small error is quite acceptable. Another example, but now not in volume, but in the area of the wall - calculation taking into account the method of laying in 0.5, one, one and a half, two or two and a half bricks.

Half-brick masonry is usually laid out using beautiful facing marks.
For 1 m2, taking into account the seams, it is required:
- single - 51 pcs;
- thickened - 39 pcs;
- double - 26 pcs.


For masonry of 1 brick per square meter, you must:
- single - 102 pcs;
- thickened - 78 pcs;
- double - 52 pcs.


A wall thickness of 38 cm is obtained when laying one and a half bricks.
The need for material in this case is:
- single - 153 pcs;
- thickened - 117 pcs;
- double - 78 pcs.
For 1 m2 of masonry, 2 bricks will have to be spent:
- single - 204 pcs;
- thickened - 156 pcs;
- double - 104 pcs.


For thicker walls of 64 cm, builders will need for every square meter:
- single - 255 pcs;
- thickened - 195 pcs;
- double - 130 pcs.

How to calculate?
In order to correctly perform the operation to establish the required amount of bricks required to build a house, you will have to break the work into several stages. It doesn't matter which one you decide to build a house: a small low one or a large two-story house with an attached garage, a winter garden or a terrace, the principle of calculation is the same. First you need to calculate the area of the outer walls. A similar calculation of the area is carried out for the interior walls.
It makes no sense to make a joint calculation, since the thickness of the walls outside and inside is significantly different.

Then you need to calculate the areas of window and door openings. In the project, as a rule, not areas are indicated, but linear dimensions. To calculate the areas, you will have to use the formula familiar from school, multiplying the height by the width. If the openings are the same, you can find the area of one opening, for example, a window opening, and multiply the result by the number of future windows. If the overall dimensions in different rooms are different, you need to do calculations for each separately.
All the resulting areas of the openings are added and subtracted from the area obtained for the walls. Finding out how much brick goes into a known volume or area is quite simple. For example, 200 sq. m of masonry in 1 standard (single) brick will leave without taking into account the seams 61 x 200 = 12 200 pieces, and taking into account the seams - 51 x 200 = 10 200 pieces.
Let's give an example of calculating the consumption of bricks. Let's say you are planning to build a two-story brick house. The width of the building is 9 m, the length is 11 m, and the height is 6.5 m. The project provides for a masonry of 2.5 bricks, and the outside is facing with 0.5 bricks, and the main wall is laid out of double bricks. Inside the building, the walls are one brick thick. The total length of all internal walls is 45 m. In the external walls there are 3 doorways 1 m wide and 2.1 m high. The number of window openings is 8, their dimensions are 1.75 x 1.3 m. Inside there are 4 openings with parameters 2, 0 x 0.8 m and one 2.0 x 1.5 m.
Determine the area of the outer walls:
9 x 6.5 x 2 = 117 m2
11 x 6.5 x 2 = 143 m2
117 +143 = 260 m2

Doorway area: 1 x 2.1 x 3 = 6.3 m2
Window openings area: 1.75 x 1.3 x 8 = 18.2 m2
In order to correctly determine the completely solid area of the outer walls, the area of all openings must be subtracted from the total area: 260 - (6.3 + 18.2) = 235.5 m2. We determine the area of the internal walls, taking into account the fact that brick walls are located only on the first floor with a ceiling height of 3.25 m: 45 x 3.25 = 146.25 m2. Without taking into account the openings, the area of the walls inside the room will be:
146.25 - (2.0 x 0.8 x 4) - (2.0 x 1.5) = 136.85 m2

It remains to calculate the number of bricks based on the previously mentioned consumption per 1 square meter:
double: 235.5 x 104 = 24 492 pcs;
facing: 235.5 x 51 = 12,011 pcs;
single: 136.85 x 102 = 13 959 pcs.
The number of units is approximate, rounded to one whole.
When external walls are erected with one type of brick, the calculation can be performed by volume.

With the same overall dimensions of the house, we will perform the calculation by volume. First, let's determine the volume of the walls. To do this, the length of one of the sides of the house (for example, a smaller one, 9 meters long) we accept it completely and calculate the volume of two parallel walls:
9 (length) x 6.5 (height) x 0.64 (2.5 brick thickness) x 2 (number of walls) = 74.88 m3
The length of the second wall is reduced by (0.64 mx 2), that is, by 1.28 m. 11 - 1.28 = 9.72 m
The volume of the remaining two walls is equal to:
9.72 x 6.5 x 0.64 x 2 = 80.87 m3
Total wall volume: 74.88 + 80.87 = 155.75 m3

The number of bricks depends on the selected type and will be for:
- single: 155.75 m3 x 394 pcs / m3 = 61 366 pcs;
- thickened: 155.75 m3 x 302 pcs / m3 = 47,037 pcs;
- double: 155.75 m3 x 200 pcs / m3 = 31 150 pcs.
As a rule, the building material is sold not by the piece, but in a batch stacked on a pallet.
For solid bricks, you can focus on the following amount in the pallet:
- single - 420 pcs;
- one and a half - 390 pcs;
- double - 200 pcs.


To order a batch of building material, it remains to determine the number of pallets.
In our last example, the requirement is for bricks:
- single: 61 366/420 = 147 pallets;
- one and a half: 47 037/390 = 121 pallets;
- double: 31 150/200 = 156 pallets.
When performing calculations, the builder always rounds up. In addition to the material directly used in the masonry, it must be borne in mind that when moving and performing work, part of the material goes into battle, that is, a certain stock is needed.

Tips & Tricks
It is generally accepted that all bricks meet the established standards in size. However, there are tolerances, and different batches of products may differ slightly. The structure will lose its perfection when using different batches of bricks. For this reason, it is recommended to order the full volume of building materials from one supplier at a time.

Only in this way is the guaranteed material purchased will differ in size and color shades (for facing brands). The estimated amount should be increased by 5%, attributable to the losses inevitable during transportation and construction. The correct calculation of the need for bricks will prevent unnecessary downtime and save the developer's finances.
For information on how much it costs to build a brick house, see the next video.













The comment was sent successfully.