Thermal conductivity and heat capacity of bricks

The thermal conductivity and heat capacity of bricks are important parameters that allow you to determine the choice of material for the construction of residential buildings, while maintaining the required level of heat in them. Specific indicators are calculated and given in special tables.
What is it and what influences them?
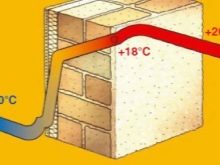
Thermal conductivity is the process that takes place inside a material during the transfer of thermal energy between particles or molecules. In this case, the colder part receives heat from the warmer one. Energy losses and heat emissions occur in materials not only as a result of the heat transfer process, but also during radiation. It depends on what the structure of the substance is.

Each building component has a certain index of heat conductivity, obtained empirically in the laboratory. The heat propagation process is uneven, therefore it looks like a curve on the graph. Thermal conductivity is a physical quantity that is traditionally characterized by a coefficient. If you look at the table, you can easily notice the dependence of the indicator on the operating conditions of this material. Extended reference books contain up to several hundred types of coefficients that determine the properties of building materials of various structures.
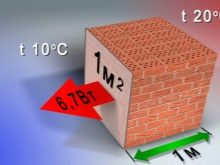

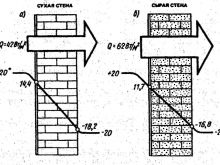
As a guideline, when choosing, three conditions are indicated in the table: usual - for a temperate climate and average humidity in the room, the "dry" state of the material, and "wet" - that is, operation in conditions of an increased amount of moisture in the atmosphere. It is easy to see that for most materials, the coefficient increases with increasing ambient humidity. The "dry" state is determined at temperatures from 20 to 50 degrees above zero and normal atmospheric pressure.
If the substance is used as a heat insulator, the indicators are chosen especially carefully. Porous structures retain heat better, while denser materials release it more into the environment. Therefore, traditional heaters have the lowest thermal conductivity coefficients.
As a rule, glass wool, foam and aerated concrete with a particularly porous structure are optimal for construction. The denser the material, the more thermal conductivity it has, therefore, transfers energy to the environment.


Types of materials and their characteristics
Brick, produced today in many types, is used in construction everywhere. Not a single object - a large industrial building, a residential apartment building or a small private house - is built without a brick foundation. The construction of cottages, popular and relatively inexpensive, is based solely on brickwork. Brick has long been the main building material.
This is due to its versatile properties:
- reliability and durability;
- strength;
- environmental friendliness;
- excellent sound and noise insulation characteristics.



The following types of bricks are distinguished.
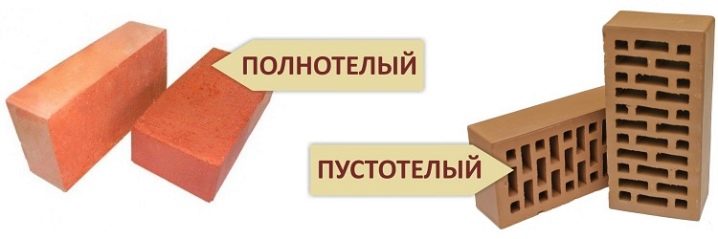
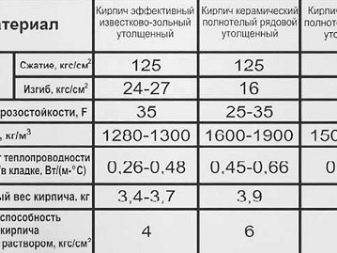
- Red. It is made from fired clay and additives. Differs in reliability, durability and frost resistance. Suitable for wall and foundation construction. Usually placed in one or two rows. Thermal conductivity depends on the presence of gaps in the product.

- Clinker. The most durable and dense facing brick.Due to its high density, a solid, solid and reliable furnace material also has the most significant thermal conductivity coefficient. And therefore it makes no sense to use it for the walls - it will be cold in the house, significant wall insulation will be needed. But clinker bricks are indispensable in road construction and when laying floors in industrial buildings.

- Silicate. An inexpensive material made from a mixture of lime and sand, products are often combined into blocks to improve performance. In the construction of buildings, not only solid, but also silicate with voids is used. The durability indicators of the sand block are average, and the thermal conductivity depends on the size of the connection, but still remains high enough, so the house will require additional insulation.
The indicator for the slotted briquette is lower compared to the analogue without internal gaps. It should also be taken into account that the product absorbs excess moisture.

- Ceramic. Modern and beautiful material produced in a wide range. If we talk about thermal conductivity, then it is significantly lower than that of ordinary red brick.
There is a solid ceramic briquette, refractory and slotted, with voids. The heat conductivity coefficient depends on the weight of the brick, the type and number of cracks in it. Warm ceramics are beautiful on the outside and have many fine gaps on the inside, making them very warm and therefore ideal for building. If the ceramic product also has pores that reduce weight, the brick is called porous.

The disadvantages of such a brick include the fact that individual units are small and fragile. Therefore, warm ceramics are not suitable for all designs. Moreover, it is an expensive material.
As for refractory ceramics, this is the so-called fireclay brick - a burnt block of clay with a high thermal conductivity, almost the same as that of an ordinary solid material. At the same time, fire resistance is a valuable property that is always taken into account during construction.
Fireplaces are built from such "stove" bricks, it has an aesthetic appearance, retains heat in the house due to its high thermal conductivity, frost-resistant, does not lend itself to acids and alkalis.
Specific heat is the energy consumed to heat one kilogram of material by one degree. This indicator is needed to determine the resistance to heat of the walls of a building, especially at low temperatures.
For products made of clay and ceramics, this indicator ranges from 0.7 to 0.9 kJ / kg. Silicate brick gives indicators of 0.75-0.8 kJ / kg. Chamotny is capable, when heated, to give an increase in heat capacity from 0.85 to 1.25.

Comparison with other materials
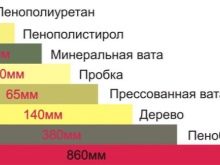
Among the materials that can compete with bricks, there are both natural and traditional - wood and concrete, and modern synthetic - penoplex and aerated concrete.
Wooden buildings have long been erected in the northern and other regions with low winter temperatures, and this is no accident. The specific heat capacity of wood is much lower than that of bricks. Houses in this area are built from solid oak, coniferous trees, and chipboard is also used.
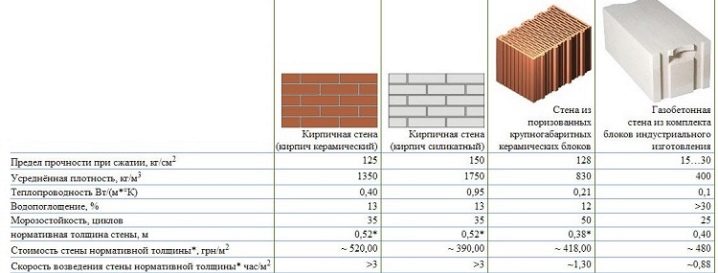
If the wood is cut across the fibers, the thermal conductivity of the material does not exceed 0.25 W / M * K. Chipboard also has a low indicator - 0.15. And the most optimal coefficient for construction is wood cut along the fibers - no more than 0.11. Obviously, in houses made of such wood, excellent heat retention is achieved.
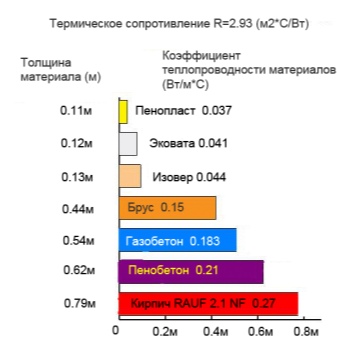
The table clearly demonstrates the spread in the value of the thermal conductivity of a brick (expressed in W / M * K):
- clinker - up to 0.9;
- silicate - up to 0.8 (with voids and cracks - 0.5-0.65);
- ceramic - from 0.45 to 0.75;
- crevice ceramics - 0.3-0.4;
- porous - 0.22;
- warm ceramics and blocks - 0.12-0.2.
At the same time, only warm ceramics and porous bricks, which are also expensive and fragile, can argue with wood in terms of the level of heat preservation in the house. Nevertheless, brickwork is used more often in the construction of walls, and not only because of the high cost of solid wood. Wooden walls are afraid of atmospheric precipitation, they fade in the sun. He does not like wood and chemical influences, besides, wood can rot and dry out, mold forms on it. Therefore, this material requires special processing prior to construction.

In addition, fire can very quickly destroy a wooden structure, since the wood burns well. In contrast, most types of bricks are quite resistant to fire, especially fireclay bricks.
As for other modern materials, foam block and aerated concrete are usually chosen for comparison with brick. Foam blocks are concrete with pores, which includes water and cement, a foaming compound and hardeners, as well as plasticizers and other components. The composite does not absorb moisture, is highly frost-resistant, and retains heat. It is used in the construction of low (two or three floors) private buildings. Thermal conductivity is 0.2-0.3 W / M * K.
Aerated concrete is a very strong compound of a similar structure. They contain up to 80% of pores providing excellent heat and sound insulation. The material is environmentally friendly and convenient to use, as well as inexpensive. The thermal insulation properties of aerated concrete are 5 times higher than that of red brick, and 8 times higher than that of silicate (thermal conductivity does not exceed 0.15).
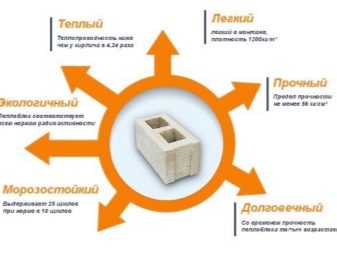
However, gas-block structures are afraid of water. In addition, in terms of density and durability, they are inferior to red brick. One of the building materials in demand on the market is called extruded polystyrene foam, or penoplex. These are slabs designed for thermal insulation. The material is fireproof, does not absorb moisture and does not rot.
According to experts, this composite withstands comparison with brick only in terms of thermal conductivity. The insulation has an indicator equal to 0.037-0.038. Penoplex is not dense enough, it does not have the required bearing capacity. Therefore, it is best to combine it with a brick when erecting walls, while a masonry of one and a half hollow bricks supplemented with penoplex will allow you to comply with building codes for thermal insulation of a dwelling. Penoplex is also used for the foundations of houses and blind areas.
Frost resistance
Frost resistance is determined by freezing and thawing cycles. This parameter is important when choosing the type of brick for laying load-bearing walls. The brand depends on the number of cycles and is indicated on the products. Facing and red bricks have the highest frost resistance, which can withstand temperatures up to -50 degrees Celsius and below. If you use sand-lime brick, its properties are worse, so the masonry will have to be done in two layers. Silicate is not suitable for building a foundation either.
In bad winter conditions, the heat in the house is retained by the heating boiler of the heating system. But in order to prevent heat dissipation, walls, floors and ceilings are needed from the appropriate material that keeps the set temperature well. The type of brickwork plays an important role during construction. The material should be chosen taking into account all parameters and weather conditions.

In the next video, you will find an overview of the thermal conductivity of SB 8 bricks.












The comment was sent successfully.