All about ceramic blocks

The word "crisis" in translation from ancient Greek means "turning point, solution." And this explanation fits exactly the situation that happened in 1973.


There was an energy crisis in the world, energy costs had to be reduced, and specialists had to look for new solutions for the construction of walls. They figured out what the wall should be in order to keep the heat in the building longer. This calculation led to the appearance of blocks of fired clay with cracks inside. This is how ceramic blocks and warm ceramics appeared.


What it is?
Another name for the ceramic block - porous block (from the word "pores"). This is a unique building material that is distinguished good environmental performance. Describing a ceramic block, one can imagine a stone that has micropores and voids inside. By using this stone, construction time is shortened.
Why ceramics are called warm: because the pores inside the block are filled with air, which is the ideal heat insulator. The pores themselves are obtained due to the combustion of medium-sized sawdust, they are kneaded together with clay. When a layer of mortar is laid, the upper and lower pores in the block are closed, so-called air cushions are formed.
It is safe to say that the ceramic block is at least 2.5 times warmer than ordinary brick. That is, the wall, the thickness of which is from 44 to 51 cm, will not require an additional layer of insulation in the form of expanded polystyrene and mineral wool.



It should be noted that in the process of laying ceramic blocks, a warm solution is also present. This solution uses light sand: having a low density, it does not transfer heat from the building to the street so well. One of the main advantages of a ceramic block is that it increases the pace of construction.
A house from such material will be built twice as fast (and sometimes 4 times faster), and this affects the overall costs. Saving is one of the most attractive points of efficient construction.



Advantages and disadvantages
The ceramic block, like any other building material, has both beneficial aspects and those that cannot be brought into an asset.
Material pluses:
- Groove-comb - such a connection is used in a ceramic block, which allows the units to be fastened on the sides, and from above and below the pores will be securely closed anyway;
- additional thermal insulation in the form of air that enters the pores, of course, pleases;
- strength a ceramic block, even if its lowest indicators are taken, is two times higher than that of the same aerated concrete;
- burnt clay aggressive external factors are not afraid, since this material can actually be called chemically neutral, it does not contain those impurities (slag), which is, for example, in aerated concrete.
And these benefits are only added to those characteristics that are indicated in the product description.


What are the disadvantages of a ceramic block:
- those very wonderful internal holes (pores), and the very presence of a slotted structure automatically makes the material more fragile - if dropped, such a block will split into pieces;
- the structural peculiarity of the block affects not only the work with it, requiring utmost care, but also on transportation, delivery, transportation;
- work with the ceramic block can only experienced, competent bricklayers - with an illiterate installation, all the advantages of the material will be leveled (cold bridges may appear, as a result, freezing);
- percussion instruments are not possible with this material - you simply cannot hammer in nails and dowels, in order to install the same furniture, you will need special fasteners for hollow ceramics (chemical as well as plastic anchors);
- to cut the ceramic block, you will need electric saw.


For housing construction, a ceramic block is a safe, largely profitable material. It is quite durable with proper installation, it does not burn, it is resistant to moisture, it creates a comfortable environment inside buildings. This material is warm, in winter you will not freeze in such a house, but in summer, on the contrary, it will be cool in it. The noise level outside in such a house will also be reduced, which undoubtedly refers to the advantages of the material.
According to GOST, the ceramic block is called a ceramic stone. It resembles its predecessors, some of the characteristics of the classic red and hollow brick are present in this material.
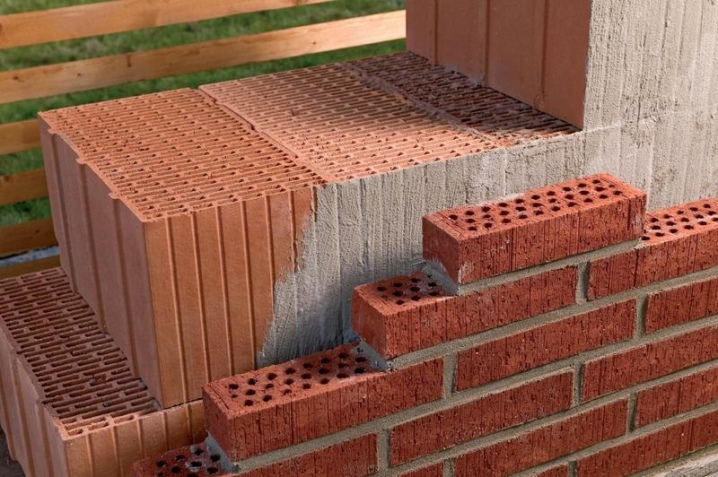

Specifications
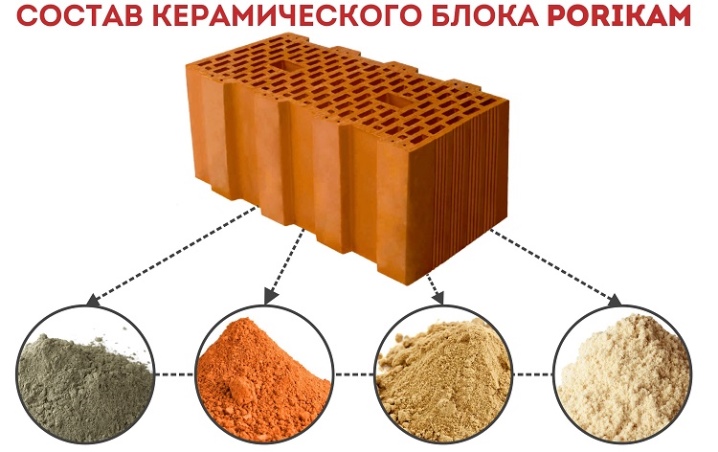
To understand exactly how a ceramic block "behaves" in construction, you should consider a little the method of its production. The clay is initially mixed with porousizing additives to help reduce the density of the material. They, these additives, affect the resulting thermal performance of the material.
What are these additives: most often sawdust, but there are also grain husks, and polystyrene (less often), and even waste paper. This mixture passes through machines for grinding clay, which is necessary for the formation of a homogeneous substance. And then the press helps to remove excess water from the material.



The next step on the way to creating warm ceramics is molding. The clay mixture is pressed with a bar through a mold (called a die), and it forms the outer surfaces, as well as the voids of the blocks. Then the clay bar is cut into pieces, the material is sent for drying to special chambers.
And it usually takes 2-3 days. Further, the material is awaiting firing in a tunnel oven, and it can already take up to 2 days or even a little more. It is at this moment that the clay becomes ceramics, and those additives that should form pores burn out.
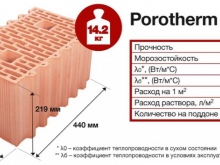
Characteristics of ceramic blocks:
- low thermal conductivity, which is provided by the very pores and voids with a melted surface and a closed volume;
- light weight - such blocks will definitely not make the structure heavier; there is no need to talk about additional load on the foundation;
- thermal inertness - a single-layer wall made of warm ceramics does not require insulation (in addition to the thermal balance, air is also supported);
- profitability, low mortar consumption - it has been practically proven that even the thickness of the mortar for masonry will be much less (the same joint with the groove and the ridge will not be completely filled with mortar);
- good sound insulation - the very structure of the blocks is such that there are chambers in the voids that have a positive effect on sound insulation;
- environmental friendliness - this is an extremely important characteristic, only natural materials are used in the manufacture of warm ceramics;
- large format masonry unit - laying one block is equal to laying 15 ordinary bricks, which means that the construction process unfolds faster;
- high bearing capacity - the stone can withstand 50 to 100 kg per square centimeter, despite its porous structure.
The service life of the ceramic block is at least 50 years. But the material can be considered relatively modern, so there are no large, serious studies with a sufficient sample of the actual service life so far.

Views
Block designations and markings may vary: each manufacturer is free to adhere to their own settings. Even the size differs, although it should rather be typical.
By form
Just like bricks, warm blocks can be facing and ordinary. Faces are usually used for wall cladding, although they are, of course, also suitable for basic masonry.Solid elements are also used in construction - with their help, straight wall parts are laid, additional elements - they are used to lay out corners, half elements - they are used for laying door and window openings.
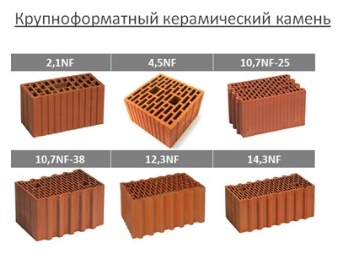

To size
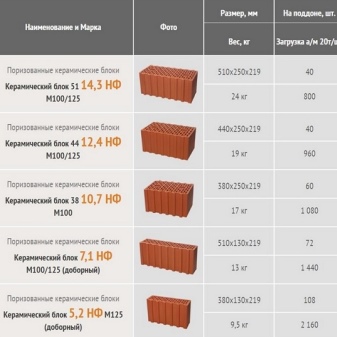
There are brands that produce stones not 138 mm high (standard size), but 140 mm. Other sizes found on the market:
- single 1NF - 250x120x65 mm (length / width / height);
- one and a half 1.35 NF - 250x120x88;
- double 2.1 NF - 250x120x138 / 140;
- porous building stone 4.5 NF - 250x250x138;
- block 10.8 NF - 380x250x219 (380 - length, 250 - width, 219 - height);
- block 11.3 NF - 398x253x219;
- block 14.5 NF - 510x250x219.
Large-format blocks, for example, are used for the construction of buildings with 10 floors. And the same standard aerated concrete with the same weight is used in the construction of houses, the number of storeys of which should be no more than 5 floors. As well as a smooth hollow brick, if we can compare further.

Manufacturers
You can only go through the leading, most famous or actively developing companies.

Warm Ceramics Companies:
- Porotherm... This is a manufacturer from Germany, which is considered one of the flagships in the market, as well as the "dinosaur" of this industry. Several factories of the company are located in Russia. The manufacturer offers on the market large-format wall blocks, additional stone (with its help, vertical seams are tied), special blocks for filling the frame, as well as products created for the installation of partitions.
- "Ketra"... A Russian company supplying ceramic blocks to the market in three sizes and, what is important, in different shades (from delicate milky to discreet brown).
- "Braer". Another domestic manufacturer, also popular and offering a line of three options for warm ceramics.
- CCKM... The Samara plant produces products that were previously called KERAKAM, and now - KAIMAN. These are stones of both small and large formats. It is interesting that the developers of the material have improved the principle of the tongue-and-groove connection: they make triangular projections on the blocks, which have a positive effect on the strength of the masonry.
The market is young, you can follow it, because its assortment and the number of new names will grow, because the material itself is considered promising.


Applications
This stone has 4 main directions, where it is used. Warm ceramics are used:
- when erecting partitions, as well as external walls of buildings;
- low-rise and high-rise construction;
- construction of industrial facilities;
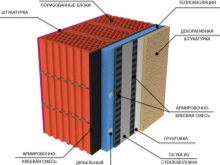
- cladding of facades, suggesting the effect of insulation.
Obviously, each of these areas involves several ramifications, which means that the possibilities of the material with which you can build both lintels and partition structures are only growing. The absence of the need to make a thick "cake" of thermal insulation often becomes decisive in the choice of material.


What myths exist about the use of warm ceramics.
- Low strength of the erected walls. It is incorrect to compare the strength of a whole wall and a single wall block. And it is the wall strength that will always take precedence in comparison. It depends on the quality of the blocks, and also on the skill of the bricklayer. Blocks in masonry, as is known, can have multidirectional loads, and the mortar itself and its masonry can both decrease and increase strength (meaning the final strength). This means only one thing: two strengths must match - mortar and block. Therefore, the manufacturer who tests the material checks the strength of the entire masonry, does not split the indicator into parts.
- When cutting or chipping, blocks can collapse... If professionals get down to business, they will cut on a special stationary type machine or use a saw with a special wear-resistant blade. And if the wall needs to be channeled, first, polymer plaster will be applied to it: this way the strobe will be even, and the partitions will be intact.
- It is definitely impossible to fasten structures to ceramic blocks. Nonsense, because as soon as porous materials appeared on the market, the request for fasteners for them was quick. And then the engineering thought "gave birth" to the dowels, suitable precisely for slotted ceramics. They are made from synthetics. And if the wall requires fastening for something heavy enough, chemical anchors help out. In this case, the chemical composition is associated with the block material, as a result of which a monolith is formed, and it holds the rod. So the system will withstand loads of hundreds of kg, although there is usually no need for such at home.
- You will never have to insulate such walls. But this is not entirely true, although there is a lot of talk about ceramic blocks precisely from the point of view of their thermal conductivity. The main thing is that the region of construction, of course, cannot escape these circumstances. Experts assure that additional insulation will not be required for walls with a block width of at least 510 mm, if we are talking about central Russia.

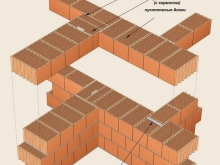
It should be noted that each manufacturer of warm ceramics supplies its product with detailed instructions, which it would be simply a crime to ignore... This manual, for example, describes options for technical solutions that are extremely useful even for experienced bricklayers (let alone the rest). There can be described the alignment of blocks with ceilings or with bases, in the same place the process of erecting a wall is algorithmized, features of masonry of corners.
An interesting point: the laying of blocks is usually carried out using a special warm mixture, but a standard cement mortar is also used. And many craftsmen consider such a replacement to be unequal, because the cement joint has a different thermal conductivity. In principle, this replacement could indeed be a construction error.


In terms of conclusions, we can say that a porous block is a good, competitive material for the construction of buildings. It is lightweight, and this alone is enough to not make a capital foundation. It is warm and has good sound insulation performance. It is problematic only in terms of the exactingness of transportation, transportation and laying. But if the bricklayers are experienced, competent, there is practically nothing to worry about.
Finally, the choice in favor of warm ceramics today is also based on the fact that it outperforms not only bricks, but also aerated concrete. That is, the status of the material becomes even higher, and it goes into the category of not only profitable, but also promising products.
And the factor that a domestic manufacturer supplies excellent warm ceramics, and even modernizes the process of its production, may be a decisive argument in favor of this material.











The comment was sent successfully.