All about potatoes

Potatoes are considered one of the most important agricultural crops, popularly even called "the second bread". A well-chosen variety allows you to get a high yield, the keeping quality of which makes it possible to save it until the next season.

general description
Potatoes, the second name of which sounds like tuberous nightshade, belongs to the nightshade family. This plant is a herbaceous perennial, the processed tubers of which are eaten. The characteristics of the culture should start with the fact that the bush can reach more than 1 meter in height. The structure of the potato stalk is quite curious. Its upper part is naked or ribbed, rises above the surface, is covered with leaves and looks quite ordinary.
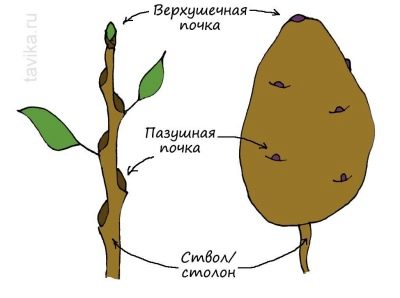
However, there is also its lower, underground part, which forms shoots in the axils of the rudimentary leaves, which should be considered underground shoots. It is on these formations - stolons, from 15, and sometimes up to 50 centimeters long, that potatoes are formed. Moreover, the stalk of the vegetable crop also serves as a root system, releasing thin roots. The leaf blades of potatoes are colored dark green. The flowers are white, pink or lilac and form corymbose inflorescences at the top of the stem.
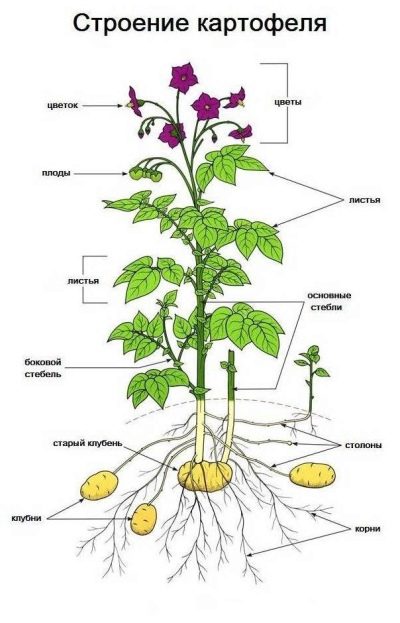
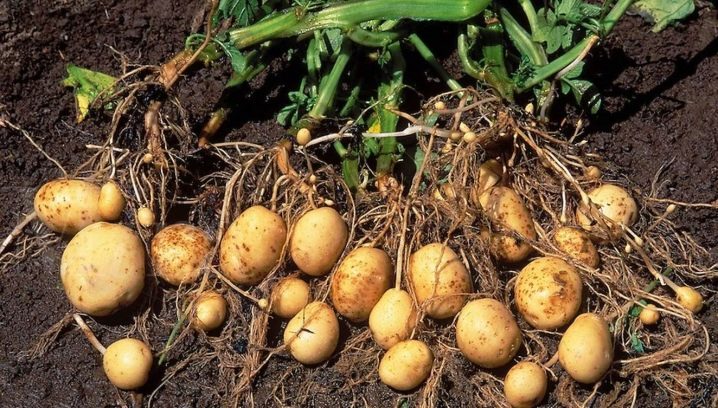
Root crops are also of particular interest. What is considered a common vegetable develops as a thickening of the top of the stolon, or rather, as a swollen kidney. Most of them ripen from August to September. Up to 22% starch is present in the pulp of the root crop, and the outer part is formed from a thin cork tissue. It should be mentioned that the root vegetable of the potato is not its fruit. The latter means a dark green poisonous berry, resembling a small tomato in appearance. Its diameter does not exceed 2 centimeters, and there is a large number of seeds inside.

Popular varieties
There are a huge number of potato varieties, the number of which reaches 5 thousand. They differ in taste, ripening times, immunity, and the volume of the harvested crop. In Russia, about 500 varieties of culture are recognized at the state level. Depending on their use, they are divided into canteens, technical, feed and universal. On the basis of the ripening period, early and mid-early, mid-season, late and mid-late varieties are distinguished.
Cultivation of early potatoes starts already in April, and harvesting is obtained in 80-90 days. In this case, we are talking about varieties "Timo", "Riviera", "Sineglazka", "Ariel", etc.

Medium early potatoes are harvested in July. Its growing season is 65-80 days, but before planting, root crops must germinate. The varieties "Sante", "Karat" and "Adretta" are usually referred to as medium early. Mid-season varieties are harvested in early August, developing in 85-100 days. The varieties "Betina" and "Nevsky" belong to this category.
Late and mid-late varieties have the best keeping quality. Their collection begins only at the beginning of October, when the mass of the tuber is 90 grams. Potatoes of the varieties "Yavir", "Roko" and "Slavyanka" ripen in autumn.

Landing
When planning to plant potatoes, it is important to decide on a place. The culture should never be established in beds where nightshades previously lived: tomatoes, eggplants and bell peppers. It is also impossible to place it in the same place for 2 years in a row.Suitable precursors for potatoes include cucumbers, radishes, cabbage, peas and beans, and green manures.
The culture will feel best on light loam or sandy loam soils. If the soil is heavy and stony, then it is better to abandon planting, otherwise the tubers will be deformed. Potatoes need very fertile soil, so fertilization will be required during the autumn digging.

It is more optimal to use components rich in both potassium and nitrogen, for example, compost or humus, 5 kilograms of which is enough to process 1 square meter of soil. The vegetable will respond well to the presence of ash - 300 grams will be enough for each square meter, as well as superphosphate and potassium salt, 30 and 15 grams, respectively. If feeding was carried out in the fall, then in the spring it will only be necessary to loosen the surface with a pitchfork. In the case of soil requiring minimal feeding, fertilization is allowed directly into the hole.
It is worth mentioning that also at the end of the previous season, it is customary to clear the garden from weeds and, after adding nutrients, dig it up on a bayonet without breaking lumps.

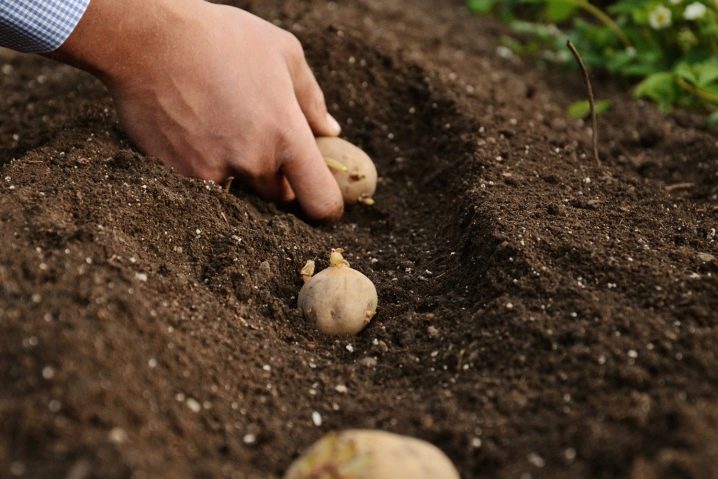
It is recommended to plant tubers at a time when the soil at a depth of 8-10 centimeters warms up to + 6 ... 8 degrees... You can determine this by the bird cherry - as soon as its flowering begins, it's time to start planting potatoes. If the material ends up in cold ground, then either its germination will slow down, or it will die altogether along with the sprout that reaches the surface. 20-25 days before planting, the tubers are taken out of the basement into a bright room, in which the temperature is maintained from +15 to +18 degrees. The specimens are sorted out, after which they are laid out in 1-2 layers for further germination.
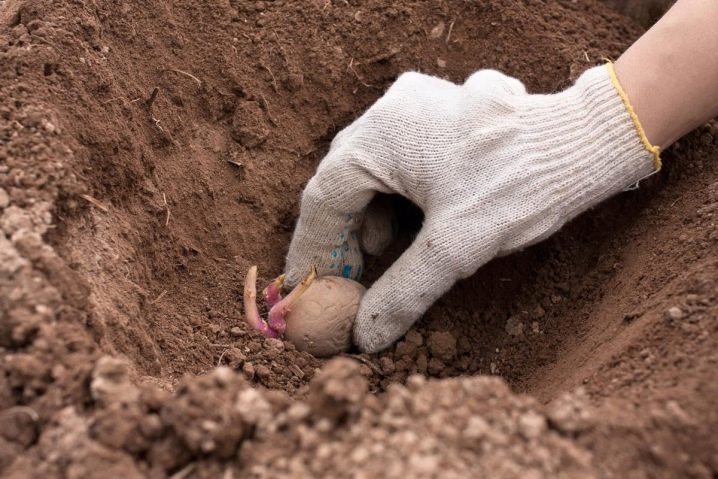

A couple of days before planting, the potato must be disinfected. It will be most effective to hold the material for 5-8 minutes in a weakly concentrated mixture of copper sulfate, boric acid and potassium permanganate. Processing should be carried out carefully so as not to damage the eyes, from which shoots are then formed.
You can also subject the tubers to greening on the windowsill in transparent containers or treatment with a mixture of complex fertilizer, wood ash, copper sulfate and potassium permanganate.

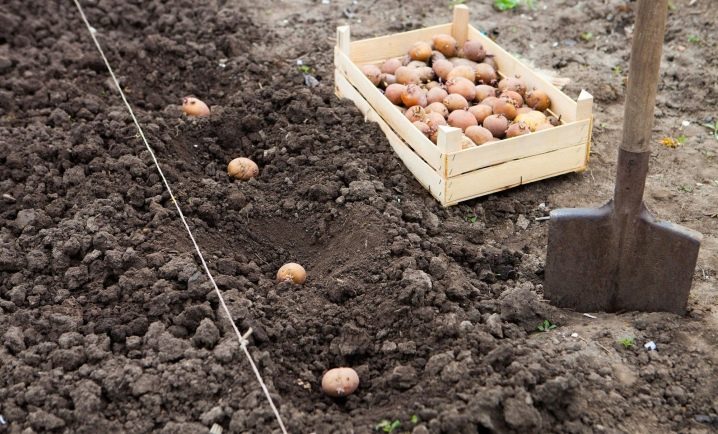
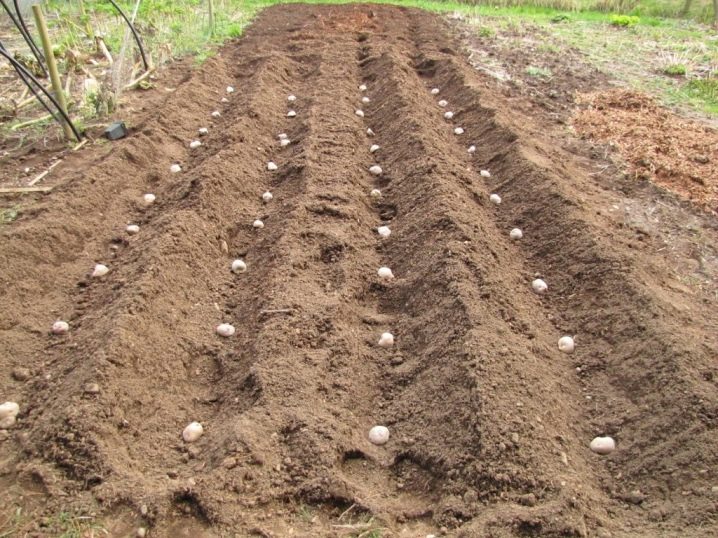
There are several options for placing tubers in the garden. Smooth variation, carried out in the holes, or tape planting are popular. For arid regions, trenching is more suitable, and excessively moistened soil is best combined with ridge planting. The burial depth of tubers is determined depending on the characteristics of the soil. On heavy clayey, the indicator is from 4 to 5 centimeters, on heavy loams - 8-10 centimeters, and on light soils - about 10-12 centimeters.

If early maturing varieties are planted, then 45-50 centimeters must be left between the rows or ridges, and 25-30 centimeters between individual tubers. For mid-season varieties, the gap between individual specimens is 30-35 centimeters, as well as 50-60 centimeters of free space between the rows. Late-ripening tubers must be separated from each other by 35-40 centimeters. The gap between the rows is maintained at 60-70 centimeters.

Care
Caring for potatoes does not seem too difficult, but it must be done in accordance with certain rules.
Watering
For the first time, the potatoes are irrigated immediately after the first sprouts appear. The second procedure is organized after the buds appear, and the third - immediately after flowering. If the summer is dry, then you can add the fourth and fifth procedures. In rainy months, watering can be avoided altogether.
It should also be mentioned that after the rain, the soil is necessarily loosened, and the bushes are huddled.

Top dressing
On nutrient-rich soils, it is not necessary to feed potatoes throughout the season - fertilizers applied before planting should be enough for this entire period. If the bed is poor, then when the seedlings appear, it will be necessary to organize feeding. For this purpose, a tablespoon of carbamide or the same amount of ammonium nitrate is diluted in 10 liters of water. When buds appear on the bush, you can think about adding a bucket of water with 1 tablespoon of potassium sulfate and 2 tablespoons of wood ash. During the flowering period, potatoes are irrigated with a mixture of 10 liters of water, a glass of mullein and a couple of tablespoons of superphosphate. Each vegetable bush requires no more than 0.5 liters of nutrient fluid.

Reproduction
Typically, potatoes are propagated either in whole tubers or in small portions. To obtain new varieties, the seed method is also used.
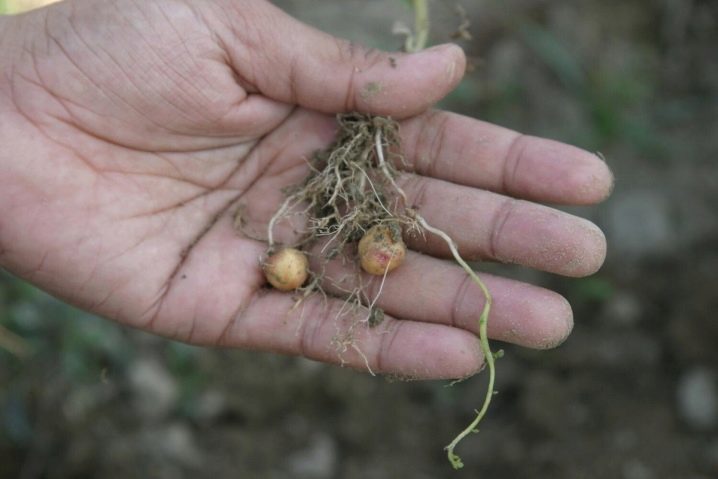

Diseases and pests
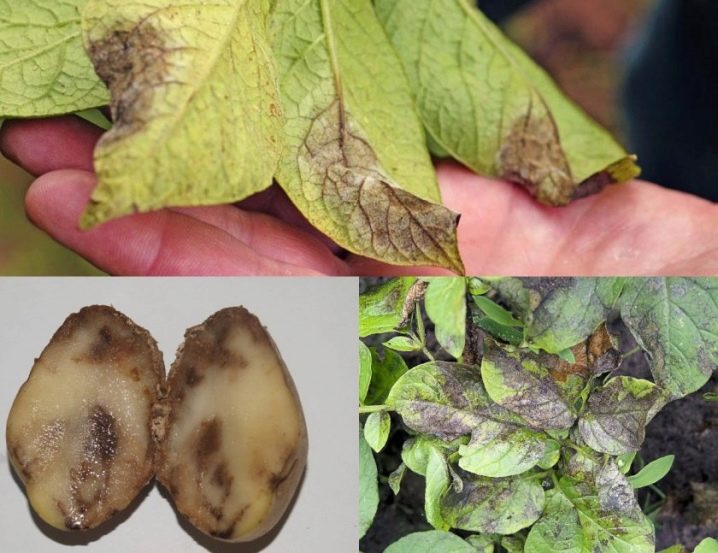
The most famous potato pest is Colorado beetle, whose larvae feed on nightshade leaves. Irreparable damage is inflicted and wirewormsgnawing tubers and stems. The attacked plant slows down in development, and in the opened passages fungi and bacteria colonize, provoking putrefactive changes. Often potatoes are sick with late blight, scab and various viruses. To cope with all the above problems, both purchased drugs and folk remedies allow. Some of them, as part of the prevention, are introduced during planting, and the other is used during the growing season of the crop.

Harvest
Harvesting begins at the moment when the leaves of the potato bush wither and dry out. However, it will be necessary to keep up with the establishment of frost. Usually, one and a half to two weeks before that, the mowing of the tops is organized, as well as the loosening of the row spacings, which provides better air access to the tubers. The first action will allow you to direct nutrients to root crops, and the second - to strengthen their skin, and therefore improve keeping quality. The procedure itself is organized on a dry and warm day.
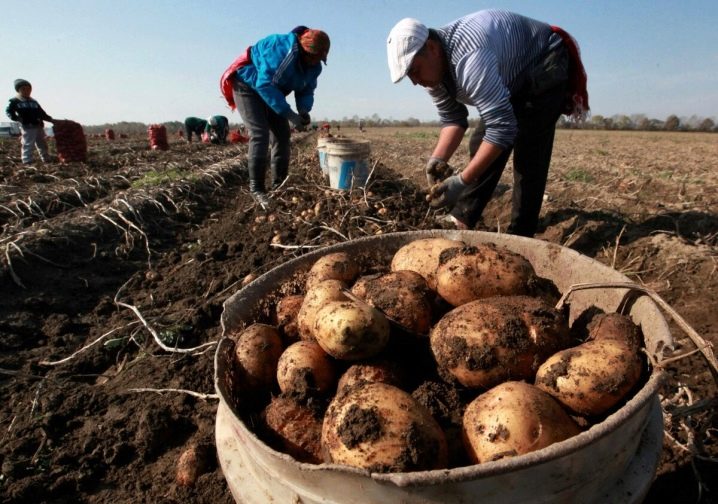

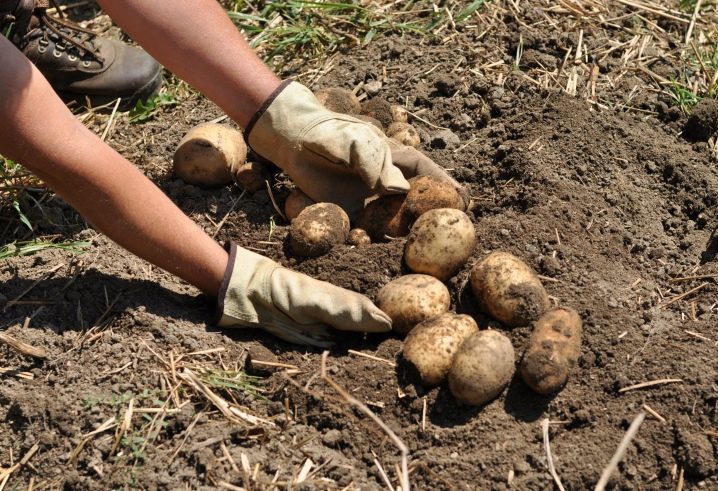
Removing potatoes from the soil is carried out using a shovel or garden pitchfork. For the first month, the extracted root crops are stored in a space where the temperature is maintained from +15 to +18 degrees and the humidity level is 85-90%. Some gardeners, however, limit this stage to 9-10 days, which should be enough for the maturation and healing of wounds.
Long-term storage is organized in an underground or basement heated to +5 degrees.











The comment was sent successfully.