How do potatoes multiply?
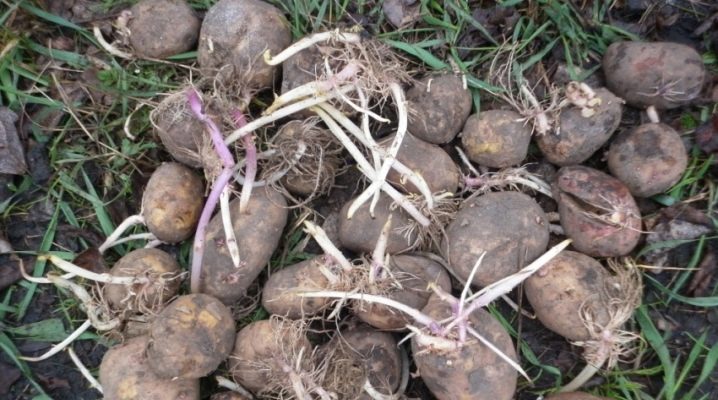

Understanding how potatoes multiply is useful not only for agronomists or breeders. Over time, even the highest quality planting material begins to degenerate, becoming more susceptible to various infections and mutations. In order to maintain high yields, vegetable growers use reproduction by dividing tubers and sprouts, by other vegetative methods.
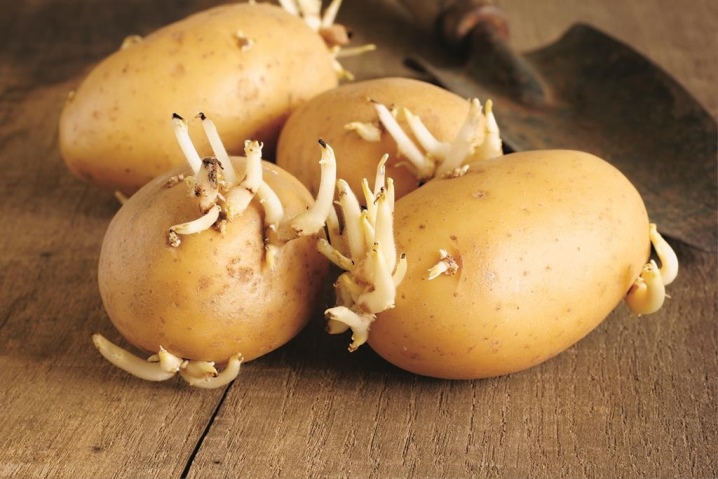

Reproduction by sprouts
The peculiarities of this method are that only the shoots themselves participate in reproduction. It is possible to plant in a similar way both very rare varieties with a limited amount of planting material, and trial or degenerating ones. Even an inexperienced summer resident can grow viable plants ready for transfer into the ground. Seedlings are obtained practically without damaging the tuber, which allows to increase the batch of seed material by 4-5 times.

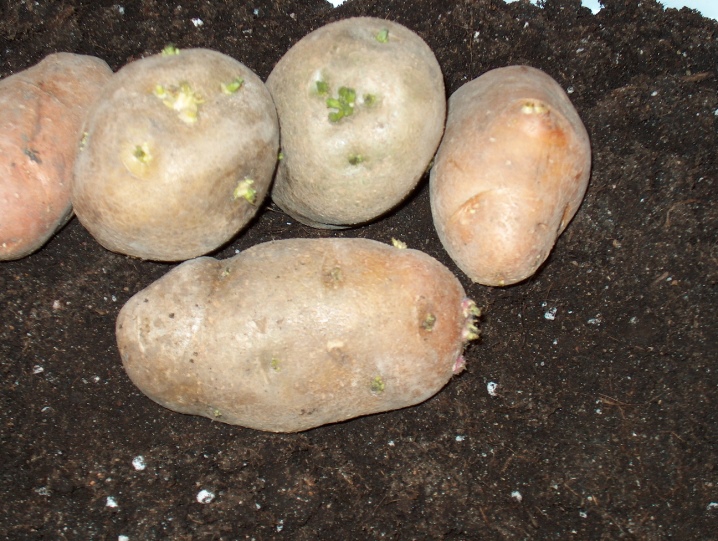
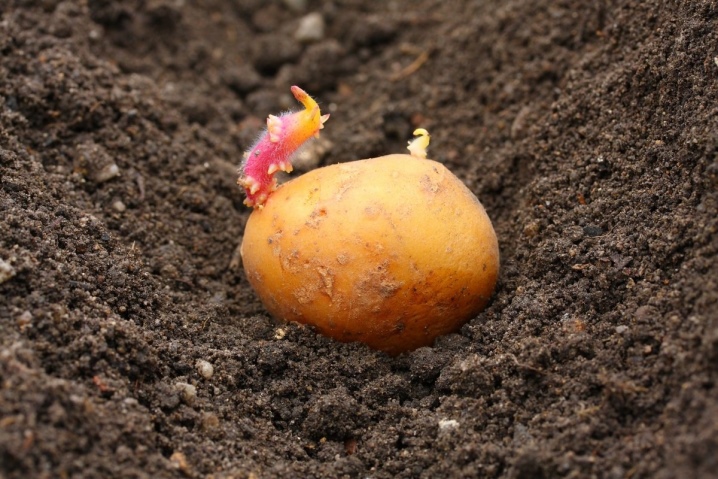
Potato sprouts actively appear when placed in the light. From some tubers, they can be taken several times a month, as new shoots appear. Potentially promising planting material is separated at the moment when the shoots reach a length of 4-6 cm. Such shoots are the most viable. But in some cases, they successfully take root and the options are half as short.
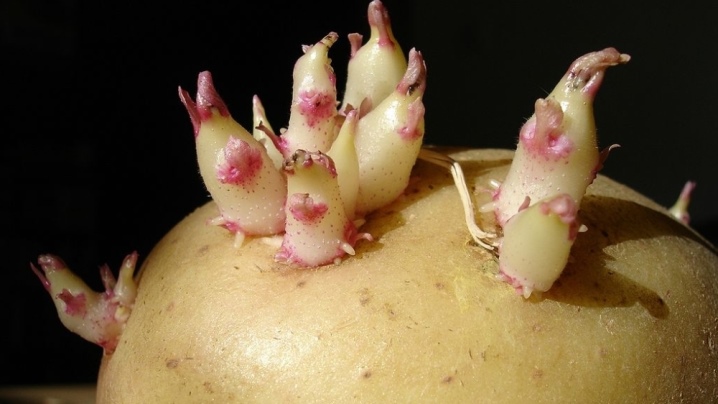

The breeding order will be as follows.
-
Separation of sprouts. They are selected carefully, special care must be taken in handling the most fragile - shadow shoots.
-
Preparation of ridges or greenhouses. The substrate should be moist, loose, nutritious. And you can also sprout potatoes on the balcony or windowsill, in containers. Planting sprouts must be carefully planned. Their germination begins 2 months before the emergence of tuberous potatoes.
-
Planting sprouts according to the scheme 50x70 mm. The soil around them is compacted. In warm climates, the most rational would be to plant immediately in a permanent place, without shelter, according to the scheme 50x20 or 60x20 cm. The garden is watered, mulched.
-
Seedling care... The aisles are periodically loosened, weeds are removed, the bushes that have grown up to 20 cm are spud. Poorly developing plants are fed with nitrogen fertilizers - nitrophosphate, ammonium nitrate, then watered abundantly.
-
If the seedlings were originally grown in a greenhouse, they will have to be moved when the bushes get stronger... It is important to know that the correct air temperature and lighting regime will benefit the abundant sprouting. It is necessary to withstand the tubers at a temperature of + 12-15 degrees Celsius. The humidity level is maintained by spraying.
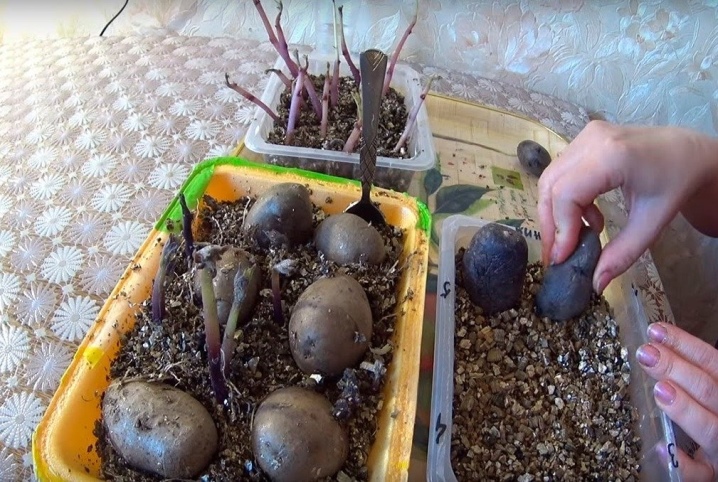

As for germination in the light and in the shade, each method has its supporters and opponents. When the tubers are placed in the dark, the sprouts will appear longer, but thinner, white or pinkish. They are pretty viable.
In the light, the formation of planting material is slower, the sprouts thicken, and their color depends solely on the varietal affiliation of the plant.
Dissection of the kidneys
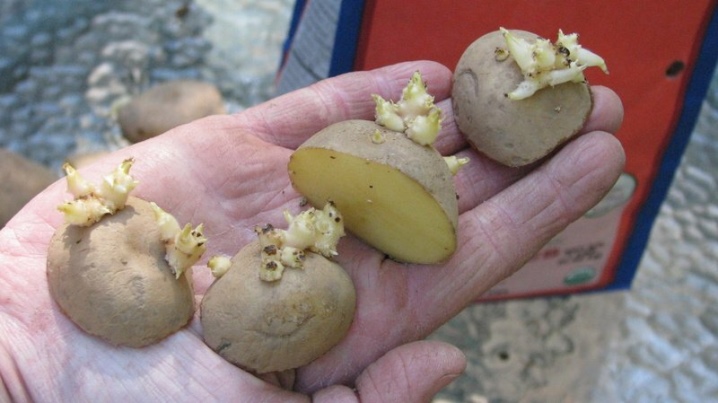
This method is also known as propagation of potatoes with eyes, sprouts. The fact is that tuberous buds carry the smallest stock of viral infections and retain all the varietal characteristics of the plant. To obtain planting material, you will need a convenient tool - a knife with an extended blade in front or a cork drill. With its help, disc-shaped elements no more than 1 cm in diameter are cut from the surface of the peel, with a peephole in the center.
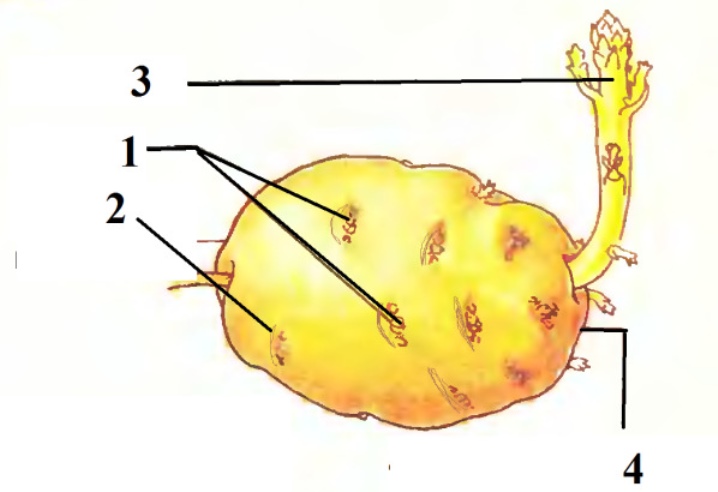
From each tuber, you can get up to 10 such blanks. They are placed on absorbent paper or other good moisture-absorbing material. Dry for 2-3 days to close the "wound". To stimulate germination, a certain temperature regime is maintained. Most of the day, the eyes are kept in a well-lit place at a temperature of 16-20 degrees, periodically moisturizing. The intensity of the growth of planting material will be beneficially affected by daily placement for 2-3 hours on Wednesday with an indicator of +40 Celsius.
Prepared buds can be planted on ridges after they acquire their own roots, give green buds... The procedure is performed simultaneously with the terms relevant for whole potato tubers.

It is not necessary to deeply deepen the discs; submersion into the ground by 30-40 mm is enough. From each plant obtained by the method of preparation of the buds, on well-prepared fertile soil, you can get up to 0.5-2 kg of tubers.
Other vegetative methods
Most often, the most common varietal potatoes are propagated by tubers - this is the main organ with which planting material is obtained. But this plant of the Solanaceae family is quite capable of forming new bushes from tops or other organs. Each species and method of its vegetative reproduction deserves special attention.

Layers
This method of obtaining seedlings also has its own characteristics. For the formation of cuttings, only healthy, clean tubers are used, previously germinated in bright light for 3-4 weeks. They are placed with their apical shoots towards the sun in specially prepared insulated ridges, containers, boxes and even flower pots. In the rows between the potatoes, only 20-30 mm are left.

After planting, a layer of peat with a thickness of at least 40 mm is poured on top. The substrate is spilled with warm water. Seedlings, while maintaining a stable temperature in the range of 18-24 degrees, will appear in 8-9 days. The stems that have grown to 50-80 mm are separated from the tuber together with the root, and planted as independent plants.
Interestingly, uterine potatoes dug up to obtain cuttings can also be placed back in the ground. It will grow as usual, but it will be somewhat delayed in flowering and harvesting. For such a plantation, it is better to immediately allocate a special area in the garden.
Tuber division
A universal method of increasing the amount of material is to obtain it from one tuber.... It is more convenient to do this in cases where there are not enough high-quality tubers suitable for planting. Cut the material with a sharp knife so that at least 1 peephole remains in each slice. The big advantage of this type of breeding is the possibility of using large tubers commonly used for human consumption. Cut slices are planted in the same way as for ordinary whole potatoes, slightly drying the slices so that they do not rot.
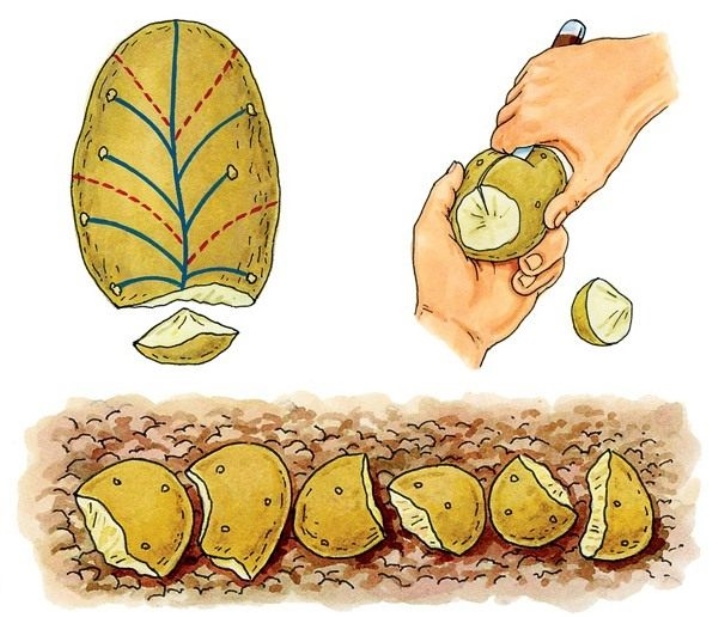
Incomplete division of the tuber is also used - to increase productivity, abundant branching of the tops. The stimulating incision helps to direct the biologically active substances consumed by the germinated material, not only to the apical buds, but also to the sleeping ones.

This is how it is shaped.
-
Take the tuber intended for planting.
-
They cut it deeply between the eyes. Inside there should be a whole core with a diameter of 2-3 cm.
-
Actions are repeated several times.

The resulting material is planted in the usual way. The result of incomplete division of the tuber will be noticeable even when young shoots emerge. They will turn out to be noticeably stronger than their counterparts, will give an abundant increase in greenery.
Cuttings
Reproduction of potatoes by cuttings looks rather unusual, but allows you to increase planting volumes without unnecessary hassle. Only the apical parts of young bushes with grown leaves are suitable for separation. Before grafting, potatoes are planted in the usual way, with preliminary germination of eyes.Then, when the bush stretches up to 20 cm, you can separate the top, germinate the roots in water, or immediately transfer the resulting green shoot to the nutrient soil.

For cuttings, it is important to provide the seedlings with an intensive growth of green mass. To do this, the soil is abundantly fertilized at the stage of filling the earth, then, after planting the tubers, it is loosened and watered. You can resort to temperature control using a covering material on the frame. In this case, the planting dates for tubers are shifted to an earlier period in order to get enough time for the rooting of the cuttings.
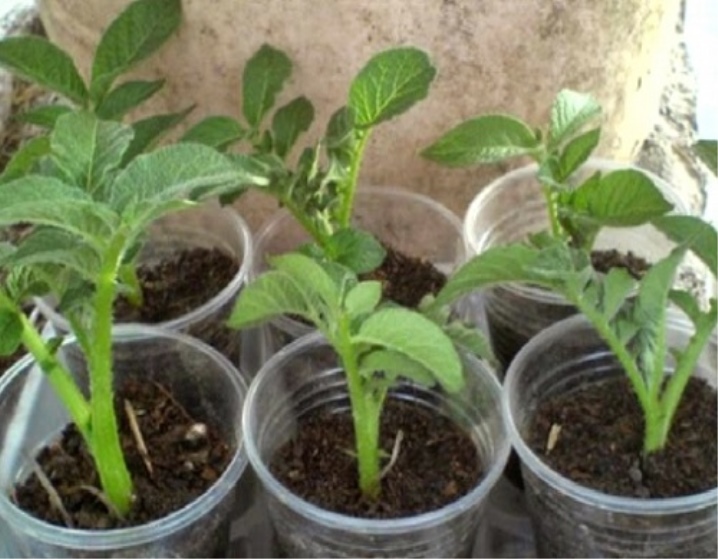

How to propagate by seed?
Generative breeding can be called rare for potatoes. Seed berries are usually harvested only from the rarest, elite varieties. The main advantage of this breeding method is the elimination of the risk of potato contamination. Viral and fungal infections are not transmitted through seeds. But for hybrids, this scheme will not work, since the collected material will not inherit the properties of the parent plant.
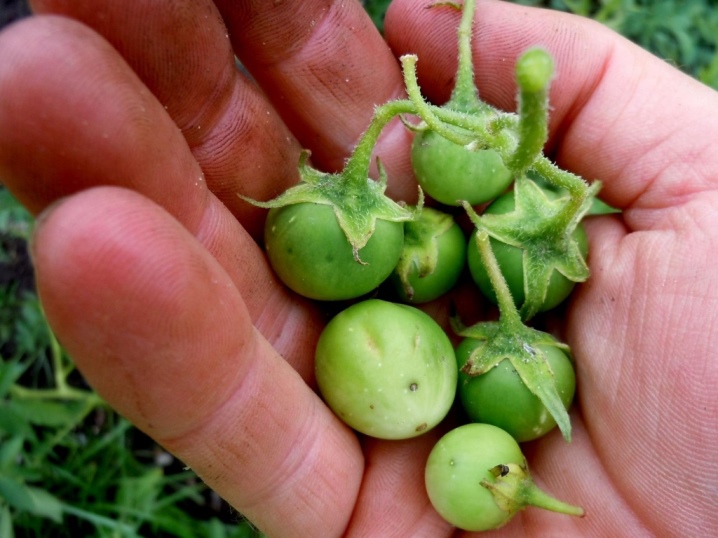

It is important to understand that with seed reproduction in the first year, only planting material is obtained. A full harvest is harvested from 2 years. The seed propagation process includes a number of stages.
-
Seed collection... It is produced in the fall, when the tops are dry and the harvest is complete. Seed berries are removed from the branches and laid out on the ground.
-
Receiving material... Rotten fruits that have begun to decompose are moved into water and kneaded. At the bottom of the container, seeds will be stored, which need to be removed and washed, dried.
-
Sowing in greenhouses. A container on a window will do as well. It is not necessary to sprinkle the seeds heavily with soil. As they germinate, they are watered.
-
Transplanting into the ground. It is carried out at the end of the period of return frosts. As soon as the danger of cold weather has passed, the seedlings are transferred to a permanent place.
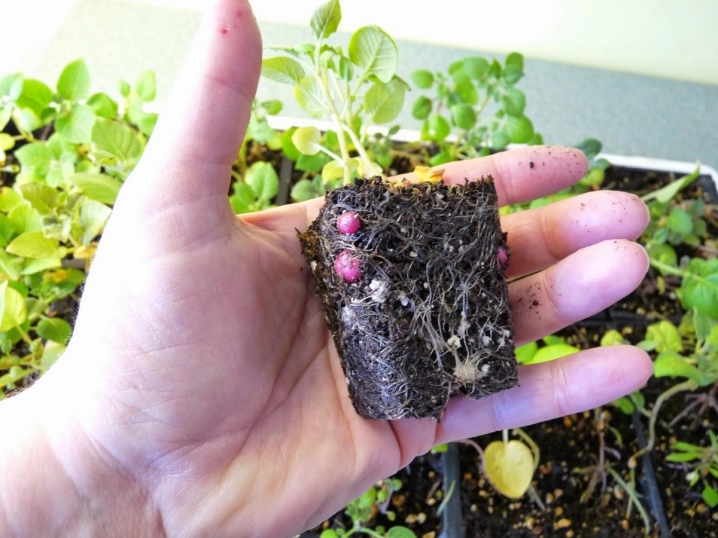

The main difficulty in planting such material is the very slow flow of all processes. Seeds germinate for a long time, they need a soil saturated with organic matter and minerals.
Maintaining the correct thermal and humidity conditions is also important. The growing season for such seedlings is longer. Growing under film takes at least 2 months.
After transplanting into open ground, the situation does not change much. Mature bushes stretch out and bloom later than others. Their yield is low, the tubers are often deformed. For subsequent reproduction, only the healthiest material is selected from the bushes that have demonstrated the best fruiting rates.














The comment was sent successfully.