- Authors: Nezakonova L.V., Pishchenko L.I., Ignatova N.M., Rusetsky N.V., Pingol A.P., Ilyashenko D.A. (Belarusian Center for Potato and Horticulture)
- Year of approval: 2012
- Appointment: dining room
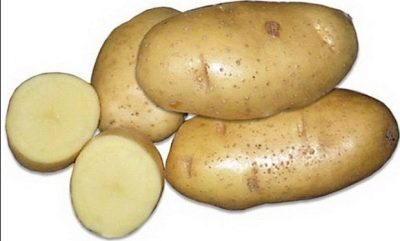
- Tuber size: large
- Tuber weight, g: 81-106
- Peel color: yellow
- Color of the pulp: white
- Starch content,%: 14,8-15,4%
- Tuber shape: oval
- Peel structure: weakly reticular
Potatoes are an obligatory food crop in the diet of Russians and not only, a tasty and healthy root vegetable in many respects. The culture is used not only in cooking, but also in medicine, cosmetology and even in construction, for example, starch for the production of fiberboard panels. Underground fruits are edible, unlike poisonous aboveground ones, they have a rich vitamin and mineral composition. The mid-late Yanka variety belongs to table varieties, has an attractive appearance, high transportability and shelf life.
Breeding history
The originators of the variety are the breeders L. V. Nezakonova, L. I. Pishchenko, N. Ignatova, N. Rusetsky, A. P. Pingol, D. Ilyashenko from the Belarusian Center for Potato and Horticulture. Yanka was approved for use in 2012.
Description of the variety
The variety has a wide range of positive qualities, which include not only excellent taste, but also much more. In addition to its widespread use in cooking, the variety has such characteristics as:
high commercial qualities;
does not tend to degenerate;
excellent resistance to mechanical damage;
good yield, keeping quality, unpretentious cultivation;
weak dependence on unfavorable weather conditions;
preservation of parental qualities in seed;
independence from climatic changes;
industrial cultivation;
strong immunity.
Disadvantages are very difficult to find in this variety, except that a slight weakening of immunity during the cold rainy season.
Characteristics of the appearance of the bush and root crops
Yanka is characterized by semi-erect, leafy shrubs, covered with medium-sized leaves. The leaf plate is open with slightly wavy edges, painted in light green tones. The variety blooms with white pleasant flowers with a medium-sized corolla. Each bush grows from 8 to 12 large (81-106 g) oval tubers, covered with a yellow dense skin. Almost no non-commodity tubers are formed. The number of small uncolored eyes is moderate, as is the depth of their occurrence. The rind is reticulate and of medium thickness.
Purpose and taste of tubers
BC culinary-type white flesh has excellent flavor and moderate spreading. During heat treatment and cleaning, it almost does not darken. The tubers contain 14.8-15.4% starch. Keeping quality indicators are stably kept within 96%, marketability is estimated at 85-95%. Potatoes have a rest period of 96 days.
Maturation
The Yanka variety belongs to the mid-ripening category: technical ripeness occurs 90-110 days after planting. However, do not forget that this is an average number, and more specific figures completely depend on the region of cultivation and its climatic features.
Yield
Yanka has an average yield, usually 195-311 centners are removed from 1 hectare. The maximum recorded indicators are 360 c / ha.
Growing regions
The variety is intended for cultivation in the North-West and Central regions.
Growing and caring
When planting, the optimal distance between the holes of 30-35 cm and 70 centimeters in the row spacing should be observed. When preparing and digging a site, you should take care of its cleanliness. It is necessary to select as much as possible the roots of weeds that can extremely negatively affect the development of plants. During plowing, manure is introduced into the ground at the rate of 250 kg per centner. A crop rotation is needed every three years. Agronomists call good predecessors carrots, cabbage, green manure and meadow grasses, as well as peas and beans.
Before planting, the tubers are germinated for three weeks at a temperature of plus 15 degrees. The ideal sprout length is 1-3, and no more than 5 centimeters. Cutting the tubers is not recommended, even if they are too large. Yanka is planted in holes, trenches and ridges to a depth of 10 cm. Further care consists in timely fertilizing with mineral fertilizers, weeding and hilling.

Planting potatoes is one of the main spring activities traditional for Russian gardeners. There are many ways to plant this vegetable, allowing you to get a good harvest in different conditions and climates. Before planting, you need to carefully prepare the planting material, correctly determine the timing, competently prepare the soil.


Soil requirements
For growing Yankees, light to medium soils are suitable in terms of particle size distribution with good lighting. But at the same time, it is worth remembering that growing on impoverished lands will not allow you to get a full return on the culture, so you should take care of the fertility of the soil and timely feeding, if there is such a need. For disembarkation, you need to wait for the soil to warm up well, usually this happens in early to mid-May. The best precursors for potatoes are corn, various legumes, and cabbage.

Disease and pest resistance
The variety is characterized by moderate resistance to the M virus and moderate susceptibility to the S. cancer, golden nematode, wrinkled and banded mosaic, rhizoctonia (black scab). It shows average resistance to late blight of leaves and tubers, to common scab, Alternaria, black leg and dry rot (fusarium). To avoid problems during the cultivation of plants, the tubers are pickled before planting. To combat known pests, insecticide treatments are used. Some people prefer traditional methods.

Potatoes are a popular vegetable crop that many gardeners planted on their site. But growing a bountiful harvest of tasty and large tubers is unlikely to succeed if the beds are not properly protected from the most common diseases and pests. Often, the development of diseases of various etiologies of potatoes goes unnoticed, so it is important to identify the problem in time and eliminate it.
















































































