- Authors: Yashina I.M., Volokhova G.I., Krasnikov S.N., Rogachev N.I., Simakov E.A., Anoshkina L.S.
- Year of approval: 2000
- Appointment: suitable for making French fries, chips
- Tuber weight, g: 65-160
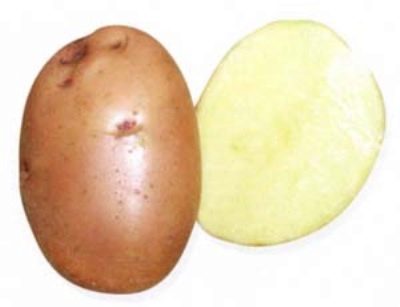
- Peel color: red
- Color of the pulp: light yellow
- Starch content,%: 18,2-21,9%
- Tuber shape: oval-rounded
- Peel structure: smooth to medium-coarse
- Eyes: medium depth
Nakra is a potato variety intended for growing in difficult climates. It is one of the subspecies especially appreciated in Siberia.
Breeding history
A group of breeders, which included Yashina, Volokhova, Krasnikov, Rogachev, Simakov and Anoshkina, worked on the development of Nakra. These breeders represented three different organizations. The variety planned for breeding was intended for areas of risky farming, and here the employees of the enterprises achieved their goal. Nakru was added to the state register in 2000.
Description of the variety
According to gardeners, Nakra is one of the best potato varieties. There are several confirmations of this:
- potatoes contain a lot of starch, so the puree turns out to be very tender, literally melts in your mouth;
- bushes give a large amount of harvest, so potatoes can be grown for sale;
- harvested tubers lie for a long time and are well transported;
- potatoes taste great.
The only negative that can be found in Nakra is susceptibility to various diseases.
Characteristics of the appearance of the bush and root crops
Nakra bushes are quite tall, besides, they are erect. The foliage is medium, with a slight glossy shine, colored green. Flower corollas are large, gather in inflorescences. The petals are painted in a red-violet tone.
The oval-round tubers can be small or medium in size. The smallest specimens reach a weight of 65 grams, larger roots - 160-165 g. The red skin can have a smooth or medium-rough structure.
The inner content of the potato is light yellow. The eyes are located at a medium depth. The starch content in tubers can exceed 20%. Percentage of keeping quality of potatoes - 95. This means that under the right conditions the variety will be perfectly stored throughout the winter.
Purpose and taste of tubers
Thanks to the large amount of starch, the variety boils well. Puree of excellent quality is obtained from it: soft, tender, crumbly, without lumps. In addition, fries, chips and other delicacies are often made from Nakra potatoes. The sweet taste and delicate aroma are preserved even when the tubers are baked in the oven.
Maturation
Nakra is a mid-season potato variety. Basically, it ripens in three months, but in particularly cold regions such potatoes can take up to 120 days to ripen. Most summer residents harvest at the end of July, but the specific dates will depend on the climate in the region. It can be August or even the beginning of September.
Yield
From a potato bush, usually 6 to 12 tubers of different sizes are obtained. Therefore, the mass will vary. It is much easier to estimate yields if you think of them on a large scale. So, basically, from 203 to 308 centners of potatoes are obtained from a hectare of soil. But some gardeners managed to bring this figure to 399 centners per hectare.
Growing regions
This potato variety is best grown in the regions declared by the originator. These are Western and Eastern Siberia, the Far East, the Volga-Vyatka region.
Growing and care
The Nakra disembarkation procedure is carried out at the end of April or in May. A previously germinated material is planted on the garden bed, so the ripening period can be reduced.Nakru is not planted where peppers, tomatoes, potatoes previously grew. If there is no other soil, then siderates are planted in it in the fall. Tubers are best planted in cloudy but not rainy weather. Before placing in the ground, Naqra is immersed in a fungicide solution. The optimal planting pattern is 0.3x0.7 m. After placement, the potatoes are watered.
The second watering will need to be done in a week. The third and fourth - at the time of budding and after the end of flowering. More often, water only if the season is dry. For irrigation, they take warm water, and the procedure itself is carried out in the evening. It is watered not only at the root, but also throughout the growth area of the bushes.
The fifth and subsequent watering is carried out every 10 days. After them, the substrate must be loosened: both near the bushes themselves, and in the aisles. You will have to huddle Nakra at least twice a season. Do this after watering or rainfall. The first hilling is carried out when the sprouts grow up to 10 centimeters, the second - when they stretch up to 20 cm. The soil for hilling is taken from the row spacing.
Fertilizers are also highly desirable to apply on wet soil. The first feeding of Nakra will be nitrogen. Rotten dung is a good option. They are fertilized with soil 2 weeks after the emergence of shoots. When the potato blooms, the substrate is watered with a potassium-phosphorus mixture. And after flowering, the tubers are fertilized with a mullein solution. For greater efficiency, superphosphate is added to the composition.

Planting potatoes is one of the main spring activities traditional for Russian gardeners. There are many ways to plant this vegetable, allowing you to get a good harvest in different conditions and climates. Before planting, you need to carefully prepare the planting material, correctly determine the timing, competently prepare the soil.


Soil requirements
Nakra potatoes prefer soft soil with a loose structure. The land must be well drained, allowing not only water to pass through, but also air. Nakra will feel comfortable on loamy and sandy loam substrates, black soil. She will also like the peat composition of the soil. It is important that the soil is well lit during the day.
Clay soils, substrates with a large proportion of sand are not suitable for a plant of this variety. Nakra will not be able to grow on acidified soil. The acidity should be in the pH range 5.5-6.5.


Potatoes are a popular vegetable crop that many gardeners planted on their site. But growing a bountiful harvest of tasty and large tubers is unlikely to succeed if the beds are not properly protected from the most common diseases and pests. Often, the development of diseases of various etiologies of potatoes goes unnoticed, so it is important to identify the problem in time and eliminate it.
















































































