- Name synonyms: Rinda
- Year of approval: 1993
- Appointment: for fresh consumption, for fermentation, for all types of processing
- Leaf rosette: with raised leaves
- Internal stump: short
- Weight, kg: 3,2-3,7
- Taste qualities: excellent
- Yield: high
- Average yield: up to 9.0-9.5 kg / m2
- Growing regions: Central, Volgo-Vyatka, North-West, West Siberian, East Siberian
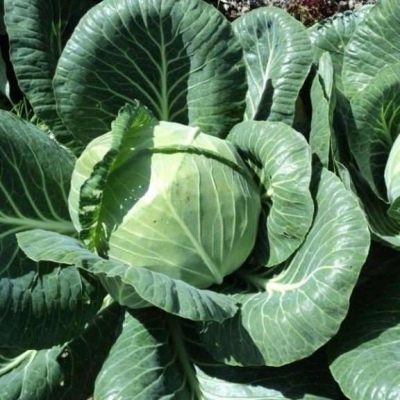
Rinda is a legendary cabbage variety. The outstanding yield and very tight, large heads of cabbage brought him fame.
Description of the variety
Rinda cabbage is a first generation hybrid. Bred by the Dutch company Monsanto Holland B. V., entered into the Russian State Register in 1993.
Characteristics of the appearance of the plant and heads of cabbage
A plant with a compact rosette of large leaves. Leaves are light bright green, with large white veins. In young plants, the foliage is slightly raised. In mature ones, it bends around the head of cabbage. The leaf stalks are short, the stem is short, the plant looks neat and impressive on the garden bed.
A head of cabbage of medium size, weighing 3.2-3.7 kg. The shape is round, slightly flattened. Individual heads of cabbage can reach 5-8 kg. The outer leaf of the head of cabbage is green, in the context of the head of cabbage is yellowish-white. The density is excellent, the heads of cabbage are strong and crunchy. The inner leaves are uniform, laid without gaps. The stump is small, short.
Purpose and taste
The taste is excellent, the head of cabbage is tender, juicy and crunchy. Cabbage is very good fresh. Suitable for any dishes: salads, cabbage soup, cabbage rolls, stewed and fried side dishes. The cabbage leaf is dense, but plastic - convenient for stuffing. In mature heads of cabbage, the leaves are stacked one to one, the cut head looks tightly packed, rich. There may be gaps in unripe heads of cabbage. The variety is also suitable for all types of processing for the winter: pickled, pickled, in salads with other vegetables.
Ripening terms
The hybrid is mid-season, heads of cabbage can be removed 123-140 days after the emergence of mass shoots. Harvested in August-September, sometimes in early August. For personal use, you can pluck young heads of cabbage already at the end of June.
Yield
The yield is very high. The yield of marketable fruits is 900-914 c / ha, which is 2 times more than for the standard variety Moskovskaya late 9. From 1 sq. m, an average of 9-9.5 kg is removed - this is 3-4 large, tight heads of cabbage. The variety is recommended for commercial production and industrial processing.
Growing regions
The variety is officially recommended for cultivation in the Central and Volga-Vyatka regions. And also Rinda cabbage is grown in Western and Eastern Siberia, in the north-west of Russia. It is a cold-resistant, hardy plant and can be grown in any regions of the Russian Federation.
Growing and care
Planting pattern - 40 cm between plants, 60 cm - between rows. Planting time depends on the local climate, the growing method and the planned harvest date. Typically, cabbage is planted from late April to late May.
When grown in seedlings, seeds are sown from March 15 to April 15. Seedlings are planted in open ground in mid-May.
The variety loves moisture, it is not very resistant to droughts.
Watered with warm water, 18-25 degrees, at the root, often and abundantly. Watering is carried out early in the morning or in the evening; on cloudy days, you can water during the day. If it is cold cloudy weather, it is undesirable to water in the evening, it is better to postpone the procedure to the morning. The quality of the heads of cabbage directly depends on the uniformity of irrigation. In hot dry weather, water at least 3-7 times a week. In a wet summer, you can water no more than 1 time per week.
If it is not possible to water in a timely manner, the soil is thoroughly loosened after each watering and mulched with straw, chopped grass, and hay. Mulch protects against weed growth at the same time.The next watering can be carried out directly on the mulch.
Watering varies depending on the age of the plant. For seedlings - 1 liter, gradually the rate for 1 plant is brought to 5 liters or more during the period of filling the heads. The most crucial periods are the beginning of the formation of heads of cabbage and their active growth. Watch out for the lower leaves. As soon as they start to wilt, watering can be gradually reduced.
Drip irrigation works best for cabbage. Watering is stopped 3 weeks before harvesting the heads of cabbage. But this should not be done abruptly. The Rinda variety is not at all prone to cracking, but it is better not to stress the plants.
Cabbage loves feeding. Ash, superphosphate, ammonium nitrate, potassium salt are used according to the usual scheme - nitrogenous in the initial periods, potassium-phosphorus during the formation of heads of cabbage. Top dressing scheme.
20 days after disembarkation of seedlings.
Another 10 days after the 1st feeding.
20-25 days after the 2nd feeding.
Like all early varieties, cabbage does not have a high keeping quality. It can be stored for no longer than 2-4 months (late ripening ones also lie for 6 months). However, in practice, the Rinda variety shows a higher keeping quality than other varieties. Due to their density, heads of cabbage retain freshness for 4 months.

To grow a rich cabbage crop, you need to know when and how to plant this crop outdoors. Planting dates are determined depending on the variety. It is also necessary to properly prepare the soil and follow the rules of crop rotation.


Soil requirements
The variety prefers loose, nutritious, well-drained soils - the plant does not like stagnant moisture. Acidity is neutral. Avoid places with dense, moist soil for planting, however, quickly drying soil is the worst choice.
Zucchini, potatoes, pumpkins, cucumbers, legumes are the best predecessors for Rinda. You should not plant cabbage where any other kind of cabbage, radish, turnip, beetroot, radish or tomato grew in the past year.

Cabbage requires particularly careful care when growing. The plant quickly absorbs nutrients, so the soil needs to be enriched regularly. Adequate amounts of minerals, organics and nitrogen must be provided. Some products can be purchased at the store, while others are easy to make at home.
Disease and pest resistance
Cabbage is a culture with an abundance of enemies, which are difficult to resist only with your immunity. This is an extensive group of gnawing insects: cruciferous fleas, cabbage fly, white turnip. The Rinda variety is hardy, but it also needs prevention of damage by these pests.
Compliance with crop rotation. Cruciferous plants are planted in the same place after 3 years, not earlier.
Getting rid of all weeds on the site - flowering weeds attract butterflies.
Thorough autumn harvesting, all the leaves and legs are piled up, in the spring, when they dry, they are burned.
Planting seedlings as early as possible. Pests are most dangerous for young plants; the spring cold partially protects against damage.
Setting sweet traps near cabbage (these can be simple cut plastic jars with a solution of water and jam).
Already damaged plantings are sprayed with a solution of 300 g of wormwood, 1 glass of sifted ash and 10 liters of boiling water. The solution is allowed to brew for 6 hours, 50 g of liquid soap is added, and immediately used.
Feeding can also help. They contribute to a more active growth of green mass.

Cabbage is a very popular horticultural crop. But growing a good, large and tasty cabbage is sometimes very difficult, because it is often affected by a huge number of diseases and pests. The main role in the cultivation of this vegetable is played by regular prevention, which helps to get a rich harvest, and prevent the occurrence of diseases and the invasion of harmful insects. It is very important to start treatment as early as possible, otherwise there is a risk of spreading the infection to still unaffected plants.
Review overview
There are few reviews. Those who planted Rinda cabbage liked the variety. Heads of cabbage lie much longer than promised, because they are large and dense. Even if the outer leaves are damaged, they are easy to remove and still leave a huge amount of pulp. For the same reasons, the variety is very good for transportation, sale and for any kind of mass processing. Heads of cabbage are powerful, dense and tight - it is very convenient to handle them when there are many of them. The variety is also easy to grow: cold-resistant, neat, very hardy, does not require special care. The yield is excellent, even the smallest fruits weigh 3 kg each, losses when grown for sale are small.