- Name synonyms: Pandion
- Year of approval: 2005
- Appointment: for fresh consumption
- Leaf rosette: horizontal
- Leaf size: small to medium size
- Leaf color: dark green
- Sheet surface: bubbly
- Outside stump: short
- Internal stump: middle length
- Weight, kg: 0,8-1,8
For lovers of fresh cabbage salads, the optimal solution would be to plant an ultra-early variety on the garden bed, which gives a stable harvest. One of the good and tasty varieties is the Pandion cabbage, created by Dutch scientists.
Breeding history
Pandion cabbage is one of the most popular species, bred by Dutch breeders of the Monsanto Holland B.V. agrofirm in 2003. In 2005, the hybrid appeared in the State Register of approved for use on the territory of the Russian Federation. Initially, cabbage was zoned for the Central region, but over time, the vegetable crop expanded the geography of growth to the North-West, Volgo-Vyatka, East Siberian and West Siberian regions. It is possible to grow a vegetable in small gardens, and on farm plantations, and in greenhouse structures, which is convenient for colder regions.
Description of the variety
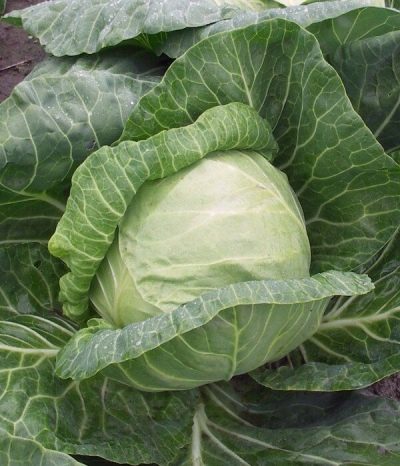
White cabbage Pandion is a compact plant with a horizontal leaf rosette. The leaves of the plant are medium, growing up to 35-40 cm. Sometimes mixed with smaller foliage. A characteristic feature is a uniform dark green leaf cover, as well as a bubbly surface, a barely noticeable waxy coating and slightly wavy edges. The outer stump is shortened, and the inner one is of medium size.
Characteristics of the appearance of the plant and heads of cabbage
The Dutch vegetable matures even and flavorful, making it popular with kale farmers on an industrial scale. The hybrid belongs to medium-fruited. The average weight of a head of cabbage ranges from 800 grams to 1.8 kilograms. The shape of the head is round, rather dense. Outside, cabbage has a bright green color, and inside it is snow-white.
Ripe heads of cabbage tolerate long transportation without significant losses, and also do not crack during storage. For long-term preservation, it is recommended to carefully cut off the heads.
Purpose and taste
Pandion cabbage is famous for its great taste. The vegetable has a pleasant crunchy taste, characterized by juiciness and refreshing aroma. The vegetable does not have fiber and wateriness. This cabbage type is ideal for adding to fresh salads, especially during the period when the body requires fresh vitamins after winter and spring. Cabbage is not suitable for storage for the winter, like most ultra-early varieties.
Ripening terms
The hybrid belongs to the early maturing varieties. Less than 110 days pass from the appearance of the first shoots to the maturation of cabbage heads. The period from planting seedling bushes to the garden to mature vegetables takes about 48-53 days. The heads ripen together, so during the first stage of harvesting, more than 60% of the total is collected. You can evaluate the taste of an early vegetable in mid-July, and full ripening and return of the fruits occurs in August-September.
Yield
The yield performance of the Dutch hybrid is excellent. The average yield is 280-513 centners per hectare of plantings. The maximum indicator is recorded at around 580 centners per hectare of plantations.
Growing and caring
Vegetables are cultivated both by seed and seedlings, but it is planting through seedlings that is more productive. Sowing seeds for seedlings is carried out from mid-March to early April. When the bushes grow and get stronger, they are transferred to garden ridges (mid-May). For planting in open ground, seedlings aged 50-55 days are suitable, and for greenhouses 45 days. The bush should have 5-7 true leaves and a strengthened root system. It is recommended to place up to 3 bushes per 1 m2. Planting is carried out according to the standard scheme - 50x60 cm. When planting a vegetable on a garden ridge, one should take into account the temperature regime - at least 18-19 degrees in the air and 12-13 degrees on the ground. Better to cultivate on a cloudy or cool day.
The agricultural technology of vegetable crops consists of standard measures: irrigation with settled or warm water, fertilizing twice during the growing season, loosening and weeding the soil, hilling (1 time per season), prevention of viruses and pest attacks.

To grow a rich cabbage crop, you need to know when and how to plant this crop outdoors. Planting dates are determined depending on the variety. It is also necessary to properly prepare the soil and follow the rules of crop rotation.


Soil requirements
The vegetable is completely undemanding to the structure of the soil. The main thing is that the soil is light, loose, and allows air and moisture to pass through well. The acidity index of the soil should be at a pH level of 5. In addition, it is recommended to saturate the soil with the necessary fertilizers before planting.

Cabbage requires particularly careful care when growing. The plant quickly absorbs nutrients, so the soil needs to be enriched regularly. Adequate amounts of minerals, organics and nitrogen must be provided. Some products can be purchased at the store, while others are easy to make at home.
Required climatic conditions
Dutch cabbage is quite stress-resistant, but prefers to grow in areas well-warmed by the heat of the sun, where there is enough light and there is a reliable barrier against drafts.
Disease and pest resistance
Pandion has good protection against fungal diseases. The culture is absolutely resistant to fusarium wilt. Dangerous pests for cabbage are considered: aphids, cruciferous flea beetles, moth and bear, which can be dealt with by preventive spraying with insecticides.

Cabbage is a very popular horticultural crop. But growing a good, large and tasty cabbage is sometimes very difficult, because it is often affected by a huge number of diseases and pests. The main role in the cultivation of this vegetable is played by regular prevention, which helps to get a rich harvest, and prevent the occurrence of diseases and the invasion of harmful insects. It is very important to start treatment as early as possible, otherwise there is a risk of spreading the infection to unaffected plants.