Japanese camellia: features and care at home

Nature has presented mankind with plants of various beauty. Among them there is an amazing, delicate and exquisite flower, sung by prose writers and poets from different countries. This is a Japanese camellia. We will tell you how to grow it at home.
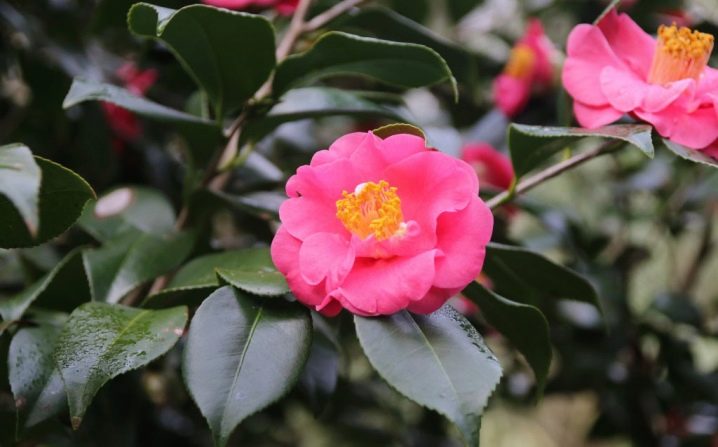

Description
Camellia is admired for its perfection. It was mentioned by Japanese chroniclers at the beginning of the first century. In Europe, the flower appeared in the middle of the 17th century and is named after a monk with the surname Camellus, who studied the plant in detail and gave its description. In Japan, an exotic culture grows in the south of the country. It is also common in China, South Korea, Taiwan.
The beautiful double flowers of japonica belong to the genus of tea families. You can meet a plant in nature in the form of a tree reaching a height of 10-11 meters or a shrub rising to 150 cm. In our country, a flower with decorative leaves is grown mainly at home. An adult houseplant or greenhouse specimen stalls at 2 meters.


Its leaves are painted in a dark green color, can be from 8 to 10 cm in length, and reach 50 millimeters in width. They are very dense in structure. The branches of the Japanese camellia are dark gray, and the young one-year-old shoots have a brownish tint. The basis of the plant is a flower that is not inferior in beauty to pink buds. It can be red, pink or white.
Breeders managed to get a large number of varieties of a spectacular flower growing in diameter from 40 to 150 mm. In structure, it can be one or in the form of a brush, it can consist of the usual 5 petals with yellow stamens surrounding it, or be a fluffy double inflorescence endowed with more than 20 petals. There are semi-double samples. This wonderful plant blooms both in winter and in spring. It absolutely does not tolerate cold weather, therefore, on the territory of our country, it can be found in houses, greenhouses, winter gardens.


Important! It is not entirely easy to grow japonica in room conditions, you need to know the intricacies of the conditions of its maintenance.
Views
There are more than 250 different varieties of camellias in the world. Gardeners are accustomed to seeing Japanese camellia in the form of a lush shrub with a large number of flowers. Its flowering lasts almost six months and falls on the time interval from November to May inclusive. In the medicine of the East, it is used as a remedy for fighting cancer. The most popular types of Japanese camellia are considered to be "Alba", which has simple five-petal flowers of white color, as well as a plant called "Winter Rose". It is decorated with snow-white or pink large buds, which are terry in structure.
The known types of Japanese camellia are as follows:
- Adolphe audusson - differs in large (up to 12-13 cm) red double flowers; red camellia blooms in spring;
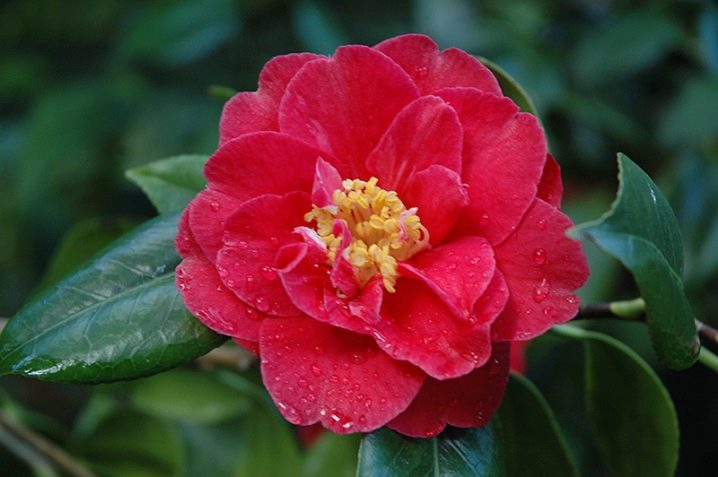

- Pink perfection - large double flowers, reaching 7-8 cm in diameter, they have a delicate pink tone; flowering period occurs in the spring;
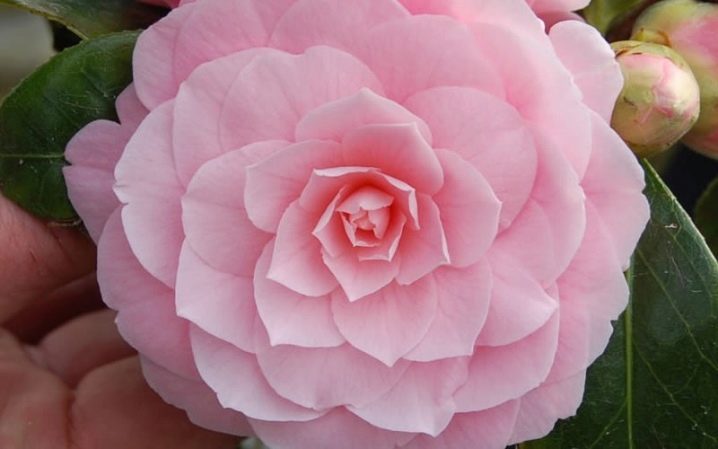

- Japonica purity - this plant has large (up to 80 mm in diameter) white flowers, is a perennial specimen and also blooms with the arrival of spring;
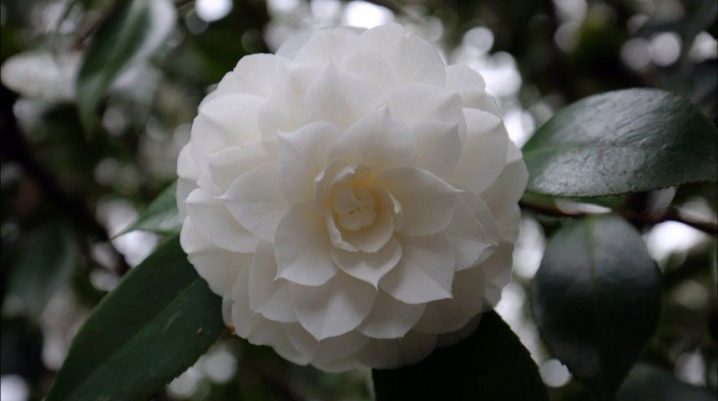

- William S. Hastie - is a bush with large (up to 5 cm in radius) crimson flowers, has lush and double buds; flowers appear in spring;
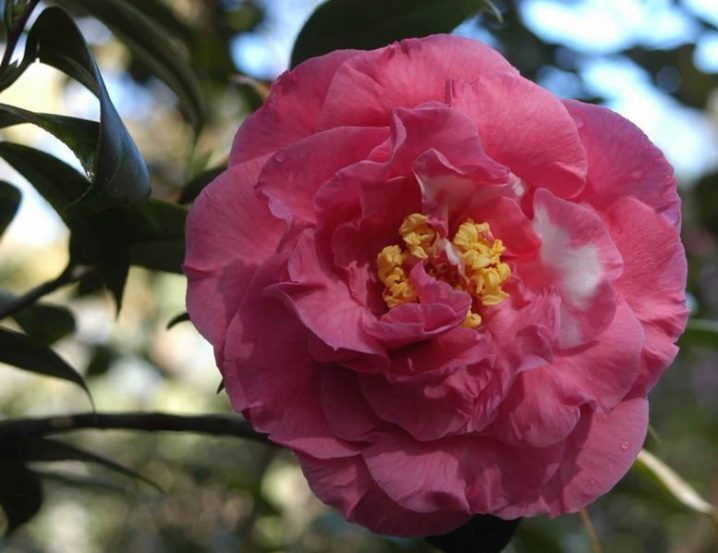

- Chandlers red - This is a red solid color camellia with large and dense flowers.

Conditions of detention
Japonica is a plant that is very sensitive to the slightest changes in its habitat. In indoor conditions, camellia can grow, but it will not bloom. In order for the plant to form flower buds, it must be in a room where the temperature can be maintained between -15 degrees and +6 degrees Celsius. The best place for a flower would be a warmed veranda, a greenhouse or any room., in which the air does not warm up above these boundaries. In summer, the japonica should be taken out into the garden or placed on a darkened balcony. If your flower spends a lot of time in a room with a high above zero temperature, then it will certainly begin to fade.
Important! The plant must be in a lit place all year round. In greenhouses, special lighting is made. Camellia's light loves diffused, not focused on the bush.


How to care?
The growing Japanese camellia should be watered thoroughly, but not poured over. After the bush has faded and plunges into a state of rest and rest, watering at home should be done less often, the main thing is that the substrate does not become completely dry in a flower pot. The soil in which the japonica will grow must be acidic, so there is no point in planting it in ordinary soil from your garden. Usually, a universal soil is sold in specialized stores, and if it is not there, then a substrate for azalea should be purchased.
You can independently prepare the soil composition at home, if you take the drainage, which is subsequently placed on the bottom of the pot. Then mix the four indicators. The sand must be combined with sod and leafy soil, as well as peat. Turf and sand are taken in the amount of one portion, and two compositions of peat and leafy earth are added to them. You can also use the bark of coniferous trees.
Important! Once a month, it is necessary to feed the japonica by introducing fertilizers used for azaleas into the soil. If the flower has buds, then the number of dressings can be increased to 2-3 within 30 days.


The plant must be pruned every 2 years. This procedure promotes the formation of a lush crown of the bush and the removal of weak shoots. It is necessary to carry out pruning, starting from the inside, thereby leaving large inflorescences to grow, which are at the tips of the branches of the bush. The procedure is performed during the autumn months such as October and November. In the southern regions of the country, where in winter the air temperature does not fall below +20 degrees, the cultivation of Japanese camellia is possible not only at home, but also in gardens. For the convenience of caring for a shrub, it is planted in late autumn or early spring, at a time when a very active growth of shoots has not yet begun.
The pit for planting camellia is made large. It should be 2 times the size of the earthy coma around the seedling itself. The soil can be additionally acidified with spruce or pine bark. A drainage is placed at the bottom of the pit, and a lump with the roots of the seedling is placed on it. Care must be taken that the root collar is not covered with soil. After that, the trunk is covered and the soil is mulched with sawdust, bark of coniferous trees or shavings. During the cold season, the mulching layer is increased.
The flower bush should grow in places where there are no drafts, as well as direct sunlight. In the period from May to July, mineral dressings are applied. For the winter, it is advisable to cover the crown and trunk, which can be done with spruce branches or material.


Transfer
Planting the growing Japanese camellia in a larger pot should be carried out every year in the spring. If your plant has grown stronger, has grown and is actively blooming, then this procedure should be performed no more than once every 2 or 3 years.The process is carried out only after the camellia has faded. In any other case, transplanting for a Japanese woman will become a great stress; it will take a long time to adapt to a new place. When the bush has grown to the size of a tub sample, the top of the soil in the tub is replaced annually.


Reproduction
In order for several flowers of Japanese camellia to appear in your home at once, it can be propagated in several ways.
Seeds
This procedure is carried out by planting seeds. Seed sowing is done throughout the entire period from spring to autumn. Before being planted in the substrate, they must first be soaked in warm water for a day in order to swell. Boxes with planted seeds or cups should be placed in a warm place and kept there until germination. The air temperature in the room should be positive within the range of 21 to 24 degrees. Watering should be done by spraying. Seedlings should appear in 30-50 days.


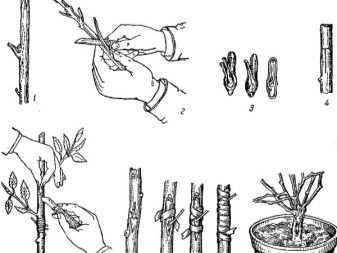
Cuttings
The cutting method is often used. In winter or in the middle of summer, small twigs up to 8-10 cm long are cut from the main bush, which are still young shoots. Each of them should have several leaves. Small greenhouses (mini) are prepared, into which soil is poured, consisting of sand and peat in equal proportions. Cut camellia shoots are planted in such greenhouses. You can make additional illumination from dim light. The seedlings are kept for 3 months. During this period, with proper care, the formation of root processes occurs, the cut cutting turns into a miniature finished camellia. After 2 years, they are transplanted into large pots.


By vaccination
A bud is cut off from the top of the japonica and grafted onto another tree. This method is difficult because the success of the event is not always guaranteed. You can plant a camellia on a tea bush as follows:
- at an angle, small branches with leaves on the crown are cut from the plant;
- horizontal cuts are made on the trunk of the tea tree; they should be at the level of 12-15 cm from the ground;
- gently push the bark on the sides and in the shape of the letter "T" make vertical cuts that coincide in length with the cuts on the camellia twigs;
- after that, the bark is pushed apart and placed in the cut Japanese cuttings;
- the bark is returned to its original position as much as possible, closing the inserted stalk with it, squeezed tightly and wrapped with tape or tape.
Important! In order for the grafting to be successful and the new stalk to receive enough nutrients, the tea bush should not have shoots below the place where the operation was carried out. They need to be removed.

Diseases and pests
Like most plants, Japanese camellia is not immune to the attacks of various insects and is affected by diseases. This happens due to non-observance of the conditions for keeping the flower. The most common pests that harm the plant are spider mites, tea moths, whiteflies, and scale insects. An easy remedy to combat them is insecticidal soap. It is sold in flower shops or specialty shops. It is necessary to make a soapy solution, combine the soap with water and spray the flower. If this remedy is ineffective, then chemicals containing insecticides are used.
Chlorosis is a common disease in Japanese camellia. The first sign of illness will be yellowed leaves. The disease is treated with "Iron Chelate", and "Ferrovit" is also often used. The flower is also struck by the cucumber mosaic. With it, pallor of the leaves is observed, their coverage with spots. For treatment, the drug "Actellik" is used. In case of fungal diseases, Japanese leaves cover black or gray spots. They fight the fungus by means of "Fungicide".



Tips for caring for camellia at home in the next video.

























The comment was sent successfully.