How to plant zucchini?

Zucchini are pumpkin crops. Place of origin - South America and Mexico, zucchini were also grown by the tribes of the Aztecs, using only seeds for food. At the beginning of the 15th century, these vegetables came to Europe, where they were used only for decorative purposes and were not eaten. Only two centuries later, the Italians began to eat small unripe fruits. Zucchini appeared in Russia only at the beginning of the 19th century.
Now it is a fairly common annual culture around the world. Zucchini have their own nuances when planting and growing. The plant is quite unpretentious, but requires attention and care. Produces a good harvest throughout the summer.


Timing
Zucchini yields its first fruits as early as 60–70 days after planting, so in favorable climatic conditions with long summers, seeds can be sown directly into open ground when the air temperature reaches 15 ° C. Zucchini bear fruit throughout the warm period and, with proper care, bring a rich harvest. Therefore, it is important to sow the crop early as conditions permit. Early planting is possible in seedlings. It is used even in the southern regions and the Moscow region to get an early first harvest. Zucchini is a thermophilic culture. They begin to grow well at + 18–20 ° C, and best of all, when the air warms up to + 25 ° C. Therefore, planting seedlings in open ground should be at the beginning of summer, in June (especially in the regions of Siberia and the Far East).
It takes about one month to grow seedlings (up to about 35 days). The timing of sowing seeds can be calculated independently based on this. For example, in the Moscow region, the air warms up enough by mid-May, which means that sowing should be done in early April. Then there will be enough time for the formation of strong viable seedlings. During this period (April-May), gardeners are already moving to summer cottages, where they begin to grow vegetable bushes at home. Along the way, experienced gardeners prepare the soil, beds and greenhouses for the summer season.
Favorable days for planting seedlings in open ground are those when the soil warms up to + 10-12 ° C and no more nightly drops in temperature are expected. If there is a threat of its decrease, it is recommended to build a temporary greenhouse from wooden frames or wire arcs and polyethylene. In the daytime, the structure can be removed for ventilation, and returned again at night. This way you can protect young plants from freezing and death.
According to popular belief, zucchini begin to be planted with seeds in the ground when the cherry blossoms.

Best predecessors
To get a rich harvest, gardeners should definitely follow the principle of crop rotation in their area. According to it, it is not recommended to grow the same vegetables or related varieties in one place for more than 2 years in a row. That is, zucchini should not be planted after pumpkin and melon crops.
Planting zucchini is best after:
- legumes;
- potatoes;
- carrots;
- beets;
- Luke.
After onions and garlic, the zucchini will grow and bear fruit well, it will not be hit by pests and diseases. The vegetable will feel great in the beds after greenhouse plants (mustard, oats). Zucchini should not be planted after other pumpkin crops (cucumbers, pumpkins, squash) because of the high risk of being damaged by bacteria, pests and diseases that could remain in the soil from the last season. Also, vegetables of related families require the same microelements for growth.They deplete the soil by sucking in the necessary substances. Therefore, zucchini will grow poorly and give a meager harvest. Disembarkation at the same place can be done only after 3 years.
It is recommended to plant beets, turnips or radishes in the vicinity of zucchini. You can plant herbs such as basil or green onions.


Preparation
Zucchini is an unpretentious crop when grown outdoors. The plant will yield a small yield even under unfavorable conditions and minimal maintenance. But in order for the number of vegetables to please, it is still worth preparing for growing a crop, finding out the sowing rules and the necessary conditions. It will not take much time and effort if everything is done correctly and in a timely manner. Some of the preparation can be done in the fall and the rest in the spring.
A place
Zucchini is a thermophilic crop. It needs a well-lit place. A site for planting zucchini is chosen protected from wind and drafts. It is not worth planting zucchini in the shade, where there is not enough natural light and the soil does not warm up during the day. In the southern regions, where the sun is abundant, it is better to plant the culture in partial shade, near the trees. This will keep moisture all day long, the leaves will not burn under the scorching rays.
The bed must be made wide so that the plants have enough space for the correct formation of the root system. Recesses are made on it under each bush for ease of watering. The water will not spread over the entire bed, and the plants will receive enough moisture. Zucchini thrive on a compost heap in a well-lit area. Sowing seeds or planting seedlings there can be carried out a week earlier than in open ground. A warm bed will generate heat and warm the soil.


The soil
With a serious approach to business, the soil must be prepared in the fall. The bed must be dug up by adding humus or semi-rotted compost. Superphosphates are often added. In the spring, the soil is dug up again and, if desired, special fertilizing (ammonium nitrate or potassium salt) is added. The soil should be loose. If the soil is clayey and heavy, add peat, compost or wood ash. The garden bed should warm up well in the sun.
If feeding was carried out in autumn and spring, then during the growth period, fertilizers will no longer be required. The lack of nutrients will be immediately noticeable: the fruits will slow down in growth, and the bushes will stop growing green mass. Then feeding can be done several times every 12-15 days.
Still, you should not overuse nutrient formulations, even organic ones. Plants are able to accumulate excess nitrogen and convert it into nitrates and nitrites, which enter the fruit. Zucchini from healthy vegetables turns into harmful ones.


Landing technology and scheme
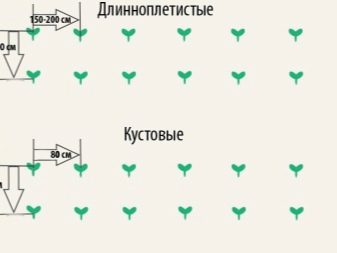
When planting zucchini, the spacing between the plants should be observed. One bush should have about 1 sq. m of land. There is no strict rule for the landing pattern. It can be placed in 50 * 50 cm squares or 40 * 60 cm rectangles. The main thing is that each plant has enough space for growth and the formation of a strong root system. On well-fertilized, loose soil, the squash is planted in separate holes in the usual way. They are made about 20-30 cm deep. It is not necessary to deeply bury the plants. The seedlings should be planted correctly, keeping a lump of earth and filling the hole so that it is slightly below the level of the garden. After planting, the seedlings must be watered abundantly. You can add peat, humus or rotten sawdust on top.
Gardeners use one of three patterns for planting zucchini.
- Tape, when the plants are planted in one row at a distance of 50–70 cm from each other, and about 1 meter is left between the rows. Plants from neighboring beds are planted opposite each other. This arrangement is suitable for large vegetable gardens.
- Chess. It looks like a ribbon, only plants from adjacent rows are planted in a checkerboard pattern.This planting allows you to save precious space on the site; you can leave about 50-60 cm between the rows.
- Square-nested, when the bushes are placed in the corners of imaginary squares with sides of 50–70 cm. On a small plot, one such square is enough, with good care it will be enough for a good harvest.

The culture loves moisture very much, so it must be watered abundantly. The soil must not completely dry out and the formation of earthen lumps. Without proper watering, the fruits will become lethargic, the foliage will dry out, and the plant may die as a result. The soil under the bushes should always be moderately moist, especially during the fruiting period. Then the amount of watering should be increased. But you do not need to water the soil - the plant will start to rot. In regions with harsh climates, zucchini can be grown in greenhouses, harvesting from early summer to autumn. On warm sunny days, the greenhouse must be opened and ventilated. Make sure that the leaves, shoots and fruits do not come into contact with the film, and that condensation does not get on them, otherwise the plant will begin to rot.
There are also unusual ways of growing zucchini, when the bushes are planted in barrels, tubs or bags of soil. This method is called portable. Separately planted bushes can be moved around the site or greenhouse, choosing the most successful places for their growth and the formation of ovaries and fruits. The capacity should be at least 5 liters in volume so that there is enough space for a large root system of the culture.
This planting method has a significant drawback - it is an unnatural formation of the root system due to lack of space. Under natural conditions, it develops horizontally in zucchini and shallow from the surface. In tubs and barrels, the roots have to go deep and form a vertical system. The plant suffers and develops poorly, the ovaries are not formed so actively.
Another disadvantage of this method is the container material for growing. Metal and plastic do not allow air to pass through, the soil in such containers is not saturated with oxygen and quickly becomes heavy and dense. For this method, it is better to choose large bags or wooden tubs.


Sowing seeds
Zucchini seeds can be planted directly in open ground or in seedling boxes at home. Some gardeners advise you to first germinate them on damp gauze or other cloth and only then plant them in the soil. It is better to use separate containers as seedling boxes right away to avoid the diving process. A container for one plant should hold about 300 grams of soil; zucchini have a large root system.
The soil for sowing should be loose and nutritious; it is better to purchase ready-made options in specialized stores. If you nevertheless decide to prepare the mixture yourself, then add humus or manure (earth and humus in equal shares) and peat (half a share) to the usual land from the site. It is also advised to add wood ash. It is better to prepare the soil for seedlings in the fall and store in the cold, so it is disinfected: all pathogens will die from the cold. The soil is brought into the house in advance so that it completely warms up, and the ice crystals melt, during a similar process they loosen the soil and soften it.
Seeds are first disinfected in a weak solution of potassium permanganate or hydrogen peroxide. Then washed with running water and dried at room temperature. The seeds are ready for sowing. Some gardeners preheat and soak the seeds. To warm up the bag with the material is placed on the battery. This improves the germination rate. After warming up, the seeds are soaked in warm water. After 1–2 days, they swell. After that, you can throw out empty and unchanged seeds - they will not sprout. After soaking, they must be sown immediately or left to germinate in a diaper or snail.


In open ground or in a greenhouse, seeds are sown 3-4 cm deep, without compacting the top layer. Watering is usually done before sowing. It is advisable to place several seeds in one hole. After germination, leave the strongest ones. For seedlings at home, seeds are sown to a depth of 0.5 cm. After that, they are watered and left in a warm, well-lit place. Seeds of pumpkin crops are placed with a sharp nose up, sprouts appear from there. If the seeds are placed incorrectly, the plant will spend extra time and energy.
The first shoots will appear in 4-8 days. It all depends on the temperature of the air and soil, humidity and the place of sowing:
- at home, seedlings can be seen on days 4–5;
- when sowing in open ground, the first shoots are expected on day 7;
- in the greenhouse - for 5-6 days.
If seedlings did not appear on day 10, most likely, the seeds were unusable or the soil turned out to be cold, as a result of which the seedlings died. In this case, sowing must be repeated using other seeds or by first germinating them on a damp cloth.


Seedling
Seedlings are planted in open ground or a greenhouse when the soil warms up to 10-12 ° C, and the daytime air temperature does not drop below + 15 ° C... Bushes should be planted very carefully so as not to injure the root system. Zucchini do not like transplanting very much, so they are not dived during cultivation. Planting is carried out 30–35 days after the first shoots, when 3 leaves have formed on the bushes. The seedlings are buried to the cotyledon leaves.
If there is a possibility of sharp drops in the night temperature or frost, cover the seedlings with foil. Empty bottles, cans and other containers can also be used. Each bush is hidden under them separately.
It is better to plant seedlings in the morning or evening, in cloudy weather. Then the seedlings will be better accepted and easier to transfer the change of place.


What can you put in the hole?
If the soil is not loose enough and has not been fertilized for a long time, then when planting in the holes, you can add a little compost, humus or peat. Wood ash is also sometimes added, it contains many trace elements that zucchini loves. Some gardeners advise placing a spoonful of the fertilizer mixture, regardless of the quality of the soil. This is done directly at the time of planting seedlings.
Experienced gardeners prepare the holes in advance, about a week before planting. The pits are 35–40 cm deep and of the same diameter. Organic fertilizers are laid at the bottom:
- manure;
- shredded tops of other plants or weeds;
- chicken droppings;
- organic kitchen waste;
- sawdust.
After that, the holes are covered with earth and peat and covered with foil. Within a week, organic matter will rot and settle. Superphosphate or wood ash can be added before planting. Mix the soil with compost and fill in the holes with seedlings. After that, it is good to shed the beds.















The comment was sent successfully.