How is zucchini different from zucchini?
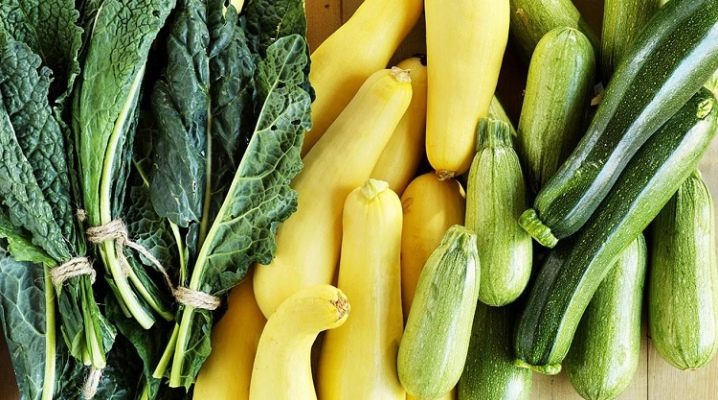

Zucchini are vegetables that are especially popular in the summer. Often times, the crop yields so much that gardeners do not know what to do with it. Zucchini seems to many to be the same fruit, just the name is different, nothing more. In fact, everything is not entirely true, and this issue is interesting to understand.
Visual differences
Yes, the one who calls zucchini a zucchini will not be mistaken. But at the same time, not every zucchini is zucchini. Because zucchini is a kind of zucchini brought to our region from Italy. To put it very simply, zucchini is a green-fruited zucchini. The Italians themselves call it "dzukina", that is, "pumpkin". And this fruit belongs to the pumpkin family, like, for example, squash, pumpkins, melons, watermelons and the same cucumbers. Even more amazing is that zucchini may well be called a berry, although it is still more customary to classify it as a vegetable.
Both zucchini and zucchini (to make it easier to compare, it is worth labeling them as different cultures) grow in bush form. But zucchini differs from its counterpart in a more compact bush (about 70-100 cm in height) and relatively small branching. He does not scatter such long loops as a zucchini, that is, it is more profitable to look after zucchini: it is easier and more convenient.


What else is different about zucchini:
- its leaves will be larger not less than 25 cm in diameter, and they often have a pattern, stains and silvery stripes;
- the leaves of the plant have prickly pubescence, but thornless leaves are also found;
- by the way, silver pattern on the leaves of the plant, inexperienced gardeners can mistake it for a disease, but this, of course, is not so;
- at the zucchini few leaves, they form a sparse bush on long stalks, which makes pollination more accessible to bees;
- the plant can be not only oblong, but also spherical (zucchini are almost always only oblong);
- the vegetable never grows to impressive sizes, unlike zucchini (the maximum plant length is 25 cm);
- by color zucchini is black, dark green, yellowish, blue, variegated and even striped;
- seeds the plants are very small, you do not need to remove them before eating the fruit.
It turns out that those who say that we can distinguish zucchini from ordinary zucchini by more compact sizes, a variety of shapes and colors, and less demanding care are right.


Crop yield
Now it is worth considering how productive both crops are. Simple math: one zucchini bush will yield 5 to 9 fruits, and zucchini - up to 20. In the latter, large female flowers are located mainly at the top of the bush: the male flowers go in bunches, and the female ones go singly. Both zucchini and zucchini have dioecious flowers, pollinated by insects. By the way, zucchini has surpassed the zucchini in this too: it forms more female flowers.
It is also an early ripening plant that ripens earlier. The fruits can be enjoyed within a week after the formation of the ovaries (sometimes even earlier)... The fruits appear in the garden in June, and they are harvested twice a week, as soon as they grow up to 15 centimeters. At this time, the skin of the plant is very tender, the fruit weighs 300 g, it is incredibly tasty, it can be cooked with minimal heat treatment.
It turns out that zucchini has surpassed the zucchini in this respect. It bears fruit better, ripens faster, and young early zucchini are very tasty. But the appearance and the difference in the yield of the plant are also not limited.


Comparison of other characteristics
There are at least 4 more indicators by which it makes sense to compare related plants in order to understand which is better.
Composition
Zucchini is a dietary product that can be safely prescribed to children, as well as to those people who have problems with the digestive tract. It is low-calorie: only 16 calories are used per 100 g. The composition of the zucchini:
- it has no saturated fat, but a lot of fiber;
- enough in the plant and vitamin C, an excellent natural antioxidant;
- lutein, zeaxanthin: these well-known sources of the vitamin are also found in good quantities in vegetables;
- one of the main chemical elements of zucchini is manganese (this element protects the body from free radicals);
- potassium in zucchini is a concern for the health of the heart muscle, blood pressure;
- There is a lot of iron, zinc, phosphorus, folic acid in zucchini, as well as vitamins of group B, K, E, A.
If we talk about the benefits of a plant for the human body, then it is essential. The same folic acid is necessary for the body as the prevention of strokes and cardiopathologies. Magnesium, which is also abundant in the plant, fights tachycardia and arrhythmia. Zucchini also contains a lot of pectin, which is a polysaccharide that is very useful for the heart and blood vessels, to lower cholesterol in the blood vessels.
Many studies have proven that zucchini is also suitable for improving the functioning of the digestive system: it prevents inflammatory processes in the intestines. Zucchini is also known as a product useful for people with a history of gout. With this ailment, an excess of uric acid appears in the body, which makes the joints very sore. So, the Italian variety of zucchini contains anti-inflammatory carotenoids, beneficial fatty acids. A vegetable simply reduces the general acidity in the body, and in case of illness in an acute period, this significantly helps to alleviate the condition.

Since the product is a dietary, low-calorie product, those who monitor weight and do not mind losing excess should definitely introduce zucchini into their diet. The product can be used in different forms, it is revealed in salads (warm and cold), in soups, in smoothies and more.
Zucchini is also not far behind its counterpart, its calorie content is insignificant. It contains a lot of B vitamins, PP, a lot of vitamin C. But still a little less than zucchini... Zucchini also contains folic acid, and it also contains pantothenic acid. Enough in zucchini and valuable for the work of the heart muscle potassium. In young zucchini 2-2.5% sugars, as they mature, this percentage will increase. Over time, the level of carotene also grows in fruits. It is interesting that there is more of it in zucchini than in carrots, but carrots undeservedly lead the rating of plants rich in this element among the people.
And in the seeds of zucchini there are those very useful Omega-3 acids, there are several times more of them than in the same eggplants, for example. There is little coarse dietary fiber in vegetables (as well as in zucchini), and therefore they are also considered a universal dietary product. Zucchini is very good for treating kidney disease (as part of a healing diet). It is also prescribed to people who have recently undergone surgery. Another vegetable is the prevention of atherosclerosis. He is advised to eat after undergoing a course of antibiotics.
In a word, it is in terms of composition that zucchini and zucchini are in many ways similar and almost equal... It is a pity that such inexpensive and healthy fruits are not often found on the menu, but they are well stored, they can be eaten in different forms, pickled. And in the summer, they can help out every day when you want something tasty and nutritious.


Taste
The flesh of zucchini is white, tender, may have a slight greenish tint, very crispy and juicy... Its taste is softer and more delicate than that of zucchini. Fruits, which are 5 days old, are considered the most delicious: they have such a thin skin that you can not peel zucchini, just add it to light salads. The most delicate pancakes, smoothies and cocktails, stews, soups are prepared from vegetables. They are good both as an integral part of dishes and as a main ingredient.The mild taste allows you to put them in salads in slices, cut into shavings and any other options, because the structure of young zucchini is pleasant, does not cause irritation.
The zucchini taste is a little rougher, but the young vegetables are also very good. The taste of a vegetable in the form of pancakes is especially vividly revealed: they cook quickly, they turn out to be soft, sweetish, refreshing. And if you add not only grated zucchini to the pancake dough, but also curd cheese and mint, then it will be a wonderful hot dish, at the same time nutritious and refreshing. Zucchini is good in stew, especially its light summer subspecies, where tomato sauce is almost not added, and the products are simply stewed in a natural broth. In a word, it is easy to distinguish zucchini from zucchini by taste by comparing two young vegetables: the taste of zucchini will be more delicate. From this point of view, the product is more profitable: it is not as much an amateur as a zucchini. Although this is all subjective, you just need to pick up good recipes.



Growing
Zucchini grows compact, which means it simplifies the very fact of caring for it, but it is a demanding culture... He is capricious in that he is thermophilic, and with the threat of return frosts, the entire crop may die. Therefore, it is necessary to prepare a film or any other shelter in case of cold weather. Zucchini is often grown in seedlings, planted in late May or early June. The plant can be called shade-sensitive, it is also demanding to the level of acidity of the soil. It requires an area with good natural light. The bushes themselves are compact, easy to care for. They must be watered in a timely manner, abundantly, spending 10 liters of water per bush.
Fertilize zucchini with bird droppings, mullein. The plant does not like waterlogging, overfeeding. And although the culture ripens early, it is distinguished by good keeping quality, which definitely needs to be used. Some varieties lie quietly until winter. Zucchini seeds can be grown by direct sowing in the ground, or by seedlings. The second method is somewhat simpler and more profitable. When sowing is planned, it is also necessary to calculate the options for returning frosts. Zucchini is thermophilic and photophilous, like zucchini, it loves to grow on the sunny side.
Both species grow well on sandy loam and loamy soils. That is, there are more similarities than differences in growing them.


Storage
The easiest way is to freeze the zucchini. So it can be stored for a long time without fear for the safety of the fruit. Let's see how to freeze a plant correctly:
- wash the fruit, separate the stalks;
- dry vegetables, cut (into slices, for example, into cubes);
- spread the pieces of zucchini on any clean and even surface so that they do not touch each other;
- send to the freezer for 3 hours;
- after the first aging in the freezer, the hardened pieces are put in a bag (you can also in a container) and sent to the freezer for a long time.
Not every product will go into storage. If the zucchini lay on the ground for a long time, it could be injured, it could be attacked by pests. Therefore, the earth is mulched to protect the delicate fruit from damage. They also do not store frozen zucchini, they are not viable. Even small scratches on the fruit must be eliminated. Zucchini is often kept in the basement. The temperature there should be no higher than +10, but also not lower than 0. The optimum air humidity for storage is 70%. On the floor of the room where the zucchini will be stored, a layer of burlap or dry straw is made. Zucchini must be laid out in one row. Between vegetables, you can lay sheets of thick cardboard so that the fruits do not touch each other.
And zucchini can be placed in a net and hung, which will not allow dents and bedsores to appear on the fruit. Only there should not be more than two vegetables in the net. It is more convenient to store fruits at home on an insulated balcony. If there are not many of them, it is better to wrap each fruit in paper, a layer of burlap, and then cover it with something to protect it from ultraviolet radiation. That's all the secrets: both plants are good both in taste and composition, plus it is not so difficult to organize their cultivation and storage.










The comment was sent successfully.