Diseases and pests of irises
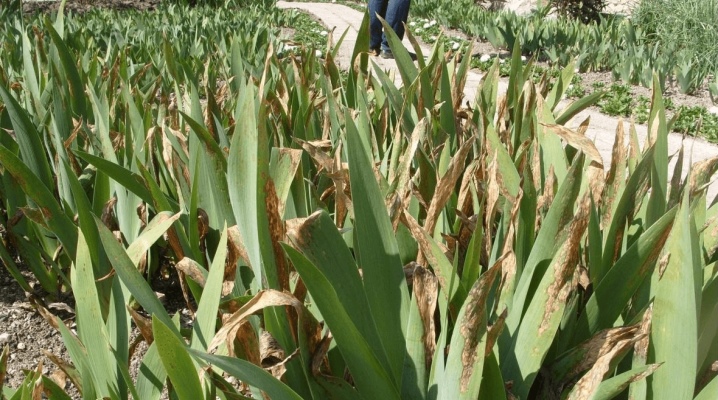

Irises are picturesque bright flowers that can become the main decoration of the garden. And although these are plants that are quite resistant to diseases and pests, but with illiterate care, this problem does not bypass them. It is important to identify the disease in a timely manner in order to have time to save the flower and neighboring plantings. Let's take a closer look at common iris diseases and methods of struggle.

Causes and signs of defeat
Ailments of representatives of the flora can manifest themselves in different ways. Sometimes the cause is not a specific disease, but errors in care. For example, a lack of flowering may indicate that the flower is planted too deeply and the root collar lacks sun. In this case, death will not occur, but the gardener may not wait for abundant flowering. It may also be that flowers have appeared, but do not bloom. The reason for this "behavior" may be a lack of sunlight - this happens if the irises are planted in too shaded areas. The flowering will also be affected by the neatness of the gardener himself. For example, if the roots are accidentally damaged during transplanting, the plant will not absorb moisture well, which will negatively affect the development of new shoots.

If the buds of the culture rot, the foliage turns yellow and dries, the flowers quickly wither, the formation of various spots is observed, then, probably, the reasons are already real diseases, the gardener must immediately start solving the problem in order to save the flower.
Incorrect growing conditions can again be a factor. So, putrefactive processes are most often caused by waterlogging of the soil and planting accuracy. And also deficiency of calcium and phosphorus or excess nitrogen can lead to such diseases.


Diseases and ways to deal with them
Several of the most common diseases of the presented culture are distinguished.
- Alternaria You can notice this fungus by the black sediment on the leaves. They gradually dry out and fly around. To avoid the appearance of this ailment, it is recommended to treat the plants with a Bordeaux mixture before and after flowering. If the specimen is already affected by the disease, then it must be eliminated so that the infection does not go to neighboring flowers.
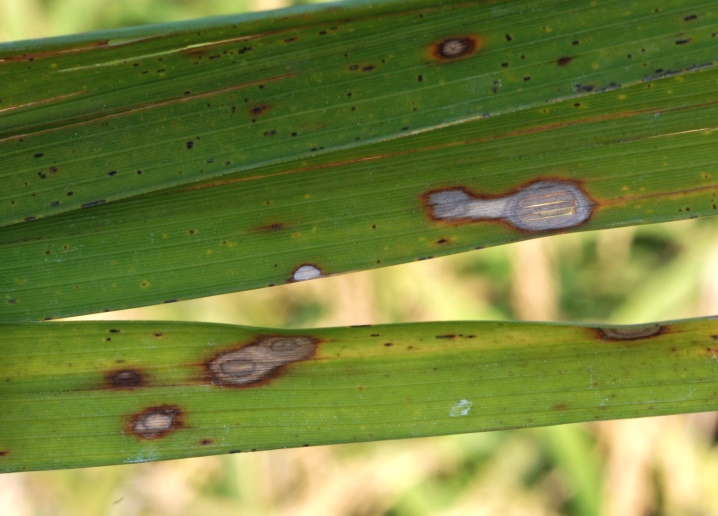

- Ascochitis. Another fungus that can be distinguished by brown spots appearing on the edges of the leaf plate. The more the disease develops, the sooner the leaves dry out. It is possible to treat a culture for this type of disease with means containing copper. Also, keep in mind that the fungus can remain in the soil as well.
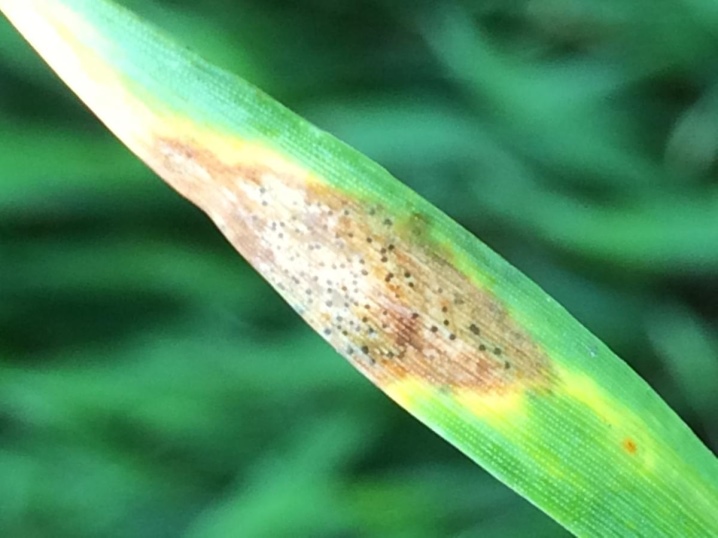

- Heterosporia. Most often, plants get sick in the second half of summer. Warm and humid weather leads to the disease. With an ailment, whitish-gray blotches with a watery edge are observed on the old foliage. Gradually, their circumference increases, the leaves die, after which the infection spreads to the inner leaves.
To combat, you can do treatments with fungicides with copper and zinc, remove old dried leaves in time.
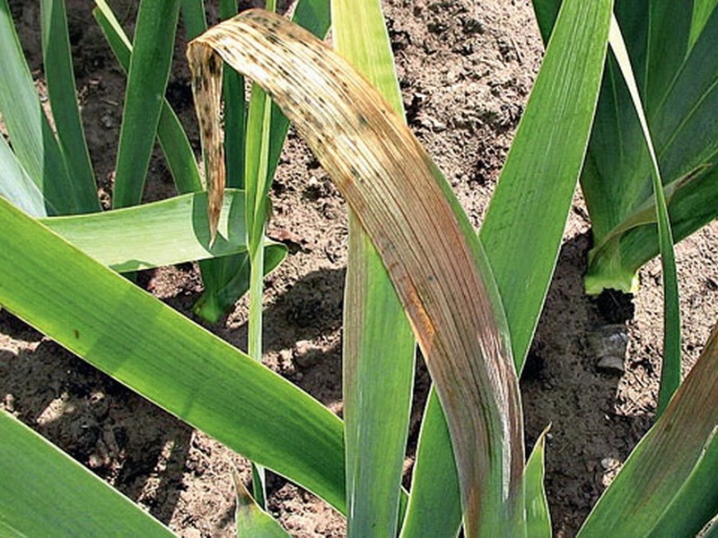

- Mosaic. This disease is spread by aphids. You can judge the presence of the disease by the lines and spots on the leaf plate. There are no methods of treatment yet, but prevention should be carried out to prevent the disease. It consists in competent agricultural technology, timely pest control, elimination of affected plants.
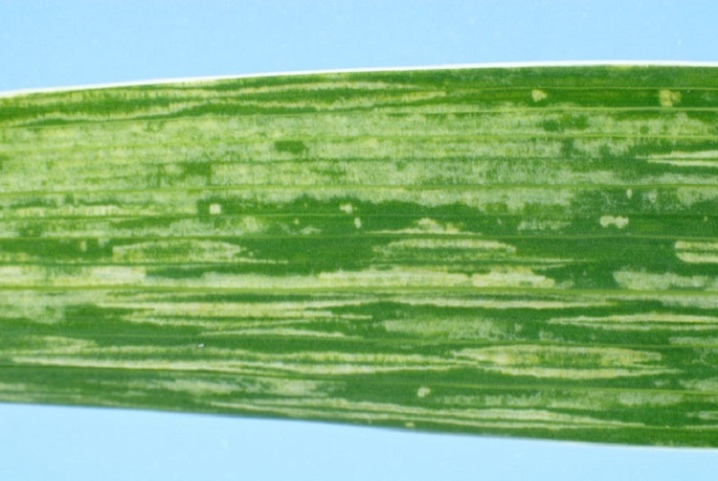

- Rust. If the leaves are covered with brown and red pustules, and the tissue around them begins to die off, then the flower is affected by rust.Gradually, the leaves wither, curl and die, deformation of the stems is observed. During treatment, all affected plant fragments are destroyed, and the rest of the plants are sprayed with a solution of sulfur until all signs of the disease disappear. As a preventive measure, it is important to observe crop rotation and perform high-quality soil drainage.

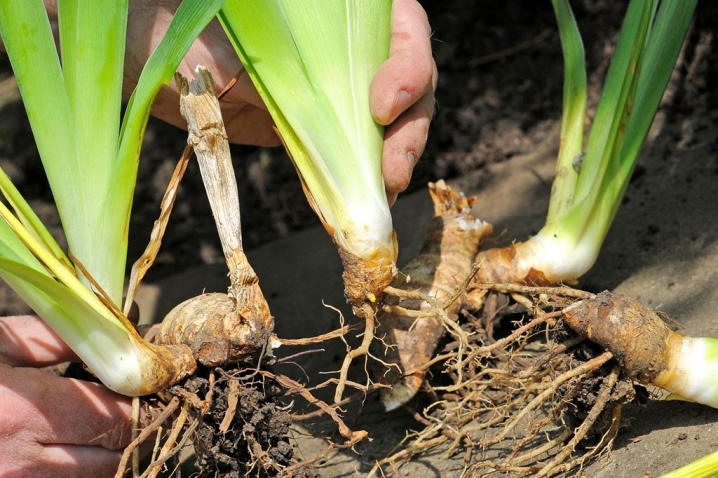
- Bacteriosis This putrid lesion is noticeable in the spring. You can recognize it by the brown spots on the leaves. Over time, damaged foliage dies off. And also a symptom of bacteriosis is an unpleasant odor from the stems. The inner roots turn into a white, fetid substance.
Infected tissue must be cut off, and the cut areas must be sprinkled with potassium permanganate. It is important to destroy cut fragments.
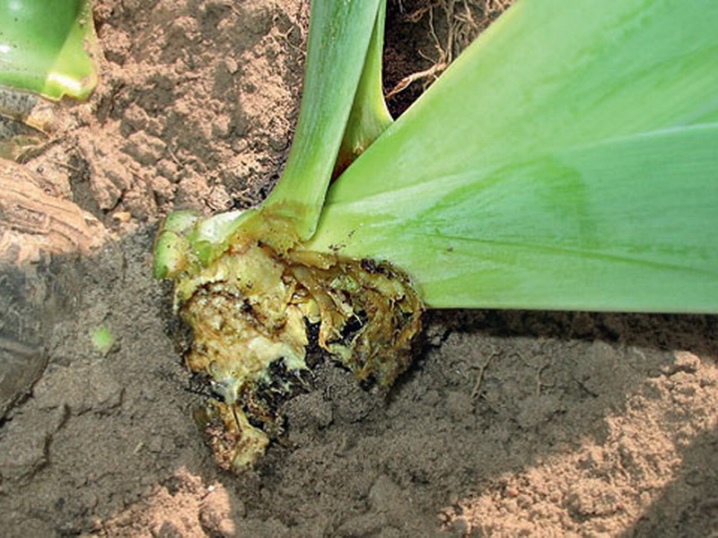

- Gray rot. This disease is caused by fungi that develop when moisture is high. In some cases, it is noticeable how the tips of the leaves and stems rot, and a gray sediment forms on their surface. Sometimes the disease attacks the roots and leads to dry rot. As a preventive measure, planting in well-drained soil is recommended. When treating, it is important to remove all affected parts in time and burn them.
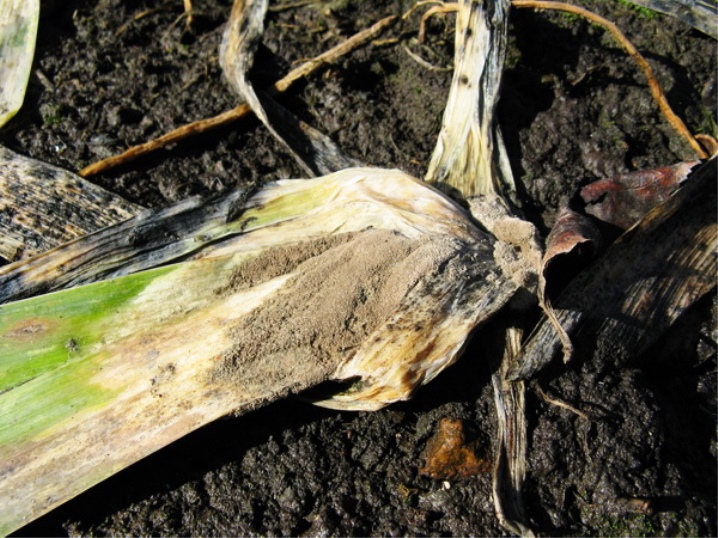

- Fusarium. This is the same dry rot mentioned above. The root system becomes its victim. Under the influence of the disease, the roots rot, along with them the leaves dry and the flowers wither. Samples destroyed by the disease must be eliminated, and the areas remaining after them must be treated with copper oxychloride. Healthy neighboring specimens must be protected from fungicide infection.
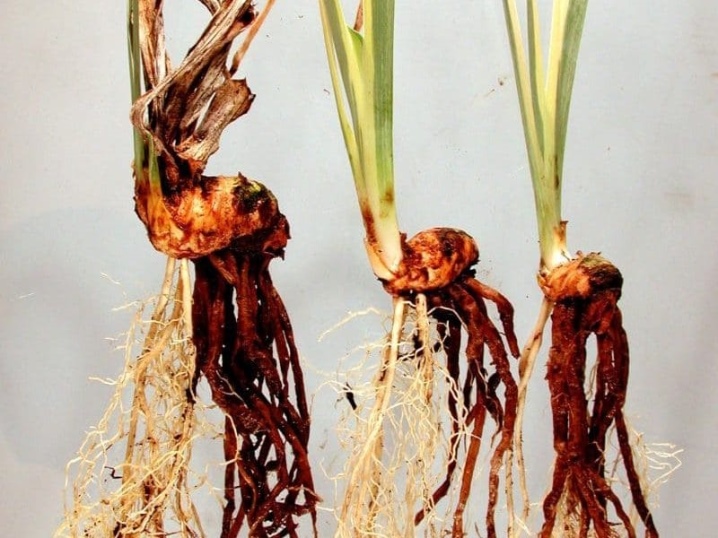

What are the types of parasites and how to deal with them?
Various insects can not only destroy flowers on their own, but also carry on themselves serious diseases from other plants, so it is also important not to postpone pest control. Some insects are the most common species for irises.
Bean aphid
This individual lives on leaves, shoots and buds. She loves to feast on the juice of flower crops, as a result of which the shape of the shoots changes, the leaves curl, their color is lost. The insect itself looks like a brown or black-green beetle.
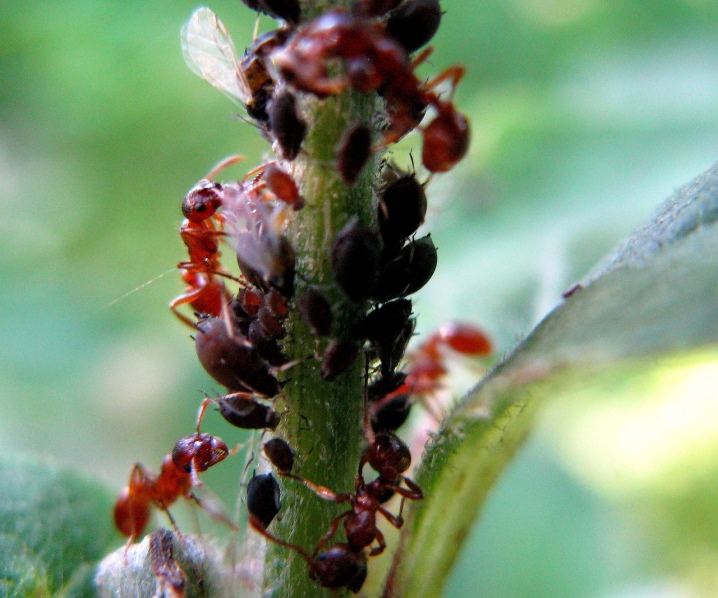

In the autumn, the female lays eggs on the root part, and in the spring larvae hatch from them, which reproduce the next generations. During one growing season, development of ten generations is possible.
To prevent the appearance of aphids, you need to carefully weed the flowers, as well as feed the plants with fertilizers containing phosphorus and potassium. Having noticed single individuals, you can remove them mechanically. If the flower was attacked by whole hordes of insects, then you need to treat the specimens with special infusions or decoctions of insecticides. A also for the fight against this pest are suitable drugs "Arrivo", "Karate", "Commander", "Confidor", "Iskra".

Onion mite
This insect looks like a bug with a brown, almost round body, its size is no more than 1 mm. He prefers to eat bulbous plants. The reason for the appearance of a tick may lie in improper storage of the planting material. If during storage the pest hit the bulbs, then it is quite likely that it will also be introduced to the flower bed. And he also loves to settle on samples that other insects have chosen before him.
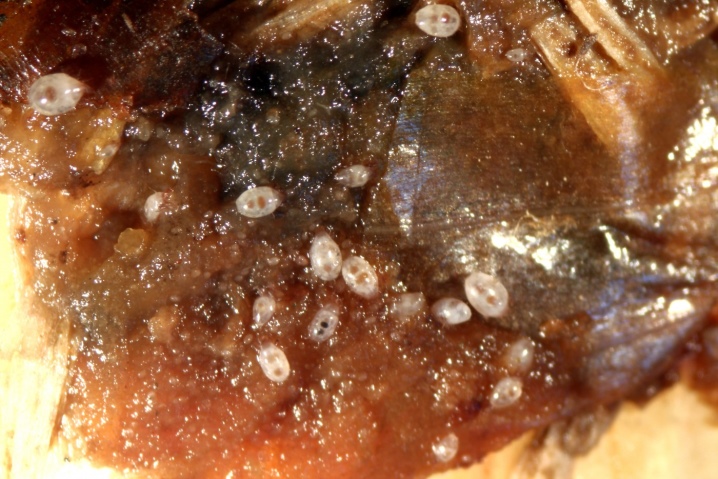
To prevent the appearance of this creature, it is recommended to pre-soak the planting material for half an hour in the Anti-mite solution. Some gardeners advise mixing the bulbs with chalk.
And alsoa carrot planted nearby will help protect the culture from these beetles - it will scare away the tick... It is important to dry thoroughly for a week before storing the harvested bulbs. It will prevent the appearance of a tick and the processing of the storage site of the planting material with sulfur bombs "Climate" or FAS within two days.

Onion nematode
Onion nematode looks like a white worm up to 1.5 mm long. He prefers to settle in seeds and bulbs, multiplies under the influence of high soil moisture. He can live in drought for several years. These caterpillars suck the sap out of the plant. As soon as the flower dies, the specimen buries itself in the ground and starts looking for a fresh specimen.
A nematode infection is indicated by plant samples that do not develop well into growth, have swollen stems and ugly flowers.
To prevent the attack of these worms, it is important to correctly observe the crop rotation, and also not to plant flowers in the same flower beds for several years. In the fight against the pest, the neighboring planting of carrots will again help. And it is also recommended to treat the storage with sulfur checkers before planting irises, dry the planting material well and warm it up at a temperature of + 34– + 37 degrees for seven days. Recommended storage humidity is not higher than 70%.
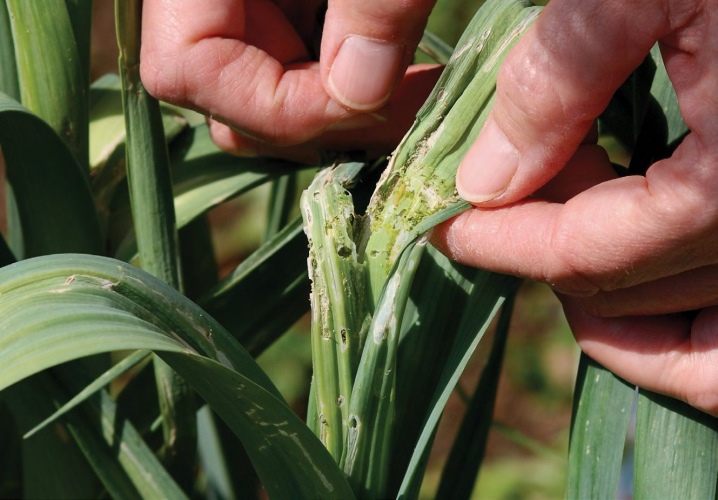

Iris fly
One of the main enemies of the presented culture. It looks like an ordinary gray-black fly. Adults and larvae crawl into the buds and feast on their petals. Chemical preparations, which are used immediately after the appearance of the peduncle, will help to get rid of this pest. In addition, the cultivation of the land under the plants will not be a superfluous measure.
The most popular means of struggle are Aktara, Aktellik, Bi-58, Decis. All affected specimens must be burned.
There are also folk ways to get rid of a fly. For example, you can treat damaged crops with wood ash, tobacco dust, mustard, a solution of bitter herbs, soapy water and alcohol before the flowering arrows emerge.
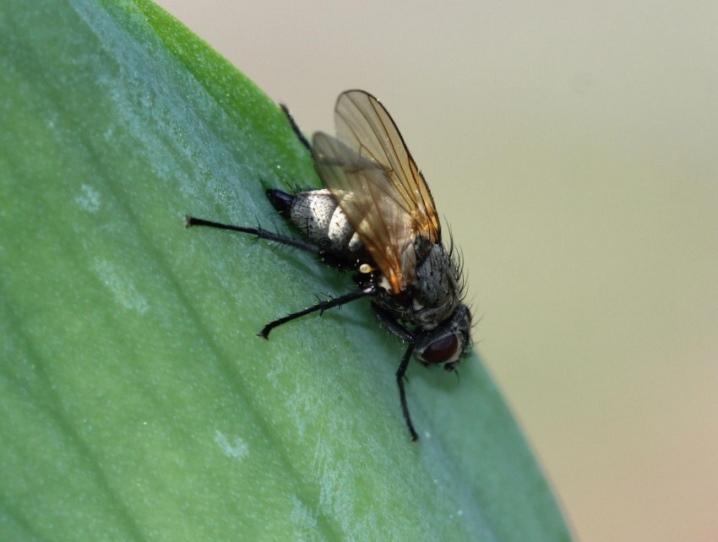

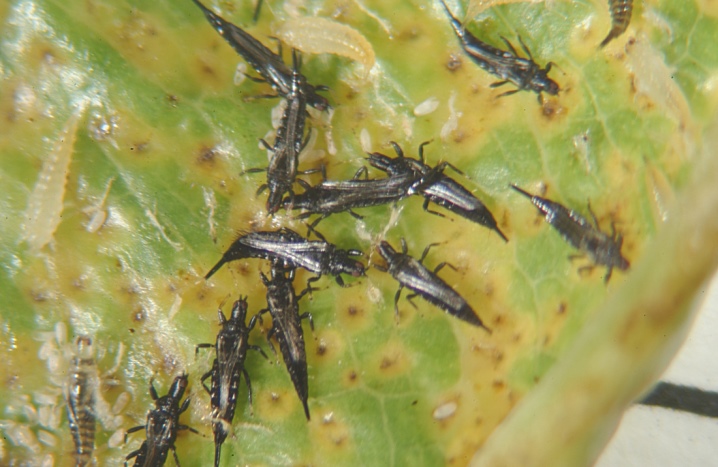
Thrips
These small creatures with narrow wings and long fringes along the edges like to settle in the axils of the leaves. Their food is cell sap. The faster thrips multiply, the sooner the leaves become covered with brown stains, and then completely dry out. The spots are also formed on the roots. You can fight thrips with a 10% karbofos emulsion. 90 g of the product is diluted in 10 liters of water and the flowers are treated once a week.

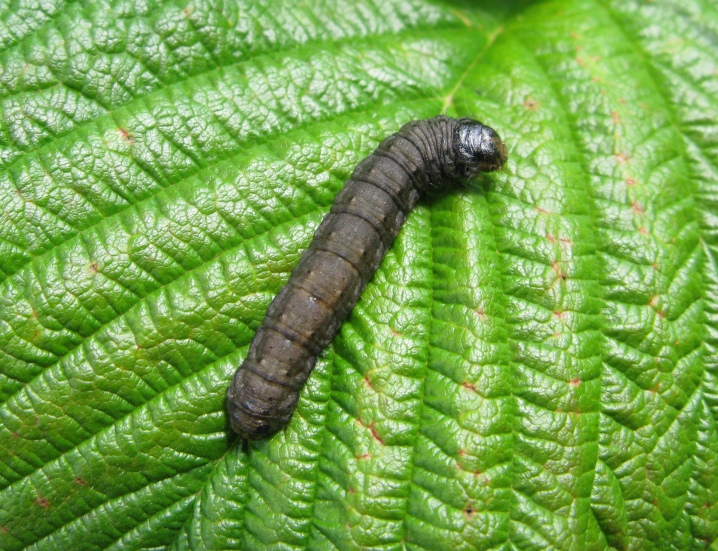
Scoops
This caterpillar penetrates the stem and gnaws out its contents. To avoid the invasion of these pests, it is important to regularly loosen the soil and avoid overgrowing the flower bed with weeds. Bordeaux liquid helps to get rid of the insect. It is allowed to process the plant with the agent only before the beginning of flowering. If the gardener missed the specified time, then you can replace the mixture with Lobel's hellebore.

Prophylaxis
As already mentioned, the most important preventive measure is adherence to the rules of agronomy. It is important to pre-inspect all bulbs, damaged specimens must be destroyed, planting material must be stored in a cool dry place and, if necessary, disinfected before planting. In order not to start insects and attack diseases, the area where irises are planted must have a high-quality drainage system and be well ventilated. The soil must contain sufficient amounts of calcium and phosphorus, as well as have the required level of acidity.
It is important to pickle the roots before planting, and remove damaged areas. All contaminated soil must be decontaminated.


Experienced gardeners prohibit the introduction of fresh manure when feeding crops. And also during cultivation, it is necessary to thin out dense plantings, and in the fall to cover the flower bed with a layer of mulch. To prevent the appearance of putrefactive diseases, too much watering should be avoided, and stagnant water should be eliminated in time. Antibiotics can be used as an effective preventive measure, but this is a last resort and should not be abused. Treatment with products containing copper effectively prevents the appearance of diseases and insects. In addition, when cutting off the affected parts of plants, it is important to disinfect the cut sites, as well as to perform the work with a well-disinfected tool.
For iris diseases, see below.







































































































The comment was sent successfully.