Chamomile chrysanthemums: varieties and tips for growing
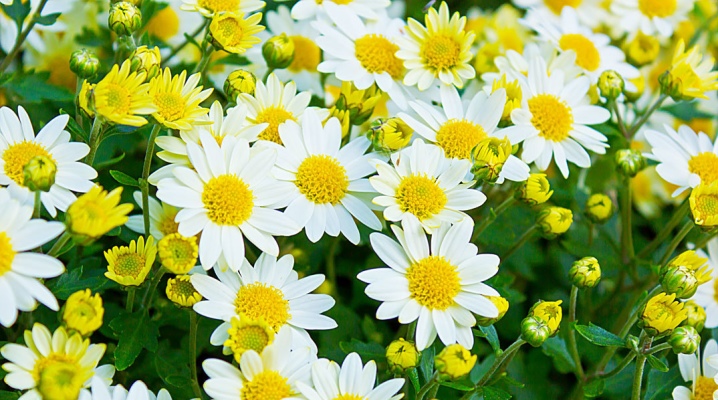

The unpretentious chamomile chrysanthemum to care for will be an excellent decoration for a garden plot or living quarters.
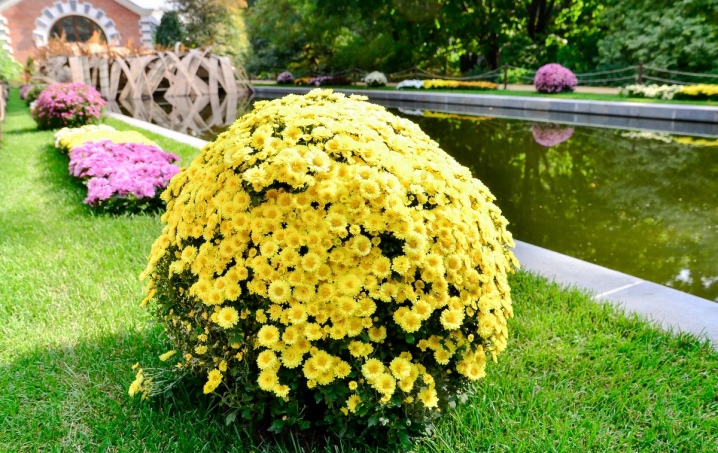

Peculiarities
Chrysanthemum is the common name for the flowers of the Astrov family, of which there are about 150 species. The favorite of many gardeners is chamomile chrysanthemum - a perennial shrub type.
Beautiful inflorescences have an umbrella shape, up to 20 of them can form on one stem. The buds usually bloom in August-September, and some early varieties can bloom as early as mid-July. Flowers delight with their long, abundant flowering and outwardly very much resemble chamomile (for the resemblance to it, the species is called so).
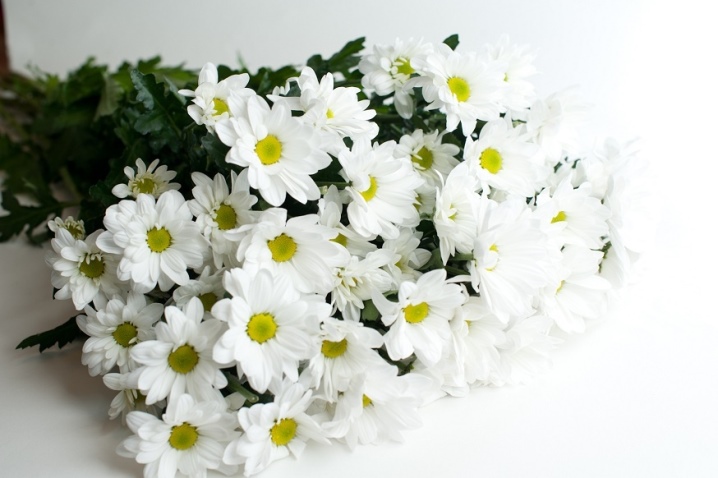

A chrysanthemum growing in an open field garden blooms for about 9-10 weeks after the first flowers appear. At home, the flowering period increases, and with careful and careful care using a UV lamp backlight, it can be year-round.
The stalks of the chamomile chrysanthemum are thick, erect, with an abundance of serrated leaves, the size of which, depending on the variety, varies from 4 to 12 cm in length and 3-6 cm in width. The plant can reach a height of 1.5 m.
A bouquet of chrysanthemums will be an excellent gift and a manifestation of a sign of attention. For a long time after cutting, the flowers do not lose their attractiveness, they calmly tolerate low temperatures, so it is appropriate to give them in the cold season as well.
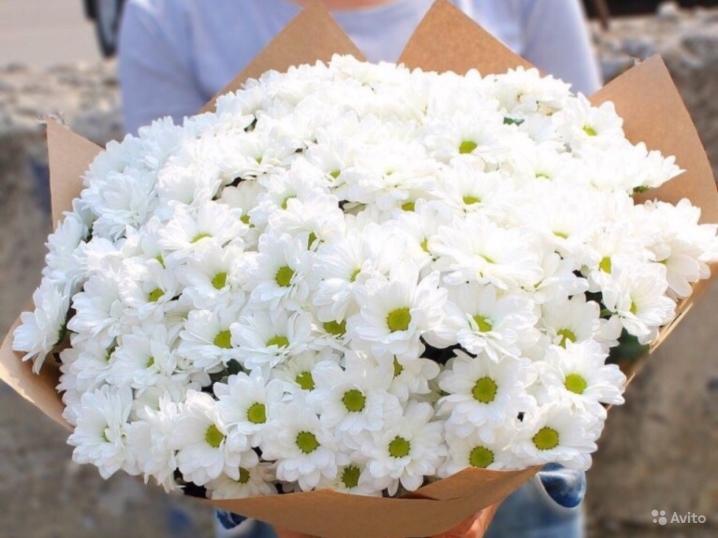

Differences from daisies
Chrysanthemums and daisies are very similar, since they belong to the same Astrov family, but they cannot be confused. The main similarity is manifested only in the structure of the inflorescences, although in daisies the extreme petals have one row, and in chrysanthemums there are several of them.


Field daisies are only white with a yellow center. Garden specimens also often have white petals, but there are also varieties of yellow, pink and pale lilac shades. Chrysanthemum inflorescences are distinguished by a wide variety of flowers and are larger in size.
There are noticeable differences in the shape and size of the leaves. The foliage of chrysanthemums is large enough with characteristic notches, in a garden chamomile it looks smoother and smoother, and in a field chamomile it resembles soft needles.


Plants also have a difference in the flowering period. Chamomile blooms throughout the summer period - from June to September. With the onset of constant cold weather, flowers are no longer formed. Chrysanthemum, on the other hand, blooms closer to September, is not afraid of cold weather and in the open field can bloom even in November.


Types and varieties
A wide variety of species and varieties of chrysanthemums have been bred, and thanks to the efforts of breeders, their number is constantly increasing. However, there are still no strict and uniform criteria for the type classification of chrysanthemums.
The types of chamomile chrysanthemums are distinguished by characteristics based on several indicators.
- The size of the umbellate inflorescences. They are large, medium or small. The diameter of small-flowered varieties is 3-8 cm. Up to 20 flowers can form on one stem. Medium-flowered species are 8-12 cm in diameter, their number on a branch does not exceed 15. Large flowers can reach up to 25 cm in diameter. No more than 8 flowers are located on one shoot, and sometimes there are single buds.
- The shape of the inflorescences. In chamomile chrysanthemums, they are of two types: simple (non-double) and semi-double.
- Flowering period. The color of early varieties begins from the second half of July to September, middle ones - from the end of September to November. There are no late-flowering chrysanthemums among the chamomile representatives growing in the garden. At home, the flowering period can be extended under special conditions.



Popular varieties of chamomile chrysanthemums.
- "Ariel". Refers to an early flowering species. It grows up to 80 cm. The first buds bloom in July, flowering ends at the end of September. Inflorescences are semi-double, large, white with a yellow-orange center, in a circle of about 12-15 cm, singly located on the stem. The foliage is a deep, deep green in color, providing an excellent contrast to the white petals.
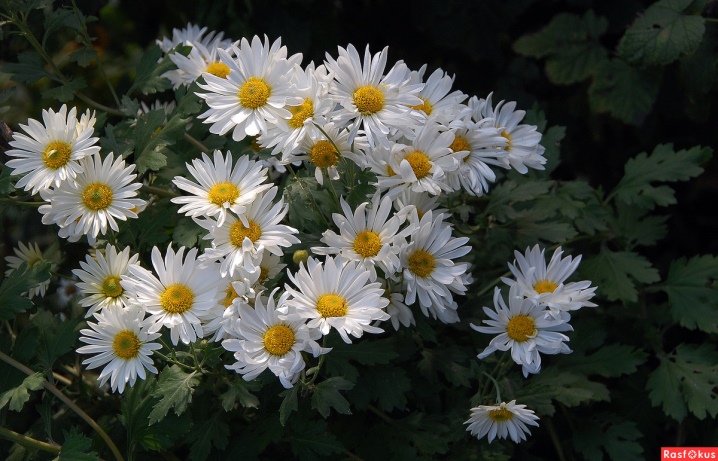

- "Bacardi". Tall bush variety. The stems are very strong and flexible, not prone to brittleness. The leaves are dark green. Flowers are non-double, 6-7 cm in diameter, with a green or yellowish center. Petals can be white, yellow, cream, pink and burgundy. 5-8 flowers are formed on one branch. Cut flowers retain their attractiveness for 2-3 weeks.

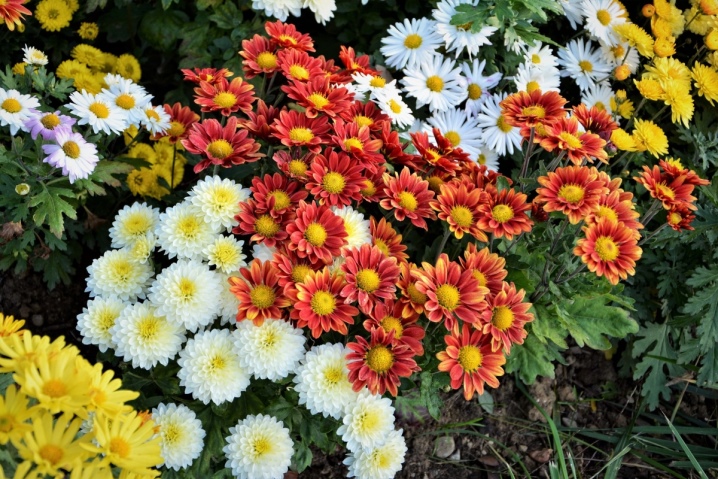
- "Evening Lights". This variety belongs to the undersized species. The height of the stems is in the range of 30-40 cm. Differs in abundant flowering during the month. Inflorescences are bright red with a yellow center 5-6 cm in size. Root growth is practically absent.

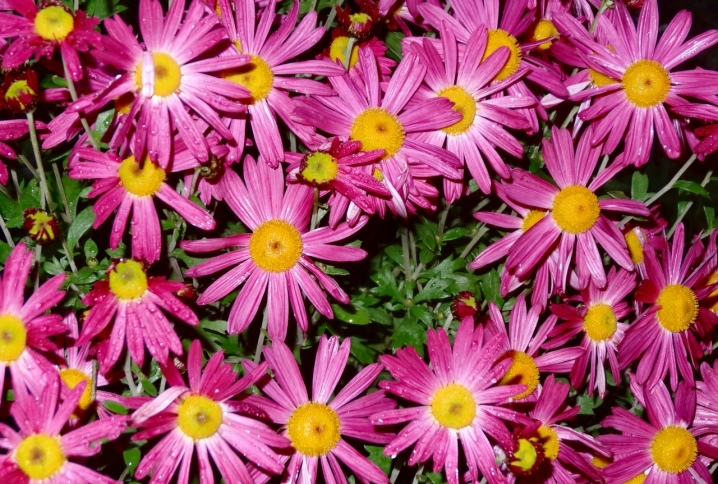
- "Hebe". Late flowering shrub of medium size. Height within 50 cm. It blooms in October and blooms until mid-November. The petals are arranged in one row and have a bright crimson hue. The size of the flowers in a circle is 5-7 cm. It is resistant to cold weather and can winter outdoors.

- Isabelle. The flower bush grows up to 70 cm. The stems are straight, but with abundant flowering they tilt to the ground, so it must be tied to a support without fail. Semi-double pink inflorescences, the diameter of which is 5-6 cm, bloom in the second half of August and bloom until the end of October.
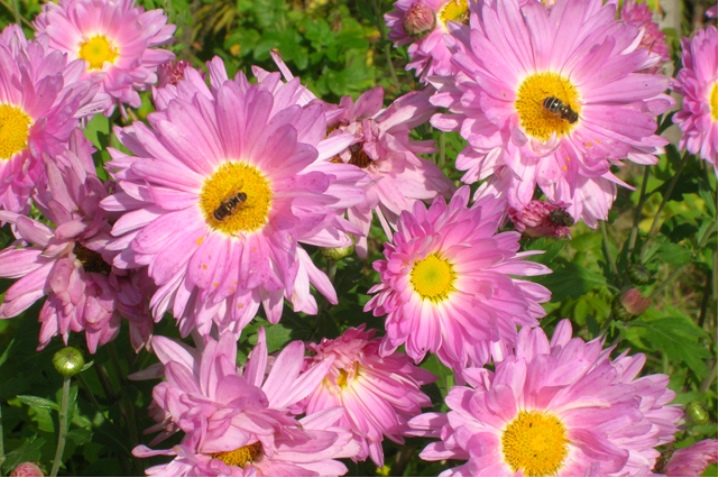

- "Kibalchish boy". A low-growing early variety, the height of the bush is about 25-35 cm. It blooms from July to October. The inflorescences are simple, 6 -7 cm in circumference, have a red or deep pink tint, mainly located on one stem.

Landing
So that chamomile chrysanthemums delight with their abundant flowering, landing conditions must be observed:
- the optimal time for planting chrysanthemums in spring is May, for autumn planting - October;
- for planting, you should choose a sunny and slightly elevated place to prevent moisture stagnation;
- planting the plant is preferable on a cloudy day.


Planting stages.
- Well preparation. When planting several specimens, it is recommended to dig holes 35-45 cm deep at a distance of 20-30 cm for small varieties and 40-59 cm for large ones.
- Landing. Put a small layer of sand at the bottom of each hole as drainage, then pour a handful of fertile soil on top and mix it with a small amount of vermicompost. Water abundantly. Carefully place a bush in the hole, not deepening the roots too much, and cover it with soil. For tall bushes, it is better to immediately put supports next to it.
- Fertilization. For better rooting and the formation of strong roots, it is advisable to add a biostimulator for plants "Kornevin" under the bush on the day of planting.
- Pinching. For the subsequent abundant flowering, you can immediately carry out the first pinching. To do this, you need to very carefully remove the growth point of the shoots without damaging the stem.


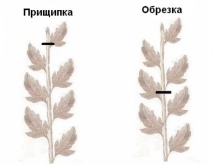
Care advice
When planting in autumn, the flower is watered only when the weather is dry and there is no rain. In spring and summer, it is important to ensure that the soil in the flowerbed is not excessively wet. Chrysanthemums do not like excessive dampness.
In the early days, it is better to shade the plant so that it is protected from bright sunlight.
Re-pinching can be done 2-3 weeks after planting. To do this, remove the upper part of the shoot with the formed 2-3 nodules.

In hot weather in June-July, chrysanthemum is watered 3 times a week, directing a stream of water strictly to the root. During this period, after the main watering, it is advisable to apply potassium-phosphorus fertilizers to form stronger buds. It is best to water the plant abundantly in the early morning so that the soil dries out throughout the day. When watering in the evening, the volume of water should be slightly less.
During the flowering period, watering should not be plentiful, 1-2 times a week is enough.

Preparing for winter
In the middle or late autumn (depending on the variety), the leaves of chrysanthemums begin to wither and petals fall off. These signs indicate that the growing season is over and the plants need to be prepared for winter.
Varieties with small and medium flowers tolerate wintering well in the open field. In October-November, you need to carefully trim the upper part of the bushes, leaving small shoots 10-12 cm high. In the southern regions, this procedure is sufficient. In the middle lane and northern regions, additional shelter is needed with spruce branches or a layer of sawdust in order to protect the plants from frost.
Large-flowered varieties should not be left outdoors for the winter. They need to be dug up, transplanted into a pot and brought indoors until spring.


Reproduction
Chamomile chrysanthemums are propagated by seed, cuttings and dividing the bush.
Seeds
You can start planting seeds for seedlings in February-March. Seeds are sown in one container and covered with plastic wrap. Watering should be done very carefully using a spray bottle. Seedlings appear in 2 weeks. When forming two leaves, the sprouts must be dived (transplanted into an individual container). For to make it easier for the sprouts to take root, you can spray them with a solution of "Zircon".
Saplings grow slowly. It is advisable to keep them on the windowsill, carrying out moderate watering, and feed them with complex fertilizer every 2 weeks. In case of insufficient lighting, you can supplement them with a UV lamp. After 1.5-2 months, when the growth reaches 20 cm, the plant can be transplanted into open ground.
In the southern regions, direct open field sowing can be carried out in May.

By cuttings
It is more convenient to carry out cuttings during the autumn pruning period. In this case, shoots 5-7 cm long are broken off and placed in a glass of water. When roots appear, they must be seated in separate containers and placed in a cool place (no higher than + 7ºC). In the spring, the seedlings are transplanted to a permanent place.
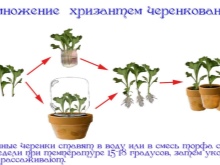


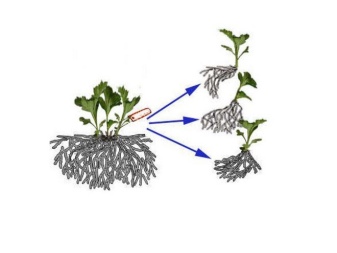
By dividing the bush
After 2.5-3 years, the roots of the chrysanthemum grow abundantly, taking away the entire supply of nutrients from the soil, which, in turn, leads to a decrease in the size and number of flowers. In this case, the plant should be divided. For this you need to dig out the bushes, and divide them into several parts with your hands or with a shovel... The resulting cuttings can be immediately planted in separate holes, creating a shadow for them from a non-woven covering material.

Diseases and pests
An attentive and careful attitude to the flower will contribute to its lush flowering and protect it from possible diseases. Chamomile chrysanthemums are susceptible to several diseases.
- White rust. Light, slightly convex spots appear on the upper surface of the leaves, which after a while turn brown. To destroy the disease, you need to remove the infected leaves and spray the bushes with antifungal drugs (copper chloride, "Abiga-Peak" agent).
- Powdery mildew. A white bloom forms on the diseased bush. For prevention, you should regularly feed the plants with phosphorus-potassium fertilizers and periodically remove the lower leaves. When the first signs of an illness appear, it is necessary to carry out the treatment with "Fitosporin-M" as soon as possible. If the defeat is strong, then it is better to treat the culture with "Pure flowers" or "Topaz".
- Stem rot. The lower part of the stems begins to darken, acquires a brown tint, then the spots pass to the leaves and the bush fades. There is only one method of struggle - burning an infected bush. If a small area of rot was found at the very beginning of the disease, then you can try to reanimate the plant by treating it with "Baktofit" or "Fongilan". You will also have to process all neighboring bushes with this composition. To prevent the formation of rot, it is necessary to ensure the necessary drainage of the soil during planting and not to abuse frequent watering.



Insects can pose a threat to chrysanthemums.
- Nematodes. Pests affect leaves and buds. First, light brown spots appear, and a little later they dry out. It is necessary to disinfect the soil with carbothion or formalin, and dig up the affected bushes and place them with roots for 3-5 minutes in a container with water heated to 60 ° C. Next, you need to transplant the treated bush to another area.
- Spider mite. These pests, attaching to the lower part of the leaves, suck out the sap of the plants, which is why they turn yellow and dry out. To destroy pests, it is recommended to spray the bushes with a mild soapy solution. If a large number of insects are found, it is necessary to treat them with the preparations "Vertimek" or "Lightning".
- Aphid. It can affect any part of the plant, which will lead to its deformation and lack of flowers. To combat aphids, the means "Akarin", "Decis", "Zubr", "Iskra" will help.



Application in landscape design
Chamomile chrysanthemums look lovely in group and single plantings. A single bush may well decorate a garden lawn.
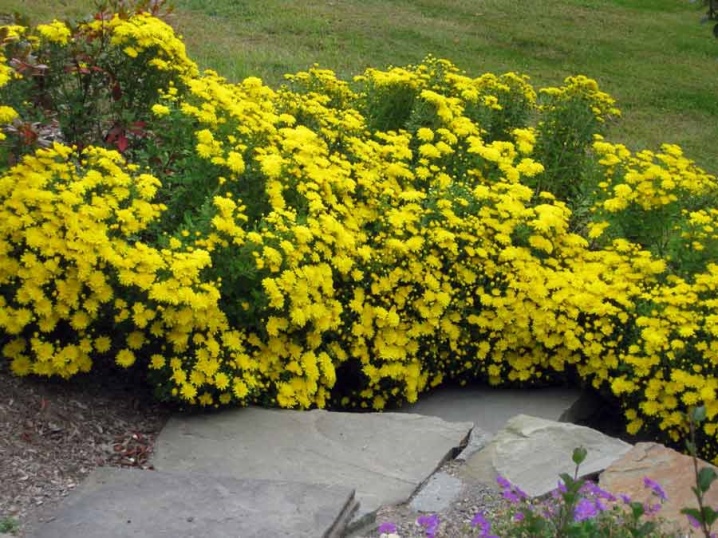

Low-growing bushes look beautiful in compositions around trees, when framing paths and borders. Perennials harmonize well next to marigolds, zinnia, coleus and balsam. Multicolored chrysanthemums planted on the same flower bed, for example, red and white, will definitely attract enthusiastic eyes. Planting chrysanthemums in mixborders also looks advantageous.


If there are coniferous trees on the site, the bushes will stand out perfectly against their background.

Daisy chrysanthemums will undoubtedly become a wonderful decoration of the garden.

How to get 10 from one chrysanthemum bush, you can see in the video below.







































































































The comment was sent successfully.