Garden carnation: varieties, planting and care
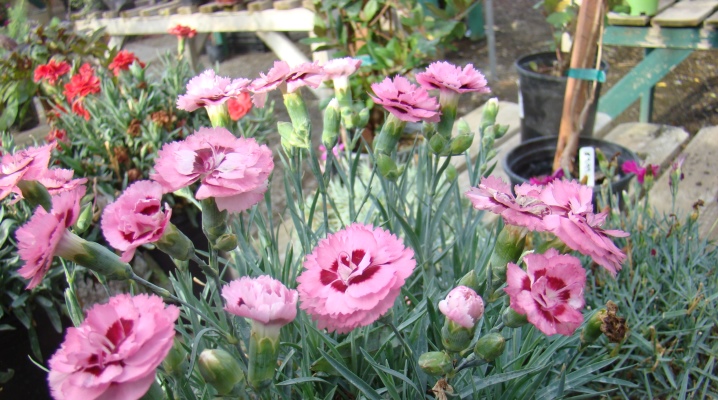

Garden carnation is a perennial plant with high decorative qualities. It is used both for creating bouquets and for decorating garden plots. A flower with a pronounced aroma perfectly coexists with other plants, thanks to which it is often used in landscape design. In order for beautiful buds to please the eye from early spring to late autumn, you need to know some of the intricacies of planting, reproduction and caring for this perennial flower.


Description
Perennial garden carnation (Latin Dianthus caryophyllus) or Dutch carnation is an ornamental plant of the Clove family. The flower prefers moist fertile soils, it is found in the temperate climate of central Europe. The type species is a medium-sized plant, the stem height is up to 80 cm. The leaves are whole, simple, covered with a light gray-greenish bloom. The length of the leaves is 12-15 cm. Flowers - single buds or collected in umbrellas 38-40 cm in diameter up to 5 pcs. Abundant flowering for 2-3 weeks. The flowering period is from early June to late October.

The plant looks like a small shrub. The stem is strong, the leaves are mostly narrow. After flowering, seed pods appear in the axils of the stems. The fruits are brown or brown in color. Depending on climatic conditions, the plant can bloom in one place for 2-3 seasons, after which it must be replanted. The rhizome of the garden carnation is poorly developed; it lies in the ground no deeper than 10–20 cm.
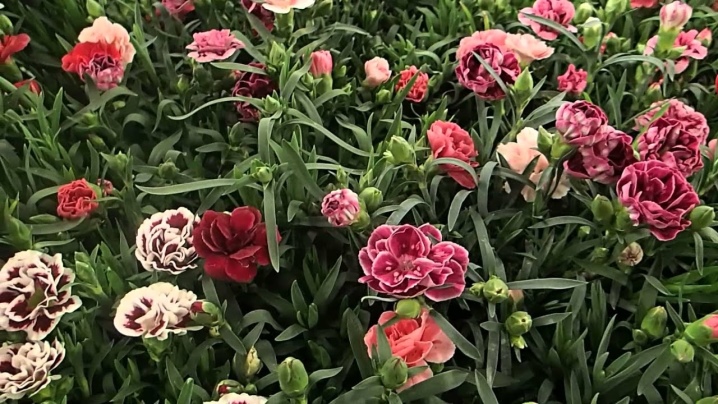
All Dianthus are herbaceous plants. Depending on the climate and growing conditions, they can give two types of shoots: with peduncles and vegetative. Carnations differ in color, number of buds and types of petals. Cultivated garden varieties are presented in a wide color palette - from pale pink to bright red or purple.



Types and varieties
There are several hundred varieties and types of garden carnations. All of them are cultivated as ornamental plants, including hybrids. The names of many species come from the appearance of the flower or where it grows.
- Turkish or bearded. She belongs to the most unpretentious varieties, tolerates cold well. This plant is of different sizes - on average, the height of the shoots reaches 55-60 cm, but there are also undersized subspecies. A distinctive feature of the species is large inflorescences, in which flowers with even or double petals are collected.



- Cirrus carnation. This perennial species is the most popular among gardeners. The medium-sized plant is used for landscape decoration and is grown in flower beds. Regardless of the variety, the height of the pinnate carnation does not exceed 30 cm. A distinctive feature of the species is its ability to grow. A perennial can bloom several times a year, thanks to which it is used to decorate personal plots and adjoining territories. It stands well in cut and retains freshness and aroma in bouquets for up to 2 weeks.
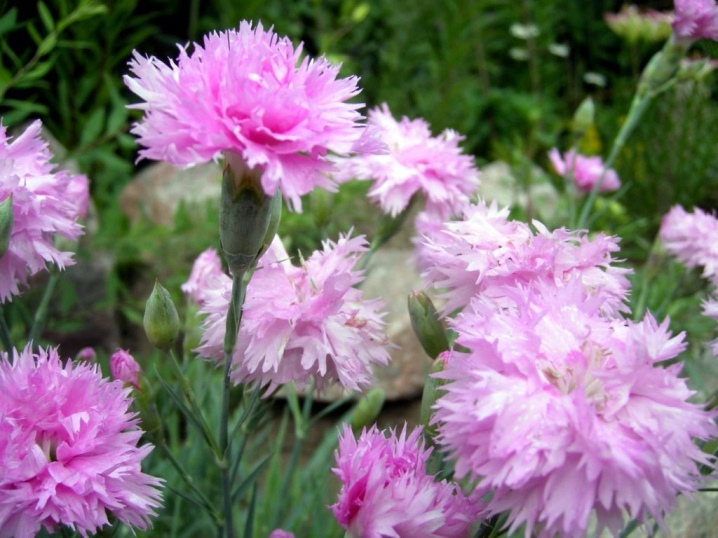

- Gardening perennial or Dutch. The plant is widely cultivated and used for cutting and arranging bouquets. It belongs to the greenhouse and is grown everywhere all year round. The species is distinguished by a large number of subspecies of different colors and heights.The length of the stems of tall varieties is 60-100 cm, medium-sized varieties - 30-60 cm, compact or decorative - up to 30 cm.


- Herb. A wild species that grows everywhere. The height of the stems is 38–40 cm. This species is distinguished by small flowers collected in small inflorescences. The color of the buds is different, pink and red shades are more common. The species does not require careful maintenance and can be grown for landscaping the site instead of grass on lawns.


- Indian. An indoor ornamental plant that is rarely found in nature. It prefers a warm, humid climate and grows outdoors mainly in Australia, South America and Africa. A characteristic feature of this species is the large white flowers collected in inflorescences. Wave bloom lasts up to two months.
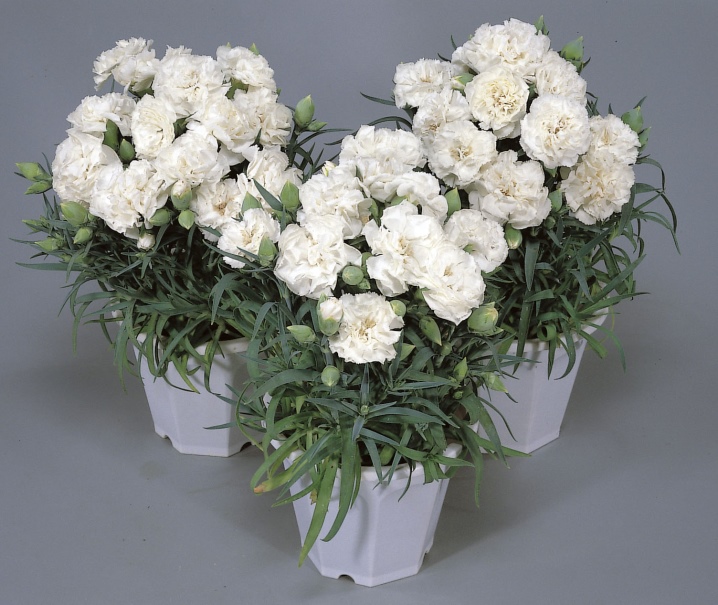

Let's take a closer look at popular varieties.
- "Shabo". The perennial has large flowers of various shades. White, yellow and scarlet buds are often found. A distinctive characteristic of the variety is a strong aroma and narrow short leaves of a bright saturated color. Velvety inflorescences on a small shrub are suitable for decorative gardening.


- "Grenadine". This variety is grown primarily for cut. Carnation with large flowers is found in a wide variety of shades. The Mediterranean is considered the homeland of the "Grenadine", but it takes root well in cooler climates. Cold-resistant and unpretentious variety looks good in flower beds.


- Carnation of Andrzheevsky. A distinctive feature of the variety is the gray stems without leaves. The petals of the buds are covered with villi and small teeth, therefore it is often called terry. The color of the flowers is usually red, rarely pink. Andrzheevsky's carnation tolerates temperature changes well, lack of moisture and feeding. The plant is photophilous and does not tolerate shade well.


- Hybrid. The popular variety is represented by flowers of various shades. It is widely cultivated by gardeners. A distinctive feature is a variegated color - there are specimens with striped petals, specks and specks.


Florists often use bright solid color carnations. Thanks to the wide color palette, different varieties of garden carnations can be used to create different compositions. Let's take a closer look at the best varieties for growing in the garden.
- Champagne. Terry golden petals emit a pleasant, delicate aroma. Flowers 5–7 cm in diameter are collected in inflorescences, which can be up to 20–25 pieces. Low stems form a neat bush. The variety is suitable for decorating flower beds and for cutting into bouquets. After a long flowering of buds (from June to October), it is recommended to bring the plants indoors.

- "Aurora" (Aurora). Shrubs of medium size have high decorative qualities. On long, upright shoots, pink buds are located, collected in inflorescences. The dense double petals open in early summer and continue to bloom until the end of October. The cold-resistant variety is suitable for temperate climates, and in the southern regions it can decorate flower beds with bright buds twice a season. Ornamental flowers tolerate well being adjacent to other carnation species.


How to plant?
Cloves are of southern origin, so they prefer sunny areas. When choosing a place, you should pay attention to the acidity of the soil - it must be neutral, otherwise the plant will hurt. Tall shrubs and trees can shade the seedlings, so it is advisable to choose a free, open area. When planting carnations in open ground, it will be necessary to lower the acidity. It is best to use dolomite flour. Planting carnations is carried out in early spring (early or mid-March), when the ground warms up enough and the air temperature reaches + 15 ° C.
Seeds for seedlings are planted in small boxes, slightly moistened with warm water and covered with a film (glass). The first shoots will appear in about 2-3 weeks. The boxes with sprouted seeds should be exposed to the sun and the foil should be opened. When the second true leaf appears, a pick is made. Plants are planted in the ground to a depth of 1–2 cm - the root collar should not be too deep. For the carnation to take root well, you need to plant seedlings at a distance of 30-40 cm from other plants.


Interesting! Garden carnation does not tolerate noise. Research has shown that flowers will grow better away from roads and other areas where there is a lot of loud noise.

How to take care of it properly?
Subject to simple rules of agricultural technology, some varieties can grow in one place for up to 5 years. The basic rules of care can be roughly divided into the following stages:
- watering;
- loosening the soil, cleaning weeds;
- top dressing;
- pruning;
- preparation for winter.



Watering should be frequent, but you should not water the plant. Stagnant moisture can lead to illness and even death of the flower. After flowering, you need to cut off the buds, shorten the stems. This will help the plant recover faster. It will be able to bloom for the second time in a season. In order to preserve a perennial flower in winter, the carnation will need to be wrapped up, and the root should be covered with a covering material.
In harsh climatic conditions, the plant can be dug up, transplanted into a flower pot and brought indoors or on a covered veranda. All varieties are suitable for wintering indoors.

Top dressing should be carried out according to the following scheme:
- 1 year - nitrogen-containing fertilizers are applied;
- 2 years - complex and mineral fertilizing.


Reproduction methods
Garden carnations are not recommended to be grown in one place for more than 2 years, so the bushes will need to be planted. There are several ways to propagate a plant.
- Cuttings. Transplanting with a cutter helps to preserve all varietal characteristics of the color, which is most acceptable for cultivated and hybrid species. These varieties take root well in another place, after a few months they are able to bloom. It is advisable to carry out cuttings at the beginning of summer. Small shoots 10–12 cm long are cut from the bush. In the lower part, you need to make an oblique cut and visit it in a sandy substrate. For rooting, they are watered and covered with a film, as when planting seeds. Shoots take root within 20–25 days and are ready to be planted in a new location.


- Division of the bush. For further rooting of the garden carnation, this process should preferably be carried out in the spring or autumn, upon completion of flowering. A healthy bush intended for propagation is carefully dug up and the rhizome is cut into pieces. Each part should have at least 3 growth buds. Each cut is planted in open ground and looked after like a young plant.


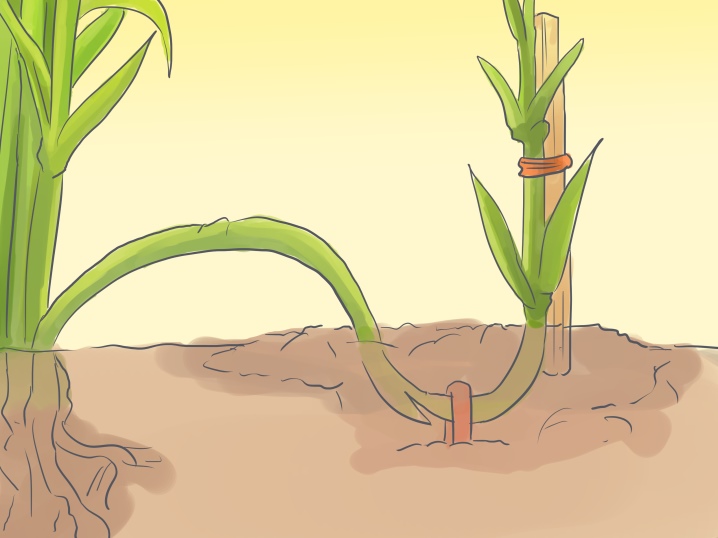
- Layers. Flowers with vegetative shoots can still be propagated by layering. At each internode, a small longitudinal incision must be made with a sharp knife. Lower the underside of the stem with the notch down and cover with earth. For rooting, it is necessary to constantly maintain soil moisture. After the formation of the root, young shoots appear, so the plant can be carefully separated from the mother and transplanted to any place.
Diseases and pests
One of the most common causes of fungal infections is waterlogging of the soil. To protect the site from fungal diseases, it is necessary to carry out preventive measures. At the beginning and in the middle of the growing season, you need to spray the stems and leaves of cloves with fungicidal preparations.
Let's take a closer look at mycoses.
- Alternaria This disease is a fungal infection of leaves and flowers that wilt and fall off. The appearance on the stems and leaves of brown spots with a dark bloom should serve as a signal that the plant urgently needs processing.
- Fusarium. This disease often goes away unnoticed, manifested by a slowdown in flower growth.
- Rust. It is often passed on from other plants. Signs of the disease are brown spots on the stem and leaves of the plant. Sick parts should be removed, cloves should be treated with Actellik, Aktara and Mospilan fungicides.



If we consider viroses, it is worth highlighting several diseases.
- Mosaic. Symptoms of the disease are small streaks or specks that dry out the leaf over time. On flowers with red and pink petals, it appears as thin light stripes.
- Mottling. If some of the buds do not bloom during the flowering period, and chlorine spots appear on young shoots, most likely the plant is infected. Over time, the flower dries up completely and dies.
- Bushiness. Strong branching and a large number of young shoots can be a sign of illness. Growth slows down, there are no buds.


It is worth paying attention to the control measures.
- Pruning and culling of affected plants. Destruction of vector pests and weeds. To destroy them, it is necessary to treat the soil and plants with insecticides. Gardeners prefer the use of folk remedies such as infusions of onion peels or potato tops. You can also plant calendula or mint between the rows.
- Particularly dangerous are the scoop, thrips and rootworm nematode. If the plant is attacked by a nematode, it must be immediately dug up and burned. The soil in the place of the sick flower will need to be additionally treated with boiling water, and then with any insecticide.


Use in landscape design
Flowers of the genus Caryophyllaceae are often used to decorate flower beds. Can be planted in single landings, in combined and mixed groups. Due to the wave flowering of different varieties, the shrubs will decorate the territory for 2-3 seasons. Perennials form soft, colored pads of thin, narrow leaves and begin to bloom in early June. Low-growing varieties are suitable for decorating rocky gardens.



In mixed plantings, the carnation feels good surrounded by the groundwort, yarrow and broom cochia. An elegant gypsophila will be a successful combination. It is advisable to refuse the neighborhood with tulips - they can infect delicate flowers with fungal diseases. Ornamental varieties take root well in greenhouses and can bloom for a large year. Flowers can be used to decorate open terraces and verandas; in combination with wildflowers, they will decorate a rocky garden. The root system of a carnation is shallow, so decorative flowers can also be planted in pots and hanging pots.
For information on how to grow a garden pinnate carnation from seeds, see the next video.







































































































The comment was sent successfully.