All About Nail Plates
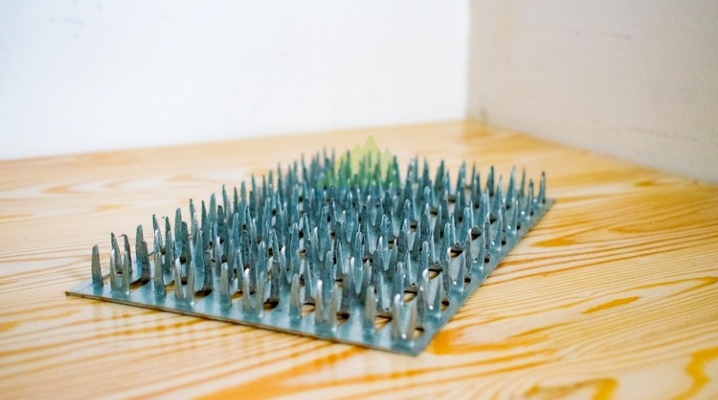

Wood is a popular material for the construction of various structures. In the process of joining wooden elements during construction, the question arises about their reliable fastening. For these purposes, various fasteners are used - most often these are nails or pins. Recently, nail plates have been used to firmly connect timber, beams or other wooden elements.
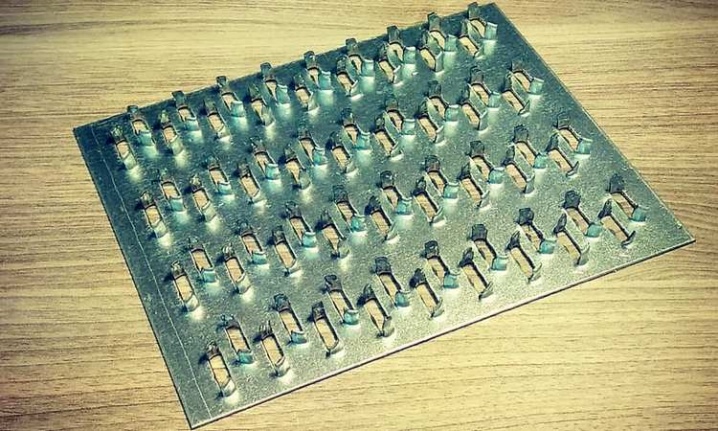

What is it and what is it for?
The nail plate is a fastener used when working with wood. It is a strip of metal with sharp teeth on the working part (analogue of nails). Depending on the type of fasteners, such pins can have different shapes and sizes. The plates have a minimum thickness, due to which such fasteners can be used at any stage of the construction of structures.

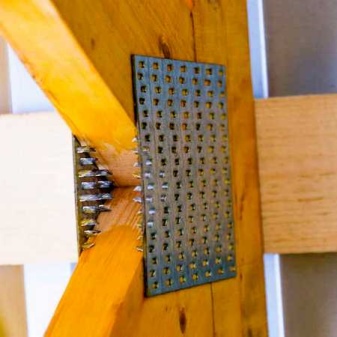
Metal toothed plates (abbreviated as MZP) are widely used in the construction of wooden structures for any purpose. They are massively used in industrial and private housing construction, when erecting timber frame structures or installing rafter systems.
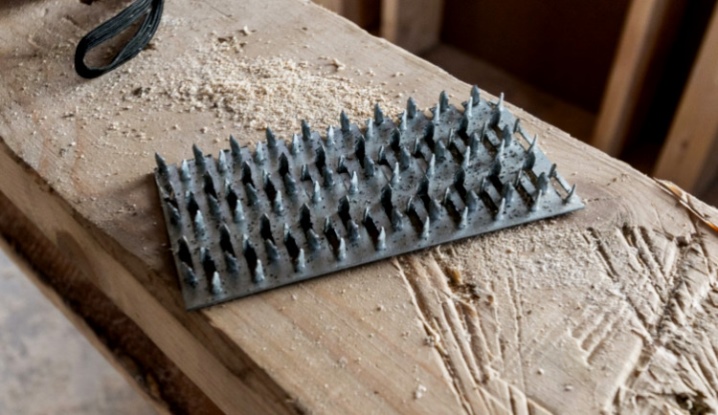

In modern construction, such fasteners are very popular due to a number of advantages:
- they connect wooden elements without protrusions;
- have a low weight, due to which they do not additionally "load" the structure;
- make it possible to mount complex systems without involving large-scale special equipment;
- provide a reliable and durable connection;
- resistant to corrosion.
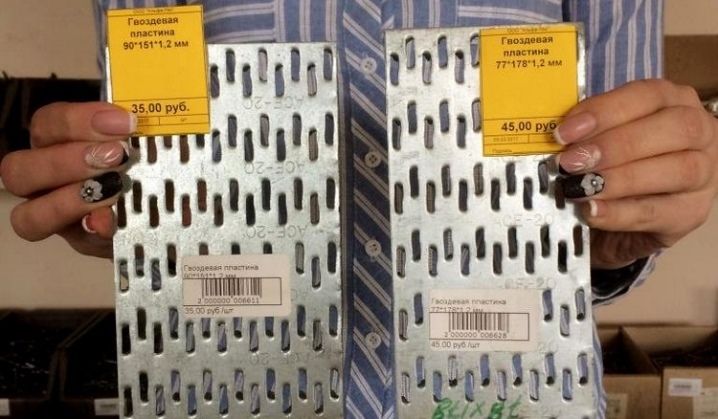

Metal nail plates are inexpensive, easy to install and suitable for all types of wood. Their main disadvantage is the impossibility of providing sufficient strength under bending loads in the joint areas.
How is it produced?
MZP is produced at industrial facilities using powerful pressing equipment. Alloyed or galvanized steel is used in the production. These materials do not corrode.
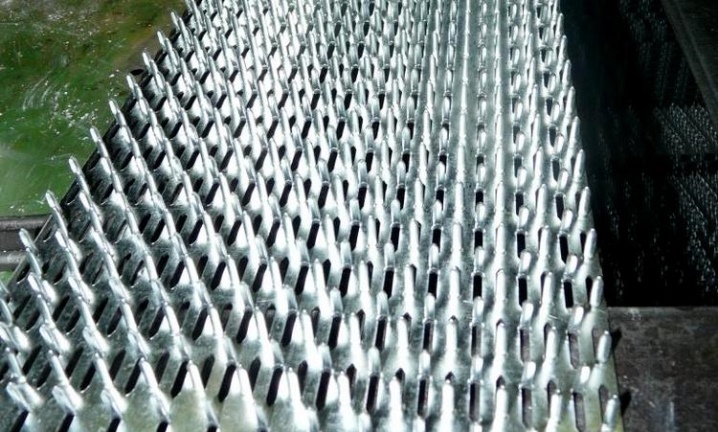

In the manufacture of such fasteners, hydraulic presses are used. With their help, by stamping, rows with sharp spikes are formed on metal plates, which easily enter the wood. The use of presses allows a variety of inexpensive nail plates to be produced in a short time span.
Views
MWPs differ in their appearance. They have a different thickness of the metal base, a different number of rows with spikes, the length of which varies over a wide range. Products made from sheet steel are marked with GP (RK) symbols, and from galvanized sheet steel - GPZ.
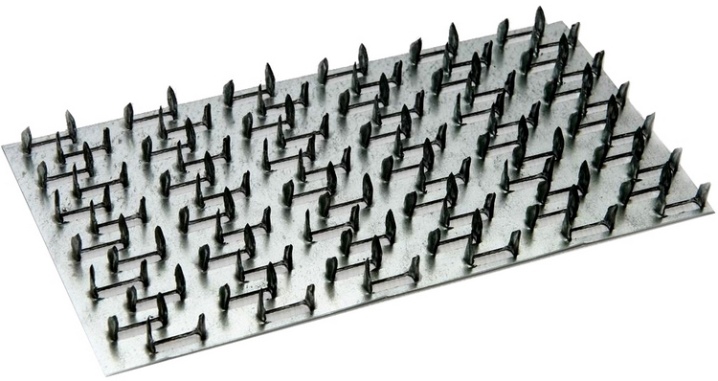
Nail plates are available with unidirectional or bi-directional pin arrangement.
- The production technology of the first fasteners is simpler and cheaper. According to it, MZP are manufactured at domestic factories. Plates with unidirectional teeth are less reliable than bi-directional pins.
- The second ones have thorns with different directions - they are located parallel to the sides and diagonals of the plate (visually, their arrangement resembles a "Christmas tree"). The production process of multidirectional nail plates is more labor intensive and financially costly. Most of these fasteners are produced in Poland, Germany and Finland.


Dimensions (edit)
Fasteners manufactured by cold stamping have a plate with a thickness of 1 to 2 mm. The metal base is made in the shape of a rectangle, its dimensions directly depend on the number of rows of pins. The width of the standard fasteners is from 20 to 130 mm, the length is from 75 to 1250 mm.
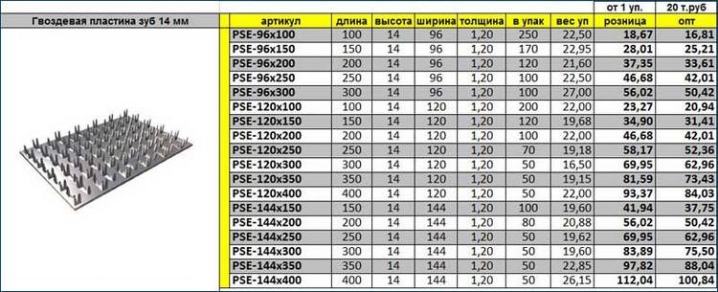
One plate can accommodate from 2 to 16 rows of teeth. The height of standard studs ranges from 8 to 14 mm. However, there are products with spike lengths up to 25 mm. Some enterprises accept orders for the manufacture of MZP according to individual sizes.
Application features
The main task of the nail plate is to securely fasten 2 (or more) timber elements (and other lumber) in one plane. Greater reliability of the connection will be achieved if dry wood that is not prone to cracking is used.
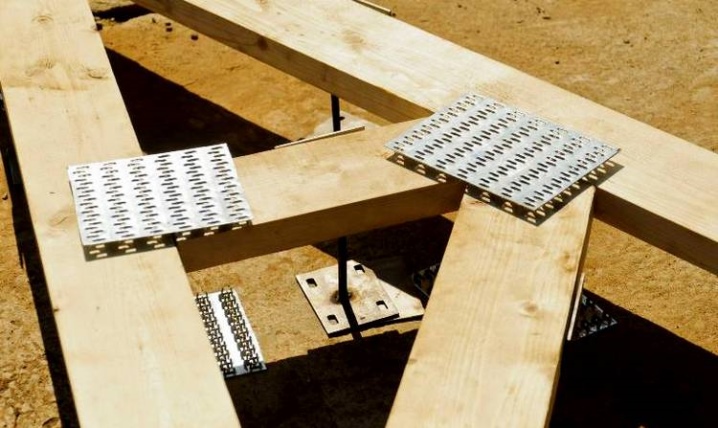

There are several nuances of installing the minimum wage.
- Each node must be fastened with plates on 2 sides.
- For a reliable connection with high strength, a specialized press should be used, which is able to fix the exact position of the metal plates and ensure the optimal speed of pressing the pins into the wood.
- It is recommended to assemble wooden structures using nail plates in workshops, after which the finished elements are transported to the construction site.
- When using MZP, it is unacceptable to use a sledgehammer or hammer. Otherwise, vibrations occur, which often lead to deformation of the teeth. When using a hammer, the proper pressure on the metal base is not ensured, as a result of which the fastening may be unreliable.
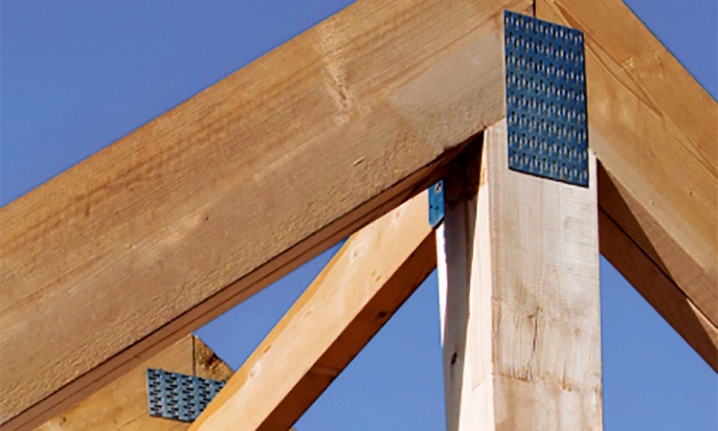

Serrated plates, subject to the fixing rules, are able to provide a strong connection for wooden elements. Such fasteners are slowly but surely gaining popularity and every year they are more actively used in the construction industry.
For detailed information on mounting nail plates, see the video below.













The comment was sent successfully.