Nuances of pruning pears in spring

A good harvest of pears is the result of competent care, in order to achieve it, unwanted branches must be removed regularly and in a timely manner. Knowing the rules and nuances of spring pruning will help create optimal conditions for the growth and ripening of fruits.
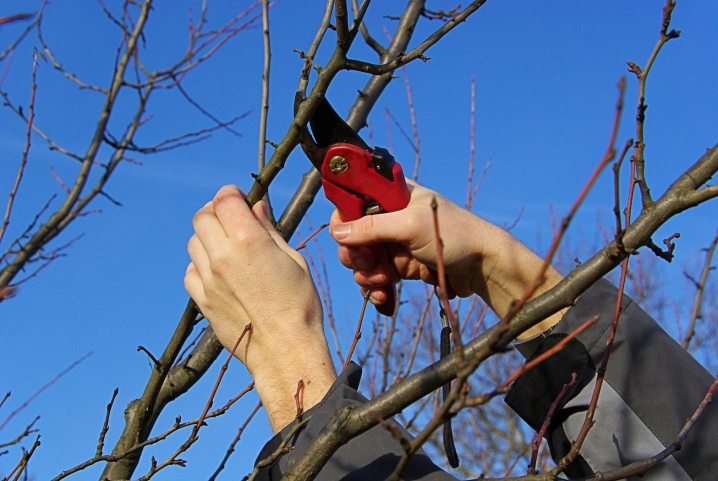

The need for a procedure
If the pears are not pruned, they will grow tall, pushing out the vertical shoots. This will reduce yields and weaken the tree's ability to withstand disease and frost.
Periodic removal of damaged or excess branches will prolong the fruiting period and improve fruit development.

Let's look at the main goals of pruning.
- It allows you to form a strong skeleton.
- The distribution of branches within the crown becomes even.
- The branches are kept in the right size for easy maintenance and harvesting.
- Access to light and oxygen inside the crown is provided - if they are not enough, the appearance and growth of buds in the shaded part of the tree will slow down or stop altogether.
- This reduces the risk of disease and pests.
- Rejuvenation of ripe and old pears, prolongation of fruiting period.
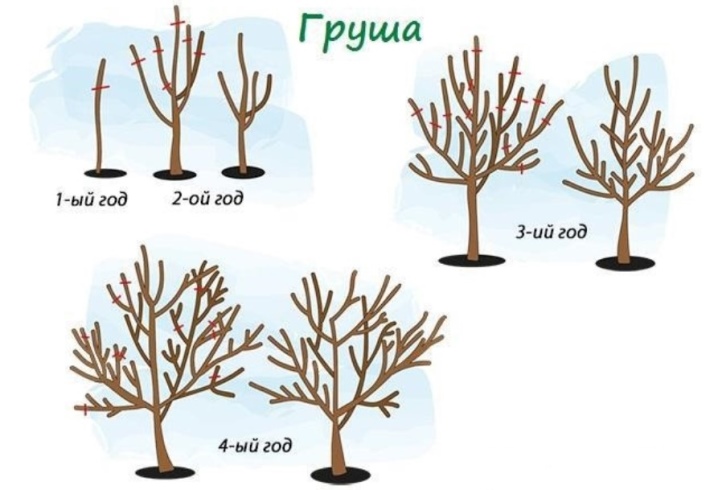
Timing
Pruning of pear trees in Moscow and the Moscow region may begin in March. In early spring, the sap will not begin to move yet. Basically, during this time, young plantings are pruned. The main edging works are carried out in late March - early to mid-April. The best time to prune is when the air warms up to 5-8 ° C and the buds have not yet begun to grow. Also consider the upcoming weather forecast.
If frost or prolonged temperature drops are predicted, postpone work until a later date.

Processing pears at low temperatures is not recommended as the tree becomes brittle. If the sap has already begun to move, then due to pruning or removing branches, the plant will lose some of the nutrients necessary for growth. But pruning can be done not only in March, work is carried out in May as well. This period is ideal for pruning mature trees. Twigs that make the crown too thick are removed. A characteristic feature of May pruning is a decrease in the growth rate of the plant.

Species overview
The processing of pears differs in terms of time and work performed, it can be divided into the following 3 categories:
- supportive (rejuvenating);
- formative;
- sanitary.
Let's consider each of them in detail.
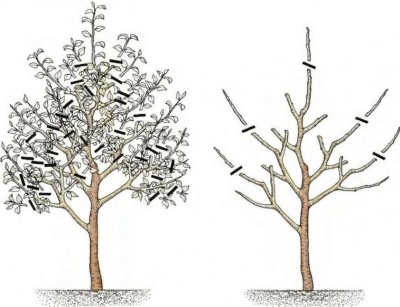
Formative
This pruning is done mainly at planting and on young pears. The growth and development of a tree depends on timely and competent pruning. The correct distribution of skeletal and vegetative branches allows you to get early fruits and form a rich harvest. On mature plants, this method is used to remove tops from the main branches.
Pruning stops the overgrowth of new shoots. This is mainly done on seedlings. This makes the branching less aggressive.
There are several types of pear tree crowns. You can choose any suitable one, depending on growing conditions and personal preferences. The most popular are sparse-tiered and bowl-shaped crowns. Let's consider each scheme in more detail.
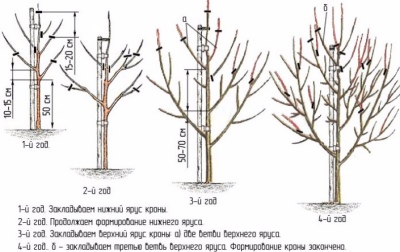
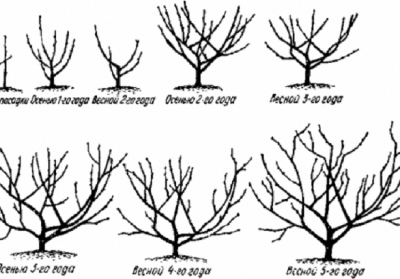
Sparse tiered crown
This type of crown, common in fruit growing, closely resembles its natural shape. In the upper part of the trunk, branches are in groups (tiers) of two or three, and sometimes one at a time. The crown begins to form in early spring in annual seedlings.On the conductor, it is necessary to set aside the boom zone at a height of 50 cm from the ground. If this distance is reduced, then in the future it will be uncomfortable to care for a ripe pear. The larger the bole, the more vulnerable the tree trunk will be to cold and heat. Count an additional 35 cm above the stem and place the first tier of skeletal branches on top of it, cut off the conductor.
During the formation of the crown, the central shoot is left 15-20 cm above the lateral branches.
In the process of processing the pear, care must be taken to ensure that the pruning is correct and that there are no stumps. Otherwise, during growth, the conductor may deviate too much to the side. Conflicting shoots should be removed as soon as they appear.
In the spring of next year, the shoots are cut off, at the first stage three strong shoots are left with an interval of 10-15 cm along the trunk. They are cut to approximately the same horizontal length. Shoots should grow evenly around the circumference, and their angle should be 100-120 °. All other side branches should be cut or temporarily bent so that they are parallel to the ground. This will artificially slow down their growth and increase the chances of fruiting.
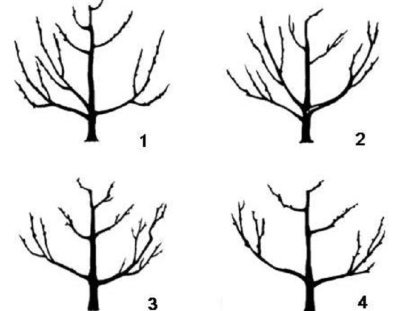
Branches up to 30 cm long can be left as they bear fruit well.
In the third year, 2-3 branches should be laid at a height of 60 cm from the lower tier, they will become a frame for the future. If the branches grow too long, shorten them. Do not work with curved branches, but shorten or trim those that thicken the crown. In the spring of the fourth year, 1-2 shoots of the third "floor" remain at a distance of 40 cm from the second. After another couple of years, the stem branches are shortened to the upper skeletal branches. The final crown height should not exceed 4-4.5 m.

Cup-shaped crown
Among gardeners, the regular cupped crown and the improved version are popular. In the classic version, the main branches are very close to each other. In an improved version, the main branches are located at a distance of 15-20 cm from each other. The size of the crown stem is from 50 to 60 cm.
In seedlings up to one year old, the branches of the crown frame are formed from three or four lateral shoots. They should be symmetrically positioned around the trunk of the tree. Other shoots should be removed and the main branches cut to the length of the upper side branches. Skeletal shoots must also be trimmed: the upper ones - 10-15 cm in length, the middle ones - 20-25 cm, the lower ones - 30-35 cm. Pruning to increase the size of the crown is carried out on the outer buds. The upper branches must face north, otherwise they will become too long and narrow.

A two-year-old pear should be trimmed as little as possible in the spring to reduce overgrowth and bring the first fruit closer.
Remove upright, inward-growing or enlarged shoots. If necessary, shorten the branches of the skeleton slightly. You can change the direction of growth by cutting off the conductor above the branch that grows in the desired direction. On skeletal branches, select two shoots that will become secondary branches and shorten them. Delete the conflicting branches.
For a 3-year-old pear, trim the skeletal branches if necessary to enlarge the crown. Secondary branches, which have overtaken the main ones in growth, also need to be cut off. Shoots that grow into the crown must be completely cut off or left two buds high. Place the fruiting twigs evenly in the center of the crown.
Sanitary
As fruit trees grow, they will show old, broken or diseased branches. Periodic visual inspection is required to identify them.
Small dead twigs can be pruned at any time of the year. Large branches should be postponed until early spring or late autumn and done before or after the growing season.
Broken branches should be removed if necessary and rings (nests) attached to the trunk should be cleaned. This is done to prevent the spread of the disease.The scraps must be burned.

Supportive
Maintenance pruning is carried out in the first ten days of March and April to rejuvenate mature trees. Remove excess shoots from all over the crown every year. Young shoots that grow vertically should always be removed. Shorten individual branches by about 1/3 to stimulate fruiting. Remove large branches and some old branches to reduce stress on the trunk.

What tools are needed?
Consider the minimum required set of tools and materials for high-quality pruning of young and mature trees.
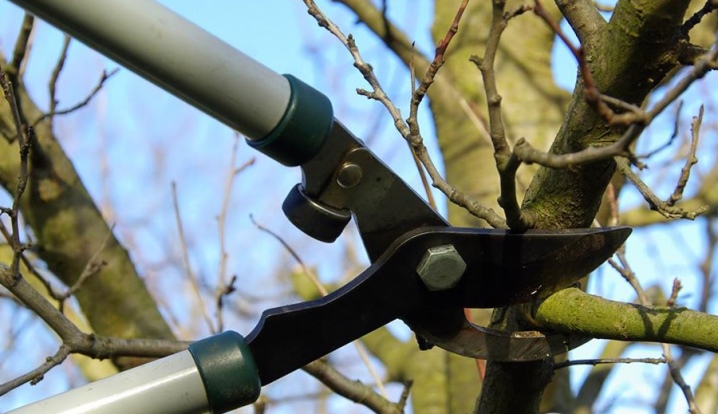
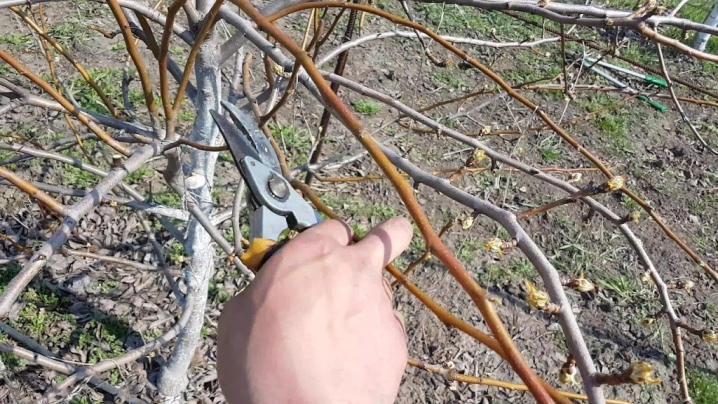
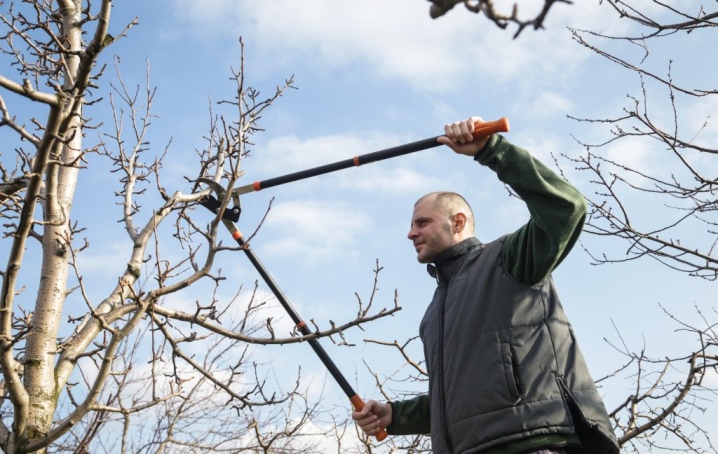
- The main tool for processing is a garden lopper (or pruner). Small shoots (up to 1.5-2 cm) can be cut with short loppers, and larger branches (up to 3-4 cm) with a long pruner.
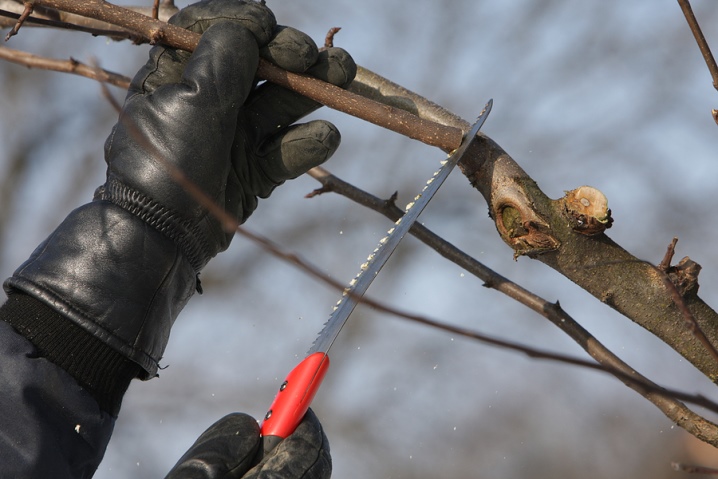
- Garden (narrow) hacksaw with a special sharpening and an ergonomic handle for a smooth and precise cut. It is designed for pruning large branches.
- Garden knife. Used for cutting, sawing, bark trimming and stripping trunks and branches.
- Steps and stairs. With their help, you can make it easier for yourself to access the sections of the crown.


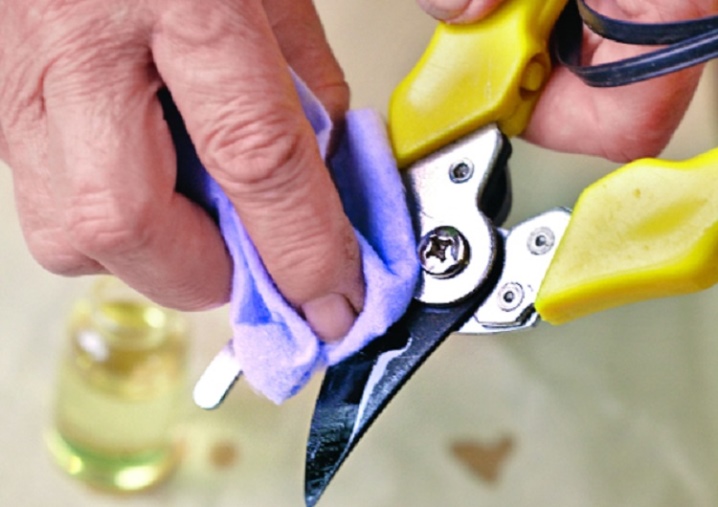
Tools for the job must be prepared in advance. Make sure the cutting edge is clean and sharp.
It is recommended to treat it with an alcohol or manganese solution and wipe it with a clean dry cloth before the procedure.
If these tools are not at hand, then the flame of a gas burner or conventional lighter can be used to lightly handle the blade.

How to prune pears correctly?
Pruning is done according to general gardening rules, but with several peculiarities. Both young and mature plants should be processed gradually to avoid over thinning of the crown. Knowing and following a few simple pruning rules can help reduce tree damage and speed up tree recovery.
- First, cut off the shoots that are growing at an acute angle from the trunk. Then lateral branches that grow perpendicular and parallel to the trunk.
- It is difficult for pear trees to cope with the stress of pruning on a large scale. All efforts are directed towards intensive regeneration. This weakens the growth of the tree and certainly reduces fruiting. If the crown of the tree is significantly increased, it is recommended to divide the work of processing the crown in half.
- If the branch is 3-4 cm thick, first make a prep cut at the bottom and then a regular cut at the top. This prevents damage to the bark of the pear when the branch breaks from its own weight.
- When removing a branch, the cut should be correct, not too deep, and flush with the ring at the base of the shoot. This will help your cuts heal as quickly as possible.

Depending on the age of the tree, there are different ways to prune the pear in the spring.
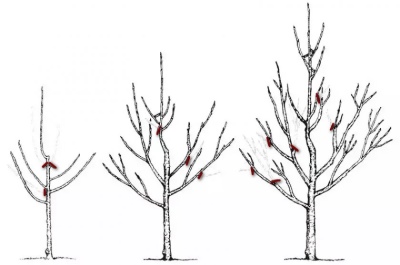
Young
The main task of pruning a young tree is to form the crown correctly.
- Pruning is not recommended in the first year after you have planted the seedlings due to their slow growth.
- After a year, young plants can be pruned to a length of 50-70 cm to promote germination.
- After a year, the central shoot should be trimmed again, leaving four or five strong side branches at a 45 ° angle. The ends of the main branches should be higher than the secondary side branches. Delete the conflicting branches.
As the tree grows, the young shoots that will bear fruit bend. They are leveled with weighted ropes or pulled over adjacent branches.
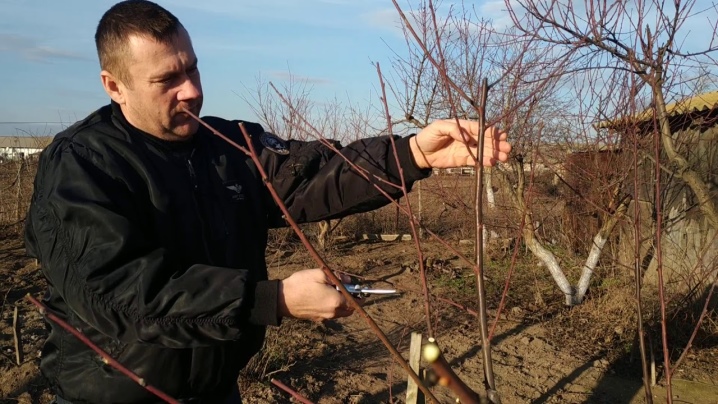

Adults
Remove excess shoots on 8-10 year old trees, including medium to large branches.
Dry or diseased branches should be cut completely.
Young, strong shoots will be used to replace older ones.

Old
The old pear tree needs significant rejuvenation. Start by trimming the top of the crown where new shoots appear, the trunk can be cut in half. The rest of the crown should be left with two tiers (5-6 branches) of skeletal branches. Create about a meter of space between the tiers.
Keep the main branches of the tree short. Do not leave them too long, as the weight of the fruit will cause them to bend towards the ground. Next, treat the tree by removing overgrown or inside branches. Old, non-fruiting branches can be safely pruned as they are no longer productive. Better to replace them with young shoots.
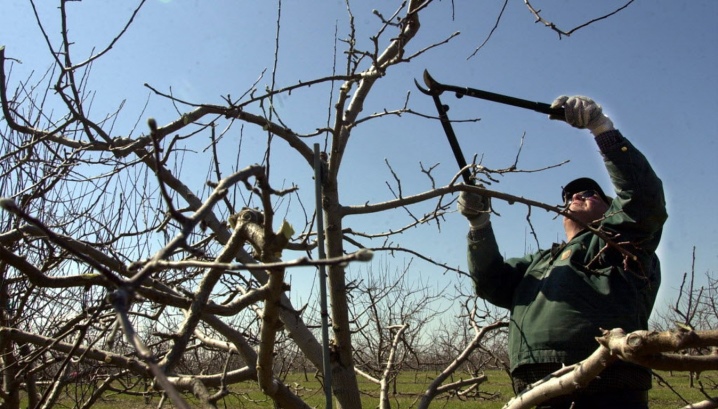

Follow-up care
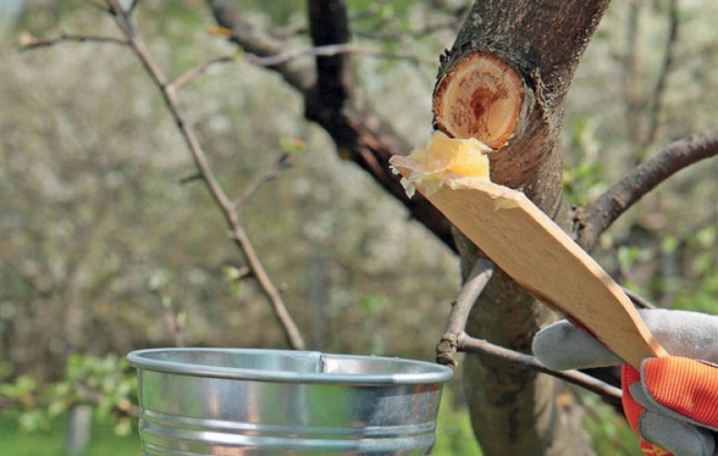
At the end of the work, all cut branches must be removed from the tree, and diseased branches must be burned. Treated areas should be treated with garden varnish or covered with oil paint.
This will help prevent disease, pests and minimize nutrient loss during juicing.
If the temperature is below 8 ° C, the garden var will not adhere well to the wood, so paint is the best option. Experts advise against fertilizing the tree immediately after processing.

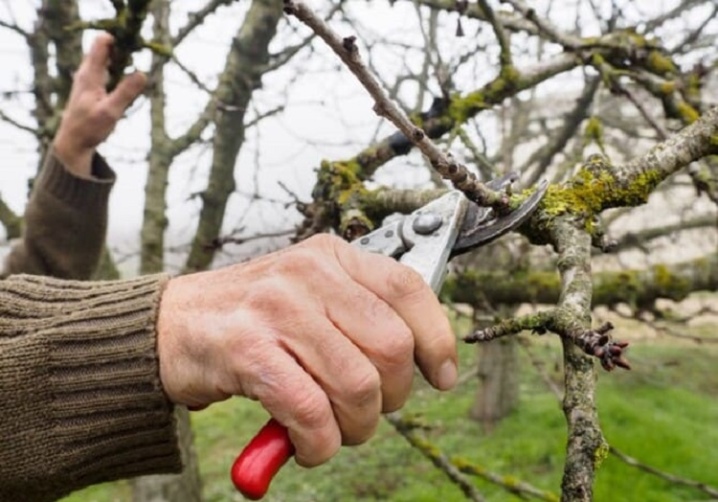
Common mistakes
The main mistake newbies make is that they only remove dry or damaged branches. This type of pruning may be appropriate when the lesion has not developed and spread beyond the outbreak. Shoots should be removed up to the first healthy bud.
Another gross mistake is crown thickening. Branches that are close to each other will bump into each other in the wind. With frequent contact, the protective coating of the shoots is damaged, so harmful insects and diseases begin to attack the tree.

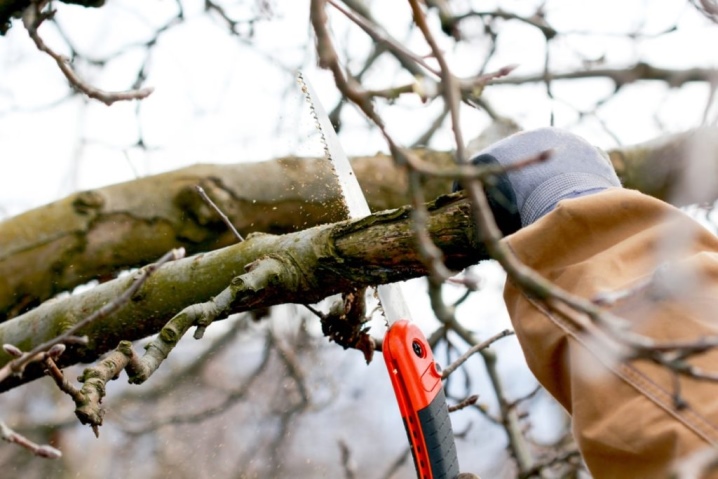
Pruning the buds is a complex procedure and can be difficult for the novice gardener.
Beginners often make the mistake of leaving a large tree stump or cutting branches at an angle. Another violation of the rules is the use of rusty, dirty tools. The former leave deep grooves and burrs in the cut, which can cause rotting. Dirty tools can cause fungus to appear on the cut.









The comment was sent successfully.