Hydrangea "Polar Bear": description, cultivation and reproduction
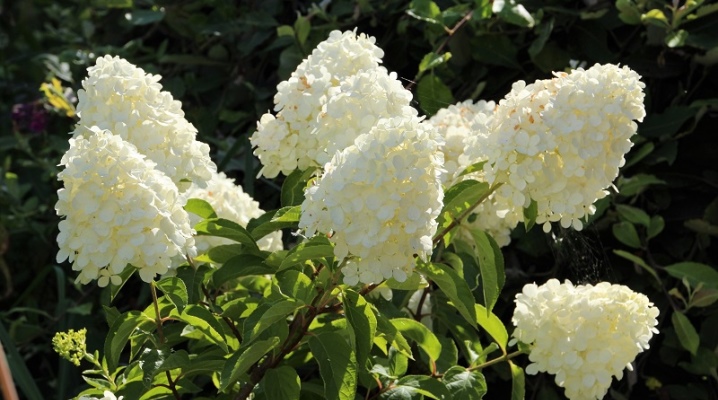

Panicle hydrangea is a favorite of many gardeners, because large, beautiful flowers easily ennoble any area. A relatively new variety of such a plant is the Polar Bear, bred in 2013. The features of this culture, as well as all the subtleties of planting and subsequent care, will be considered in our material.


Description of the variety
Polar bear is the result of crossing two popular varieties of the paniculate subspecies. They are called Limelight and Grandiflora. "Limelight" is famous for its excellent resistance to cold weather and has an extraordinary pistachio shade of flowers. "Grandiflora" has massive flowers, but its disadvantage is that they are too heavy for shoots and can even break them. Nevertheless, Polar bear has no such disadvantages. Hydrangea "Polar Bear" is a rather large and spreading shrub that reaches a height of two meters and a diameter of one and a half. Shoots are straight, very strong, do not break off under the weight of heavy inflorescences. The foliage is elongated, has a beautiful green tint that does not fade in the hot summer months.
The inflorescences are massive, conical, about 40 centimeters long. The shoots are densely covered, making the plant look airy and weightless. There are two types of flowers in the inflorescences: fruiting and sterile. Fruit flowers soon fade and fall off. The barren ones are much larger, initially their color will be pistachio, and already in the fall the petals turn white, and then turn pink.
Polar Bear blooms from the very beginning of June to the end of autumn.


Landing
Before planting a hydrangea on your own plot, you need to carry out several preparatory measures. The first of these is the choice of the landing site. Since Polar Bir is very demanding on water, it is not recommended to plant the plant under or near trees. They will take up precious moisture, contributing to the development of diseases in hydrangeas. The place should not be too sunny, the best option is an openwork shade. If there is too much light, the culture may not bloom.
The second point is the time of planting the plant in the ground. In regions with a warm climate, hydrangea is planted in the fall, with a cold one - in early spring. In addition, it is important to choose the right soil. Acid or neutral soil with good moisture is suitable, for example, chernozem or loam.
Alkaline soils are best avoided, but if there is no choice, they should be acidified with iron sulfate, peat, or pine needles.


The planting hole is prepared in a day. For this a hole is made in the ground, commensurate with the root system of the seedling or slightly wider... About three buckets of water are poured there, then it is absorbed all night. In the morning, you can pour soil, flavored with top dressing, into the hole. It will be the earth itself, humus, peat and sand. Earth and peat should be taken in 2 parts, the remaining components are taken one by one. A good solution is to add some superphosphate as well. After most of the soil is already in the hole, a seedling is placed on top and its roots are well straightened. The root collar does not need to be buried, since the deep location of the latter can cause rotting. Then the ground is well trampled and watered, a bucket of water on the bush will be enough.
An important point is the mulching of the crop, this helps to retain moisture and for the first time protects against bacteria and pests. You can mulch with bark, sawdust or peat. The layer of mulch should be at least 9 cm. In addition, young seedlings will need to be covered so that they do not suffer from wind and sunlight. As for the distance, between each bush you need to maintain a distance of at least a meter, and even better - one and a half. The distance between other crops and trees is 3 meters or more.


Follow-up care
"Polar Bear" is a very beautiful, but demanding plant to care for. Consider the mandatory rules that the gardener will have to follow.
Watering
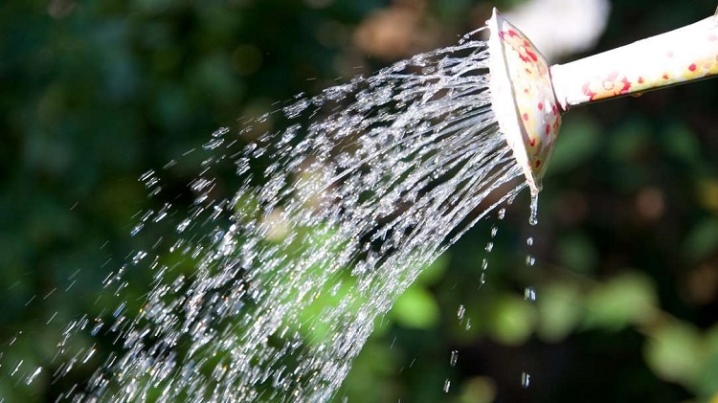
Polar bear is incredibly fond of moisture and, with a lack of it, quickly begins to fade. Therefore, watering should be systematic. If the summer is hot, you need to supply water at least three times a week, 15 liters will be enough. In cool seasons, the plant needs watering once every one and a half weeks, the amount of water is the same. But when the summer is rainy, watered according to the situation, it is quite possible that 5 times per season will be enough.
Every third watering, many gardeners use potassium permanganate, adding about 2 g per bucket of water. This simple remedy will be an excellent prevention of fungal diseases. Pour water into the trunk circle, avoiding contact with leaves and stems. The liquid is served early in the morning or in the evening, only warm, settled water is used.
After watering, the plant is loosened, if necessary, mulch.

Top dressing
In the first two years, you do not need to give any additional fertilizing, the hydrangea is quite enough of those substances that it receives from the soil. Everything changes with the beginning of the first flowering. Here, top dressing becomes a mandatory step in crop care. Panicle hydrangea is an unusual plant, and this is manifested in the fact that the saturation of the color of the petals is directly proportional to the acidity of the soil. The most beautiful and brightest flowers grow on acidic soil. That is why, before flowering, gardeners use acidifying drugs. After flowering, potassium and phosphorus are preferred.
The very first fertilizer feed takes place in May. To do this, choose complex preparations that will help the plant recover after the winter months. The fertilizer is dissolved in water, following the instructions. As a rule, there are two such dressings, the second follows 14 days after the first. In addition, it is possible to accompany complex fertilization with organic matter, it will not harm the plant.


In early June, it is important not to miss the time of acidic dressings, which will help the hydrangea bloom more beautifully and more magnificently. The fertilizer is prepared as follows: 45 grams of potassium sulfate and 70 grams of superphosphate are dissolved in one and a half buckets of water. Also, such feeding is carried out in July, thanks to it, next year it is possible to achieve excellent flowering. In mid or late October, panicle hydrangea is fertilized for the last time. This top dressing is designed to facilitate wintering. For her, they take fertilizers for hydrangeas.
What can not be used in dressing:
- chalk;
- ash;
- dolomite flour.
All these substances do not contribute to soil oxidation, in addition, they are harmful to hydrangeas.


Pruning
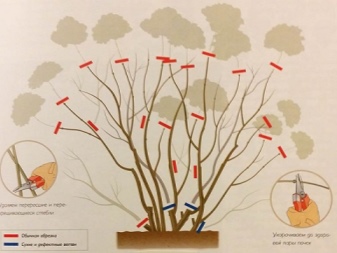
There are two types of pruning hydrangea paniculata: thinning and rejuvenating. The first type is used so that the culture does not grow too much. Such pruning will be needed in the fourth year, it is done in March and just before the onset of frost. In March, all frozen and weakened branches are removed. Shoots are cut by 2/3. As for the autumn pruning, it is needed to prevent the shoots from breaking off under the weight of the snow. At the same time, brown inflorescences and shoots are removed, which are most knocked out of the general range of the bush. If you do not carry out thinning pruning, then over the years this will lead to shredding of flowers, thickening of bushes and various diseases.
Rejuvenating pruning is done only in the spring. This type of pruning is needed for old plants, which are cut so that only a stump remains. In a year or two, such a plant will acquire new, succulent shoots.

Fight disease
In fact, the Polar Bear hydrangea rarely gets sick. If this does happen, the reasons may be:
- wrong choice of soil and site for planting;
- poor care, excess or lack of fertilizers;
- excess moisture, contributing to the development of the fungus;
- too dense plantations.
One of the most common hydrangea diseases is chlorosis. This insidious ailment is the result of a lack of nutrients in the soil. Depleted soil leads to the fact that the leaves turn very yellow, and the plants become weak. Such drugs as "Antichlorosis" and "Chelate" will help to cure the bushes.
Also, do not forget about feeding with iron and watering only with settled water.


In addition to chlorosis, rot can also affect the hydrangea. With white rot, shoots and foliage become brown, and the roots rot. Fungicides will help well in the treatment. Gray rot is more dangerous for the culture. The stems become watery and may even have holes in them. Gray rot progresses on rainy and humid days, covering an ever larger perimeter of the site. To get rid of the misfortune, diseased parts are removed and burned, healthy plants are sprayed with "Fundazol".
Besides, panicle hydrangea can also be susceptible to powdery mildew and septoria... Like rot, these diseases are fungal in origin and are difficult to treat. To avoid any dominance of the fungus, it is necessary to prophylactically treat the plants with fungicides.


However, if there is at least some chance with the fungus, then there is hardly anything that will help with viral diseases. Ring spot will be one of the main diseases. It can occur because the material was not tested during planting, the plant was cut with an infected pruner, and much more. With spotting, spots form on the leaves, subsequently the foliage curls and dies. Such a plant will not bloom. Unfortunately, it must be destroyed.
As for pests, snails, spider mites and aphids are especially annoying in this case.
- Snails eat absolutely all parts of the plant, adore moisture and shade. Many gardeners collect them by hand, but you can also put bowls with special preparations that will scare away intruders.
- The tick braids the foliage with the finest cobwebs. In the early stages, a soap solution helps against it; in advanced cases, only strong insecticides will be useful.
- Aphids not only suck out all the juices from the hydrangea, they are also a carrier of diseases. Soap solution will also help against such a pest, as well as the "Akarin" and "Commander" products.


Preparing for winter
"Polar Bear" is a very hardy plant that can withstand cold even down to -40 degrees. Nevertheless, shelter for young seedlings is required. They can be covered with burlap, as well as overlaid with spruce branches.
Adult and old plants do not need shelter, but you still have to mulch the trunk circle. For mulching, you should use dried grass, sawdust, pine needles, peat.
The mulch layer is at least 20 centimeters.


Reproduction
The main way of propagation of culture is cuttings. To carry out the procedure correctly, you will need shoots 1 year old, not too large, but strong. For three days they are placed in water, and then cut so that there are four internodes on each cuttings. The places where the tissue was cut must be well treated with growth accelerators. Further, the cutting is buried 2/3 into the ground, consisting of one part of sand and the same amount of peat. The seedling is covered with polyethylene on top. The cuttings are kept cool and humid, and when green shoots appear, they are planted in open ground.
Besides, panicle hydrangea can be propagated by dividing the rhizome... The bush is removed from the ground, lightly shaken off. Then it must be divided, but so that at least a couple of growth buds remain on each part. Places of cuts are dipped in a manganese solution and planted in a new place. It is important that at the same time a little old soil remains on the roots, so the plant adapts faster. As for propagation by seeds, it is not recommended to use it here. Firstly, it is incredibly difficult, and secondly, no one can guarantee that the grown plant will exactly copy its “parents”.
This can lead to the fact that varietal characteristics are completely lost.


Review overview
Most gardeners who have chosen the Polar Bir hydrangea for their plot are happy with the purchase. And this is not without reason, because such a plant is very hardy, it is easy to propagate it. Moreover, it is incredibly beautiful and will decorate the site with its large, heavy inflorescences, perfectly combining with other crops. Many are also satisfied with the fact that cut plants stand for a long time as a bouquet, pleasing the eye.
It is rather difficult to find negative reviews, because Polar Bear has practically no flaws. Negative feedback is left mainly by beginners who, due to inexperience, find it difficult to take into account all the rules and subtleties of keeping hydrangeas, as a result of which they can be susceptible to diseases and pests.


Examples in landscape design
Polar bear looks very elegant and beautiful, therefore it is successfully used in landscape design. Let's consider several options for its use.
- Solo. This type of hydrangea looks great alone, so you can easily plant just one bush to contrast with other garden crops.
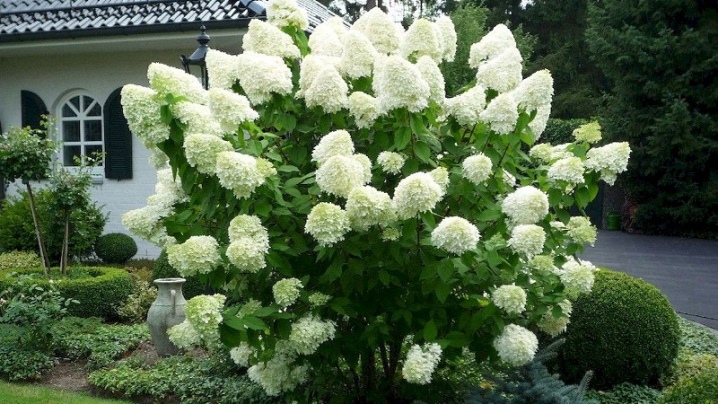

- No less exquisitely large bushes frame the paths. It is best to plant this type of hydrangea along the edges of wide stone paths, complementing the design with round or square bushes.
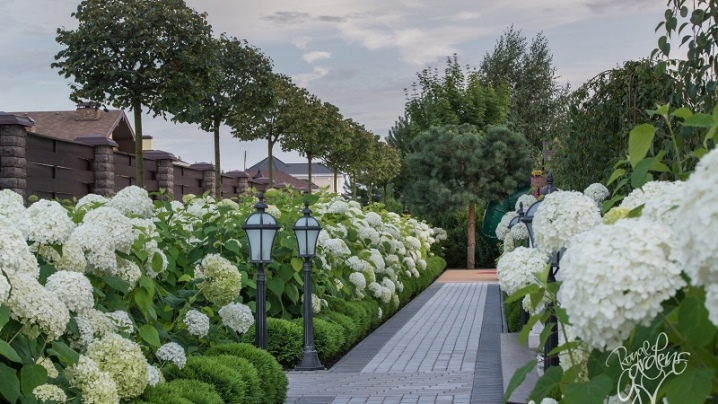

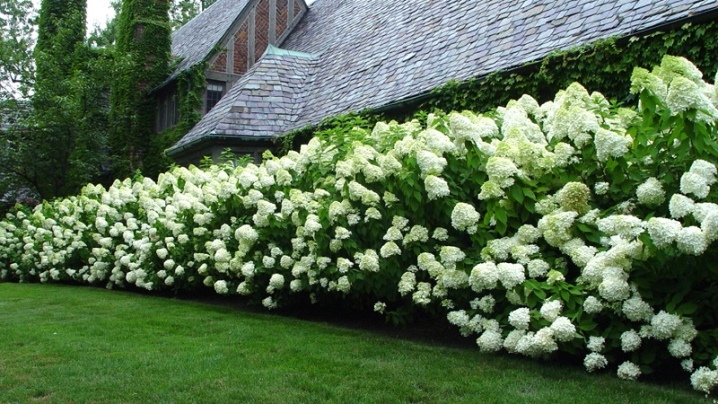
- The polar bear is often used as a hedge. This photo shows how exquisite clusters of these stunning plants look.

In addition, panicle hydrangea of this variety is used:
- in combination with conifers;
- in combination with perennial or creeping plants, low trimmed bushes;
- with honeysuckle and grapes.



In the next video you can take a closer look at the Polar Bear hydrangea.



































































The comment was sent successfully.