Stalked hydrangea: description and varieties, planting and care
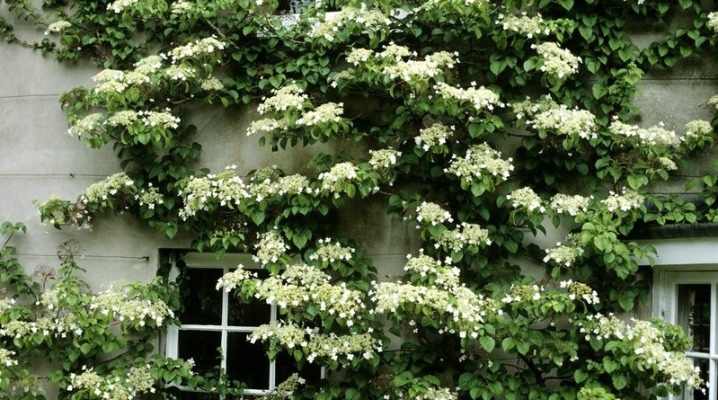

Curly petioled hydrangea does not have a solid trunk and looks more like a liana, moreover, it is characterized by all the qualities of an ornamental plant and lush flowering. This is the reason for the interest in this culture, not counting such advantageous properties as unpretentiousness and increased frost resistance.
Peculiarities
The homeland of such an unusual and beautiful plant as petiolate hydrangea is the east coast of Asia. Its natural place of growth is deciduous and coniferous forests located on Sakhalin Island, Korea and Japan. Climbing liana, as it is often called for climbing branches, is a perennial culture, with the help of aerial roots capable of climbing any supports to a great height, in particular, this applies to such a variety as "Petiolaris".
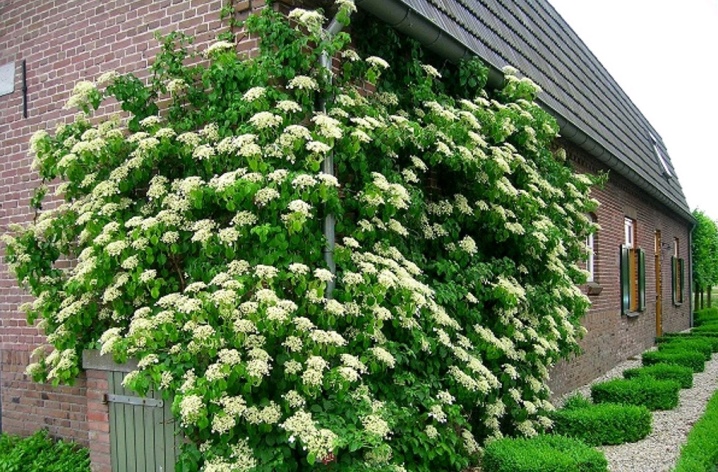

To get a complete picture of the climbing hydrangea variety, it is worth studying its description.
- The length of the liana depends on the variety and climatic conditions - in cold regions it grows up to 5-6 m, and in the south it can reach 20 m.
- The leaves are 10 cm long, dark green in color, attached to the branches with long stalks, they are round, large and have a pointed tip and a rough underside.
- The shrub is considered fast-growing, adding 0.5-1 m in length annually.
- The branches are covered with brownish-red bark and, in combination with dense foliage, manage to braid the supporting structures already in mid-April.
- Greenish and white flowers, collected in large corymbose inflorescences, growing up to 20 cm, appear in early summer and continue to bloom until the end of August. They are generously scattered over the crown and exude a unique aroma of fresh honey.
- The root system of hydrangea is strong, developed, grows in the upper layer of the soil, and aerial roots help it climb over any surface.
Petiolate varieties prefer acidic soil, they are not afraid of even extremely low temperatures (-30–35 degrees), since the plant has fantastic winter hardiness.



The liana-like culture can be used as a ground cover ornamental plant, ideal for vertical decoration of walls, partitions and other structures.
Varieties
The petiolate hydrangea has several varieties with interesting names, they are highly valued by gardeners for their decorative appearance, resistance to low temperatures and ease of maintenance.
- "Petiolaris" - the highest variety, capable of growing up to 25 m. Its climbing branches twine around the trunks and crowns of other trees, and in the absence of support they spread along the ground. The plant is distinguished by a complex inflorescence in the form of a corymbose panicle.
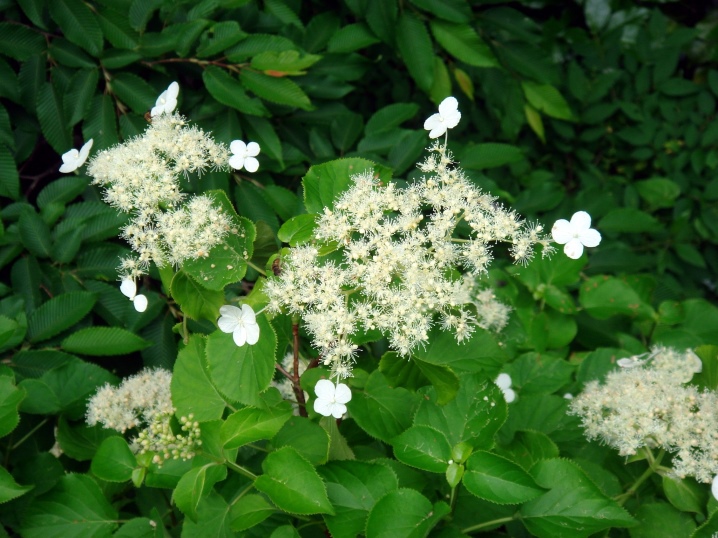

- Small petiole shrub "Winter Surprise" - a variety with a height of 2 m and boiling white flowers, its green foliage has the ability to change color to reddish, purple and burgundy. The flowering period takes place in late spring and early summer.


- "Cordifolia" - undersized shrub 1.5 m high, slow-growing (the growth of young shoots is 10 cm per year). The hydrangea has large round leaves, the upper part of which is green, the lower part is white. In the inflorescence there are two types of flowers: asexual white and fertile - yellowish. The plant is highly resistant to frost and disease.
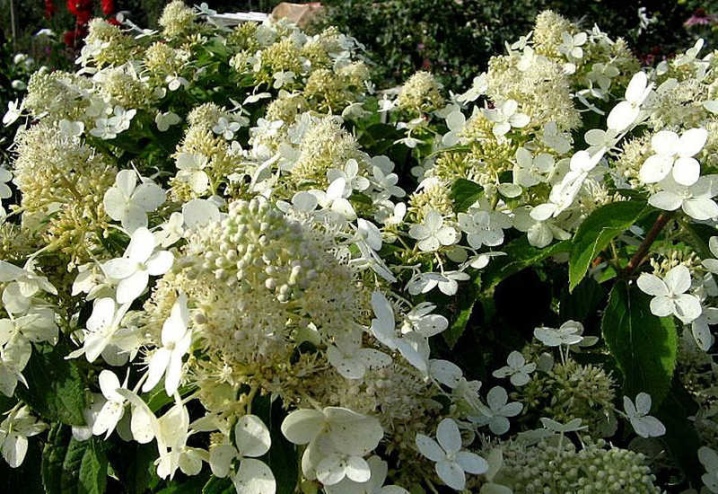

- Climbing hydrangea "Take e Chance" - liana up to 6 m high with rounded large leaves up to 10 cm in size, they have a white edging and a marble pattern. The hydrangea has creamy white flowers with a honey scent that bloom in early summer.
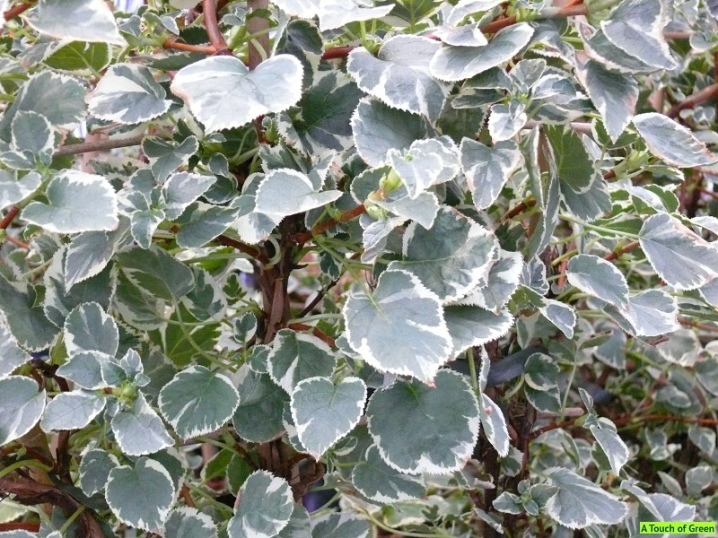

- The most beautiful type of petioled hydrangea is the Miranda variety. This is a tall plant, reaching a height of 6-10 m. The culture grows by almost a meter annually, has snow-white honey flowers. Its green leaves with small notches are framed with a yellow border. Flowering lasts 2 months - from mid-summer to September.


- Newly developed variety "Silver Lining" has an unusually pure, white color of the petals, the green outer and lower red sides of the leaves, which become completely burgundy in autumn. The shrub reaches a height of 2 m, but can be used as a bright unusual carpet, creeping along the ground.


How to plant?
Before planting, determine the place for the climbing hydrangea. It is not recommended to place the plant in the shade, as this will form a limited number of flowers, and their size may be smaller than usual. It is necessary to choose an area with diffused light or an open place where the bush will be in the sun only early in the morning and in the evening. There should be no large trees and shrubs nearby due to the moisture-loving culture. Liana is not afraid of strong gusts of wind, but young plants must be protected from it.
The soil for hydrangeas needs acidic, drained and fertile soil. The presence of lime in its composition should not be allowed, a large amount of sand is also undesirable, since because of this, the roots may receive less moisture.
The composition of the soil should include the following components: clay, leafy earth, humus, sand and peat.


Planting is carried out in the spring in the first decade of April or in October before the onset of a cold snap. Ready seedlings with closed roots are planted together with an earthen clod. If you use your own material - shoots at the age of 2-3 years, their roots must be kept in water for 24 hours.
Planting holes are harvested 1.5-2 weeks before planting, the size of the hole should be 2 times the size of the root system. For group planting in open ground, the holes are placed at intervals of 1.5 m.You should think in advance about the supports for the creeping hydrangea.


The main stages of disembarkation:
- laying on the bottom of the drainage pit, optimal materials - pieces of brick, expanded clay, pebbles, layer thickness 10 cm;
- a prepared nutrient mixture mixed with garden soil is placed on top of the drainage;
- the hydrangea is lowered into the middle of the pit, the roots are straightened, covered with soil to the first bud;
- after compaction of the earth, the near-trunk area is well spilled and sprinkled with mulch - pine bark, wood chips, sawdust and peat.
In the Moscow region, in the absence of snow and severe frosts, young bushes of climbing hydrangea will have to be tied up, laid on the ground and covered to avoid freezing.
At first, the vine does not grow too quickly, but it can bloom in 2, 3 and even 6 years, it all depends on the conditions created. And only adult plants in one season can give an increase of 1 m.



How to take care of it properly?
The rules for caring for petiolate hydrangea represent a number of requirements.
- It is necessary to water the plant no more than 2 times a week, but it depends on the weather. On hot, dry days, you will need to irrigate twice in 7 days. You also need to carry out sprinkling - spraying the crown 3-4 times a week, in the morning and evening. In case of inclement weather that lasts for a long time, the vine is watered once every 30 days. For irrigation, soft, warm water, previously settled, is always used.

- Fertilization is important for the hydrangea to bloom abundantly. In the spring, with the beginning of the growing season, you will need to feed the plant with a mixture of potassium sulfate (20-30 g), carbamide (20 g), "Superphosphate" (30 g) per 1 sq. m.In June and August, liquid manure diluted in water 1: 10 is prepared for irrigation; compost in the amount of 20 kg per bush is also suitable.
A weak solution of potassium permanganate is needed for watering to increase the strength of the shoots.



- Periodic pruning is necessary if hydrangea is used for vertical landscaping. The procedure begins when the culture reaches 3 years of age, it is carried out in early spring. The event is necessary so that the vine covers the support completely and throws out larger inflorescences, in addition, the uncut bush loses its decorative appearance. When cutting, 6–7 of the strongest and healthiest branches are left; on the branches of the current year, 3 to 5 pairs of buds are kept. In autumn, diseased and dry shoots, dried flowers are cut off.


- Climbing varieties of hydrangea, experts advise to tie up and fasten to supports so that they grow correctly.

- The petiolate culture tolerates even severe cold and critically low temperatures, but young shoots can die in winter, so they need to provide a reliable shelter. For this, the vines are removed from the supporting structures, bent down and laid on plywood sheets or boards. Fallen leaves, spruce branches are poured on top and covered with a non-woven cloth.


- Hydrangea is resistant to diseases and insects, but is not completely immune from infection, therefore, care should include preventive treatment of the shrub with insecticides and antifungal drugs.


Reproduction methods
Traditionally hydrangea bred by cuttings, dividing and rooting cuttings, and petiole varieties are no exception.
- Experienced gardeners prefer to propagate climbing shrubs. cuttings, the cutting procedure is carried out on summer days - for this, shoots are taken from the top of a plant with two internodes. To plant a twig, you need to remove the 2 lower leaves, and then soak it in a growth biostimulator. For hydrangeas, a substrate containing peat, humus and sand is suitable. The cuttings are placed in a nutrient mixture and covered with a film, after which they ventilate and moisten the soil for about a month.
When roots appear, you can plant the plants and leave them until spring planting, or immediately assign them to a permanent place in the garden.



- Layers culture is bred from May to late summer. Prepare the soil under an adult plant, loosen it and water it. A small incision is made on the long lower branch, it is tilted to the ground and mulched with peat. In the spring, the cuttings are separated from the mother bush and planted in the selected area, by which time its roots are fully formed.


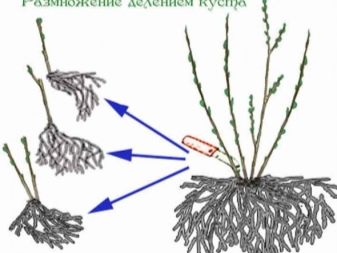
- It is allowed to propagate the petiolate variety by dividing the root system... When transplanting hydrangeas, part of the root with shoots is separated from the shrub, the aerial part is cut off to 2 buds, roots that are too long are shortened and treated with a manganese solution. The seedlings can be planted immediately and provided with good watering for 30 days to speed up adaptation.

Seed propagation is also feasible, but does not guarantee a plant identical to the mother. The seeds are sown in small pots with soil mixture and drainage 2 cm thick. The seeds are not buried, but sprinkled with a thin layer of nutritious soil and covered with polyethylene. When seedlings appear, the film is removed and the soil is regularly moistened. The grown seedlings can be rooted next year.


Diseases and pests
Improper farming practices and violation of the rules of keeping leads to diseases and the attack of harmful insects.
Ailments that are common in culture.
- Significant lightening of the foliage may indicate the presence of chlorosis. In this case, the leaves of the plant die, but at first they turn yellow, and only the veins retain their green color. By these signs, you can recognize the disease. The reason is the uncontrolled use of humus, an increased percentage of lime, which the culture does not tolerate, and a deficiency of iron in the soil.All that needs to be done is to feed the shrub, organize watering with acidified water, spray the plant with such products as Ferovit, Antichlorosis, Ferrilene or iron chelate.


- Another nuisance is rot, white or gray. In the first case, the fungus affects the root system, because of which the branches turn black and become covered with a white coating, the fungicide "Fitosporin" will help to cope with the problem. In case of damage by gray rot, black spots appear on the stems and leaves, and then the blooming liana can be cured with the help of fungicidal preparations - "Pure flowers" or "Fundazola". These diseases result from excess nitrogen in the soil and excess moisture stagnating at the roots.


- The plant can also get sick with a viral disease, for example, ring spot. This pathology is characterized by wrinkling of the leaves, their dying off and the death of the bush. There is no special drug for treatment, as a result of this, it becomes necessary to destroy the affected shrub. It is dug up and burned, and the soil is disinfected.
The disease can develop due to non-sterile gardening equipment, pests that carry germs, and poor quality planting material.


- A gray bloom that forms on the underside, and then on the outside of the foliage, as well as the appearance of spots - greenish and yellow - indicates an infection with powdery mildew, leading to the wilting of the hydrangea. In this case, you need to use the drugs "Skor", "Topaz", "Fitosporin".


If the petiole culture does not grow well, does not bloom and looks painful, there is reason to assume that it is affected by pests. The most dangerous species for the plant are leafy green aphids, gall nematodes and spider mites. In relation to them, acaricidal anti-mite agents and insecticides are effective - the systemic preparation "Tanrek", "Commander".
A prophylactic agent against viruses and fungi is spraying with Bordeaux mixture (in early spring and autumn), insecticides are applied to the soil before planting, and the seedlings are treated with copper sulfate. In addition, to prevent the emergence of pathogens, it is important to remove weeds and any plant residues in a timely manner.



Use in landscape design
Knowing about the amazing ability of a plant to occupy all free space and braid supports of the most different shapes, landscape designers are happy to use culture to decorate their backyard areas.
- Often petiolate varieties are used to decorate pergolas, open terraces and gazebos. They are used to decorate garden arches and building facades.
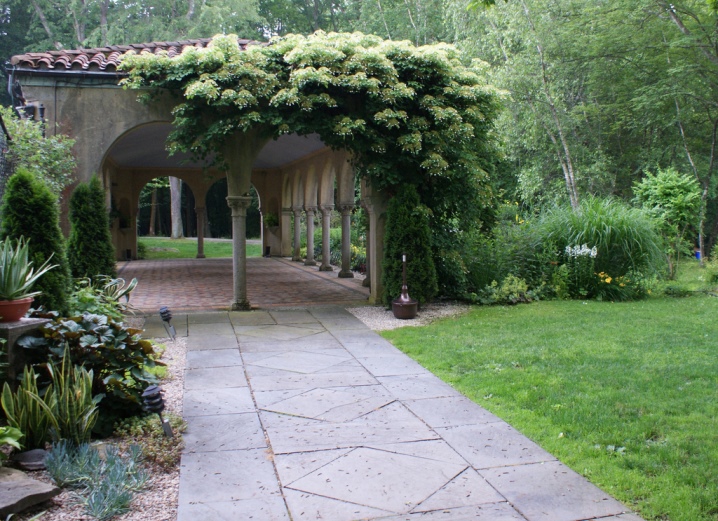

- With the help of a plant, it is possible to create a green corridor or a tunnel, you just need to build a frame that it will braid.
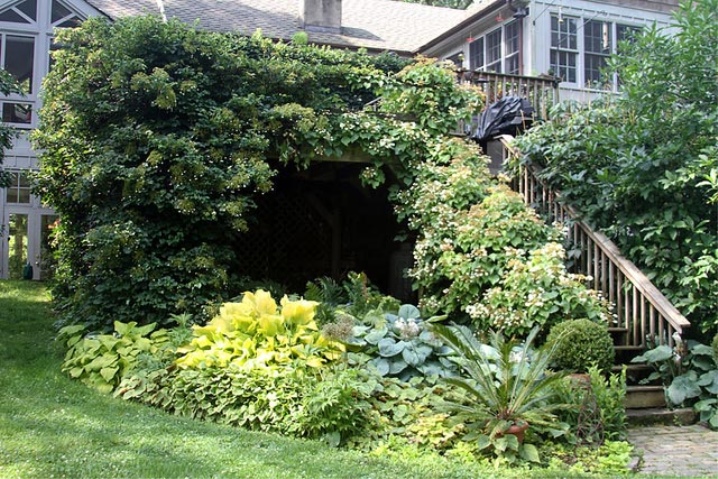

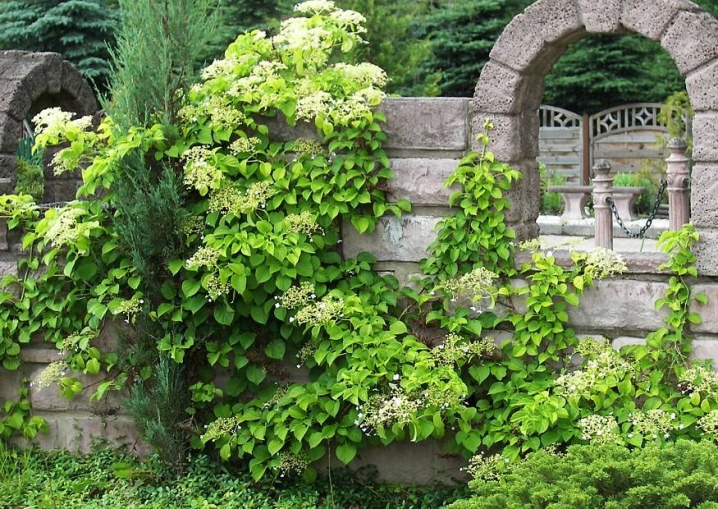
- Climbing shrubs of different varieties are suitable for wall decoration, but it is better not to choose wooden ones that need periodic paint renewal. But walls made of brick or natural stone are suitable for this.

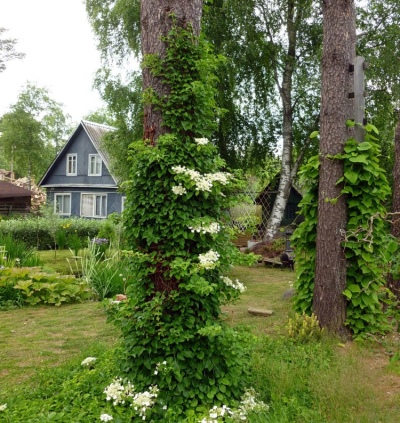
- The climbing hydrangea can be used to shape large and strong oak, maple and pine trunks. As a result of braiding with flowering liana, these plants will look like ornamental trees.

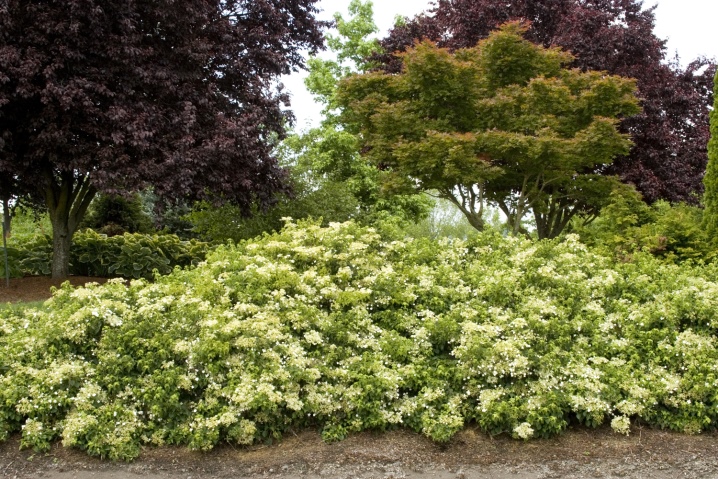
When placed on the ground, a solid carpet of beautiful leaves will look luxurious, but at the same time hydrangea, as a rule, does not bloom or there are very few flowers. On the other hand, it makes no sense to decorate a garden plot in this way, since it will be impossible to walk along it.
Therefore, such coatings are good only for small decorative slopes and hills.

Review overview
Gardeners speak warmly of liana-like hydrangeas, and not only because of their decorative effect. For many, such qualities as frost resistance, rapid flowering, usually occurring as early as 2-3 years are important., the ability to quickly occupy the space provided, improving the appearance of the site.However, there are climbing species that bloom flowers only for 7 years, so many shrub owners believe that this plant is for the patient.
Some owners report amazing things - their petioled hydrangea variety blooms beautifully, being in full shade, since the sunlight obscures the shade from the house. Apparently, the owners took good care of other parameters of care, and, in particular, about the composition of the soil, and as a result, a sun-loving plant feels comfortable with almost no one.


In order for flowering to begin sooner, many summer residents and owners of private country houses advise not to plant a crop on the north side, and also try to transplant it as rarely as possible, since this procedure delays the appearance of flowers by 1-2 years.
For the care of petioled hydrangea, see below.



































































The comment was sent successfully.