What kind of soil does hydrangea like and how to acidify it?

A plant such as a hydrangea has a beautiful appearance, but its beauty directly depends on the state of the soil in which the culture grows. If you are going to grow this tree or shrub in your garden, you need to know what soil composition is suitable for it.
Ground requirements
The success of hydrangea cultivation and its lush flowering is closely related to the choice of a site for planting. In addition to the fact that it must be calm and sunny, the composition of the earth is extremely important.
The plant loves a fairly fertile, loose, well-draining soil, but it grows and blooms well on sandy, clay and loamy soils and peat bogs, preferring a slight acidity. Therefore, experienced gardeners often add needles to the nutrient substrate for planting, and also mix the prepared soil with rotted leaf litter.
The main requirements for the soil for hydrangea:
- nutritional composition;
- lack of stagnant moisture;
- good air permeability of the earth, allowing the roots to receive a sufficient amount of oxygen;
- for different plant varieties, a soil of low or medium acidity is required, preferably within a pH range of 5.5.


At the right acid level, a garden hydrangea looks healthy, and its flowers come in a variety of blues, blues and purples.
When the composition changes towards a decrease in the concentration of acid, and this occurs in the process of the life of a culture that takes it for growth, development, flowering, the flower petals turn pink, then acquire a lilac tone, and the green foliage loses its depth and brightness and gradually turns pale.
Novice gardeners should study what a plant looks like at different acidity levels in order to be able to fertilize and oxidize the soil on time:
- flowers turn purple at 4 ph;
- blue petals indicate a value of 4.5;
- if the concentration varies from 4.8 to 5.5, the color is pink and blue;
- a deep pink tint is observed at 6.3-6.5 ph;
- bright pink and light pink color is typical for 7 ph and above;
- at neutral values, the color of the petals is usually white or bluish, but this does not apply to those flowers on hydrangeas that do not have natural pigments and always remain snow-white.
Observing these changes, you can understand that it is time to acidify the soil under the shrub or tree.


Home hydrangea also needs a nutritious soil, mainly clayey and with a higher acidity. Before planting a plant, a drainage layer must be laid on the bottom of the container, and the near-stem part is mulched in the same way as in a garden culture. Indoor shrubs, similar to street ones, react to a decrease in acidity with multi-colored flowers, so you need to constantly feed and acidify their soil.
How to make the right composition?
The soil for indoor and garden plants may differ, in addition, for different varieties of hydrangea, you need to choose the right composition. For example, tree-like crop species are more unpretentious to the quality of the land, they can grow and bloom remarkably on loamy soils, the main thing is that it optimally allows water and air to pass through, and this requires a drainage layer.
In particular, a species such as hydrangea can grow even with a small amount of lime in the ground, while for other varieties this can cause disease... Most of all, loose compositions with an acidity of no more than 6.5 units are suitable for woody varieties, but humus from the fallen needles of pine, larch or fir must be added to them.
For large-leaved hydrangeas, choose a location next to conifers such as juniper, thuja, and heather plants. The soil mixture for these varieties should include peat, sod and leafy soil, sand and humus.
Panicle hydrangeas love loamy compositions, and for their planting, as a rule, equal parts of coniferous compost, peat and brown forest land are used. But they also need artificial acidification.


It is important to consider all these points at the same time when a street hydrangea is planted, you need to carefully prepare the land for planting:
- it needs to be dug deep enough and enriched with a peat mixture, humus and mineral additives;
- place a layer of gravel, expanded clay and sand on the bottom of the hole;
- the nutrient substrate should consist of coarse sand, clay and black soil in combination with sod soil;
- it is necessary to plant the plant after the soil has been acidified with special preparations, vinegar solution or ammonium sulfate;
- it is important to mulch the surface of the near-stem zone after planting with compost or peat - this will retain water and prevent drying out.
Constant acidification as the crop grows is important, as well as fertilization throughout the growing season. The best option is to add useful trace elements and organics to the soil every 2 weeks.

How can you acidify the earth?
It is possible to bring the composition of the soil to the desired acidity concentration using materials such as sawdust, bark, high peat and fallen leaves, but there is not enough natural acid in them, therefore sulfuric acid solutions will be required.
To acidify the soil for hydrangeas at home, it is recommended to prepare acidified water and water the plant with it. But since the composition of tap water may contain alkalis and is not always suitable, you first need to determine the level of its acidity and, if necessary, add certain agents to it.
- An electrolyte containing some sulfuric acid and nickel sulfate. Only 1 ml of this substance is needed for 10 liters. This volume is enough to water one hydrangea. Additionally, it is allowed to add ammonium nitrate to the solution.
- Once a month, to maintain the optimal acid level, citric acid is used - 1 teaspoon of powder is taken for 12 liters.
- Oxalic acid is also suitable for acidification, which must be diluted in an amount of 1.5 tsp. 10 liters.
- Potassium nitrate (potassium nitrate) is also a suitable acidifier for hydrangea, taken in a proportion of 40 g per 10 liters of liquid.
- Another option is malic acid, vinegar 9%, taken in a volume of 100 g per 10 liters, however, the latter is undesirable for oxidation, since its effect is short-lived, and the soil microflora is disturbed.



Certain advantages are possessed by such a remedy as sodium succinate (succinic acid), with which you can not only increase the acidity:
- the drug stimulates the development of hydrangea roots;
- increases the plant's resistance to diseases and attacks of harmful insects;
- the product is safe for all parts of the culture;
- helps to activate the synthesis of chlorophyll;
- does not accumulate in soil and plants.
As for the significant drawback of this composition - acidification of the earth, this minus for hydrangea is an advantage. In addition, sodium succinate is considered indispensable for diseases of various horticultural crops, including hydrangea. It contributes to the rapid regeneration of the plant and its recovery when exposed to unfavorable factors.
Chemicals that increase acidity - sulfur, ferrous sulfate. Potassium aluminum sulfate is used in the form of alum (20-40 g) to give the petals an unusual color.

How to acidify correctly?
To optimally acidify the earth, you should be guided by the established rules of this procedure.
You need to start with an analysis of the composition of the earth. This is done in the spring before the hydrangea is planted:
- using a chemical meter using reagents;
- a special device with a sensor that is placed in the ground;
- with litmus paper, when acidity is recognized by a test strip.
You can apply a soil test in the form of tablets, placed in a container with earth dissolved in water. In addition, the popular way of measuring is also suitable - pouring vinegar over the earth. If the soil begins to foam, bubble and sizzle, then the environment is alkaline and reaches pH 7 or more.
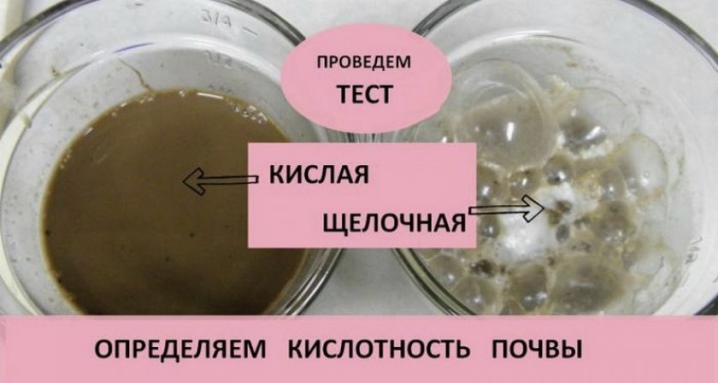
Loose and light soil is easier to acidify. It is enough to add a mixture of organic fertilizers to it, including:
- sour high-moor peat with an acidity of 3.5-4.5 units;
- matured compost from fallen oak leaves, capable of not only oxidizing the earth, but also enriching it with humic substances and minerals;
- natural raw materials - needles of spruce, pine, fir and coniferous rotted sawdust;
- perennial perennial sphagnum moss, which, among other things, will serve as drainage.
These substances will acidify the soil for a long time as it decomposes and, at the same time, will make it more fertile, which, of course, is important for a flowering culture.
However, this method is not suitable if you need to quickly increase the acidity level.


Heavy soils, mostly clay, require oxidation with fairly strong chemicals. The most effective among them.
- Finely dispersed colloidal sulfur. It significantly raises the acidity indicators (by 2.5 units), for this it is enough to add 1 kg per 10 sq. m of land. Sulfur is brought in during deep digging (15 cm deep) in autumn, and the result can be expected in a year or a little earlier.
- Iron sulfate - a softer remedy that acts much faster. After 30 days, you can oxidize the soil by 1.0 unit, if you process 10 sq. m, adding 0.5 kg of substance.
- Other mineral oxidants can oxidize the soil with a slight acid deficiency - this is potassium sulfate, used in autumn, ammonium nitrate - a nitrogen-containing additive, which is used in spring, and ammonium sulfate, which is relevant during digging of soil in autumn. Potassium aluminum sulfate is added once every 2-3 weeks.
Acidic water is used for irrigation, but you need to use it, precisely observing the proportions in the manufacture of various solutions, and water the soil once every 15 days.



Normalization of the soil composition is an important condition for the growth and flowering of hydrangeas, therefore, this indicator must be maintained at the same level, using the methods most suitable for each variety.
For what kind of soil hydrangea loves, see below.



































































The comment was sent successfully.