All about growing peas
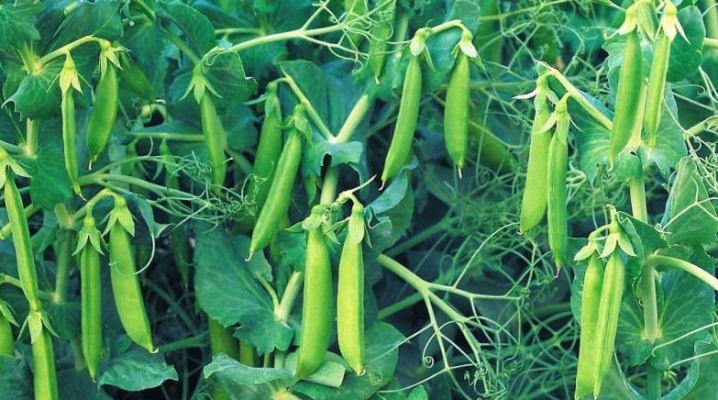

Green peas are the most popular vegetable garden. For many people, this is one of the most anticipated summer crops, since it departs quite quickly and you can feast on it for a very short time. You can grow peas in your own garden. It is worth figuring out how to do it correctly.


Seat selection
The correct cultivation of green peas begins with choosing the right conditions for this.
Climatic conditions
The plant is quite cold resistant, so it can be sown in almost any region. For the seedlings to begin to germinate, a temperature of +5 degrees is enough. It will be okay if short-term frosts return, since the plant survives if the temperature does not drop below -6. It is necessary to sow green peas in the last decade of April. So then it will turn out to achieve the required temperature indicators. In order for the ovaries to form, they must be +15, and the fruits - at least +17 degrees.
As for the early ripening varieties of peas, they will also survive drought. Such varieties are planted only in summer: in June or early July. Even in the absence of watering for a long time, they are able to extract water from the soil themselves.

The soil
Peas do not have any special requirements for the soil. But the richest harvests, as practice has shown, are obtained on loose loamy soils. Also, the plant develops well on sandy loam soil, in which there are a lot of phosphorus-potassium substances and humus. The soil should not be overflowing with nitrogen, as the crop can hardly tolerate its excess.
The same applies to the increased acidity of the substrate. Better if it is neutral.
In case of increased indicators, it is recommended to calcify the soil. If the clay content is high, additional sand is added, and if - sand, then, on the contrary, a small amount of clay.


Compatibility with other cultures
Peas themselves are a very useful crop for other plants. Its roots enrich the substrate with nitrogen, which is needed by most crops. As for the neighbors for this bean plant, gardeners prefer to plant it next to strawberries, for example. These crops mutually increase each other's yield indicators.
Consider other plants that can be planted nearby.
- Zucchini... They grow wonderfully with peas on the same bed, as it gets food for them from the soil.
- Cabbage... The vegetable protects peas from rot, strengthens the roots.
- Potato... When planting in holes with potatoes, lay a pea. This allows you to save the vegetable from the Colorado potato beetle.
- Carrot... The specific smell of carrot tops scares away pests from legumes.
- Beet... When planting peas next to it, the culture can not be tied up.
- Corn... As with beets, it will support the peas.
- Cucumbers... For them, peas are an ideal neighbor that does not take up much space.


Legumes are not planted next to:
- tomatoes;
- garlic;
- onions;
- fennel;
- sunflowers;
- basil;
- wormwood.


Crop rotation
It is no secret that crop yields largely depend on crop rotation. The following predecessors are suitable for green peas:
- early potatoes;
- plants of the pumpkin family;
- cabbage;
- tomatoes;
- beet.
Peas are not planted after it, as well as after other legumes, such as beans. Peanuts are also a bad precursor.If in the previous season peas grew in a certain area, then they can be planted in the same area only after 4 years.

Preparation
Before planting peas in open ground, you need to properly prepare both the soil and the planting material itself.
Priming
The soil for planting must be prepared in the fall. The earth in this zone is well dug up. Then they introduce into it half a bucket of compost, superphosphate (35 grams) and potassium chloride (25 grams). The proportions shown are based on 1 square meter.
If the soil is acidic, 1 sq. m, 0.1 kg of ash is introduced. Then the substrate is thoroughly dug up and irrigated again.


Planting material
Most plants need pre-sowing seed treatment, and peas are no exception. First, the peas are carefully examined. Those that have stains and deformations are immediately removed. The material is then immersed in salt water. The peas remaining at the bottom are removed and washed, the rest can be thrown away.
It is also recommended to germinate the material. This can be done in two ways:
- by placing it in warm water for 16 hours, which must be changed every 3-4 hours;
- putting it in a moistened gauze for a day and closing it in a container.
Among other things, peas are treated with boric acid before planting. Dilute 2 grams of the product in a bucket of water, then heat it to 40 degrees and put the seeds in the composition for 2-3 minutes. Boric acid guarantees excellent pest prevention.


How to sow?
Pea sowing technology does not present any particular difficulties for the summer resident. Consider the planting process step by step.
- The first step is to loosen and level the soil. Then small trenches are dug in it. Their depth is from 5 to 7 cm, and the distance between the furrows themselves is 20 cm. If the pea variety is high in stature, then the gap between the grooves should be doubled.
- Then the grooves are filled with humus mixed with wood ash., there is a small layer of soil on top.
- The grooves are well watered, and then grains are added to them. It should be planted to a depth of about 5 centimeters. A distance of 7 cm must be left between the peas.
- The peas are covered with soil and watered. At first, they must be protected with a mesh with fine cells or a film, since the material is easily pulled apart by birds.


Care
The process of cultivating peas implies many nuances, without which it will not be possible to grow a decent crop. From the moment of planting, it should take about a week and a half before the first shoots appear. Every 10 days, gardeners add new peas, and this should be done until the last days of June.
Watering
Proper watering is one of the main stages of green pea farming. Despite the fact that the plants in the open field are relatively drought tolerant, abundant irrigation will allow the fruits to gain sugar content. Before the start of bud formation, peas are watered once a week, but when it blooms and bears fruit, you will have to irrigate it often: 2-3 times in 7 days. If the heat and drought are too strong, water more often. One bucket of warm water is consumed per square meter of planting.
The same watering steps are carried out for the plants cultivated in the greenhouse.

Top dressing
Plants planted in the country will need a certain amount of dressing. When the sprouts have just appeared, they are not yet able to produce nitrogen, so it must be introduced artificially. For this, the plants are fed with an infusion of green weeds or a mullein, in which a tablespoon of nitrophoska is dissolved.
When the seedlings mature and begin to form buds, they will need minerals... Any legume mix will work. They are bred according to the instructions, and then the soil is irrigated. Dry mineral complexes are used during flowering. They are simply buried in the ground.


Garter
Most often, peas have a stem that spreads along the ground. Or it may fall off under the weight of the harvest.It is impossible for the culture to come into contact with the soil, so it is better to tie up such stems. You can use several options for this:
- pegs with ropes;
- special nets designed for climbing crops;
- support rods;
- arched structures for greenhouses.
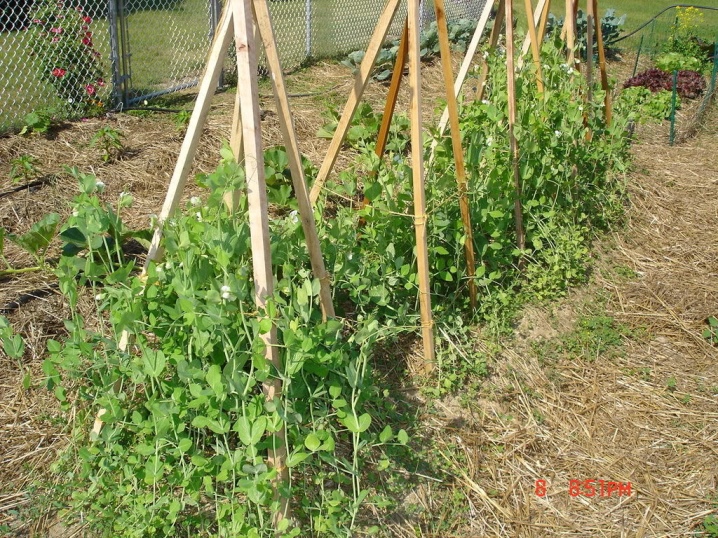

The garter is carried out when the length of the pea stalk reaches 0.1 m.
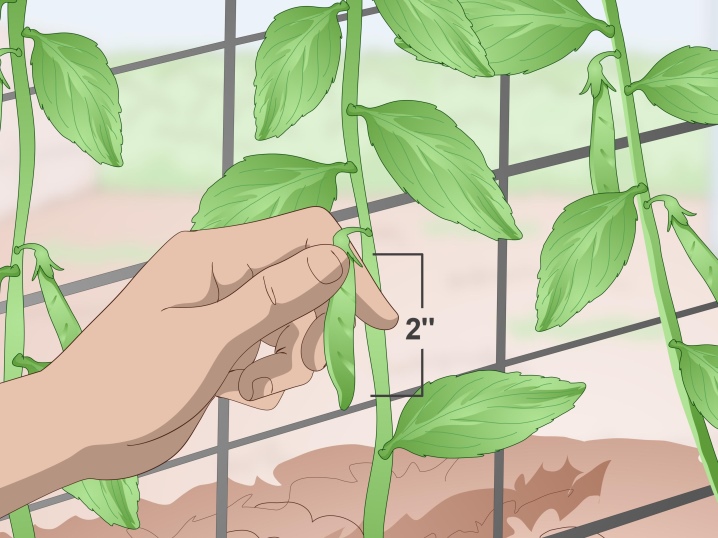
Pinching
You can pinch green peas. So it gives richer yields, and also does not increase at too high a rate. The pinching is performed when the growth of the stem stops at around 0.2 m.
Loosening and weeding
If you want your culture to grow healthy, you need to take care of the soil on which it grows. The soil must be loose so that oxygen can always penetrate to the roots of the peas. Therefore, the soil between the rows must be slightly dug up. The first loosening is carried out two weeks after planting. It is produced to a depth of no more than 7 centimeters, while peas must be hilled.
It is recommended to harrow the soil before and after watering. When the procedure is carried out for the first time, weeding is carried out at the same time. At the second stage of loosening, it is recommended to mulch the soil.

Diseases and pests
If the crop is poorly looked after and the required agricultural practices are not followed, it can undergo various diseases. You can see a description of the most common ones below.
- Powdery mildew. Occurs due to too dense plantings. White patches of plaque appear on the leaves. For treatment, colloidal sulfur is used at a concentration of 1%.
- Rust... It is characterized by the appearance of brown spots, similar to blisters. Then these spots turn black. You can treat the disease with Bordeaux liquid at a concentration of 1%.
- Root rot... We are talking about its Fusarium subtype. Rot causes yellowing and death of foliage. The disease cannot be cured. It is necessary to dig up and burn the diseased peas. Subsequently, the earth is dug up, removing all plant residues.
Now let's look at the most active pests.
- Pea moth... The insect caterpillars are very gluttonous, quickly eat fruits. To fight them will allow tobacco dust and a decoction of tomato leaves.
- Aphid... This insect will find its place everywhere. Eats foliage, causes it to curl. First, the leaves are treated with soapy water, and then any strong insecticide is applied.
- Bruchus... This is the second name of the pea weevil. Beetle larvae gnaw fruits, damage peas. You can fight the pest with the help of "Karbofos".


Why don't peas sprout and what to do?
As already mentioned, the first pea seedlings appear one and a half weeks after sowing. If there are no peas for about 14-15 days, you need to look for the reason. Here are some common options.
- Poor quality material. You may have bought expired, bad seeds, or you may have stored yours incorrectly.
- Wet planting... Peas should only be planted dry.
- Bad light... If you planted peas in the shade, they may not sprout. Either it will rise, but it will be weak.
- Too deep immersion in the soil. In this case, the sprouts will not be able to break through to the surface.
- Birds... Remember if you protected the polka dots with a net after planting. If not, birds can easily dig it up.
To avoid these problems, always buy planting materials from trusted suppliers. Germinate your seeds, but remember to dry them before planting.
Place peas in lighted, open areas, away from trees. Follow the planting rules and protect with nets until the time of germination.

Cleaning and storage
The ripening time for different varieties is different, moreover, much depends on the climate. But mostly peas ripen a month after flowering. Sugar varieties are ready in two weeks, brain varieties in three, husk varieties in an even longer period.
If the weather is sunny, then the pods can be harvested every couple of days.And if the sky is overcast and it is cool outside, then the collection is recommended once every 4 days. Peas are mostly eaten fresh. It is not stored for too long, so in 5 days you need to have time to eat the collected amount. Store it in the refrigerator.
Peas can be frozen to keep them longer. Canned peas, which are indispensable before the New Year, are also a popular preparation. By the way, peas can also be dried. To do this, wash it, and then put it in boiling water for a couple of minutes. After that, the peas are taken out with a sieve and immersed in cold water. Then they are placed on a baking sheet covered with parchment and sent to the oven for 60 minutes (the temperature should be 50 degrees). Cool, put it back in the oven, but already at a temperature of 70 degrees. After cooling, the peas are poured into a glass jar and sealed.


Useful Tips
A few additional recommendations will help to get a good harvest of sweet peas:
- dig up the soil thoroughly before sowing;
- buy seeds of those varieties that are the most unpretentious and have good immunity;
- do not delay harvesting, as in this case the growth will slow down;
- if you want to extend the "life" of peas until July, sow new peas;
- if you have a very hot climate, sow peas as early as possible because it is difficult for a crop to grow ovaries in the sweltering heat.











The comment was sent successfully.