What does root rot look like and how to get rid of it?
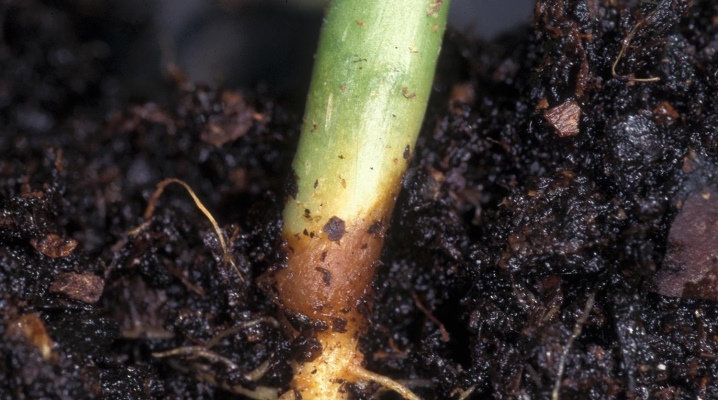

Root rot is a disease that affects plants. It occurs in eggplants, sugar beets, garlic, wheat, peas, strawberries, cereals and other types of crops. Seedlings and adult vegetation suffer from it.

What it is?
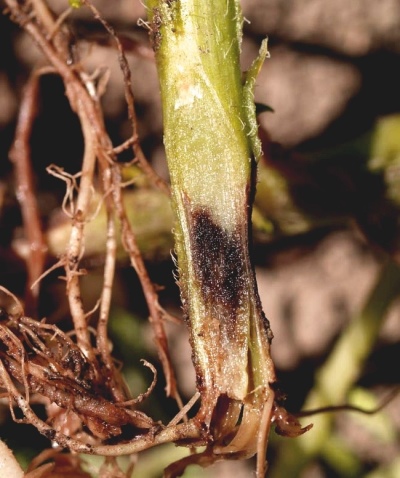
This disease is also called "black leg". It leads to the death of the tip of the main rhizomes. The neck with adventitious roots turns black, which leads to tissue thinning, the formation of numerous constrictions. A bloom of white or pink appears on the affected areas.
The growth of adult plants stops, yellowness appears on the leaves, they wither, the shoots dry out, the set vegetables and berries crumble.

When removed from the soil of the affected horticultural culture, its rhizomes fall off the stem. Root rot often leads to the death of plants.
Prolonged waterlogging of the soil leads to infection. Rot prevents oxygen from reaching the rhizomes, the plant weakens and dies. The disease develops due to irrigation with cold water, planting crops in insufficiently heated soil, sharp temperature fluctuations.

Rot can attack healthy vegetation when normal irrigation is restored. In such cases, the infection is caused by pathogenic fungi in the soil. They do not make themselves felt for a long time. Even a single waterlogging of the soil can be the reason for the multiplication of the "black leg". Sometimes seeds are the source of the disease.
How to treat?
To treat rot at the roots of strawberries, melons, watermelons and other crops, chemical and biological preparations are used. Copper sulfate has proven itself well in the fight against this scourge. The main thing is to properly cultivate the land in order to achieve the maximum effect.

Biological products against rot are one of the most effective remedies. Fighting the "black leg" is not easy, but it is really possible to defeat it.
For the treatment of plants used:
-
brilliant green;
-
"Metronidazole";
-
"Glyocladin";
-
fungicide tablets.
Experienced gardeners know what root rot looks like and what to do to kill it.
Seeds are treated with fungicide, soil is irrigated, plants are sprayed. To eliminate rot on the roots, a solution is made: 3 ml of the drug is dissolved in 2 liters of liquid. During the season, it is used from 4 to 5 times. The last treatment should be carried out no later than 20 days before harvest.

Effective in the fight against root rot "Fundazol", which is a contact-systemic fungicide. They are treated with seeds and sprayed with vegetative vegetation. Flower bulbs are immersed in a solution and kept for 3-4 hours. For 2 liters of liquid, 10 g of the drug is required.
Potato tubers and other vegetables are treated with a fungicidal solution. In this case, 10 g of the drug is dissolved in 0.5 l of liquid. The foliage and soil are treated twice with a solution having a 0.1% concentration.
It is also possible to destroy root rot with the help of the "Maxim-M" preparation. One ampoule is required for one liter of liquid. The prepared substance must be used within 24 hours. Plants are sprayed or watered with a solution.

"Glyocladin" is a biological preparation in tablets. It does not need to be dissolved in water first. During the picking of seedlings, tablets are applied to the soil. This can also be done when replanting vegetation to a permanent place.
Another drug in Alirin-B tablets. For 10 liters of liquid, 2 tablets are required.Processing is carried out three times with a weekly interval.

Biological product "Trichodermin" is used for plant therapy at the initial stage of diseases. It can be in suspension or powdery consistency.
Plants are irrigated or sprayed, 5 g of the product is dissolved in 1 liter of liquid.
Folk methods
To combat black rot, folk methods are also used.
To disinfect the soil, a solution of potassium permanganate is used. Foliar treatment is performed with a solution of 3% consistency. For irrigation of seedlings, a 0.2% solution is used.
Damaged areas on the stems in the area close to the roots are sprinkled with charcoal or ash.
In addition to fungicides, at the first symptoms of infection, horticultural crops are provided with "emergency assistance" by removing the infected parts - stems or rhizomes. Diseased plants are dug up and subjected to a thorough examination. If the rhizomes are soggy and darkened, the plant will not survive.
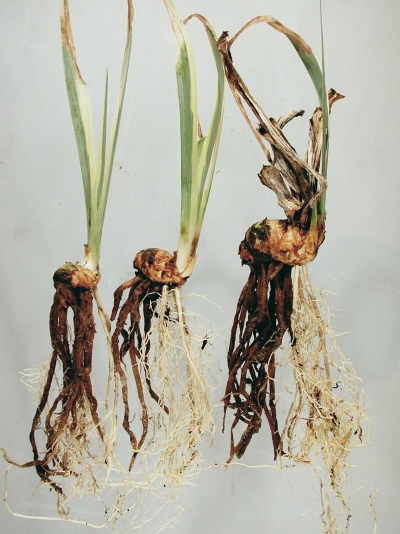

If the overwhelming majority of the roots are firm and healthy, they are thoroughly rinsed with water. After that, rotten roots, foliage with shoots are cut off. The upper parts of the healthy stems must also be removed to balance the reduced-root part located above the ground. The cultures are transplanted into new soil and placed in a shaded area. Irrigate carefully after the plant takes root in a new place.
If the soil is too wet, the risk of developing fungus increases, since moisture is the main cause of its appearance. The problem can be solved by adding gravel to the soil. This increases the permeability of the soil.

Many special agents are used to destroy the fungus. It is enough to visit a store that sells garden products and get advice on this matter. The seller will tell you how to properly use fungicides. But first you need to correctly establish the type of pest that has infected the rhizomes of the plant. Root samples may need to be sent to the laboratory. Not all types of fungus are curable.
Prevention measures
The main preventive measure is the control of the level of moisture and temperature of the soil.
Seedlings must be planted in loose soil that allows air to pass through well. The ideal option is a mixture of turf with humus and an admixture of river sand or decomposed peat.
For watering seedlings, use warm water, the temperature of which is at least 20 degrees. Irrigate as the topsoil dries up.
At the first symptoms of a disease of single plants, remove them from the beds so that the problem does not become widespread. You need to remove a little soil from above, add peat with dry sand and sawdust.

In the case of indoor flowers, they must be planted in containers that have drainage holes.
At the stage of growing vegetables and ornamental plants of annuals, observe the crop rotation. This will prevent the accumulation of fungi in the soil, provoking the development of infection.
Avoid over-irrigation of plants, watch out for water accumulation.

In the fall, control and check the rhizomes of ornamental crops, if a fungus is found, dig up the affected specimens.
Before starting planting, assess the soil moisture level and, if necessary, take action.
When choosing plants for planting, give preference to specimens that are less susceptible to root rot damage. Take care of the moisture permeability of the earth in advance, dig up the beds before planting seedlings, add compost.
Analyze the condition of the site, if there are wet places, build beds on a hill, and mix in good soil.

The appearance of rot on the roots is provoked by a variety of pathogenic fungi. It is important not to waste time and take timely measures so that it does not destroy all the plants, get rid of the misfortune at the initial stage, using various methods for this.














The comment was sent successfully.