What does root rot look like in cucumbers and how to treat it?
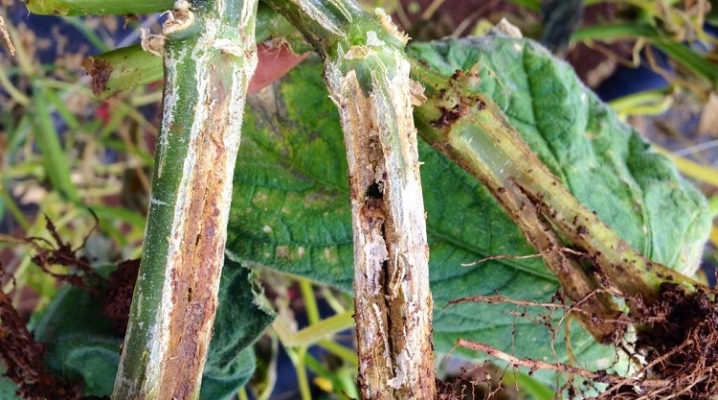

When deciding how to treat root rot in cucumbers, you should first make sure that the plant is affected by this particular disease. Sometimes, with similar symptoms, completely different reasons turn out to be the source of problems. If the root system is affected by rot, treatment with drugs and folk remedies will help to cope with it.
Description
Fungal diseases are one of the main sources of danger for the harvest of vegetables at their summer cottage. Root rot in cucumbers is also caused by this pathogen. The defeat of the roots occurs by transferring the spores of the fungus by contact or through the air. The diseased plant looks quite specific. It begins to wilt, the leaves wilt, if untreated, up to 80% of seedlings and up to 40% of adult shoots can be lost.
Most often, root rot manifests itself when growing greenhouse plants.... Cucumbers, as a moisture-loving culture, are among the first to be hit, melons, watermelons and other melons are also under threat.
The lesion develops quickly, most often it manifests itself after transplanting plants when they are grown in seedlings.



Reasons for the appearance
Root rot of cucumbers is formed under the influence of a whole complex of factors. As a rule, phytoparasite damage and mechanical damage to the underground part of the plant are combined here, as well as the creation of favorable conditions for the reproduction of fungi. Most often, root rot is called Fusarium - this disease is caused by pathogens Fusarium spp living in the soil (Fusarium solani, Fusarium oxysporum and others). These imperfect fungi affect plants in open and greenhouse ground, but they mainly affect the root collar, the underground part remains healthy.
Real root rot on cucumbers can be caused by completely different phytoparasites:
- Ascochyta cucumis;
- Pythium spp;
- Rhizoctonia solani;
- Sclerotinia sclerotiorum.
It is known that plant roots weakened by a fungal infection are often additionally affected by nematodes, bacteria, mites, and insect larvae. Conditions conducive to the development of the disease include a decrease in soil temperatures to a level below +15 degrees or their increase to +28 degrees or more. Indirectly, the formation of a favorable environment for fungal infections is also influenced by the increased content of salts in the soil.
And also the following factors can be attributed to the reasons for the development of the disease:
- gnawing the root system by pests;
- lack of natural light;
- sharp fluctuations in atmospheric temperatures;
- excessive watering with cold water;
- lack of moisture.
Cucumbers are at high risk, easily affected by fungal diseases... That is why special attention should be paid to creating conditions for their cultivation. Sometimes infection occurs in a different scenario. Pests present in the soil damage the roots, after which they are attacked by fungal infections. The active colonization of the affected parts of the plant by polyphages and microorganisms also contributes to the intensive release of toxins.


Signs of defeat
It is quite easy to find diseased plants in a greenhouse or outdoors. The first sign is wilting of the leaves. Shoots looking healthy the day before can fade literally overnight. Initially, the affected area will not be too large, 1-2 leaves per plant.Gradually, absolutely everything will sink. At the next stage, the leaves begin to dry out and die off. The lack of sufficient moisture from the roots leads to a discoloration of the plate. It turns yellow, becomes fragile.
After leaf necrosis, changes affect other parts of the plant. The ovaries die off, the already formed zelents do not develop. In the early stages of infection, plants can still be saved. At the later ones, it remains only to eliminate the plantings. The root system is also changing. Its color becomes spotty, with a predominance of brown and brown shades.
With a long course of the disease, the roots darken and begin to decompose. There is a smell of rotting organic matter in the greenhouse.


Treatment
Root rot damage to cucumbers most often occurs in a greenhouse, where favorable conditions for the spread of fungal spores are easily formed. In the open field, microorganisms living in the soil contribute to the infection. It is advisable to treat the disease only in the initial stage, when the lesion did not affect the planting too deeply. When most of the leaves wither, only complete reorganization can be done, with the destruction of plants, processing of the soil and the beds located next to it.
Root rot rarely affects very young cucumber seedlings. It is possible to save them if signs of damage are detected by carrying out agrotechnical measures. For example, adding soil helps to fight the problem, contributing to the formation of new, young root shoots. In this case, it is necessary to raise the level of the ridge by 3-4 cm, after removing the leaves in the lower part of the stem, and then laying it on the soil surface. After waiting for rooting, you can again fix the stem on the trellis - on average, this takes no more than 10-15 days.
And also the following measures of influence are referred to agrotechnical methods of combating root rot of cucumbers:
- breeding and planting resistant hybrids;
- disinfection of the greenhouse and soil;
- control of plant residues after harvest;
- regular replacement of the topsoil;
- enrichment of the earth with zinc and manganese sulfate.
Timely adoption of measures can significantly reduce the risks of infection of new plantings, prevents the development of fungal diseases when they are detected on other crops.


Chemicals
It is necessary to fight root rot in cucumber seedlings when transplanting into open ground. You can treat the soil before planting with a strong solution of potassium permanganate or special chemicals. You can get rid of the potential threat in the form of contaminated seeds by soaking them in a disinfecting composition, following the manufacturer's recommendations. To remove root rot on plants outside the growing season, you can use sanitization. Preparations for it are available in the form of tablets, powder, suspension.
Copper sulfate and other fungicides are applied only until the end of flowering. Biological agents such as "Trichopol", can be used even during fruiting. A properly selected composition will help remove root rot if the lesion has not affected a significant part of the plant's organs. Simply pouring water on drying plants will not work. The fight against root rot requires a systematic approach. All preparations used in the framework of chemical treatment are divided into groups based on the timing of their use, safety for plants.
In indoor conditions, the most effective are fungicides that are part of the group of organophosphate pesticides. Several means can act in this capacity.
- "Previkur Energy VK"... A new generation fungicide manufactured by Bayer. Presented in the form of a liquid concentrate. Well suited for combating rot and fungal infections on melons. The tool additionally stimulates the growth of shoots, a set of green mass, is applied at the root.
- "Consento"... A highly toxic modern fungicide for humans to combat root rot and other fungal diseases of plants. Provides a deep systemic effect, not suitable for processing during fruiting.
- Ridomil Gold. A toxic organophosphate fungicide capable of fighting root rot by penetrating deep into plant cells. Requires careful use and careful dosing.
Fungicidal preparations of this group are suitable for preventive soil cultivation, watering seedlings and plants during the formation of green deciduous mass, flowering. They are most effective in the greenhouse planting of cucumbers.


Biological drugs
This includes funds that are not able to accumulate for a long time in the organs and tissues of plants. They have a lower toxicity class, are suitable for use in open and closed ground, do not penetrate deep into cells.
All drugs in this group are usually divided into 3 main categories.
- For pre-sowing disinfection of seeds. Of the preparations suitable for soaking inoculum, it is possible to allocate funds "Baxis Zh", "Fitosporin" with the prefix M or Zh, "Sporobacterin SP".
- For disinfecting soil irrigation, seedlings, root application. This group includes funds under the following names: "Trichocin SP", "Baktofit SP", "Gamair KS".
- For spraying during vegetative development. It uses the preparations "Fitosporin-M", "Pseudobacterin-2 Zh", "Baxis Zh".
Timely treatment helps to ensure effective protection of plants from root rot. It is only important to react in time to the manifestation of signs of the disease.


Folk remedies
Root rot control can be carried out without the use of pesticides. True, it will be difficult to count on significant success in this case. And yet, garden owners practice the use of improvised means in eliminating fungal infections. For example, you can dust the affected roots with crushed chalk or ash to prevent the spread of rot. The dried wounds will heal, the plant will have chances of survival and further development.
A number of effective folk remedies can be noted.
- Baking soda solution. For him, 50 g of powder is dissolved in 10 liters of water. Watering is carried out in 2 steps. First with warm water, then with a solution - in the root zone. The disinfecting effect of the product will help destroy fungal infections.
- Brilliant green solution. This medicine contains copper, which is one of the most effective remedies for combating fungus. For preventive purposes, a solution is prepared from 1 drop of brilliant green in a bucket of water, for medicinal purposes the amount of the active substance is increased 10 times. The introduction is made by pouring the solution under the root.
- Chalk-based chatterbox (6 tbsp. L.) and copper sulfate (6 tsp), dissolved in 1 liter of water. The composition covers the accessible parts of the plant root.
Popular methods of struggle are useless if the infection has already gone quite far. Deep damage to the roots with rot requires the elimination of all plantings, followed by soil reclamation and disinfection.


Prevention measures
You can prevent the possible development of root rot in cucumbers by taking care of preventive measures. If signs of damage are detected in other crops, it is necessary to intensify work in this direction. It is worth considering that cucumbers are most vulnerable to fungal diseases when entering the fruiting period. At this point, the risks of developing the disease reach 50%.
Several simple steps can be considered effective preventive measures.
- Regular ventilation of the greenhouse. Excessive humidity, combined with lower night temperatures, contributes to the defeat of the roots by fungal infections.
- Watering with warm water. It avoids hypothermia of the underground part of the shoots.
- Regular change of planting site. It is recommended to transfer the greenhouse once every 2-3 years; in the open field, cucumbers are placed in new beds with each new season.
- Removal of crop residues from the root. You can not leave withered whips in the ground. Rotting organic matter promotes the spread of pathogenic microorganisms.
- Disinfection of soil and greenhouses. It is carried out in the fall, after harvest, in the spring, before the transfer of seedlings. The soil is poured with a solution of copper sulfate in a proportion of 0.3 liters per bucket of water. It is necessary to spill the soil at least 7 days before planting. The inside of the greenhouse also needs to be thoroughly washed with a solution of copper sulfate.
- Seed disinfection... Sometimes fungal spores get to a new planting site in this way. It is necessary to soak the seeds in a solution of "Fitosporin" or in diluted potassium permanganate. Additionally, you can apply a stimulant of root formation and growth.
- Compliance with the accuracy of planting. If the plants are too close, the risk of developing fungal diseases increases. The optimal planting density of cucumbers is no more than 3 bushes per 1 m2.
Preventive measures can also include soil mulching. It helps prevent excessive cooling of the roots when night temperatures drop. You can mulch the soil both in the greenhouse and in the beds without shelter.


Resistant varieties
Among the agrotechnical measures used in the fight against root rot in cucumbers, one can single out the planting of plants that initially have increased resistance to fungal infections of any type. Breeders have already developed a sufficient number of such varieties and hybrids.
Summer residents can only take them into service, and then make the right choice when looking for seed material.
- "Masha". Hybrid with early ripening, begins to bear fruit after 35-40 days from the moment of germination. Differs in high productivity, greens do not have a bitter taste, suitable for canning and fresh consumption. Suitable for outdoor cultivation, resistant to most fungal diseases.
- "Nightingale"... An early hybrid that supports natural pollination. Designed for planting in open ground or under temporary film covers, it has comprehensive protection against most diseases. The fruits ripen on the 42nd day from the moment of germination, are of medium size, excellent taste.
- "Thumb Boy". An ultra-early ripening hybrid that bears fruit on the 37-39th day after germination. Differs in branchiness of lashes, high productivity, a large number of ovaries.
- "Martin"... Hybrid of early ripeness, refers to bee-pollinated plants. Can be grown outdoors or under plastic. The fruits are covered with large tubercles, reach 14 cm in length, do not taste bitter. This hybrid is resistant to almost all diseases.
- "Goosebump F1". A hybrid with medium ripening times, suitable for planting in open ground and in greenhouse conditions. Its resistance to root rot is average. This is a good option for growing for salads, as well as for pickling and pickling.
- "Spring F1"... A hybrid resistant to a whole complex of diseases, characterized by unpretentiousness in cultivation. The ripening period of the fruits reaches 48-55 days, they are formed in bunches, 2-3 pieces each, reach 120 mm in length. The hybrid is suitable for canning.
And also varieties and hybrids "Malvina", "Topolek F1", "Connie F1", "Autumn gherkin" are considered resistant to root rot. They are not comprehensively protected, but they are able to effectively resist the development of fungal infections.


In the next video, you will find a very simple way to cure root rot on cucumbers.













The comment was sent successfully.