Rules for growing wisteria in central Russia
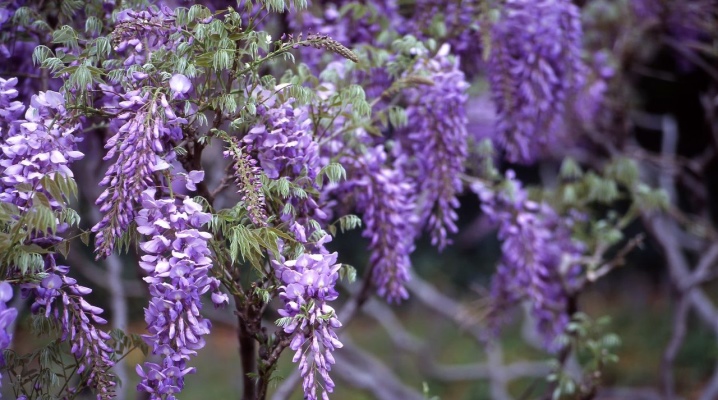

One of the most extraordinary and luxurious plants that adorns any garden plot is wisteria. Its beauty during the flowering period is remembered by any person. It is almost impossible to see the green leaves through the delicate flowers. The plant seems to be forming into a living dome, and this is actually an unforgettable sight. The homeland of wisteria is North America and East Asia, which means that the plant loves to grow in warm climates. But there are also frost-resistant varieties that can be grown even in the Moscow region. Let's talk about the rules for growing wisteria in central Russia.
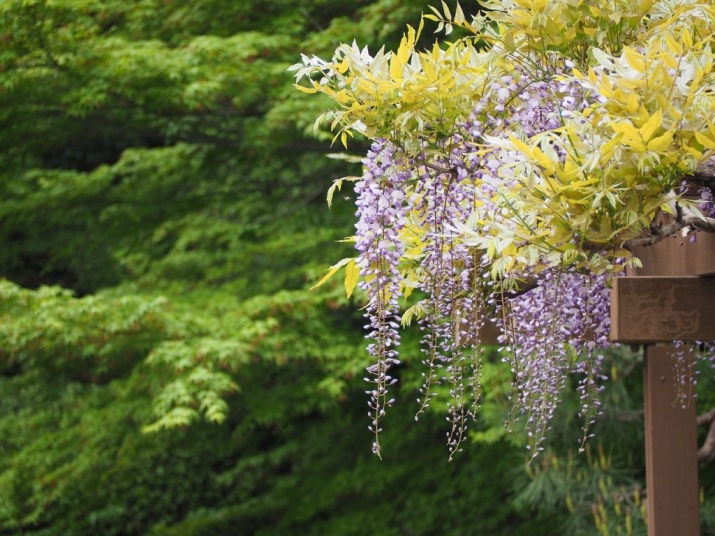






Suitable species and varieties
Wisteria (its other name is wisteria) is a perennial liana of the legume family. Strong branches can reach a length of 10-11 m. They spread in different directions, if supported, twist clockwise. Young stems have a thin and drooping skin.
With proper care, timely pruning, it will be possible to grow a 20-meter high wisteria with a spreading dome. Wisteria leaves are pinnate, can consist of 9-20 oval lobes.



By its nature, the wisteria vine has a positive attitude to heat. She loves to grow in subtropical climates. Most often found on river banks and in forest thickets. Garden varieties of wisteria grow on the Black Sea coast and in the Crimea. In central Russia and in the Moscow region, frost-resistant wisteria species can be grown.
- Chinese wisteria "Blue Sapphire". This variety is distinguished by leafy branches. In the wild, the plant can grow up to 20 m in length. The leaf plates are large, pinnate. Young shoots sink strongly, but over time they rise and become one with adult branches. The flowers on the lianas are pale purple in color.


- Wisteria "Blue Moon". A frost-resistant variety with the ability to easily tolerate low air temperatures and a sharp arrival of cold weather. And it's not about -10 degrees. "Blue Moon" can easily withstand -40 degrees of frost. In addition, the presented variety boasts rapidly growing deciduous vines, each stem reaching 8 m in length.


- Floribunda Wisteria. A distinctive feature of this plant is abundant flowering and a large number of flowers. With the right care, growing floribunda will yield amazing results. The plant will grow up to 10 m in height and each time during flowering it will attract the enthusiastic glances of others.
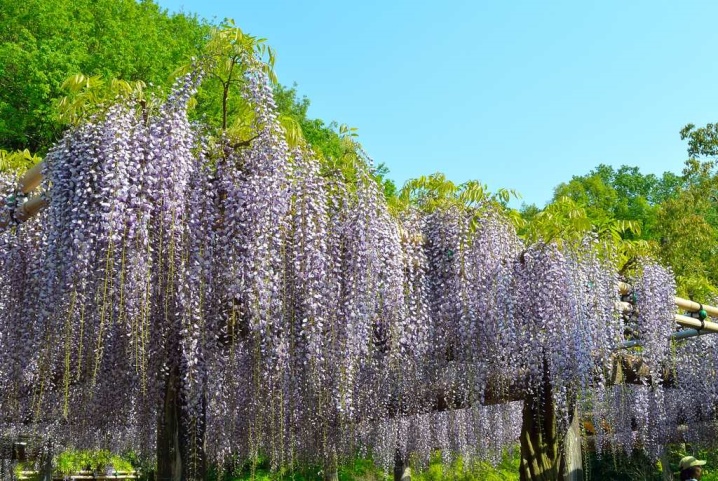

- Wisteria "Alba". A perennial variety of a deciduous plant that grows freely in the cold conditions of the Moscow region. The length of the downward-flowing shoots reaches 25 m.The stems are massive, their diameter ranges from 30-35 cm.
With proper care, the growth of young shoots can be directed in the desired direction. Once the stems have hardened, it will be impossible to change their shape.


- Wisteria "Summer Cascade". A majestic vine that adorns the garden at any time of the year. Easily tolerates cold down to -35 degrees. Multiple inflorescences on young shoots reveal the full beauty of the plant in June. Young flowers initially have a pronounced blue-purple color, but after several weeks in the sun, the juiciness of the color disappears, which does not affect the natural beauty of the plant.
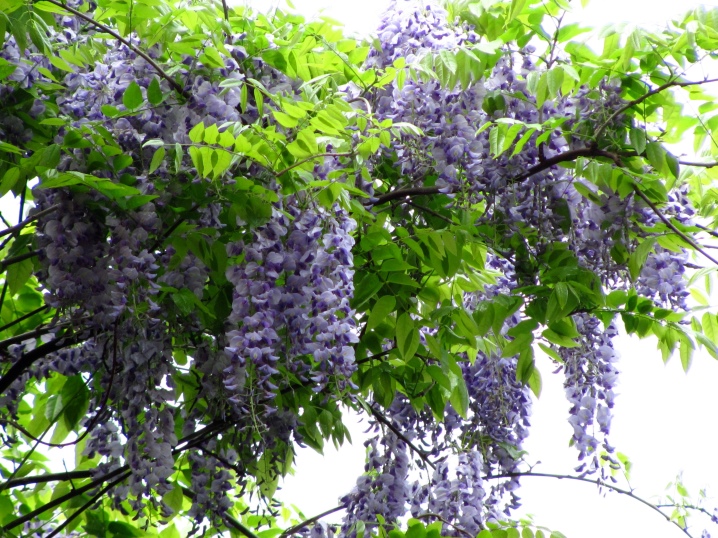

Landing
One of the important factors in planting wisteria is the right place. It should be remembered that wisteria requires attention. It should always be in front of the gardener's eyes so that the process of growing and subsequent development of the plant is under constant control.It is best to view the sunny part of the garden area so that the bright rays of natural light cover the wisteria for at least 7 hours a day. The soil for planting must be fertile and moist.
You can plant wisteria near the entrance to the garden or near the porch. The plant will look good near a decorative gazebo.
The main thing is to remember that when growing, you will have to put special supports that will support the vines. These retention mechanisms must be made of durable material.


The ideal time for planting is autumn and spring. Before planting, the soil on the selected part of the garden plot must be drained so that water can easily penetrate through it. Then a hole is dug, the diameter of which is several times the root ball of the seedling. The excavated soil is mixed with compost and filled with a small amount of mineral fertilizer with a high nitrogen content. The root of the seedling is placed in the center of the harvested hole so that the base of the stem is flush with the soil surface. Fertilized earth is sprinkled on top.


Care
Proper care of the planted wisteria consists in the timely moistening and loosening of the soil close to the trunk of the plant. Also, wisteria must be fed and pruned. Not fulfilling the specified care conditions, you will get a plant that may not grow properly, and under certain circumstances will simply die.
It may seem to some that it is almost impossible to grow wisteria on your own. However, many gardeners have proven by their own example that this opinion is wrong.


Watering and feeding
It is necessary to water the wisteria when the soil, close to the root system, has dried out 4-5 cm in depth. This vine loves moisture very much, but this does not mean that the plant needs to be poured. Stagnant water in the roots of wisteria can lead to unpleasant consequences.

Top dressing of wisteria is carried out several times during the growing season. There should be no nitrogen alone in the fertilizer. All members of the legume family absorb the required amount of nitrogen from the air. And its excess will negatively affect flowering.
With the onset of spring, compost is placed under the plant. A 5 cm layer of mulch is laid on top. This will help retain moisture and control the growth of weed grasses. Most gardeners enjoy watching wisteria bloom naturally, however, the process can be accelerated and made more active. To do this, in the spring, you will need to fertilize the soil around the wisteria with bone meal, and in the fall, add a little phosphate to the soil.


Pruning
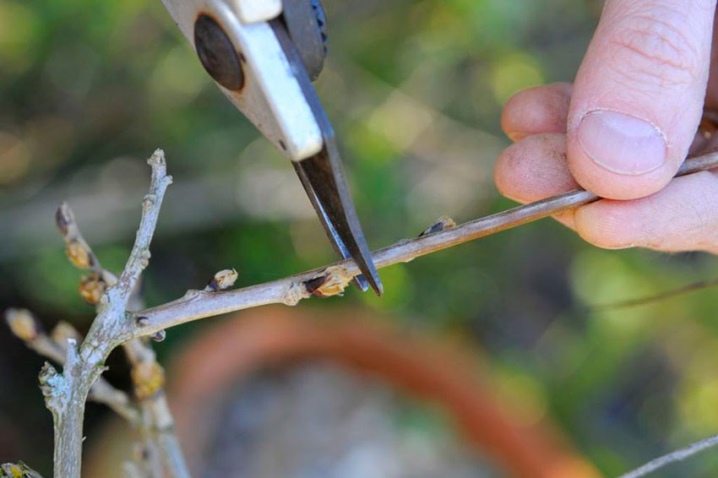
The main secret of a beautiful and high-quality wisteria flowering is the timely pruning of the plant. Primary pruning is done at the end of the winter period; last year's shoots are cut almost in half. The remainder should contain several young buds.
To create a compact tree crown, the pruning procedure is carried out not only at the end of winter, but also in summer, as soon as flowering ends. Too spreading strong shoots must be trimmed once every 2 weeks before the end of the summer period. In autumn, the plant should not be disturbed.

Formation
Some gardeners remove the lower straps of wisteria, securing only the main stem. Thus, they form the crown of the plant in the shape of a tree.
And this has its advantages, the main of which is the absence of the need to build massive structures to support heavy vines.
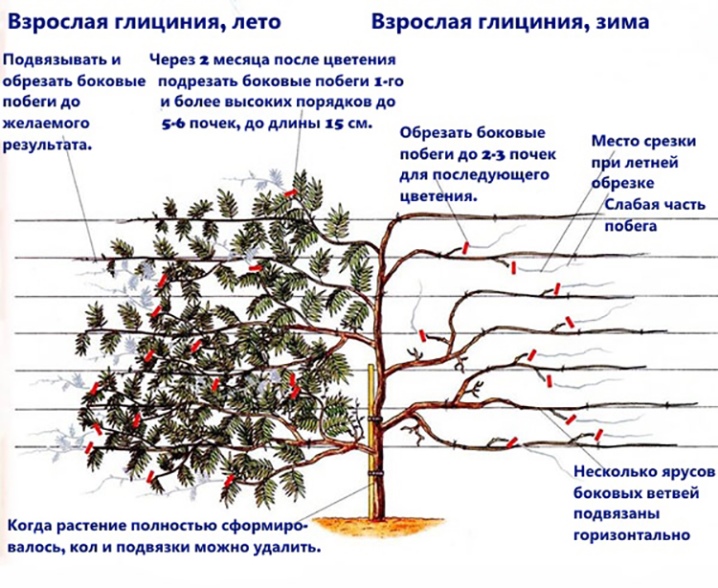
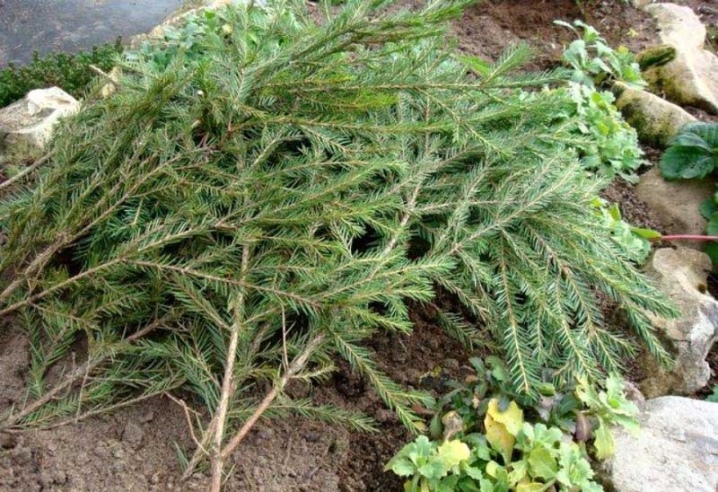
Wintering
Adult wisteria does not need shelter from the winter cold. In general, it is impossible to hide it from the winter cold, since the plant already has decent dimensions. But young seedlings in terms of cold weather have a much harder time.They do not tolerate a drop in temperature, which is why the gardener in the first years of the life of the wisteria needs to remove the vines from the supports, lay them on the ground, cover them on top with spruce branches or leaves that have fallen in autumn. A with the onset of warm spring days, you will have to hurry up and remove the warm blanket from the vines, otherwise the wisteria will start to rot.

Reproduction methods
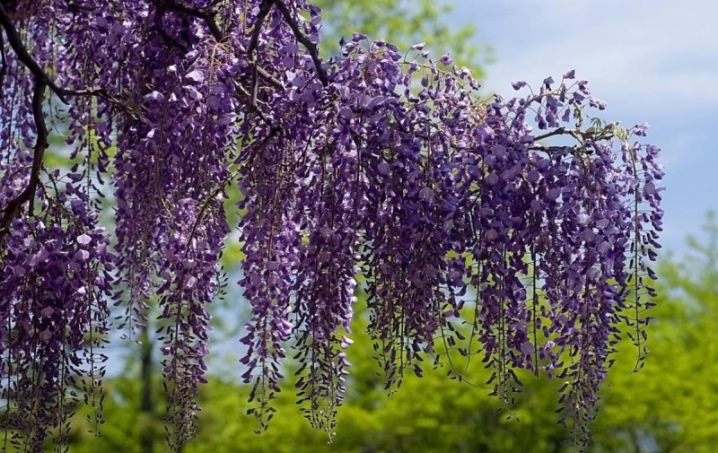
Today There are 4 ways of propagation of wisteria: layering, cuttings, seeds and grafting. However, the latter method is used only in plant nurseries. The remaining methods are practiced by ordinary gardeners. In this case, the method with layering assumes a spring-summer period, and cuttings and seed propagation are used exclusively in spring.

Seeds
Sowing of planting material takes place in greenhouse conditions in the last days of November or in the first days of December. Not having time with the autumn sowing, you can carry out the procedure in the spring, in the first days of March, but already in open ground, which is much better for the plant. The soil mixture for autumn plantings is harvested according to a certain formula.
Take 4 parts of leafy soil and mix with 1 part of sod soil and sand. The first shoots will appear 25-30 days after sowing. A week later, young sprouts are exposed in a lighted area, but not in direct sunlight.
As soon as 2 leaves appear on the seedlings, the seedlings are transplanted into the beds. In winter, young seedlings are sure to take cover. It is recommended to transplant a plant to a permanent place no earlier than next spring.
The process of growing wisteria from seeds is considered the longest. It will be possible to see the beauty of flowering only after 15 years.


Cuttings
For propagation of wisteria by cuttings, cut off parts of annual plant branches, the length of which is about 20 cm, will fit. To root the shoot, you will need to prepare a special substrate, which contains 3 parts of sod soil, 1 part of sand, 1 part of humus and 1 part of peat. On the lower part of the selected cutting, the leaves are removed, only 2-3 leaves remain on the crown.
In a container with soil mixture, a hole is made with a depth of 5 cm. A stalk is installed in it. The ground around the hole is compacted. From above, the sprout is covered with a plastic bag or cut off plastic container. The planted stalk is placed in a lighted place.
From time to time it is necessary to check the ground, if necessary, moisten. The roots of the cuttings will begin to form 5-8 weeks after planting. After 5 years, wisteria will delight the gardener with exquisite inflorescences with an extraordinary aroma.
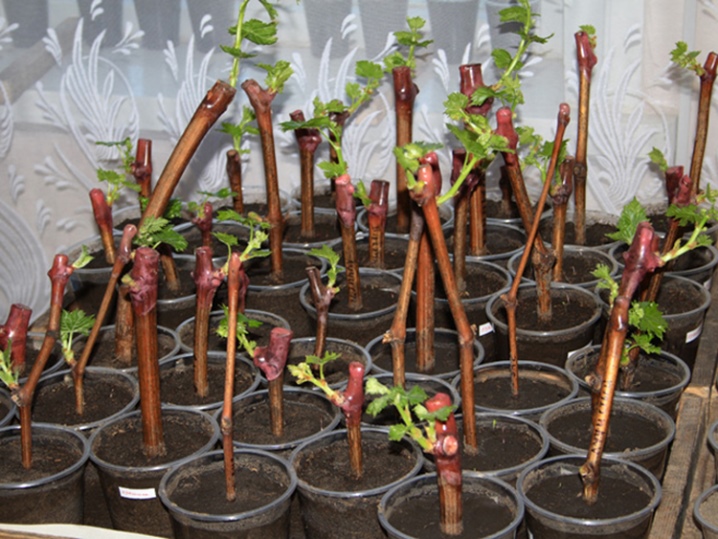

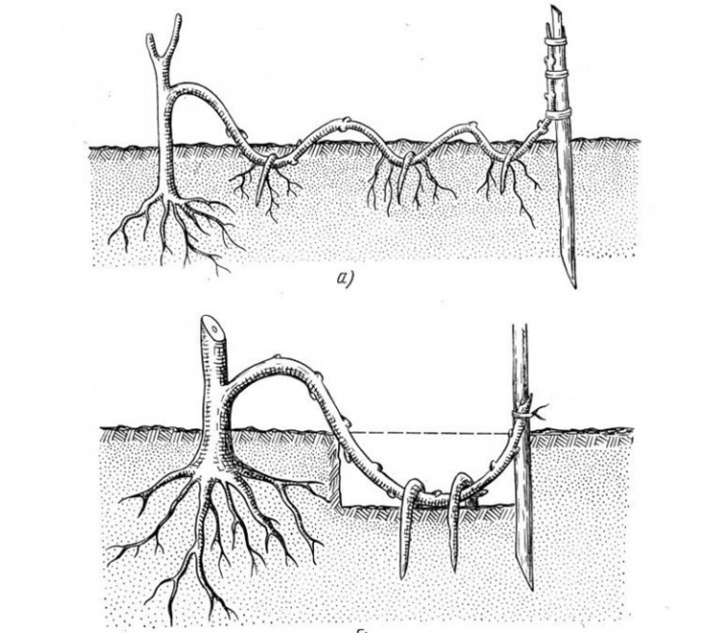
Layers
One of the strong perennial shoots is selected as a suitable layer. An oblique cut is made in the middle. A pot of fertile soil is placed under the incision. The shoot is fixed in the container with staples, then sprinkled with soil. The top of the incised branch is lifted up and fixed on the support.
During the entire summer period, the plant must be moisturized. And by the last days of August, the cut seedling has its own root system. The sprouted cut is separated from the maternal vine and transplanted to a permanent place of residence.
Diseases and pests
The main enemies of wisteria are: aphids, leafworms, mealybugs and Japanese beetles. Every gardener can get rid of most of the pests presented. This does not require special knowledge and radical actions. But in the case of the Japanese beetle, everything is much more complicated. In the scientific world, the Japanese beetle is known as the Japanese beetle (Popillia japonica). These pests are dangerous in that they gnaw tunnels in the woody part of wisteria, disrupting the supply of moisture and nutrients to the plant.
It happens, nematodes appear on the roots of wisteria... Their vital activity contributes to the emergence of root nodes.Also, the plant can be infected with fungal infections, which primarily attack the root system. If the plant is left untreated, it will gradually wither and eventually die.


Review overview
Based on the feedback from gardeners living in central Russia and in the Moscow region, we can safely say that the process of breeding and planting wisteria is not difficult. Aftercare is as easy as with other plant species. The only experience arises with the arrival of cold weather. But do not worry, frost-resistant varieties of wisteria are ready to withstand even 40-degree frost.
As for diseases and pests, as gardeners say, who fruitfully grow wisteria on their own plot, if you take proper care of the plant, no infection will stick to it.
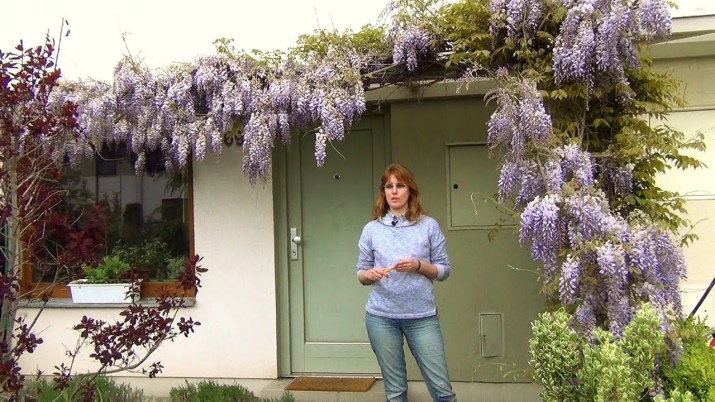






Examples in landscape design
When designing a garden plot where wisteria grows, you can use many interesting solutions. Few people paid attention, but the sprawling wisteria is successfully combined with white tulips or daffodils growing at the foot of the liana trunk. Summer bloom is one of the most unique periods in the life of wisteria. And to emphasize the beauty and charm of this process will help garden hibiscus and daylilies.
Many landscape designers offer to arrange wisteria vines in the form of a falling cascade along the facade of a residential building. On the one hand, this idea may seem absurd, in fact it will turn out to be quite the opposite.
The main thing is to remember that the branches of wisteria become heavier with age and can damage the pipes.


For information on how to grow wisteria, see the next video.




































































































The comment was sent successfully.