Features of growing wisteria
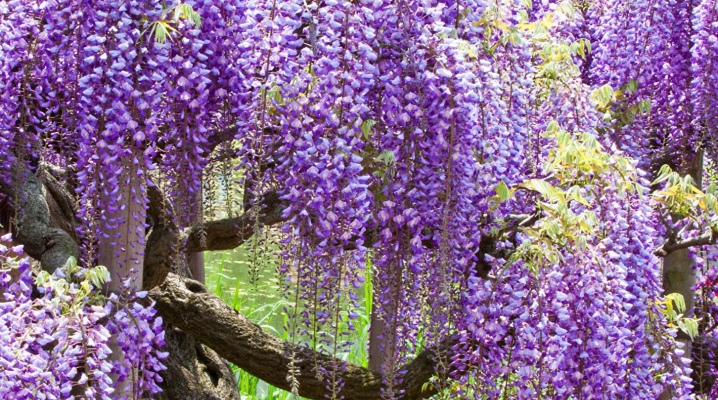

Wisteria is a very bright and expressive flower native to the tropics. This plant looks beautiful even when compared to other ornamental trees. Gardeners lose a lot if they do not understand how to properly grow such a crop.

Landing dates
The cultivation of wisteria is greatly hampered by the plant's exceptional thermophilicity. It will develop in full force only in the southern regions of Russia and in the Transcaucasus.
The second name of the culture - wisteria, was given to it in honor of the discoverer of the species. For a very long time, it was it that dominated botanical literature and gardening manuals. In open ground, the culture is usually planted in the spring months, waiting for the ground to warm up thoroughly; any frost can damage it.
If it was not possible to plant wisteria at the beginning of the growing season, you can find a suitable time in the fall. But this can be done only in the southern regions. Already in the suburbs, such a maneuver is unlikely to give a good result.
Wisteria develops normally only at an air temperature of at least 10 degrees. Therefore, experts advise choosing a spring planting.


Seat selection
Liana is very demanding on development conditions. For her, only open areas are suitable, where the sun shines for at least 6-7 hours a day. At the same time, the fact that the site is open does not mean that the protection against drafts can be ignored. Of course, you need to take into account the design characteristics of a particular place. It's one thing if wisteria grows on its own, and another if it is used to decorate the wall of a house.
Nutritious and loose soil allows for the best results. The weak alkalinity of the soil is also critical, since excessive deflection in both directions is harmful. It is even advisable to occasionally add a certain amount of lime. On other soils, growth will be less active.
Good drainage is desirable as wisteria suffers from water accumulation.


How to plant?
Wisteria is highly susceptible to air pollution from exhaust fumes. Therefore, culture can develop optimally only in places with an optimal ecological situation. It can be planted in pre-prepared holes with dimensions of 0.6x0.6x0.5 m. It is advisable to shorten the shoots of wisteria in order to achieve the most generous flowering. Normally, the branches should be up to 0.3 m long.
To plant a vine correctly, you need to immediately lay compost in the hole. Immediately after planting, wisteria is watered as thoroughly as possible. At the beginning of adaptation, the culture stops growing, which is quite normal. As soon as this time is over, the growth rate will pleasantly surprise the growers. Quite often, wisteria is planted with layering.
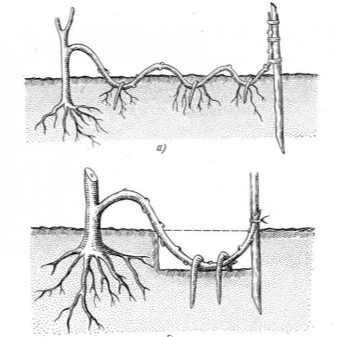
Shoots from last year can also be used. In early spring, they are carefully laid out on the surface and covered with soil. To plant the layers correctly means to give the shoots at least a year for full rooting.

Sometimes wisteria is also grown from seeds. You cannot plant them directly into free land - the plantings will freeze out. Sowing seeds for seedlings is advised in November and in the first decade of December. To do this, I use a substrate based on:
- 4 pieces of leafy land;
- 1 piece of woody land;
- 1 part sand.
It is better to cover the newly planted seeds with a thin (0.1-0.2 cm) layer of the same sand. It is very important: then they are abundantly sprayed from a spray bottle. The container is covered with glass or polyethylene for the entire period of germination in order to maintain an ideal microclimate. The container must be kept where the temperature is not lower than 22 and not higher than 25 degrees. We'll have to constantly monitor the moisture content of the earth.
You can expect the first shoots to appear in 20-28 days. By the end of the first month, the container with seedlings is moved to a well-lit place not exposed to direct sunlight. As soon as the first 2 leaves appear, the seedlings dive. At the same time, they are transplanted with a lump into another container.
The transplanted liana must be spilled immediately with an unsaturated solution of potassium permanganate.


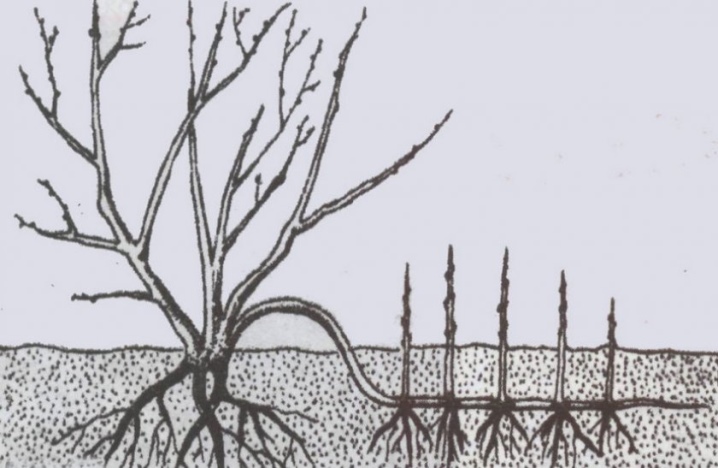
It is useful to take into account some other subtleties. So, the use of cuttings is popular due to the preservation of all the valuable features of the original specimen... With the onset of spring, near some (not all at once, of course) last year's shoots, they dig a row 0.2 m deep.There they lay soil saturated with nutrients and thoroughly spill it with water. Of course, the land must be carefully checked and decontaminated.
The shoot just above the buds is slightly incised and placed in the hole. You can avoid raising the layers by pinning. Be sure to also sprinkle them with soil. Shoot tops are not covered to provide ventilation. They are only tied vertically to a small support.
Next, you need to look at how rooting is going on in the leaf nodes. Depending on this, the shoot can be separated after 12-18 months. With good development of the root system, the layers are immediately transplanted to the designated place in the garden. But sometimes the roots develop very poorly. Then the plant is not kept in the same place for more than 18 months, but is grown in pots.
Florists can use wisteria and woody cuttings for propagation. They must be cut in the autumn months, taking planting material from the middle sections of mature shoots. All suitable twigs should have at least a couple of buds in an area of 0.05-0.08 m in length. Cuttings planted in the ground are kept at a temperature of 3 degrees until the onset of spring heat. In April or May (when the risk of night frosts disappears), the seedlings are transplanted into containers filled with garden soil.
Sprinkle it with moistened sand before planting. Cuttings should be planted strictly vertically to a depth of 0.04 m. The gap between adjacent seedlings is 0.1 m. In the spring they will have to be transplanted into peas for subsequent growing. After 12 months, wisteria is planted in a permanent place in the garden.
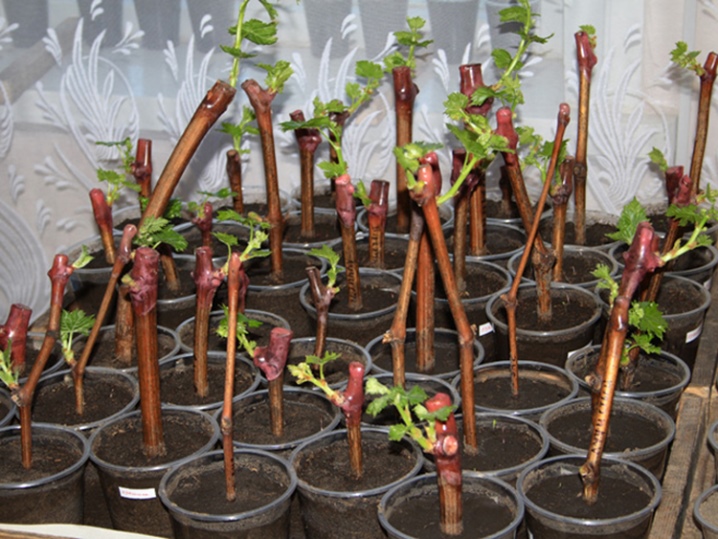

Sometimes winter root grafts are used. This method is notable for its increased complexity, but it allows you to convey all the key characteristics of the variety. In the fall, you need to dig off-grade seedlings and separate the root system (provided that the root thickness is at least 0.06 m). The seedlings are transplanted into containers with sand and kept in the dark and cool. You need to bring them to a warm place in December or January.
After 12-14 days, cuttings with a length of 0.06 m need to be grafted. It should be a varietal planting material with two buds. Exactly under the lowest of them, an incision is made at an acute angle. The same incision is prepared on the rootstock so that they touch more tightly. Vaccination sites are thoroughly fixed with a garden plaster.
The seedlings prepared in this way are placed in a container containing a nutritious substrate. The vaccination site cannot be deepened. The container needs to be covered with glass. It must be kept at a temperature not lower than 15 degrees and at a humidity of 80%. With the right approach, shoots can be expected to appear in 14-15 days; when the vines take root, they are transplanted into the ground.

Care rules
Watering
It is impossible to properly grow wisteria without systemic watering. The plant will need irrigation during the spring and summer months. The soil must be kept moist continuously and overflow must be carefully avoided. Reinforced irrigation is required when a drought occurs, otherwise the flowers will crumble.
Watering from September 12-15 should be done less often, otherwise wisteria will not be able to enter into hibernation fully.

Support
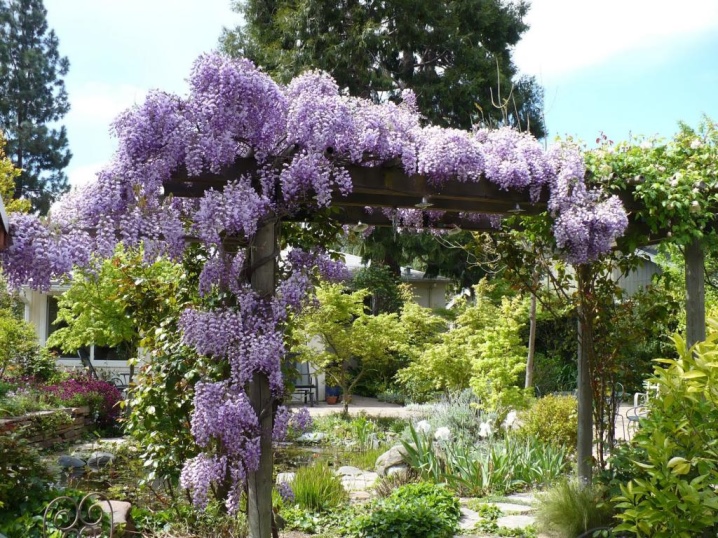
This plant is characterized by increased windage (exposure to wind). Therefore, it is at least possible to grow wisteria outdoors in the garden for the first year only with support. The garter of young shoots should serve for a long time and successfully withstand strong winds. If you just put a support, the vine will wrap around it chaotically, and it will be quite difficult to remove it to prepare for winter.
Plants growing without support will wrap around each other or wind up on the first hard surface that comes across.

Top dressing
If the soil is fertile enough, fertilizer should be applied no more than 2 times a month. Feeding wisteria is practiced only in spring and summer. Immediately after planting, the plant is rarely fed. Subject to the planting technology, it should not lack nutrients. If it is clear that the tree will soon bloom (but is not actively blooming yet), ready-made mineral mixtures should be used.
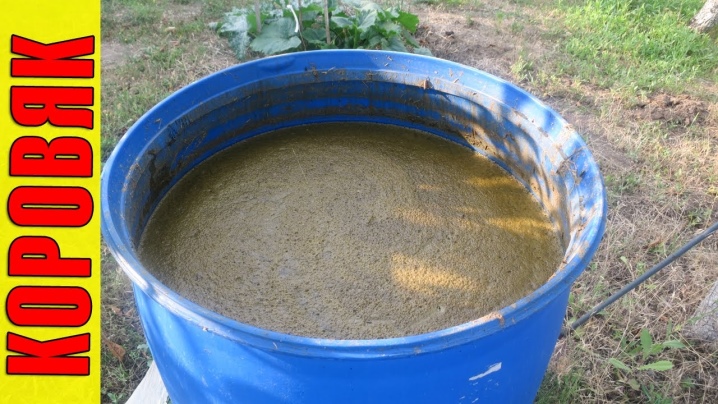
Liquid preparations containing potassium and phosphorus are used 3 times a month at regular intervals. Nitrogen compounds are required to be used only at the very beginning of spring, when it is required to increase the green mass. Experts advise to alternate complex formulations and organic feeding. Most often, mullein diluted 20 times with water is used. Once a summer, wisteria bushes are spilled with a solution of chalk (0.1 kg per 12 liters).
Once a month, while the growing season is in progress, fertilizers with a small amount of nitrogen are used. Excessive feeding with them will lead to a decrease in flowering and increased development of the green part of the plants. Mineral compositions are required to be laid in the ground only after intensive watering. An extremely concentrated solution can burn roots in dry soil. Wisteria cannot be fed during the winter months.

Pruning
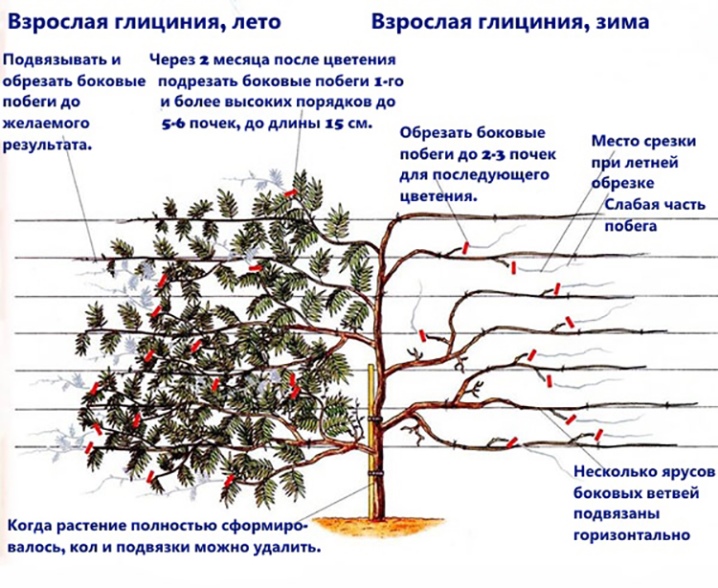
Timely pruning leads to the loss of an attractive vine shape. It will grow chaotically, and the flowers will lose their beauty. Usually the plant is shortened 2 times per season. They choose the right moment at the beginning or in the middle of summer, and the second time the procedure is carried out after the end of the leaf fall. At the same time, lateral shoots are removed in the first place, because they can interfere with the growth of new flowers.
Sometimes it becomes necessary to change the length or geometry of the bush. There is nothing wrong with additional cropping. Wisteria will stop producing flowers for just one year. If done correctly, then flowering will resume.
With competent systematic pruning, long-term development of wisteria is guaranteed, and it will not even require rejuvenation.
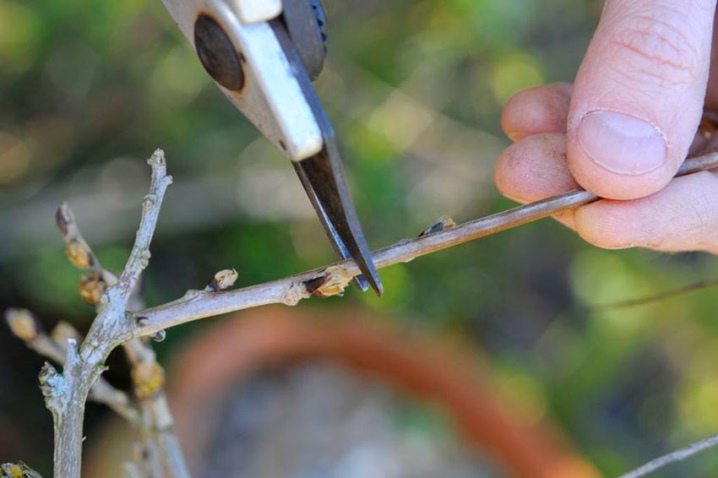

You can regularly prune a crop starting from 2-3 years of development. Pruning should be done in August for the first time. Fresh growths should be cut into 3-4 buds. In the spring, it is advised to get rid of frozen, dry or overly refined shoots. Some gardeners shorten in winter:
- main escape;
- branches cut in summer;
- side shoots.
The standard vine is formed, giving preference to one developed shoot. Other branches are mercilessly removed. With very poor flowering, part of the root system is cut off. It is chopped off with a shovel at a depth of 0.3-0.4 m. It is necessary to retreat from the main trunk by 1.5-2 m.
Preparing for winter
Wisteria (even frost-resistant varieties) is prepared for the cold season, getting rid of dried flowers and shoots for a start. The next step is to remove the branches from the supports and lay them around the trunk. Shoots should be covered with agrofibre and plastic wrap. It is recommended to fill the ground with the top. Young specimens of wisteria are covered even more thoroughly, sprinkling the trunk with soil or covering it with spruce branches.
The nuances of caring for this plant in the garden area also depend on the growing region. In the suburbs, you can limit yourself to the choice of a sunny plot and drainage of the land. The recommended depth of planting holes is from 0.25 to 0.3 m. Shelter for the winter must be done. In the Urals, due to the colder climate, you will have to take care of the plant more carefully. There it must be carefully protected from drafts. With the approach of winter, the root system is covered with a backfill of crushed peat. Conditions in Siberia are even more difficult, since wisteria may not survive the long severe frosts. Usually in Siberian regions this plant is not grown outdoors. It is cultivated in tubs and taken out into the street only upon the onset of stable heat.

In the middle lane, the approach to growing crops is the same as in the Moscow region. But we must take into account the risk of long cold weather. Therefore, in a number of places you have to make a very solid shelter. Sandy soil for wisteria in the middle lane needs to be fertilized, and clay soil should be mixed with sawdust, humus and crushed bark. Compliance with these rules allows you to guarantee long flowering.
In the Leningrad Region, only well-lit areas are suitable for wisteria. It is advised to add sand mixed with superphosphate to the planting pits. The seedling must be buried in the ground dug from them. Greenhouse conditions for seedlings are created using hoods. They will have to be opened regularly to ventilate and water the wisteria.
In the Rostov region, in contrast to the Leningrad region, Chinese and multi-flowered varieties can be used. In the north, such a liana grows very rarely, and even if it does not die, it will look very unpresentable due to poor flowering. In the south, the chances are much better. And still, wisteria is advised to be thoroughly insulated when winter approaches.
To simplify the wintering of an exotic guest in the Moscow region, in the Urals and in more severe places, you can use a homemade container. Its volume must be at least 40 liters. Any tub or garden barrel is suitable for this purpose. In the fall, the vine is transferred to a heated room. There it is watered 1 time in 7-8 days and provide illumination for 6 hours every day at least.

For more information on the features of growing wisteria, see the next video.




































































































The comment was sent successfully.