Wisteria: description, types and varieties, use in landscape design
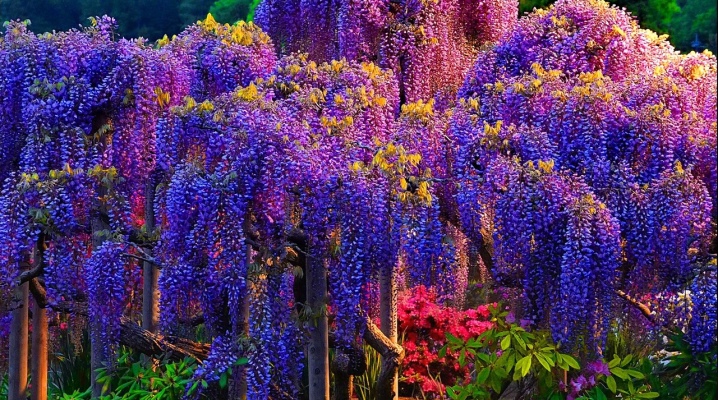

Wisteria (another name is wisteria) is an exquisite and original flower that gardeners highly appreciate for its graceful appearance. It is also widely used by landscape designers. Twigs can decorate any composition, they look fresh and interesting. We will talk about the features of the plant and the nuances of its cultivation in our article.
Description
Wisteria is a treelike vine that grows mainly in the tropics. It belongs to the legume family and is found in the hot and humid regions of North America and East Asia.
This tree can be either deciduous or semi-deciduous. All over the world, it has won the fame of an ornamental shrub, but it takes root only in a subtropical climate. On the territory of Russia, wisteria can be seen in nature only in the Crimea.



This perennial shrub can reach a height of 15-18 meters. Its shoots are either naked or pubescent, and the branches hang down like vines. The vine can have a diameter of up to 40 centimeters, it rises, tightly braiding the support. Wisteria grows very quickly, and its age can reach 120-150 years.
This weaving liana has alternate leaves up to 30 centimeters in size. Shades of green can vary.
As for flowering, American varieties delight gardeners from mid to late summer. Asian species are more frost-resistant and bloom at the end of March, and the process lasts until the very end of spring. The flowers of Chinese wisteria bloom 2 times a year: in May with the opening of the leaves, and in September with the arrival of autumn.



The clusters in which the flowers are collected resemble bunches of grapes and can reach from 10 to 80 centimeters. Wisteria blooms either on the whole tree at once, or starting from the lower branches and gradually moving up. The flowers are predominantly blue in color, but some varieties are famous for their white and pink buds. The aroma from them is simply magical, very intense.
After the end of flowering, fruits appear on the tree. They are approximately 15 cm long leguminous pods and have dense pubescence. The seeds are located inside. They are rounded, deep brown in color.
It should be noted that wisteria is a poisonous plant.


Types and varieties
There are only 9 types of wisteria, but the most popular are Chinese and abundantly flowering. They are most often used by landscape designers for decorative purposes. They can be found in parks and gardens of various countries, however, given that the plant is thermophilic, it requires a certain climate. So, let's look at the varieties in more detail.
Chinese
This species can reach a height of 18-20 meters. In a young liana, the leaves are pubescent, in an older one, they become smooth and glossy. Flowers are collected in voluminous brushes and can have a predominantly lilac or purple hue. The length of the brushes reaches 30 centimeters. Some terry forms have milky corollas.
The inflorescences bloom at the same time, and the plant forms a graceful flowering cascade. The buds open when the first foliage begins to appear, and the process continues throughout the summer. Some varieties can bloom twice a season: in late spring and closer to early autumn.


It should be noted that feathery leaves are located around the inflorescences, which looks very beautiful. Liana perfectly takes root in the conditions of the city, it is gassed, and the presence of dust is not afraid of it. It can also withstand short temperature drops down to -20 degrees Celsius.
Available in varieties such as Blue Sapphire, Alba and Prolific... They have blue-blue, white and violet-blue buds, respectively.



Profusely blooming
This wisteria is also called multiflorous. It grows up to 8-10 meters in height. The leaf plates are quite long, about 40 centimeters. Together with the blooming of the leaves, the liana is covered with two-colored violet-blue buds, however, in comparison with the previous species, the process takes place 2-3 weeks later.
Flowers open first on the lower shoots, gradually moving upward. The process lasts until about the middle of the first summer month, but some varieties boast double flowering, the second wave of which covers the plant in July-August.
Breeders are working on the development of garden forms of wisteria. They can be presented in different colors, as well as in terry varieties. There are ornamental shrubs with variegated leaf plates. And also varieties are presented that can boast of frost resistance, surviving cold snaps down to -23 degrees Celsius.


Lovely
Wisteria is beautiful, not too high, only up to 10 meters. The flowering process takes place from May to the end of June. White, purple and lilac buds gather in small inflorescences that cover the bush.
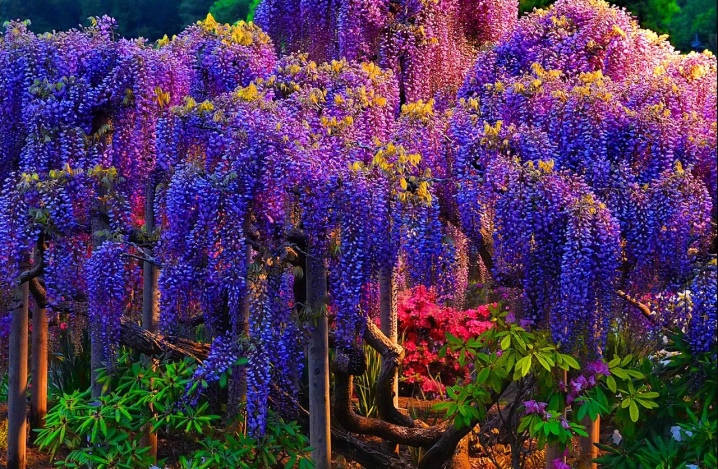

Shrub
This variety is quite common on the Crimean coast. It can grow as a standard tree in special containers. Reaches a height of 12 meters and has violet-blue inflorescences.


Japanese
Most varieties of Japanese wisteria have snow-white buds, but some varieties, for example, Rosea, are distinguished by pink inflorescences. It can grow in the Caucasus. However, it is less often used in landscape design, as it does not look very impressive, and at the same time it cannot boast of winter hardiness.
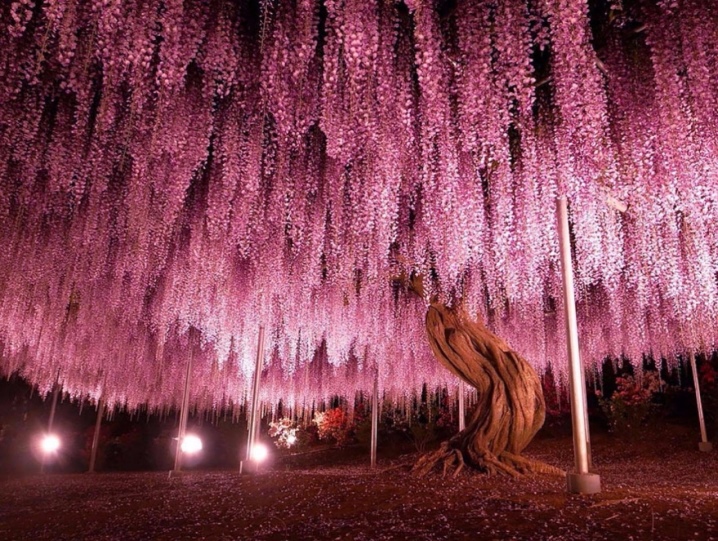

Large-leaf
The flowering process is relatively short, about two weeks. It begins with the arrival of summer, when the shrub is covered with blue inflorescences, which have a length of 20-25 centimeters. One of the most famous is the Blue Macrostachia variety.
It should be noted the frost resistance of this variety. Some varieties can withstand fairly harsh winters with temperatures as low as -37 degrees Celsius.

Landing subtleties
Growing wisteria begins with choosing a place to plant it. The procedure should be approached as carefully as possible, because the life expectancy of a shrub can be up to 150 years. You need to stop in an area where there will be enough light, because the plant does not tolerate shading and must be in the sun for at least 6 hours daily.
The landing site should be fairly warm and free from cold winds. The southwest and southeast are perfect. It is imperative to have a support that must stand very securely and withstand even heavy loads.
The soil is also worth taking care of. Liana needs light and fertile soil. And also it must be well permeable, since excess moisture or strong liming can lead to the occurrence of various diseases, for example, chlorosis, during which the leaves will lighten a lot and look unhealthy.

Experts advise be sure to tie up the shoots, although in some cases they can wrap around the support on their own. The garter will make it easier to prepare the plant for winter when you need to remove the shoots from the support, otherwise problems may arise.
Planting is done in spring or autumn. Its scheme is quite simple.First, you need to dig a hole with a depth of about the root ball, but at the same time exceeding it by 2-3 times in width. The soil is mixed with compost, and nitrogen-containing mineral fertilizers are added.
The root system is located right in the center of the hole. To prevent the seedling from deepening, its base should be slightly above the ground level. The earth is compacted and thoroughly watered.


Care features
Wisteria cannot be called a particularly demanding plant, however, planting it and forgetting about all kinds of care will not work. It will be necessary to carry out certain activities in agricultural technology in order to achieve active growth and abundant flowering. Let's consider the main points.
Watering
This moment is very important, since wisteria cannot be called a moisture-loving plant. If the liquid is in excess, this will lead to discarding of buds and shoots. At the same time, in hot weather, spraying will be an excellent option. It may even prove to be a good alternative to watering for a while. By spraying, it will be possible to exclude stagnation of moisture in the ground.
When the spring is dry, watering should be fairly abundant. During the growing season, it must be reduced, and towards the end of September it must be stopped, in general, in order to give the vines time to prepare for winter.

Top dressing
In order for a vine to develop actively, you need to know when and how to feed it. The plant needs fertilizers, since it is able to gain a height of up to 5 meters during the season.
Top dressing will need to be alternated. At the very beginning, mineral fertilizers are suitable. 10-20 grams of the product is enough for 1 m2. In the future, organic components are also added. You can use a regular mullein infusion once a week.
Wisteria can be fed with ash, which is also helpful in preventing pests. To deoxidize the soil, watering with water with the addition of chalk will be required - about 100 grams per bucket.


Pruning
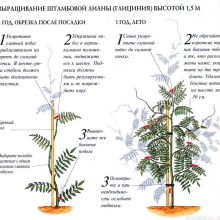
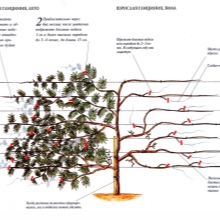
How abundantly wisteria blooms is influenced by pruning, which must be done at a certain time. The procedure is carried out with the onset of spring, together with the removal of the shelter and the garter. Last year's growth must be removed by 2-3 buds. It is also necessary when you need to shape the crown.
To lay flower buds, you must properly cut the bush. With the beginning of summer, last year's shoots are strongly cut off, branches up to 30 centimeters in size should remain on the bush. By the end of August, the new growth is also removed by 4-5 buds.
If you plan to grow a climbing liana, you need to cut off the side shoots to the maximum. The fact is that they affect the formation of greenery, and not the number of inflorescences. For a standard tree, the trunk is important, the rest of the shoots must be cut off.

Preparing for winter
Some varieties of shrubs are considered winter hardy, but most often wisteria does not tolerate cold weather. In order to protect it from frost, it is necessary to remove the shoots from the support and lay them on the ground. A couple of buckets of earth are poured out from above, then agrofibre is stretched, and the plant is covered with spruce branches.
Young growth in the winter period most often dies, but this is not scary. In the future, these shoots are still cut off. It is not necessary to remove adult and strong plants from the support, they are able to withstand the cold in their normal state.

Reproduction methods
If we consider the methods of reproduction, it should be noted that gardeners choose predominantly vegetative. However, liana can also propagate by seeds. This procedure is lengthy, and the result is not always desired.
Seminal
Nevertheless, the seed method does take place, and one cannot but dwell on it in more detail. The work requires adherence to a certain sequence.
First of all, the seeds should be planted in the greenhouse. The procedure is carried out at the very beginning of winter. In the spring, planting in the ground is possible.
It is necessary to prepare the soil mixture. To do this, take one part of turf and sand, as well as 4 parts of leafy land. The substrate is mixed, and seeds are laid out on it and a little sprinkled with sand. A film is stretched on top or glass is placed - this will help to ensure the necessary level of humidity. Then the site must be closed from light so that the seeds germinate in the dark.


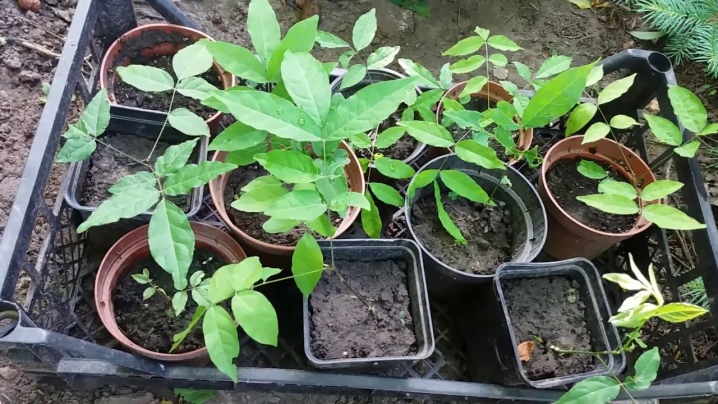
The first shoots appear in 3-4 weeks. They open up but are still slightly shaded. A pick is done after the appearance of two leaves. The sprouts are transplanted into pots. Every day, for a couple of hours, the seedlings are taken out into the street so that they can harden. In this case, it is important to avoid the presence of drafts.
It should be noted that the seeds sprout about a quarter. Sprouts can take root for a long time, and even if successful, it is possible that varietal characteristics and rich flowering will not appear in full. Flowers appear 6-10 years after planting.

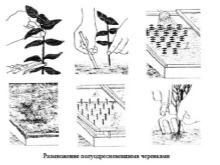
Vegetative
Cuttings can be rooted in both spring and summer. This will require one-year-old shoots up to 25 centimeters in size. An oblique cut is made to the middle of the stem, this area is placed in a soil mixture made of peat, humus and sand, taken in equal parts with sod land.
Rooting occurs almost 100 percent if you add a growth agent in advance. The top of the vine must be tied to the support. Already with the onset of autumn, you can transplant to a permanent place.
Wisteria propagates by root cuttings, but the procedure will take a little more time. In March, the plant is dug up, both young and large roots are cut from it, after which it is planted again. As a result, young roots will appear, and adventitious buds and stems will grow from them. In autumn, young roots with shoots are separated with pruning shears, placed in a fungicide to exclude the appearance of diseases, after which they are planted in special containers with soil mixture, located in a warm room, for the whole winter.

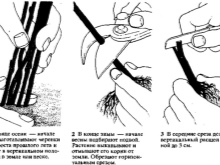
In spring, the shrub can be transplanted to a permanent place. However, this method can harm an adult plant, because its root system is repeatedly injured. This can adversely affect growth and flowering.
Often, gardeners choose propagation by layering. It is carried out in the fall, when the foliage falls. Large lower shoots are incised and attached to the ground or placed in special trenches. The soil is poured on top, and the top with several buds remains on the surface.
Already in the spring, before the vine enters the stage of active growth, the stem is separated from the bush... Over the summer, it will have time to take root, and in the fall, young wisteria can be transplanted to a permanent place. Placement in open ground occurs with the establishment of heat, when the possibility of frost is excluded.

Diseases and pests
Growing any culture, you must constantly monitor its condition. Wisteria cannot boast of resistance to microorganisms and pest attacks. For this reason, prevention is very important.
Clover mites, leafhoppers or green aphids are especially dangerous. And also a lot of unpleasant moments can be delivered by caterpillars. Acaricides and insecticides will help to cope with pests. In some cases, folk remedies will help.



If the soil is highly alkaline, the shrub may be at risk of chlorosis. It manifests itself in the lightening of the sheet plates. The introduction of root dressings containing iron salts in the composition will help to save the situation.
If the planting took place not so long ago, and the plant is still very young, it will be advisable to transplant it to a new place. In other cases, treatment should be carried out using the formulations "Antichlorosis" or "Ferovit". It is recommended to opt for foliar spraying.
And the plant is affected by powdery mildew... It appears as a white, cobweb-like coating that covers the leaves.Wiping will not help, moreover, it is labor intensive if the bush is quite large. They will help to cope with the scourge of fungicides. Best of all, Fundazol and Vitaros help. Each drug has instructions for use, which must be carefully read before use.



Use in landscape design
Wisteria can be planted near a house or fence. She is able to create a spectacular hedge. With the help of certain varieties, for example, Chinese and multi-flowered, you can even decorate balconies and street gazebos.



These vines are often used in vertical gardening. They do not require much space, and they look very original. They very quickly wrap around the support, creating a kind of green partition. This helps to hide the imperfections of the site from prying eyes, presenting it in a favorable light. And also the corner will be reliably hidden from the scorching sun and piercing wind.


Wisteria looks great next to other flowers. Snow-white tulips, yellow daffodils or bright purple hyacinths go well with it. This will be a great finishing touch to the look.
Liana can also grow in tubs or pots. It can be placed in a conservatory or greenhouse. However, this climbing plant is most often found in the garden.



For more information on the features of growing wisteria, see the next video.




































































































The comment was sent successfully.