Wisteria macrostachia "Blue Moon": description, planting and care
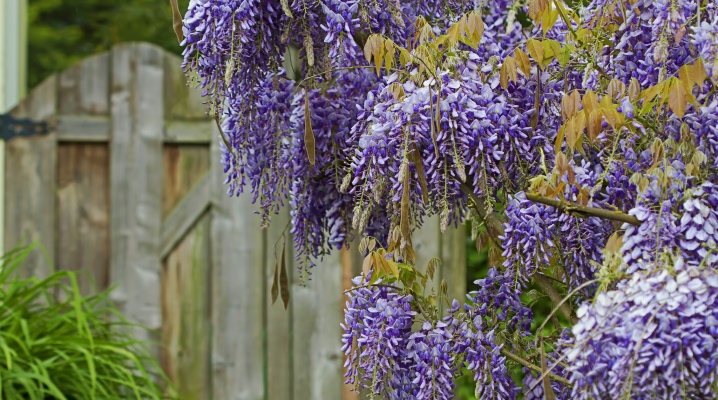

One of the most favorite plants among gardeners is wisteria macrostachia "Blue Moon". This plant is a perennial vine. At night, lavender inflorescences have a silvery tint, so the flower is called "Blue Moon", which means "Blue Moon" in English. Perennial is suitable for creating hedges and arbors. And how to plant and care for this interesting plant, we will consider in more detail in the article.


Description
Blue moon wisteria is an ornamental deciduous plant. An adult liana can grow up to 7 meters in height. The shape of the inflorescences is rather unusual, and their shade depends on the variety. Usually flowers are painted in a delicate blue, lavender with a blue tint or purple. The neck area of the flowers is yellow. Inflorescences are collected in small clusters, their length can reach 30 centimeters. Shiny, pinnate leaves of a rich green color, their length can be 30 centimeters or more.
Young leaves are slightly pubescent. The root system of wisteria is quite powerful, the leguminous fruits look like beans.


The Blue Moon variety is considered the most winter-hardy hybrid of its kind. Such a vine can withstand even 40-degree frosts. For a very long time, gardeners could not achieve results in breeding this type of wisteria. However, experts managed to make a frost-resistant plant out of liana.
Another feature of this culture is flowering, which is observed as many as 3 times per season.



Landing
For planting perennial vines, you will need 2 seedlings, the root system of which must be closed. This factor affects the adaptation of the plant, making it less painful. Wisteria can be cultivated in any soil. It is best to plant in a slightly alkaline site. It is also recommended to add humus to the soil and drain it well. Strongly acidic peat soil is not suitable for growing vines.
Before planting wisteria, dig a hole 25 centimeters deep and fill it with organic fertilizer. Humus works best. You can prepare a mixture of heated foliage, river sand and clay soil. The plant is planted by the transshipment method, without deepening the area of the root collar.



The seat should be well lit. CWisteria branches need sunlight for normal development. The plant also needs to defend itself well during the cold season. Therefore, the presence of a wall near the seat will help protect from drafts and wind. Due to the peculiarities of wisteria, it is recommended to plant it in a calm and warm place. The shoots of the plant are strongly woven, for this reason it needs supports, which are installed near the vines.


Care
The Blue Moon wisteria variety is rather unpretentious in care. To ensure the plant grows well, it is recommended to adhere to simple rules for its maintenance.
Temperature regime
This type of vine can withstand any temperature, even the lowest. However, warm weather will be more favorable for flowering. During the active growth and development of wisteria, it is necessary to receive a normal amount of sunlight and heat, so the air temperature should not fall below +20 degrees. In winter, the plant will withstand frost down to -40 degrees Celsius.

The soil
The plant loves light soils, the moisture content of which should be relatively low. The soil must also be highly permeable. During planting, it is advisable to fill the hole with a soil mixture purchased from a specialized store or prepared by yourself.
Watering rules
Waterlogged soil negatively affects wisteria. To avoid this, you should systematically spray the plant. Regular watering of the liana is required during the period of rapid flowering, as well as growth. In this case, the wisteria flower should be watered once a week.
In autumn, the number of water procedures is reduced, in winter the plant does not need them at all.

Pruning
This process directly affects the flowering of perennial vines. Therefore, it is important to prune twice a year.
Transfer
Young vines with a fragile and weak root system can be replanted annually. However, it should be borne in mind that wisteria flowers do not tolerate this process well. After planting the creeper in a new place, it is at rest for a long period of time.
If the plant has grown strongly, transplanting is prohibited.
Top dressing
Top dressing is needed to make leaves and flowers rich and colorful. Wisteria is fed with compost, mineral fertilizers, and chalk solution.



Reproduction
There are several ways to propagate the Blue Moon wisteria. The most popular of them are propagation by air layers and using cuttings. Least often they resort to seed propagation of vines, since this process takes a long time and does not preserve the varietal characteristics of the variety.
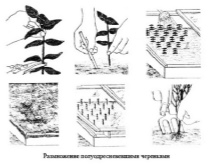
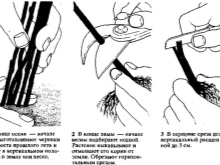
Cuttings
Shoots are harvested in the spring. Young annual stems are selected. A small oblique incision must be made in the central part of the shoot. Next, the planting material is placed in the nutrient soil. The deepening is done to the level of the notch. By autumn, when the roots of the cuttings are sufficiently strong, the transplant of seedlings is carried out.

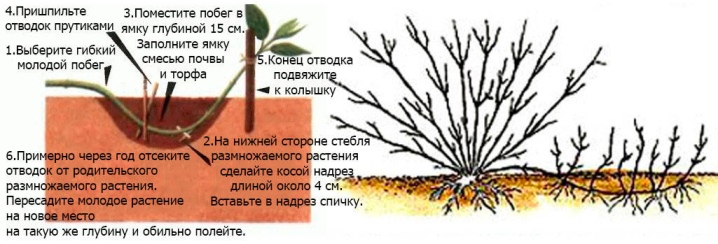
Layers
This method is great for propagating wisteria. After the leaves fall off, it is necessary to root the plant. This is usually done in the second half of the fall season. The lower part of the shoots should be carefully tilted and dug in. Full rooting of the vine will happen only after a year.
When roots appear on the shoots, they can be separated from each other and transplanted into open ground.
Seed propagation
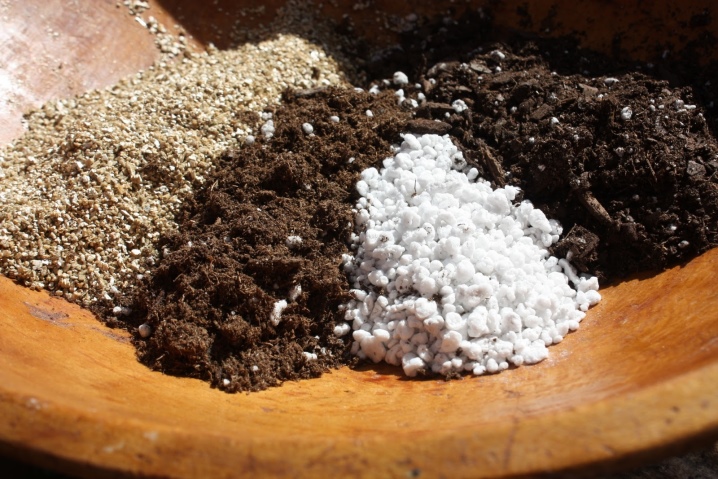
If you are harvesting wisteria seeds for seedlings, it is best to start in December. If the seeds are harvested for sowing in open ground, then this process should begin in March. The seeds are sown in small containers, which are filled with a special soil mixture. It can be prepared at home, for this you need to mix in a 1: 2: 1 ratio:
- sand;
- leafy ground;
- sod land.

The soil must be moistened, and then the seeds must be placed in it. The planting material is covered with sand. You can also use wood ash. Then, for sowing, you need to make a small greenhouse. You can build it from glass or film. The structure must be stored in a dark place for two weeks. After the first shoots appear, the container with seeds is placed in the light.
After the seedlings are fully grown, you can plant them in open ground.


Diseases and pests
Wisteria is distinguished by a high degree of resistance to various viruses, moreover, it is rarely affected by pests. If the rules for caring for the plant are violated, there is a risk of infection of the vines. Problems can usually be caused by multiple parasites.
- Green aphid. This pest sucks the juice from the leaves of wisteria, which greatly harms it. To cure the plant, gardeners recommend using insecticides.
- Clover mite. The appearance of this parasite is not difficult to notice. The leaves of the creeper acquire a bronze color. The tick spoils not only the decorative appearance of the plant, but also negatively affects its health.It is not difficult to cure wisteria from this ailment, it is enough to apply any acaricide.
- Caterpillars. It is important to carefully observe the plant in order to notice the appearance of such a pest as a caterpillar in time. If you do not take any measures to treat the vine, it can be completely destroyed. Insects feed on perennial leaves, which later become sieve-like.
To avoid the appearance of caterpillars, wisteria is sprayed from time to time with special biological preparations.



How to grow wisteria, see below.




































































































The comment was sent successfully.