How to care for hippeastrum so that it blooms?

One of the most common problems with growing hippeastrum is the lack of flowering. In most cases, the reason is improper care and the creation of uncomfortable conditions for full development. In our article, we will talk about what requirements must be met in order for the plant to delight you with its beautiful flowering.

Features of the flowering period
First, some general information. Hippeastrum belongs to the genus of amaryllis bulbous plants, the birthplace of the culture is the southern part of the American continent. In total, there are about 80 different plant varieties, but thanks to the efforts of breeders, about 600 hybrids of this regal flower have been bred.
Long bloom - about two months. At the end of the dormant period, the plant throws out a long peduncle, the height of which, depending on the variety, varies from 30 to 85 cm, each has 2-4 tubular or funnel-shaped flowers with a diameter of 25-30 cm. The color can be dark red or orange, as well as pink, scarlet or milky white.


Hippeastrum reproduces quite easily - by "children", as well as by seeds or scales of bulbs. Moreover, after pollination of different flowers, you can get a unique flower of a new shade.
In order for hippeastrum to delight you with its decorative flowers, it needs a sufficient amount of light and the obligatory creation of a dormant phase, during which the plant gains strength to prepare a new flowering.
In favorable conditions, flowering occurs twice a year, moreover, experienced flower growers can even achieve the ejection of the peduncle by a certain date.
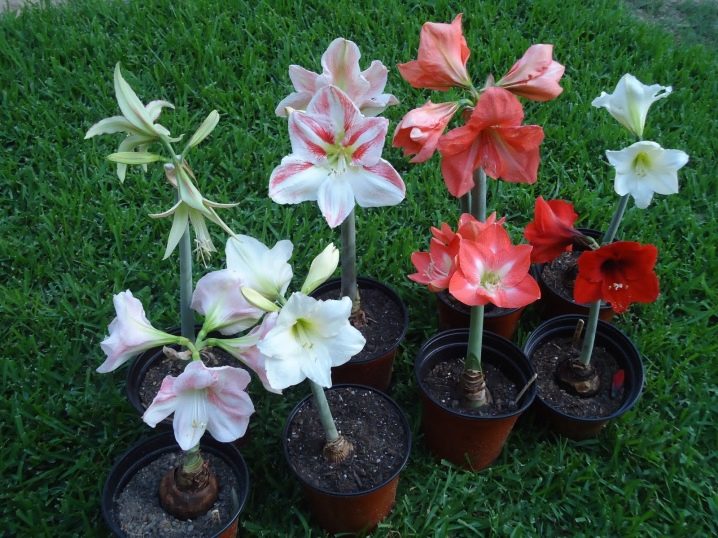

Why doesn't it bloom and what to do?
So, let's dwell in more detail on the factors that lead to the fact that hippeastrum produces only leaves and does not bloom in indoor conditions.
Lack of transfers
Hippeastrum should be planted in rather small containers, so the bulb very quickly sucks out all the nutrients and mineral elements necessary to maintain the normal life of the plant, literally braiding the entire earthen lump with its thin roots. If the root system has become cramped, then the only solution to this problem will be the earliest picking into a container of a larger diameter - it is desirable that the new pot is 3-4 cm wider than the previous one., all resulting voids should be filled with a new nutrient substrate.

Lack of fertilizer
To emit a healthy and strong peduncle, the hippeastrum requires a sufficient amount of phosphorus and potassium fertilizers, so every two weeks it must be fed - for this, it is introduced in turn ground wood ash and superphosphate. You should not use preparations with a high nitrogen content, since in this case the growth of the green mass is stimulated, and the plant no longer has the strength to form the peduncle, in addition, the excess amount of nitrogen preparations makes the plant vulnerable to fungal infections.
When optimizing the feeding regime, you can wait for flowering only for the next season, since the culture needs time to fully enrich it with nutrients and lay strong peduncles for the future period.

Incorrect conditions of detention
To form a flower, the hippeastrum requires comfortable living conditions. You will not see a flower if the temperature regime in the room is not observed, while the phases of active growing season and the dormant period should be clearly distinguished. So, in the summer, the plant will not enter the flowering stage at temperatures less than +20 degrees and excessively high humidity (more than 70%). Hippeastrum does not need foliar spraying and should be avoided even on very hot and dry days.
The most comfortable temperature for throwing out peduncles is considered to be + 23-28 degrees with a humidity level of about 55-65%.

Large pot size
An overly deep container in which hippeastrum is grown can also be the reason for the lack of flowering. The fact is that in such a situation, the plant directs all its forces to the enhanced growth of the main and daughter bulbs, as well as roots and green mass, it simply does not have enough nutrients to set the peduncle. In this case, you will either have to be patient and wait until the bulb reaches the desired size, or transplant the culture into a container of the appropriate volume - it is desirable that the distance between the roots and the walls of the container is about 25-30 cm.
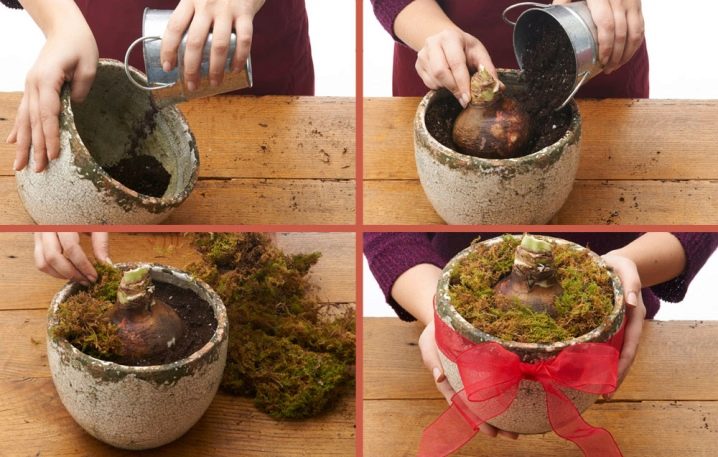

The bulb is too deep
Do not bury the bulb too deeply - it should be buried in the ground by half, or even better - by a quarter. It may seem to novice growers that this is quite inconvenient and the bulb in this case will fall out, however, the plant rather quickly develops and deepens its root system, so that the adult plant is quite firmly held in the substrate, while its upper part will not melt into the ground and into to a lesser extent, it is attacked by insect pests.
To plant the bulb correctly, use a small life hack - visually divide it into 4 parts and then deepen it by 1/4 or 2/4, depending on the original dimensions of the seedling.

Lack of a dormant period
The main condition for the flowering of hippeastrum is a full dormant period preceding the phase of active vegetation, otherwise the culture will not be able to recover after the last flowering and after a year it will simply not have the strength to enter the same phase. Before starting to bloom, the culture must devote all its forces to the formation of the peduncle and the restoration of the deficiency of nutrients.

At the end of flowering, the usual conditions for caring for the plant should not be changed: watering and applying the necessary fertilizers are carried out according to the same scheme for another month, after which all manipulations are completely stopped and the seed pods are removed. The peduncle itself and the leaves are removed only after they themselves begin to die off - visually this is noticeable by the change in density and shade. It happens that the leaves remain elastic - in this case there is no need to remove them, they will not interfere with the resting phase. It is imperative to ensure high humidity and partial shade - this is necessary so that your hippeastrum does not go into increased growth.
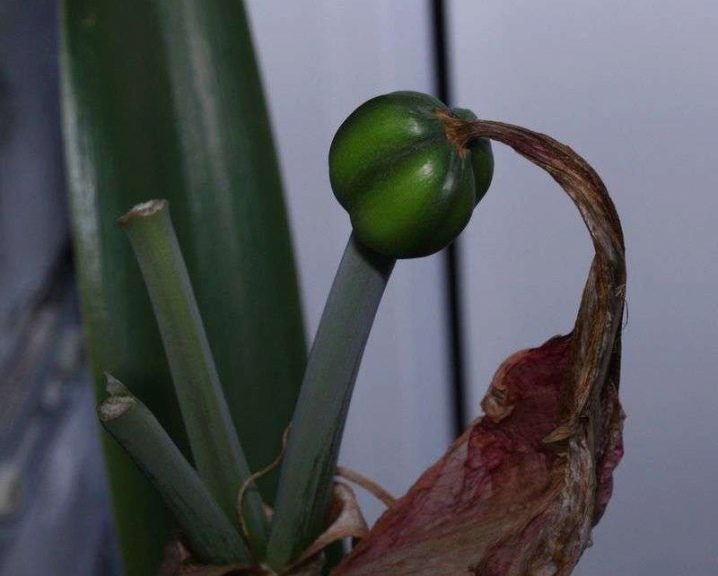

During this period, the flower should be watered once a month, and if the room has high humidity, then irrigation can be completely excluded.
Diseases and pests
Often, the reason for the lack of flowering is the destructive effect of insect pests or disease.
One of the most dangerous infections for the hippeastrum is considered stagonosporosis, which is popularly known as the "red onion burn". The development of such a pathology can be guessed by the appearance of small dots and brown-red stains on the surface of the bulb. If urgent measures are not taken, the disease will spread to the ground part, which will inevitably lead to the death of the flower.
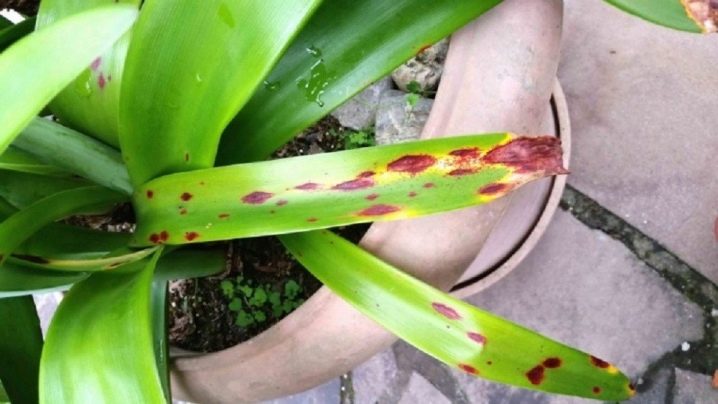
When the very first signs appear, you need to take a sharp, sterilized knife or scalpel, remove the bush from the pot and carefully cut off all the affected areas, touching 4–6 mm of healthy tissue next to the affected area. After that, all sections must be treated with a powdery mixture of "Fundazol" and crushed coal, taken in a ratio of 1 to 1. Then the roots are cleaned of the earth and transplanted into a new container with a new substrate. By the way, the latter is recommended to be additionally treated with a hot solution of potassium permanganate. The bulb is buried quite a bit - this will make it easier to control its condition. When the risk of re-infection has passed, you can slightly add soil to the container and continue caring for the crop as usual.
Late blight and anthracosis plants develop when hippeastrum is grown in open ground, the causative agent of the infection is fungal spores, which, in conditions of high moisture levels, quickly spread to healthy parts of the flower; moreover, if the plant has any mechanical damage or it lacks potassium, the spores spread much faster.


The signs of the disease are the appearance of dark spots on the leaf plates and bulbs, as well as the loss of turgor. As in the previous case, you should cut off all damaged areas, remove diseased sheets, then “powder” all parts of the plant with a mixture of coal and “Fundazol”, and treat the ground with a solution of 1% Bordeaux liquid.

The attack of pests greatly weakens the culture - as a result, not only is there no flowering, but also the general condition of the plant deteriorates significantly, and if timely measures are not taken, then it can die in the shortest possible time. Most often, hippeastrum affects the mealybug, spider and onion mites, as well as the scale insect. To reduce the likelihood of infection with such parasites even at the stage of diving the hippeastrum into the open ground, it is necessary to treat the soil mixture with copper sulfate.
If parasites are found, they must be washed off with a napkin dipped in a concentrated solution of laundry soap, and if this measure is ineffective, then all green parts of the hippeastrum should be treated with insecticide twice with an interval of 2-3 weeks.
How to avoid mistakes in care?
In order to prevent all the difficulties associated with the lack of flowering of the hippeastrum, it is necessary to adhere to the following preventive measures:
- transplant the plant into slightly larger pots every yearso that the new containers exceed the previous ones by 3-4 cm;
- disinfect new substrate - for this, the earth is calcined, subjected to preliminary freezing or treated with a pale pink solution of potassium permanganate;
- follow the rules of vegetation - hippeastrum should not be planted outdoors next to other bulbous plants;
- maintain correct irrigation regime;
- care for a plant - timely apply all the necessary fertilizers;
- provide culture with the necessary resting phase in winter;
- right bury the bulb into the substrate;
- provide hippeastrum growing in open garden plots, protection in rain and strong wind.
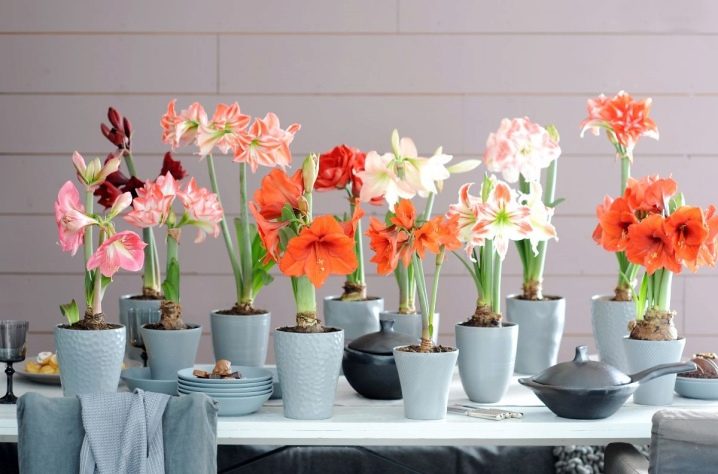

And in conclusion, we will give some useful recommendations.
It happens that the mother's bulb forms "babies" - they need to be planted, then as they grow up, they can also bloom. If you do not do this and leave them, then instead of growing their own roots, they will deplete the mother's bulb. By the way, if the bulb is less than 5 cm in diameter, then it does not need to be sent for winter sleep - first, it must grow a little.

If you think that the peduncle of the hippeastrum is too short and has stopped in its growth and development, then you need to remove the pot from the windowsill and put it on the floor - in this stressful situation for the plant, the peduncles begin to actively search for a source of light, grow and can slightly rise. However, do not overdo it - a thick, but short stem will be much better for holding large flowers than a long, but thin one.
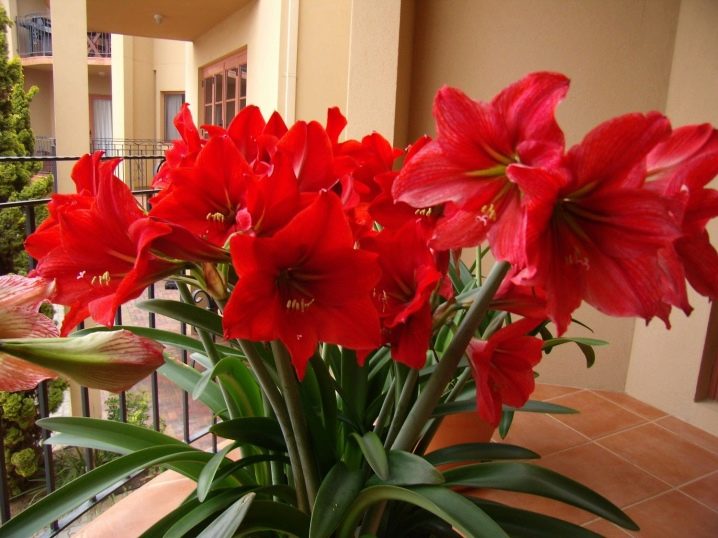

You should not cut off the entire peduncle before hibernation: in its juicy pulp there remains a rather large supply of nutrients that will be useful to the plant.It is enough to remove one seed box, and as soon as the peduncle has given up all its reserves, it will fade, and it will be possible to pull it out of the bulb without any problems.
Before buying a flower, be sure to check all its botanical features. The fact is that some hippeastrum do not require winter dormancy, therefore, deceiving the plant, you will only lead to its death, most often this applies to varieties with orange and yellow flowers.
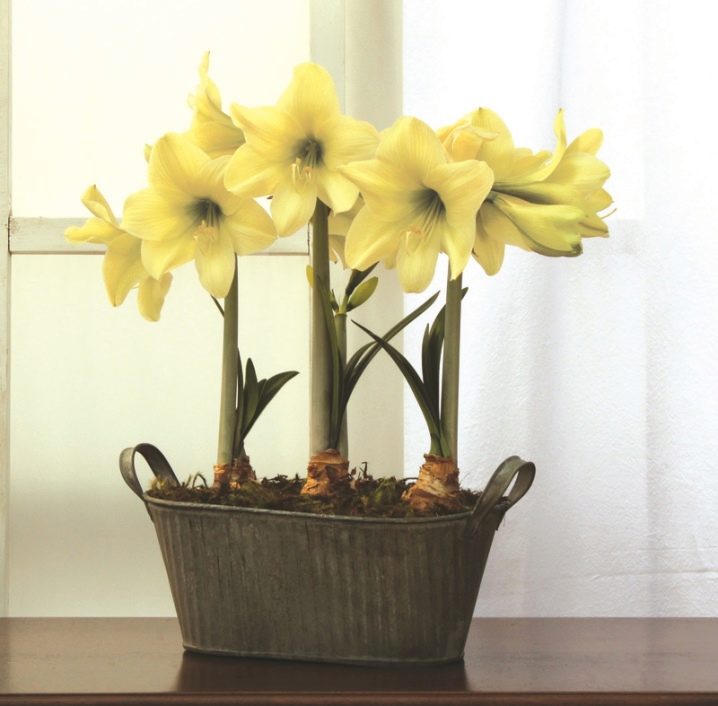

We hope our tips will help you make your hippeastrum bloom at home, especially since the rules here are very simple - in the summer the flower should "walk" more and gain strength from feeding, and with the onset of autumn it should be put to bed, in winter or spring it itself will bloom.
How to prepare hippeastrum for flowering is described in the video.




























The comment was sent successfully.