All About Windmills
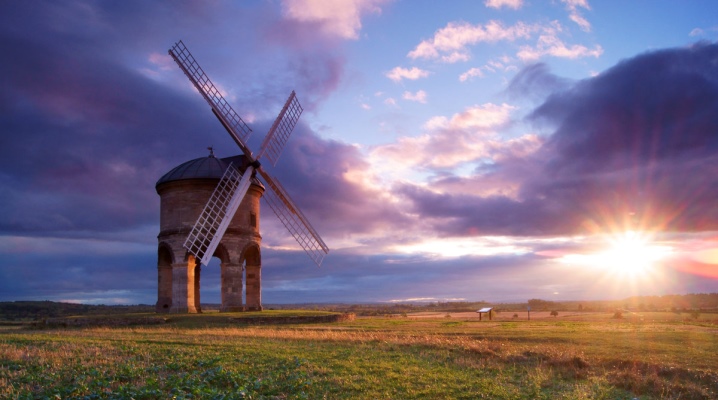

Knowing everything about windmills, what it is and how it works, is necessary not only out of idle interest. The device and description of the blades is not all, you need to understand what the mills are for. Suffice it to say about windmills and their construction for electricity, about other economic value.


History of origin
The mills were created at a time when the mass cultivation of wheat and other cereals began. But they could not immediately use the force of the wind to rotate the structure. In ancient times, the wheels were turned by slaves or draft animals. Later, they began to create water mills. And finally, after all, there was already a wind structure.


Despite its apparent simplicity, in reality, on the contrary, it is very complex. It became possible to create such a product only when taking into account the load from the wind and with the correct selection of the duration of the mechanism for a specific task. And these tasks were very diverse - both chopping wood and pumping water. The earliest models - "goats" - were built in the same way as a wooden house.
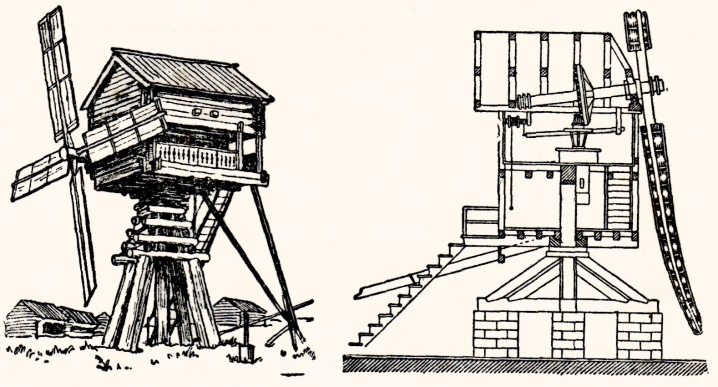
Then the so-called tent mills appeared, which have a fixed body, only the top with the main shaft rotates.
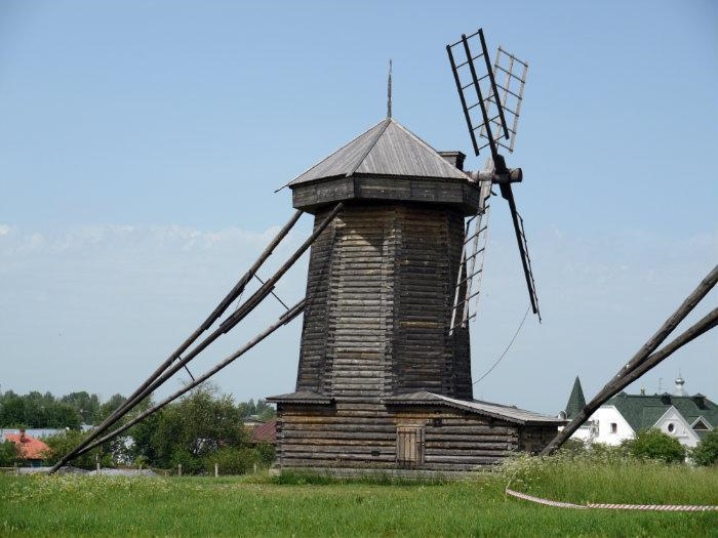

Such models are capable of driving 2 millstones and therefore are distinguished by increased productivity. The mill was considered, which is typical, not just a utilitarian tool. She was given great importance in myths, legends and fairy tales. There were no countries where such ideas were absent. There were various motives of myths: people immured during the construction of the foundation, spirits living at the mill, hidden treasures, mysterious underground passages, and so on.


Device and principle of operation
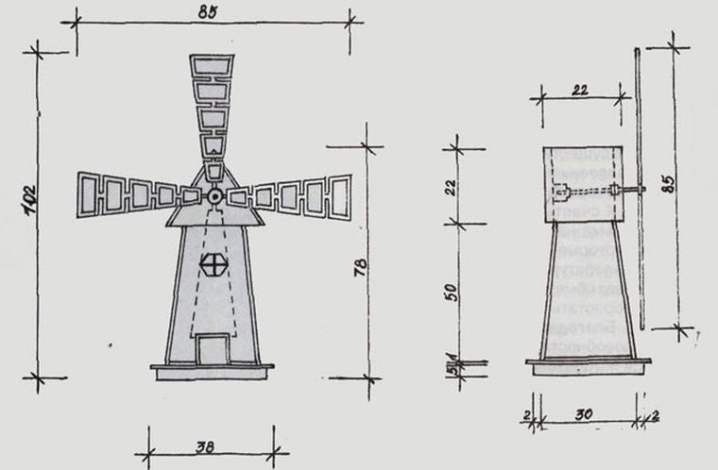
A windmill works because the air currents act on the blades and set them in motion. This impulse goes to the transfer device, and through it - to the actual working part of the mill. In older models, the blades were increased to several meters. Only in this way was it possible to increase the area of contact with air currents. The value is selected in accordance with the main function and the required power.


If the mill is designed with the largest blades, then it can grind flour. This is the only solution that ensures efficient twisting of heavy millstones. Design improvements have been made possible by the development of aerodynamic concepts. Modern technological development makes it possible to provide a good result even with a relatively modest wind contact area.


Immediately behind the blades in the circuit there is a gearbox or other transmission mechanism. In some models, this turned out to be a shaft on which the blades were mounted. The other end of the shaft was equipped with a tool (unit) that performed the work. However, this design, despite its simplicity, was gradually abandoned.
It turned out that it is very dangerous and unreliable, and it is unrealistic to stop the operation of the mill, even in the most serious case.
The gearbox version turned out to be much more efficient and elegant. Gearboxes convert the impulse from the spinning blades into useful work. And it is worth disconnecting the parts of the gearbox, you can quickly stop work. Therefore, the mechanism does not spin in vain, and even a sharp increase in the wind is not so scary. Important: now mills are used exclusively for electricity.


But even the appearance of the first mills was a real revolution in technology. Of course, today 5 - 10 liters. with. on the wing seem to be a completely "childish" size. However, in an era when there were not only motor scooters, but also several centuries before steam locomotives, this turned out to be a tremendous achievement. In the XI-XIII centuries, man received power at his disposal, which was inaccessible in the previous era. The power supply of the economy immediately increased significantly, and that is why, in many respects, a sharp take-off of the European economy became possible during that period.


Advantages and disadvantages
It is most convenient to compare a windmill with a water analogue. The water structure has a long history and is independent of wind changes. Water currents are much more stable. You can also use the force of ebb and flow, which is completely inaccessible for a wind turbine. These circumstances led to the fact that the prevalence of water mills was many times higher in any states of the Middle Ages.


The force of the wind for grinding grain, as already mentioned, began to be applied later. This solution, in addition, entailed significant additional costs. However, in Holland in the 15th century, and especially from the beginning of the 17th century, other advantages of windmills were appreciated. They pushed chains with ladles that removed the groundwater. Without this innovation, it would have been impossible to develop a significant part of the territory of the modern Netherlands.
In addition, a windmill can even stand in a dry place and not be tied to a body of water.
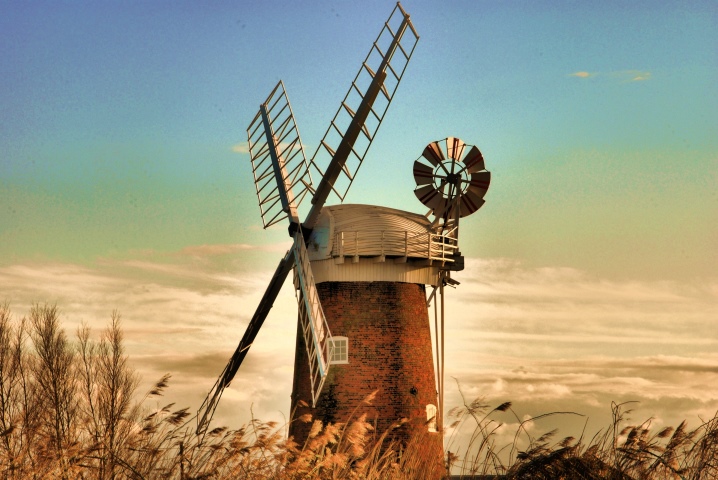

In Holland, windmills became popular for another reason. - there are westerly winds blowing almost continuously, carrying air from the Atlantic Ocean towards the Baltic Sea. Therefore, there were no special problems both with the orientation of the blades and with the use of technology. Nowadays, it is most appropriate to compare windmills with water mills not in terms of quality and grain grinding capabilities, but in terms of suitability for power generation. The stability of the power supply decreases, the cost of network energy rises, and therefore it is so important to choose the type that suits you.


Wind farms operate on virtually infinite resources. As long as the Earth has an atmosphere and the sun illuminates the planet, the winds will not stop. Such devices do not pollute the environment because, unlike diesel and gasoline systems, they do not emit toxic substances. However, it is impossible to call a wind power plant completely environmentally friendly, because it creates a lot of noise, and in a number of countries they even impose legal restrictions on it. Finally, the windmill cannot operate normally during bird migration seasons.
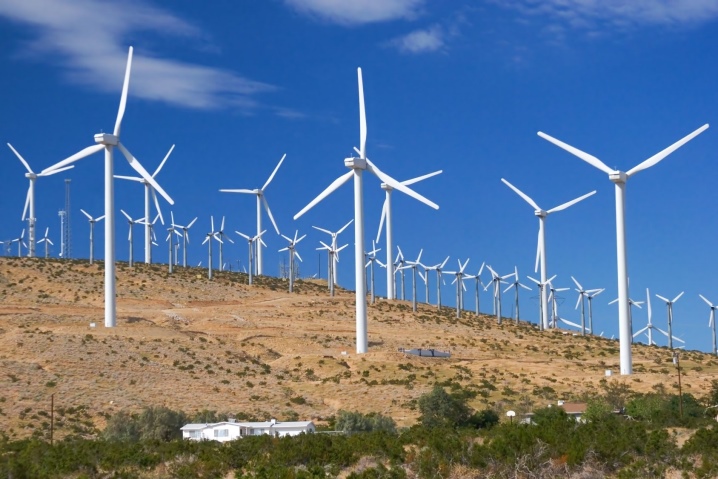

In Russia, there are no noise or calendar restrictions yet. But they can appear at any time. And in any case, a wind farm - both a modern wind turbine and a classic mill - cannot be located in the immediate vicinity of housing. In addition, the real efficiency is determined by the season, time of day, weather, terrain; all this directly affects the air flow rate and the efficiency of its application.


Another disadvantage of the wind farm is the already noted wind instability. The use of batteries partially solves this problem, but at the same time complicates the system and makes it more expensive. Sometimes it is also necessary to additionally use other energy sources. But the windmill is installed quickly - taking into account the preparation of the site, it will take no more than 10-14 days. A lot of space is required for such an installation, especially considering the span of the blades and the space that should be free for safety reasons.
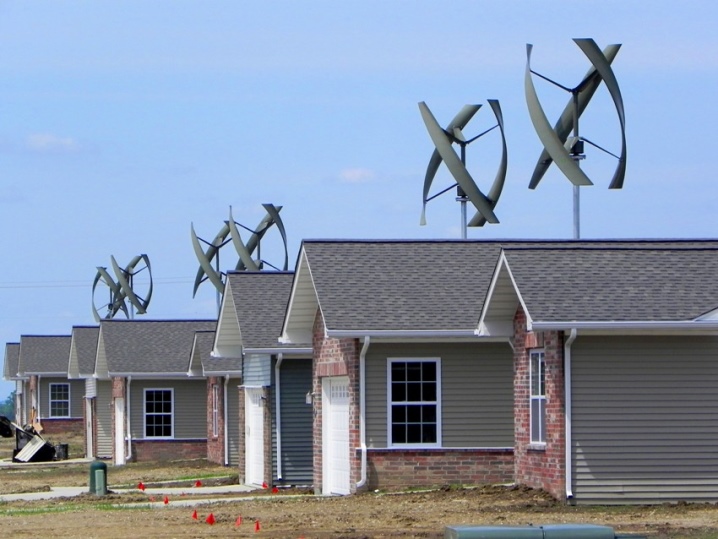

Type overview
Windmills of flour-grinding production worked with 1 or 2 millstones. Turning to the wind occurs in two ways - by gantry and hipped. The gantry technique means that the entire mill is completely rotated around the oak wood post. This pillar was mounted in the center of gravity and not symmetrically to the body. Turning to the wind consumed a lot of energy and was therefore very difficult.
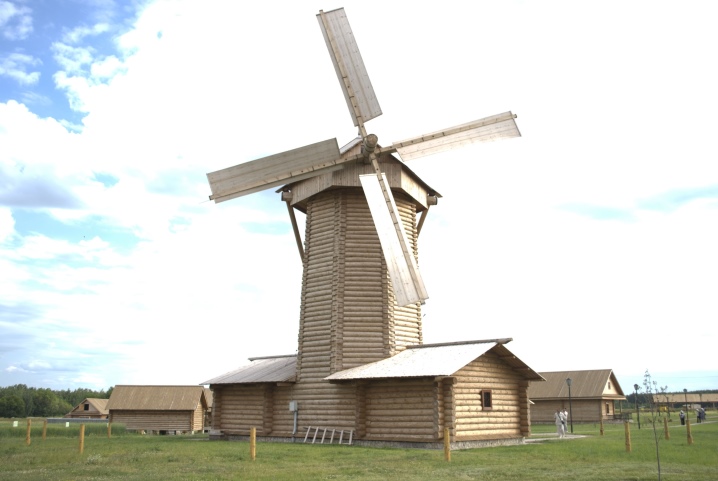

Traditionally, gantry mills have been equipped with a single-stage mechanical transmission. She effectively twisted the stub shaft. The Bock mill was also made according to the gantry method. A more perfect option is a tent (aka Dutch) scheme. In the upper part, the building was equipped with a swing frame that supported the wheel and was crowned with a hipped roof.

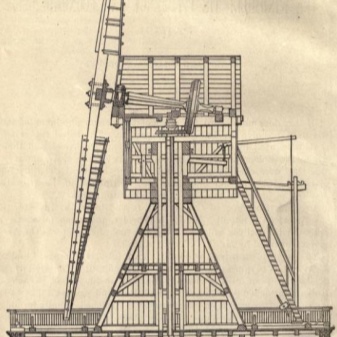
Due to the lightweight construction, turning to the wind takes place with much less effort. The wind wheel could have a very large cross-section, since it was raised to a great height. In most cases, the tent mill was equipped with a two-stage transmission. The intermediate structure is of a quiver type mill. In it, the turning circle was located at a height of 0.5 of the body, an important subspecies is a drainage mill.
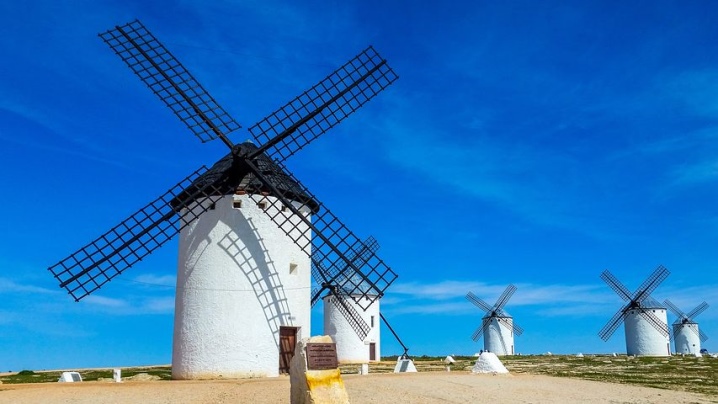

Windmill speed has in the past been limited by the strength of the transmission device. Restrictions were associated with wooden wheel cogs and tarsus. As a result, it is impossible to increase the coefficient of application of wind energy (efficiency). The teeth themselves and the shanks for them were made according to a template from high-quality dry wood. Suitable for this purpose:
- acacia;
- Birch;
- hornbeam;
- elm;
- maple.
The wheel rim of the main shaft was made of birch or elm. The boards were laid out in two layers. Outside, the rim was carefully trimmed in a circle; bolts were used to hold the spokes. The same bolts helped tighten the discs. The main attention in improving the design was paid to the execution of the wings.
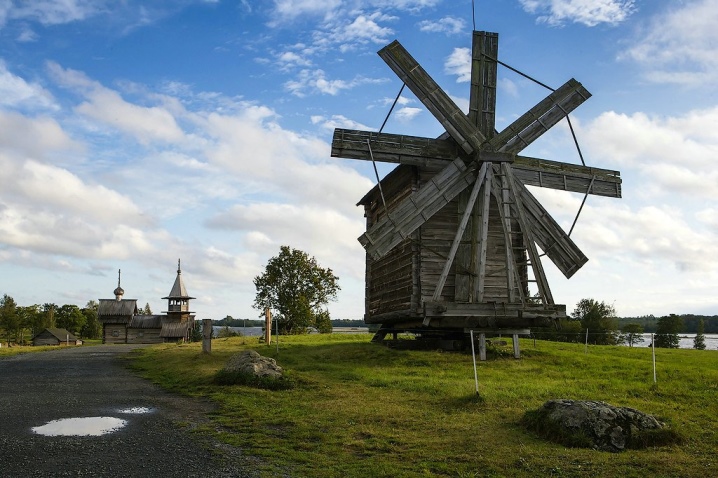

In fairly old mills, the wing grilles were covered with canvas. But later the same function was successfully performed by boards. It was also found that spruce planks fit better. Initially, the wings were created with a constant wedge angle of the blade, which varied from 14 to 15 degrees. It is quite simple to make them, but too much wind energy was wasted.
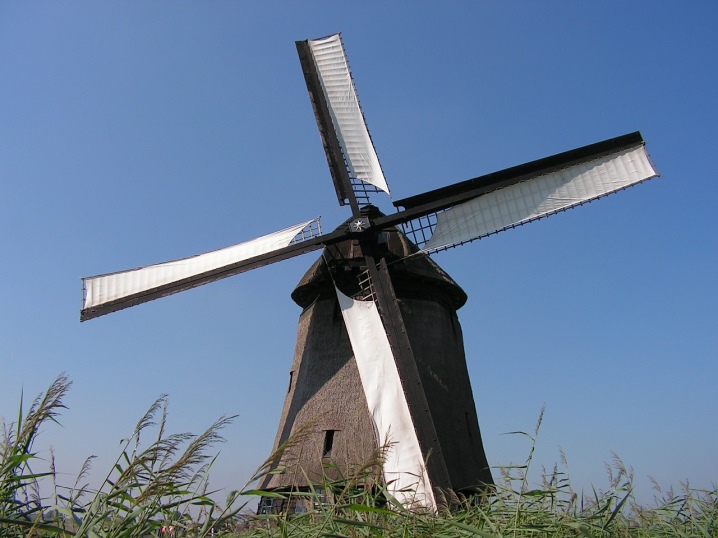

The use of a helical blade made it possible to increase the efficiency up to 50% in comparison with the older version. The variable wedge angle in the tip ranged from 1 to 10, and at the base from 16 to 30 degrees. One of the most modern options is with a semi-streamlined profile. Towards the end of the period of tent mills, they were built almost exclusively from stone. In some cases, of course, the wind system was connected to a water pump, which made it possible to irrigate the land.
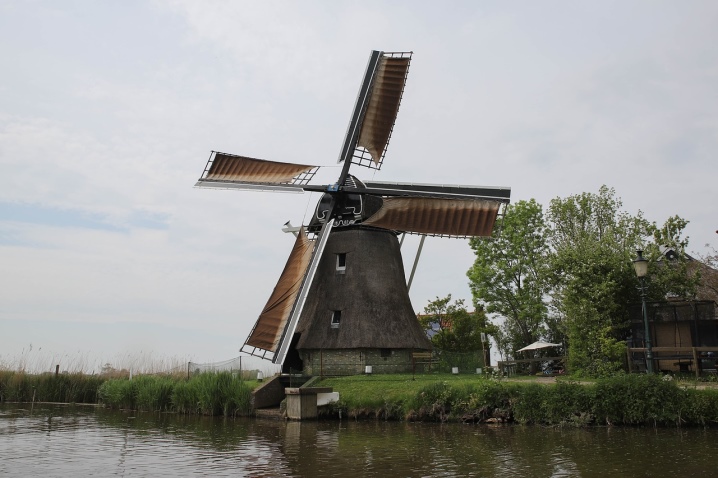

In the earliest type of such structures, as in flour mills, it was possible to reduce the wing area by partially removing the sail or opening the blinds. This solution made it possible to prevent damage even with increased wind. But still there was the problem of a low-speed wind turbine with a large number of blades or with a large wing width. The reason is quite obvious - it’s a very serious, frustrating moment. The solution was found by the German company Kester, which produced the Adler wind wheel with a minimum of blades and a significant distance between them; this design already had an average speed.
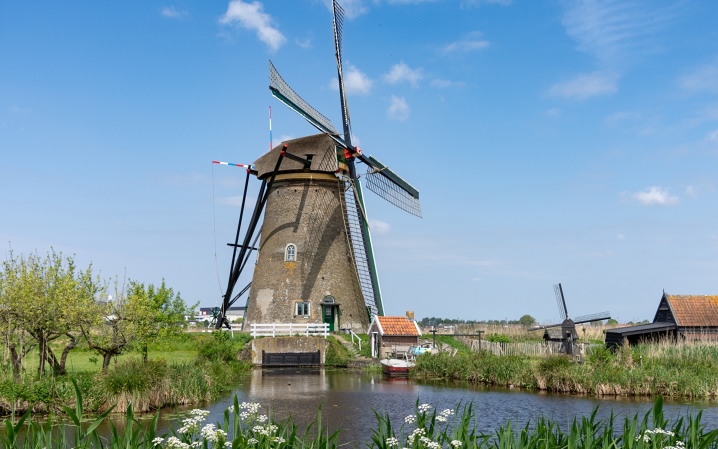

Even more advanced designs on the suction side of the wings were equipped with special valves. Therefore, the adjustment took place automatically, which ensured the highest possible performance. In working condition, the holding of the valves was provided by a spring. Everything was designed so that because of these valves, even with active movement, there was no strong resistance. If the set speed was exceeded due to centrifugal force, the valves were turned.
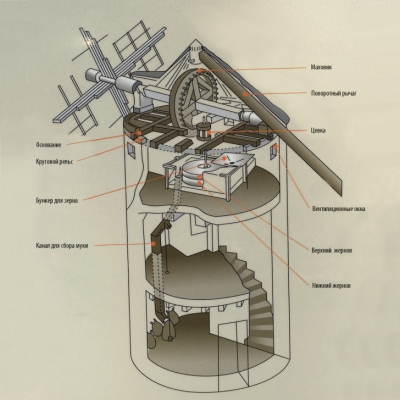
At the same time, the resistance to air flow increased, it was used much less smoothly and not as efficiently as usual. But normally it was possible to reduce the straining moment. During the 18th and 19th centuries, windmills were already used all over the planet. They ceased to be made by semi-handicraft methods, they began to produce multi-blade wind motors made of metal at factories. By the end of the 19th century, only a few models were devoid of the functions of automatic adjustment of the torsion rate and rigid fixation of the wheel in the direction of the motor.

In industrialized countries, hundreds of thousands of sets for mills were already being made a year.... The production of improved economical models, designed primarily to generate electricity, has also begun. The power of such systems is relatively low, usually not exceeding 1 kW, most often it was envisaged to be equipped with wheels with 2-3 paddle-type blades. The connection to the generator takes place through a reducer. To store energy in such systems, batteries of small and medium capacity were used.


Construction features
There are a number of nuances to consider when building a mill.
Seat selection
It is important to consider the rotation of the blades. Therefore, there should be no extraneous buildings and structures nearby. It is advisable to choose a flat area, otherwise the building may be skewed. The site is cleared of all vegetation and other interfering things. They also take into account how everything will look externally.

Tools and materials
You can even build a windmill from plywood, durable plastic or metal. Nobody also forbids combining them. But nevertheless, the classic approach is optimally matched to the use of a wooden board, timber, plywood. Polyethylene is used for waterproofing, and roofing material for the roof. That's why we also need hammers and nails, drills, saws and other tools for wood construction: planers, angle grinders, buckets and brushes.

Foundation
Despite the decorativeness of most windmills, the construction scheme still involves the preparation of the foundation. Digging a hole and pouring mortar is optional. It is quite enough to use the layout of a bar or logs. Usually the design is close to a trapezoid in shape. The inner and outer frames are connected using vertical posts placed at a given angle.


Walls and roof
When covering the structure, pay attention to the openings of windows and doors. The mounting point of the blades is also critical. Doors are installed with auxiliary fasteners. Beams with blades can be reinforced with a bar. Upholstery is possible with any material that provides a hermetically sealed surface, the most colorful is wood.
Roof shape is chosen individually. Smooth and straight coverage is no worse than an angle set. A layer of roofing material will provide sufficient waterproofing. The front roof is obtained using boards or plywood. There is no need to use more decorative finishes.



Installation of a wind generator
The mill should be placed on a dry, prepared area. Anchors are used as needed to ensure the rigidity of the anchorage. Be sure to check with laws and regulations so as not to have problems. In any case, the recommendations for electrical safety and grounding are also followed. It is necessary to connect the generator through wires of a certain section and in "street" insulation.


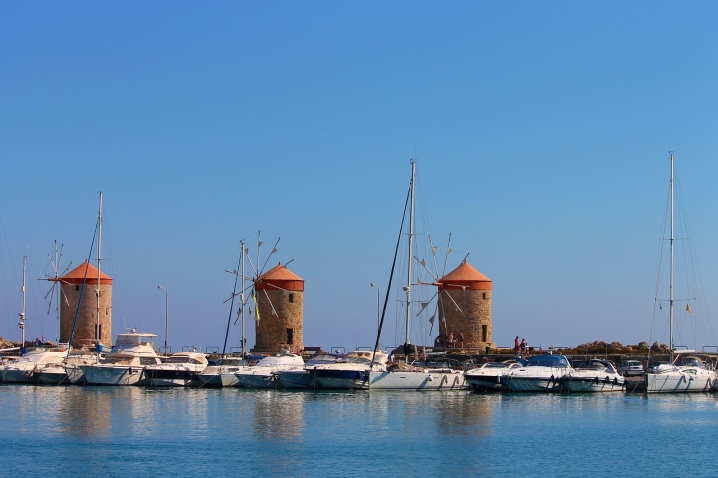
The most famous old mills
Rhodes mills, located near the port of Mandrnaki, crushed grain for a very long time, which was delivered directly to the harbor by sea. Initially, there were 13 of them, according to other sources - 14. But only 3 have survived to our time and are preserved as monuments. On the island of Öland, the situation is approximately the same - instead of 2,000 mills, only 355 survived. They were dismantled at the beginning of the last century, because the need disappeared, fortunately, the most beautiful buildings survived.

Also worth noting:
- Zaanse Schans (north of Amsterdam);
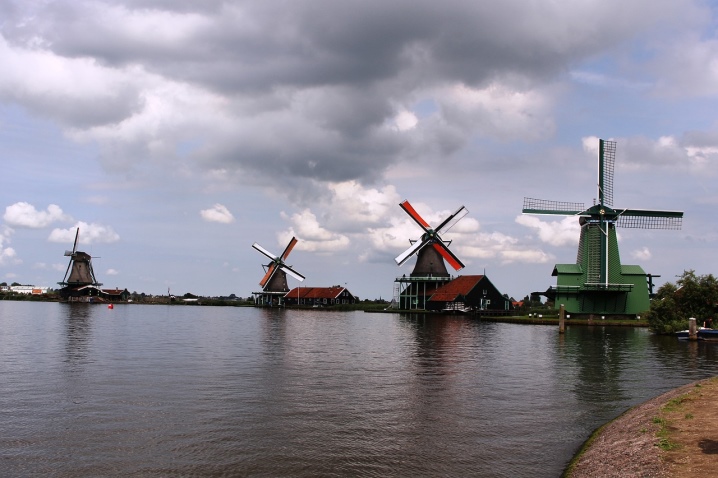

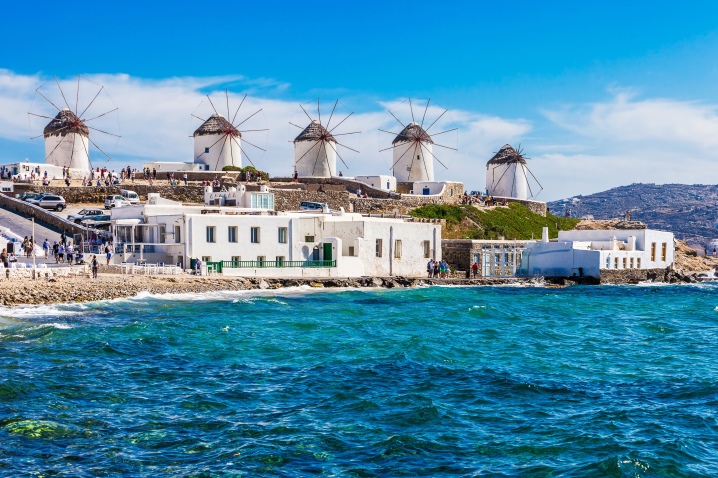
- the mills of the islands of Mykonos;

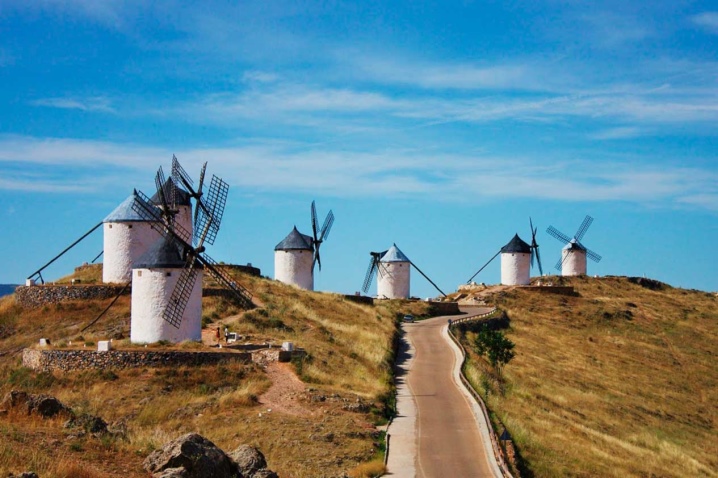
- the city of Consuegra;

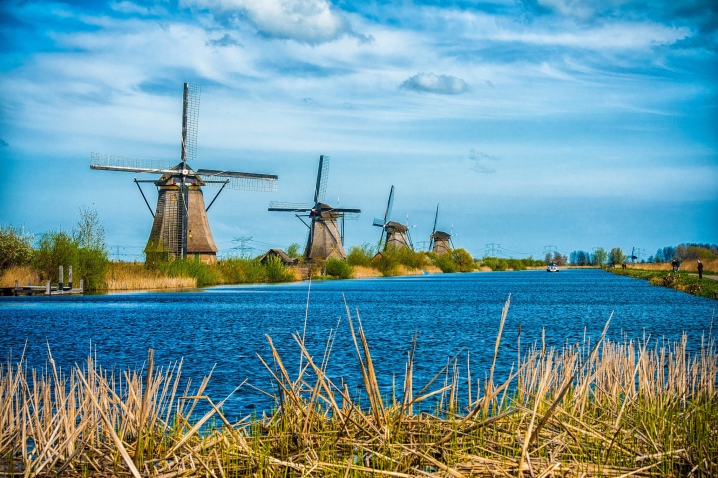
- the Kinderdijk mill network;

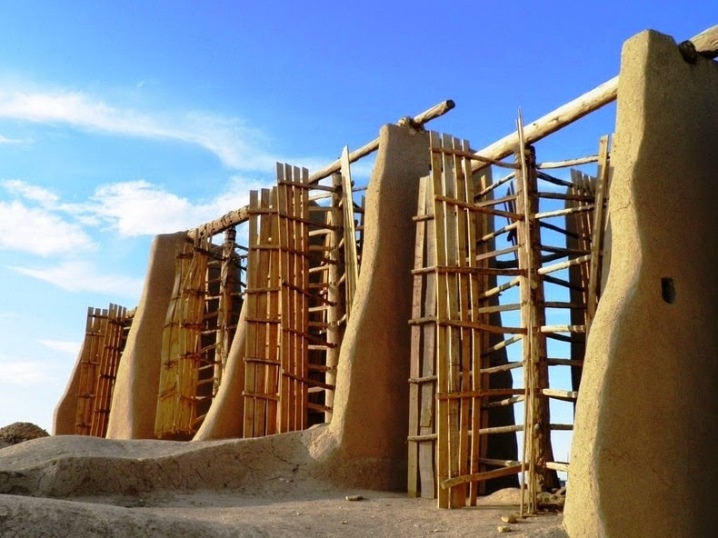
- windmills of Iranian Nashtifan.














Thanks. Very valuable material. I want to build a mill. I will share a story with you. I grew up in a big village. After the war, it decreased by more than 2 times. And before the war there were 700 households and 3.5 thousand inhabitants. It was divided into 2 parts by a small rivulet, stretching for more than 3 km. And from each line there were also branches of other streets, forming, as it were, a comb. At the top of each scallop were huge squares, which included the central square, and above it, a forest of windmills. On one side there were 53 windmills, on the other - 35. In addition, there was a water mill on the river, and beyond the village (on the other river) there were 2 more water mills, one of which worked all year round. In the center of the village there was a mechanical mill called Corpus. All this was destroyed, demolished and destroyed during collectivization in the 30s, at the direction of the delegates who came from above. The millstones of each mill were broken into small stones. The mechanical was transported to the regional center (it is still some kind of flour milling enterprise). And only in the place of the Corps (on the remains of the structure) was the flour-grinding mechanic allowed. And they took a garnet (bucket scoop) of flour for grinding the bag. People picked up the remains of the stones and began to invent table mechanical mills for themselves. But the villains went through and checked all the houses. Everything that was destroyed. Oh, how good the mills are in Holland ...
The comment was sent successfully.