Synchronous generator: device, types and applications
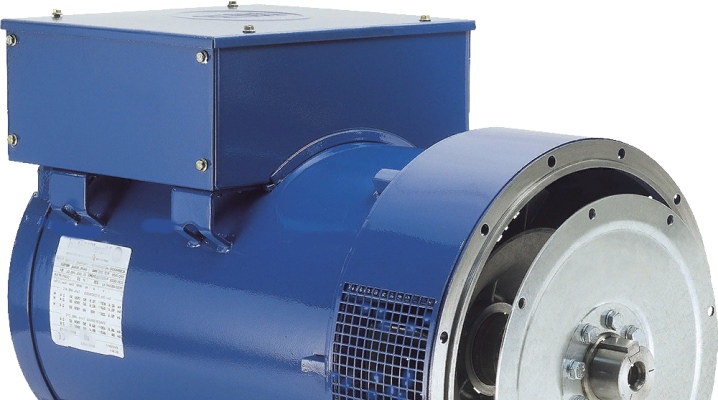

A synchronous generator is a special device through which it is possible to convert any energy into electrical energy. Such devices are mobile stations, thermal or solar batteries, and special equipment. Depending on the type of generator, the possibility of its use is determined, so it is worthwhile to understand in more detail what the device is.


History of creation
At the end of the 19th century, Robert Bosch's company first developed something similar to a generator. The device was capable of igniting an engine. During the tests, it was revealed that the machine is not suitable for permanent use, but the developers were able to improve the apparatus.
In 1890, the company almost completely switched to the production of this equipment, as it gained great popularity. In 1902, a student of Bosch created an ignition using high voltage. The device was able to produce a spark between the two electrodes of the candle, making the system more versatile.
The beginning of the 60s of the XX century was the era of the spread of generators around the world. And if earlier the devices were in demand only in the automotive industry, now such units are able to provide whole houses with electricity.

Device and purpose
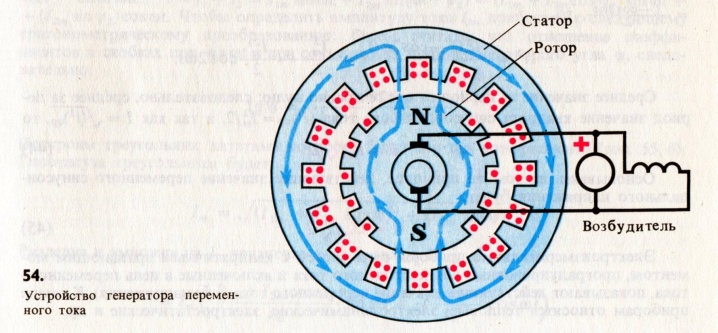
The design of such units involves only two main elements:
- rotor;
- stator.
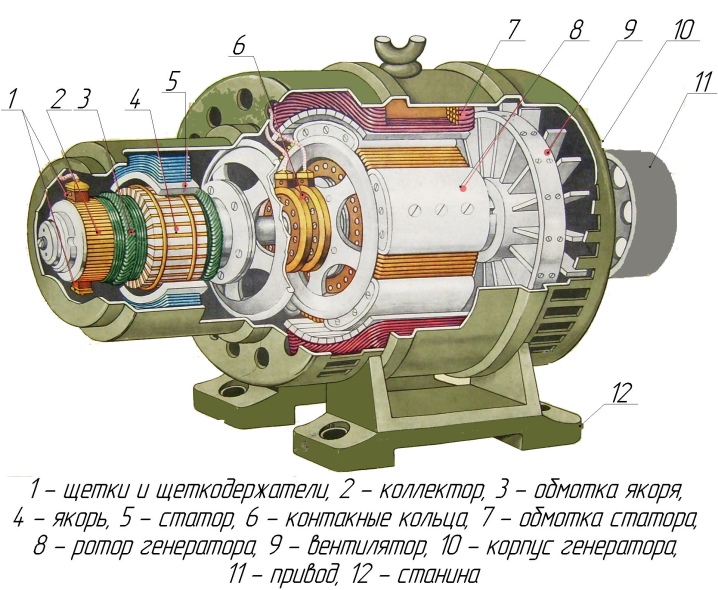
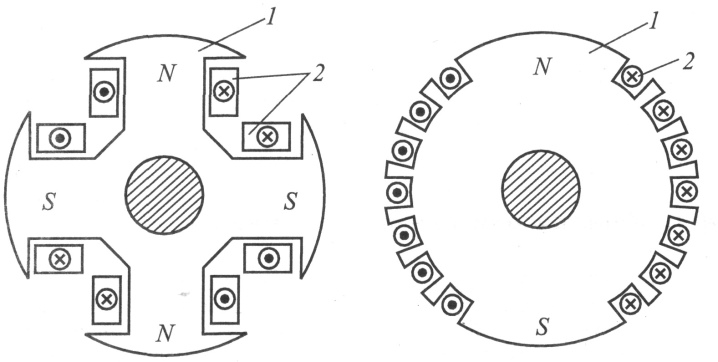
In this case, additional elements are provided on the rotor shaft. These can be magnets or field windings. Magnets have a toothed shape, the poles for receiving and transmitting current are directed in different directions.
The main task of the generator is to convert one type of energy into electrical energy. With its help, it is possible to provide the required amount of current to dependent devices so that they can be used.
Specifications
To assess the performance of a generator, you need to look at its characteristics. In principle, they are the same as for a station that generates direct current. Several factors are the main parameters of the assessment.
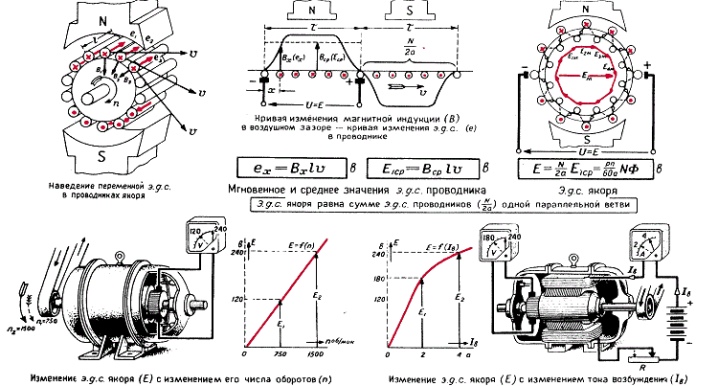
- Idling. It represents the dependence of the EMF on the strength of the moving currents responsible for the excitation of the damper coil. With its help, it is possible to determine the ability of the chains to magnetize.
- External characteristic. Implies a parallel relationship between coil voltage and load current. The value depends on the type of load applied to the device. Among the reasons that can cause changes, there is an increase or decrease in the EMF of the unit, as well as a voltage drop across the windings of the installed coil, which is placed inside the device.
- Adjustment. Represents the relationship that forms between field currents and load currents. Ensuring the operability and protection of synchronous units is achieved by monitoring this indicator. This is easy to achieve if you constantly adjust the EMF.
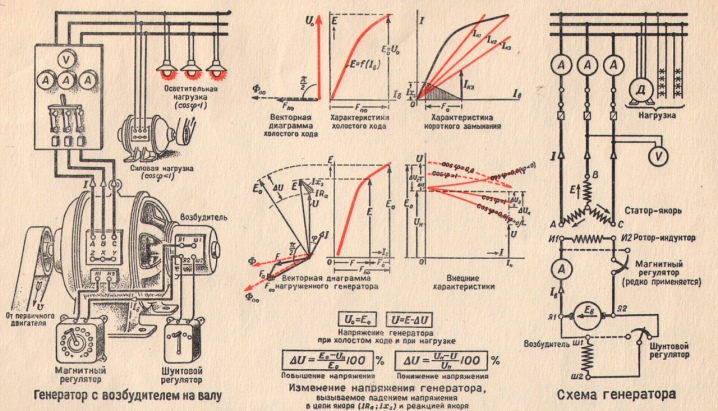
Another important parameter is power. The value can be determined by means of EMF, voltage and angular resistance indicators.
Operating principle
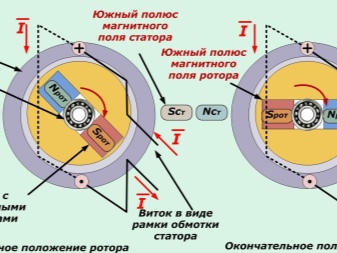
It's not so difficult to figure out how the device works. It consists in rotating a magnetic frame in order to create an electric field. In the process of rotating the frame, magnetic lines appear that begin to cross its contour.The crossing contributes to the formation of an electric current.
To determine where the flows of electrical energy are moving, it is necessary to use the gimbal rule. It should be noted that in some areas the current movement is opposite. The directions are constantly changing when you reach the next pole, which is located on the magnet. This phenomenon is called alternating current, and the connection of the frame to a separate magnetic ring can prove this condition.
The relationship between the magnitude of the current in the frame and the speed of rotation of the rotor of the system is proportional. Thus, the more the frame rotates, the more electricity the generator can supply. This indicator is characterized by the rotational speed.
According to the established standards, the optimal speed indicator in most countries should not exceed 50 Hz. This means that the rotor must perform 50 vibrations per second. To calculate the parameter, it is necessary to agree that one rotation of the frame leads to a change in the direction of the current.
If the shaft manages to turn 1 time per second, this means that the frequency of the electric current is 1 Hz. Thus, in order to achieve 50 Hz, it will be necessary to ensure the correct number of frame rotations per second.
During operation, the number of electromagnet poles often increases. They can be delayed by reducing the speed at which the rotor rotates.
The dependence in this case is inversely proportional. Thus, to provide a frequency of 50 Hz, it will be necessary to reduce the speed by about 2 times.
In addition, it should be noted that in some countries other rotor rotation rates are set. The standard frequency is 60 Hz.
Views
Today manufacturers produce several types of synchronous generators. Among the existing classifications, several deserve special attention. First of all, it is worth considering the division of units by design. Generators are of two types.
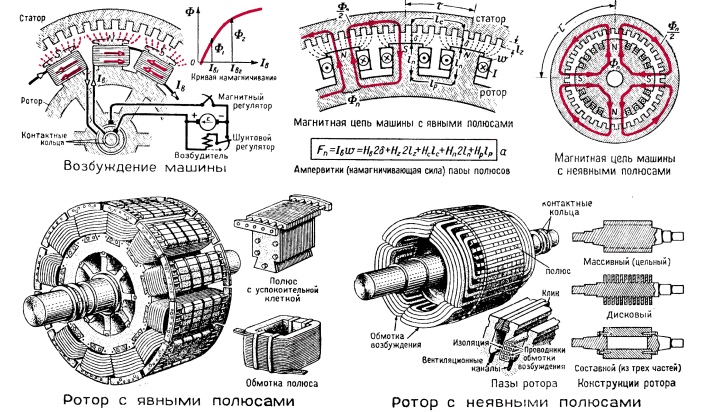
- Brushless. The design of the generator implies the use of stator windings. They are placed so that the element cores are aligned with the direction of either the magnetic poles or the cores that are provided on the coil. The maximum number of magnet teeth should not exceed 6 pieces.


- Synchronous, equipped with an inductor. If we are talking about adjusting machines operating at low power, then DC magnets are used as a rotor. Otherwise, the rotor is the inductor winding.


The following classification implies the division of mobile stations into separate types.
- Hydrogenerators. A distinctive feature of the device is a rotor with pronounced poles. Such units are used to generate electricity where there is no need to provide a large number of revolutions of the device.
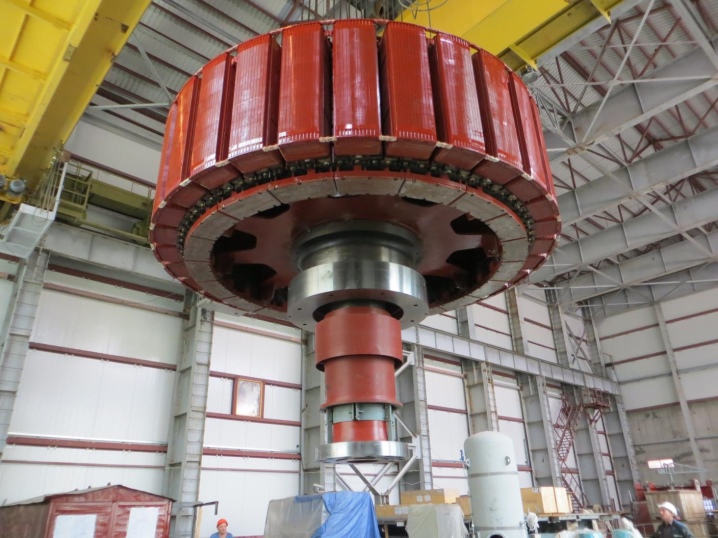

- Turbine generators. The difference is the absence of pronounced poles. The device is assembled from various turbines, it is capable of increasing the number of rotor revolutions several times.
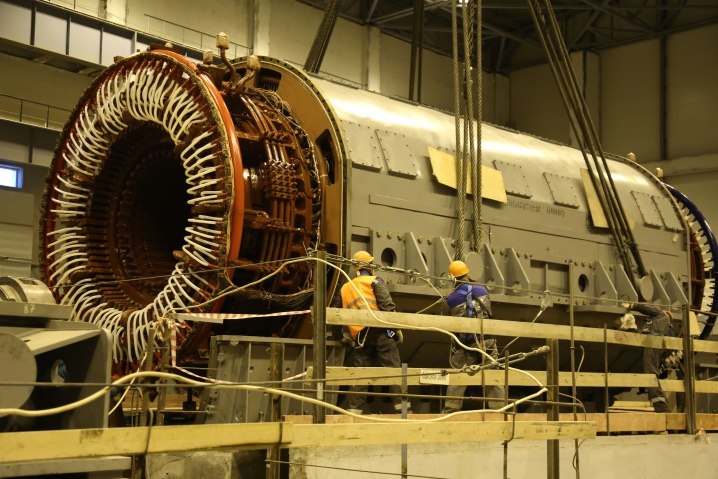

- Synchronous expansion joints. It is used to achieve reactive power - an important indicator in industrial facilities. With its help, it is possible to improve the quality of the supplied current and stabilize the voltage indicators.
There are several common models of such devices.
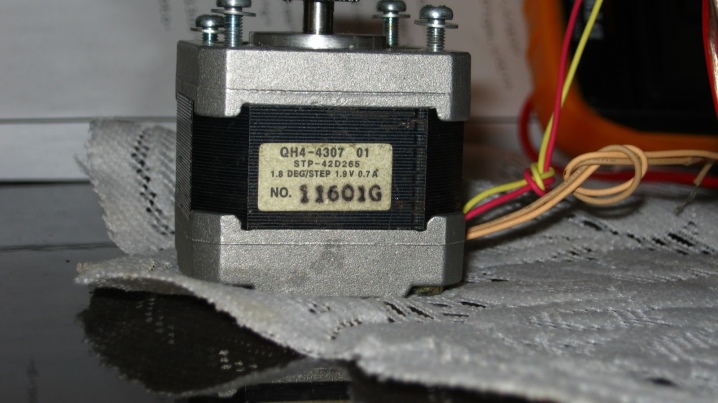
- Stepper. They are used to ensure the operability of drives installed in mechanisms that have a start-stop cycle.

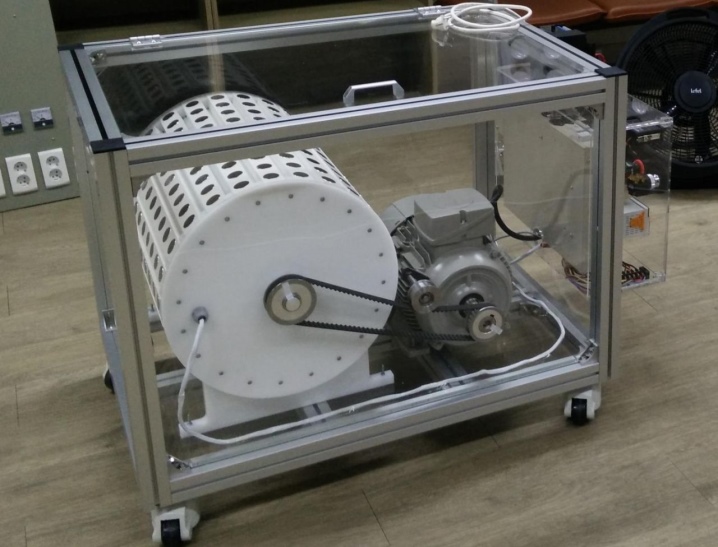
- Gearless. Mostly used in stand-alone systems.

- Contactless. They are in demand as main or backup mobile stations on ships.
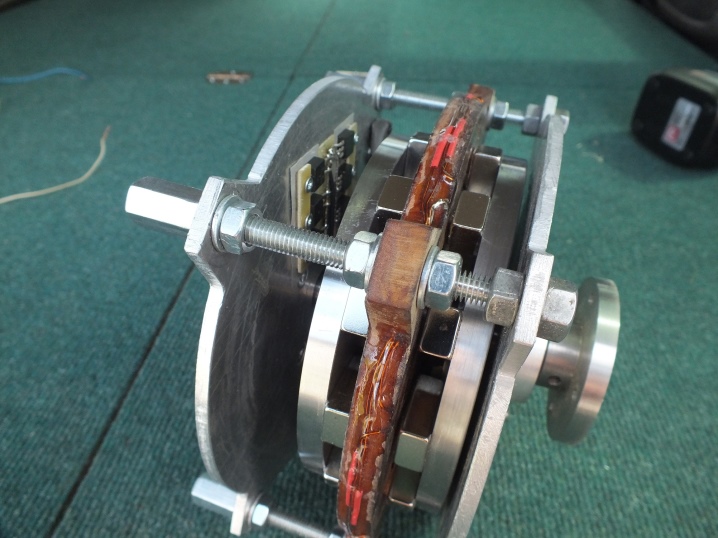

- Hysteresis. Such generators are used for time counters.
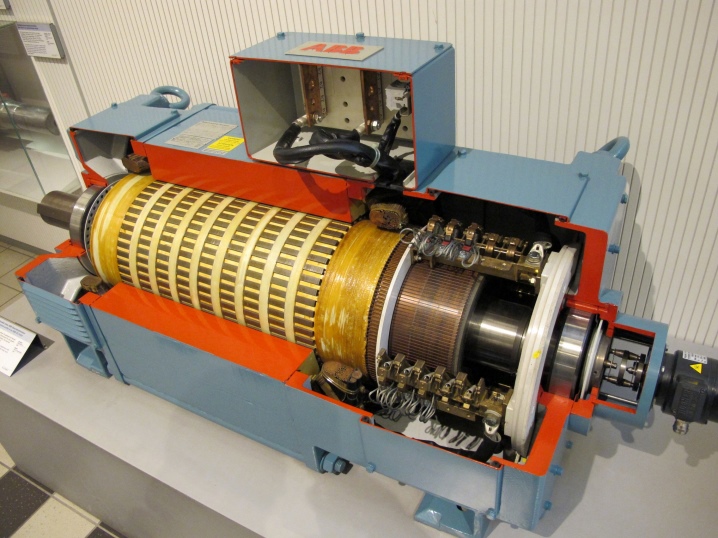

- Inductor. Ensure the operation of electrical installations.
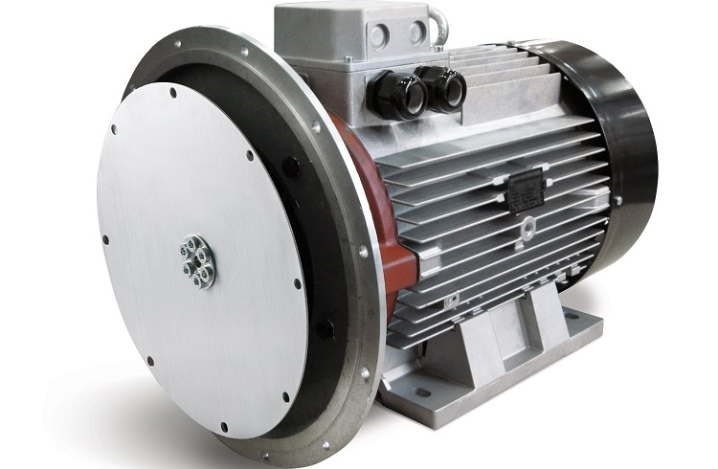

Another type of unit division is the type of rotor used.In this category, generators are divided into salient-pole and implicit-pole devices.
The first are devices in which the poles are clearly visible. They are distinguished by a low rotor speed. The second category has a cylindrical rotor in its design, which does not have protruding poles.
Application area
Synchronous generators are devices designed for the production of alternating current. You can meet such devices at various stations:
- atomic;
- thermal;
- hydroelectric power plants.
And also the units are actively used in transport systems. They are used in various vehicles and ship systems. The synchronous generator is capable of operating both autonomously, separately from the electrical network, and simultaneously with it. In this case, it is possible to connect several units at once.
The advantage of AC power plants is the ability to provide the allocated space with electricity. Convenient if the object is located far from the central network. Therefore, the units are in demand among the owners of farms located in settlements remote from the city.


How to choose?
When choosing a generator, it is important to find a suitable and reliable device that can provide electricity to the allotted area. First you need to decide on the technical parameters of the future device. Experts advise paying attention to:
- the mass of the generator;
- dimensions of the device;
- power;
- fuel consumption;
- noise figure;
- duration of work.
And also an important parameter is the ability to organize automatic work. To understand how many phases a future generator needs, it is necessary to determine the type and number of electrical appliances that will be connected to it.
For example, only consumers with one phase can be connected to a single-phase electric generator. Three-phase significantly expands this indicator.
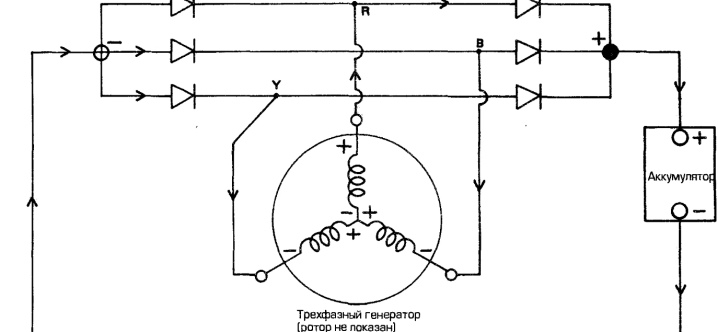
However, the purchase of such a mobile power plant is not always the best decision.
Before purchasing, it is additionally recommended to take into account the load that will be exerted on the device during its operation. Each phase should be loaded with a maximum of 30% of the total. Thus, if the power of the generator is 6 kW, then in the case of using sockets with a voltage of 220 V, it will be possible to use only 2 kW.
The purchase of a three-phase generator is in demand only when there are many three-phase consumers in the house. If most of the appliances are single-phase, it is better to purchase an appropriate unit.
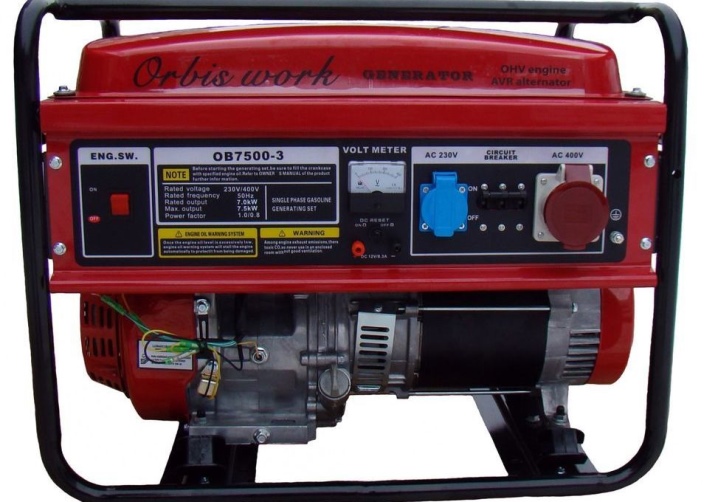

Exploitation
Before starting the generator, it must first be adjusted. First of all, they adjust the frequency of the device. This can be done in two ways:
- change the design of the unit, having foreseen how many poles are necessary for the operation of the electromagnet;
- provide the required shaft speed without any design changes.
A striking example is low-speed turbines. They provide a rotor rotation of 150 rpm. To adjust the frequency, use the first method, increasing the number of poles to 40 pieces.
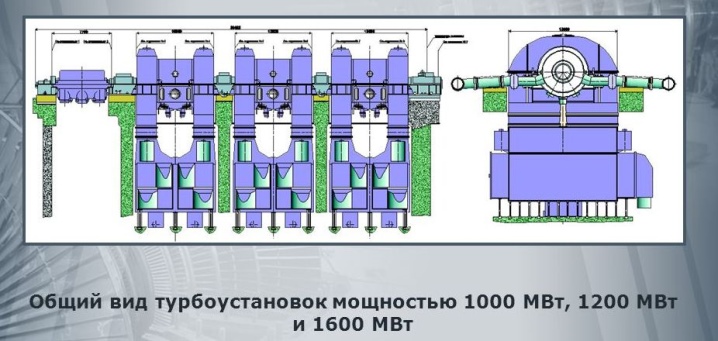
The next parameter to be configured is EMF. It becomes necessary to adjust due to changes in the characteristics of the incoming loads acting on the mobile station.
Despite the fact that the EMF of the induction of the device is associated with the rotor and its rotations, due to safety requirements, it is impossible to disassemble the structure in order to change the parameter.
The EMF value can be changed by adjusting the generated magnetic flux. It will need to be increased or decreased. The winding turns, or rather, their number, are responsible for the value of the indicator. And also the power of the magnetic flux can be influenced by the current generated by the coil.
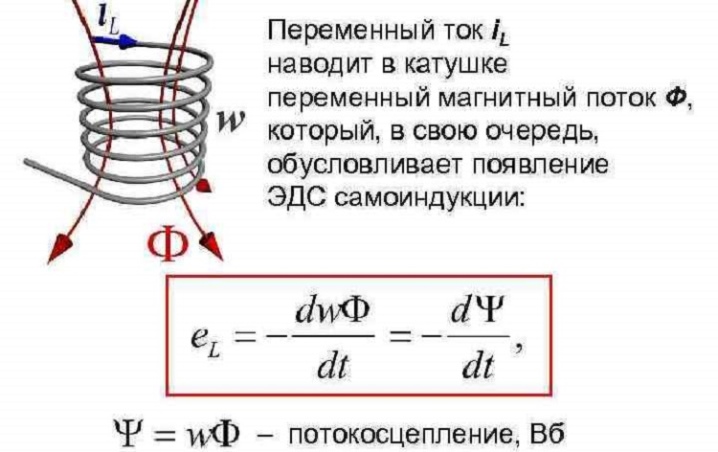
Adjustment involves the inclusion of several coils in a chain.To do this, you need to use additional rheostats or electronic circuits. The second option requires setting the parameter using external stabilizers. This ensures reliable service.
The advantage of a synchronous mobile station is the ability to synchronize with other electric machines of a similar type. At the same time, during connection, it is possible to match the rotation speeds and ensure a zero phase shift. In this regard, mobile power plants are in demand in industrial power engineering, where it is very convenient to use them as a backup power source to increase production capacity in case of heavy loads.
See below for synchronous and asynchronous generator.













The comment was sent successfully.