Varieties and selection of lock nuts

The topic of varieties and selection of lock nuts is very relevant for any home craftsman. There are modifications with an M8 ring and an M6 collar, nuts with a lock in other sizes. To figure out what these fasteners are and how to tighten them, studying GOST is not enough - you will have to pay attention to other nuances and familiarize yourself with the recommendations for use.


What it is?
The best way to explain what a lock nut is is to compare it with conventional samples. The "classic", when interacting with the bolt, guarantees a completely reliable connection. But this persists only until stable intense vibrations appear. After some time, they break the mechanical adhesion, and weakening, unscrewing begins. In theory, the stopper can be provided with locknuts and lock washers.

However, such a solution unnecessarily complicates and increases the cost of the design. In addition, the more links in the system, the lower its reliability and stability.
That is why lock (self-locking) nuts are in great demand, and their importance only grows over the years. There are quite a few types of such fasteners. The release of lock nuts in Russia is regulated by GOST standards.
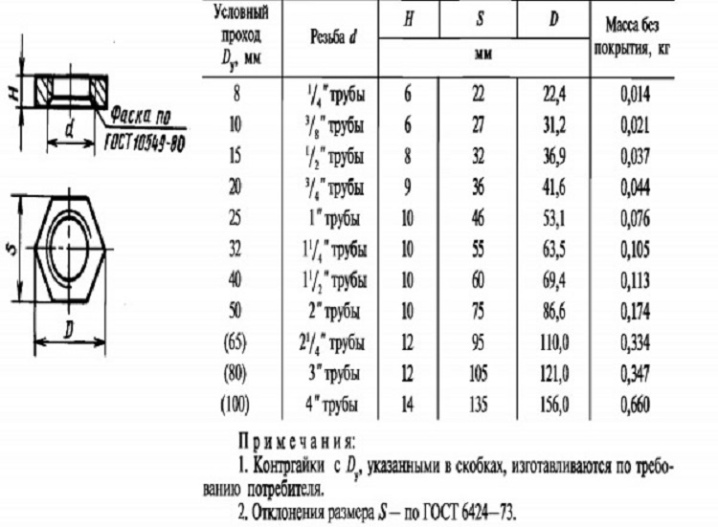
So, hexagonal steel nuts with automatic locking must meet GOST R 50271-92. Products without galvanic coating are designed for temperatures from -50 to 300 degrees. In the presence of electroplating, the maximum permissible heating is 230 degrees. If the nut contains inserts made of non-metallic materials, the critical temperature level is 120 degrees. The standard regulates:
-
test load voltage;
-
Vickers hardness level;
-
Rockwell hardness level;
-
the amount of torque.
Self-locking nuts can save the prevailing torque even with multiple tightening and unscrewing. The chemical compositions of the steels used are also standardized. The nut inserts responsible for the prevailing torque cannot be made from steel alloys - completely different materials are needed for this purpose. Fasteners made of free-cutting steel also comply with the standard (if its use does not violate the supply agreement). The highest sulfur content in nut steel should be 0.24%.
The regulation strictly prohibits the use of hydrogen brittle material. This is especially important when applying special coatings.

If they are used, special technological methods must be applied that will reduce the risks due to hydrogen embrittlement. When testing nuts with a test load, stripping or crushing of the thread is unacceptable.
The standard strictly stipulates the temperature requirements during operation - stable use at an air temperature of + 10 to + 35 degrees. If necessary, an additional study of these properties can be carried out by means of a full-scale test. The standard covers self-locking nuts made of solid metal or with non-metallic elements that have:
-
triangular cutting ISO 68-1;
-
combinations of diameters and pitches specified in ISO 261 and ISO 262;
-
large groove gap (M3 - M39);
-
small groove gap (М8х1 - М39х3).

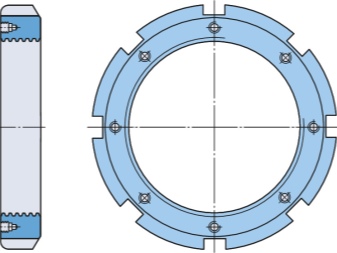
Overview of types and sizes
In one of the options, the "interference" method is used. The thread has some positive tolerance. When the part is twisted, intense friction is created between the turns. It is this that fixes the fasteners on the bolt rod; the connection will not lose stability even with strong vibration.
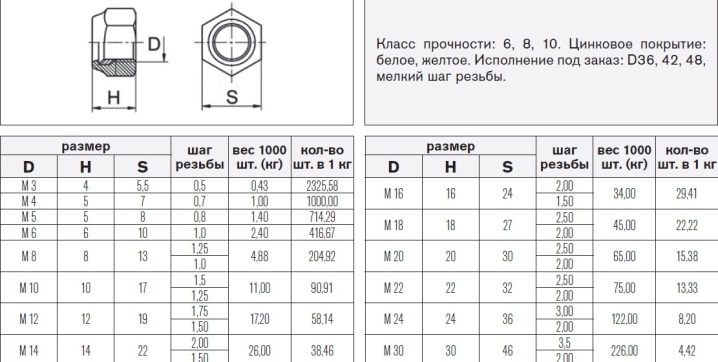
However, there is an increasing demand for the lock nut according to the DIN985 standard; it is equipped with nylon rings, and this solution also allows you to damp (absorb) vibrations.
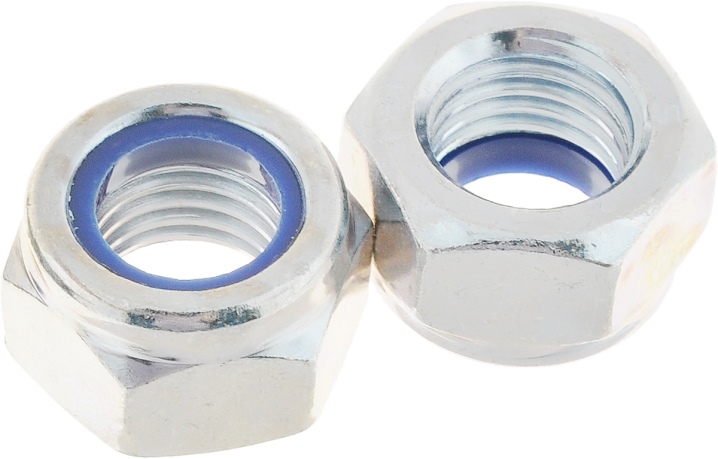

Some versions come with a nylon ring. Usually their size ranges from M4 to M16. Fasteners with an insert can be of strong or extra strong design. Most often, it is supposed to be used in conjunction with a bolt (screw). In some cases, additional equipment with a washer is practiced; its role is to reduce the risk of untwisting the connection.

Sometimes the self-locking nut has a flange - it is easily recognizable by its hexagonal shape. There are also versions with a collar, which additionally aids in locking. As for the size, everything is simple and strict here:
-
M6 - from 4.7 to 5 mm high, the grip height for the key is at least 3.7 mm;
-
M8 - with a groove pitch of 1 or 1.25 mm (the second option is standard, other dimensions are indicated in the order and in the marking);
-
M10 - standard height from 0.764 to 0.8 cm, with the lowest level of key grip 0.611 cm.



Appointment
Obviously, lock nuts are in demand in almost any application where reliability is needed, despite powerful continuous vibration vibrations. They are especially important in aircraft. You can find a lot of self-locking nuts in any plane, helicopter, and even in many large UAVs. Of course, such products are also widely used in the automotive industry. But self-locking nuts are also used in the production of construction vibratory rammers and jackhammers, as well as a number of other equipment.


What to consider when choosing?
All-metal products are good where small local distortion of the thread is acceptable. It is useful to be interested in whether the compression was performed by the radial method, by the axial method, at an angle to the axial thread from the end or at an angle to it from the end ledge. As for models with a spring-type threaded insert, they are equipped with a crimped coil, which guarantees the elasticity and reliability of the fastener clamping. All such products must have screw-in and out-out torques in accordance with the requirements of ISO 2320. The flange is welcome - it increases overall reliability.
When purchasing large quantities of nuts, you must have a special torsion torque meter. Torque wrenches with an error of 2% or less are suitable as a replacement.
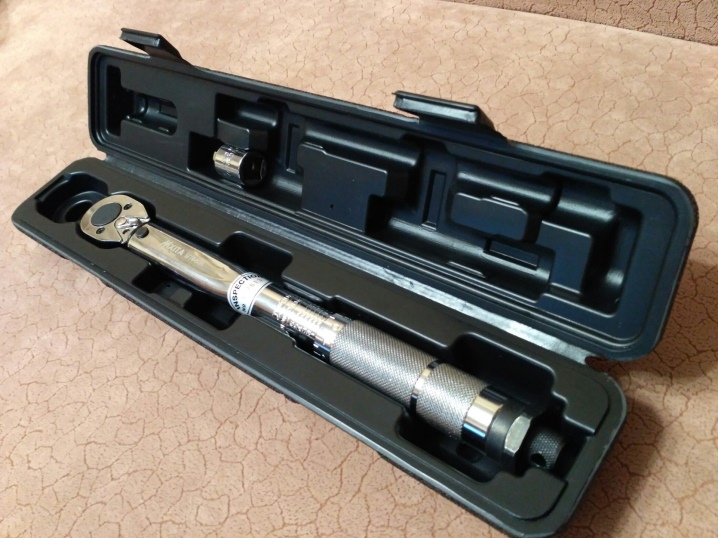

The tightening force can only be measured with instruments with a maximum error of 5%. Of course, all measurement results are verified with the regulatory documents and accompanying materials for the products. It is worth considering that models of nuts with a toothed support end on the flange are completely devoid of the prevailing moment. For them to work effectively, an exact match in the size of the attached part is required.
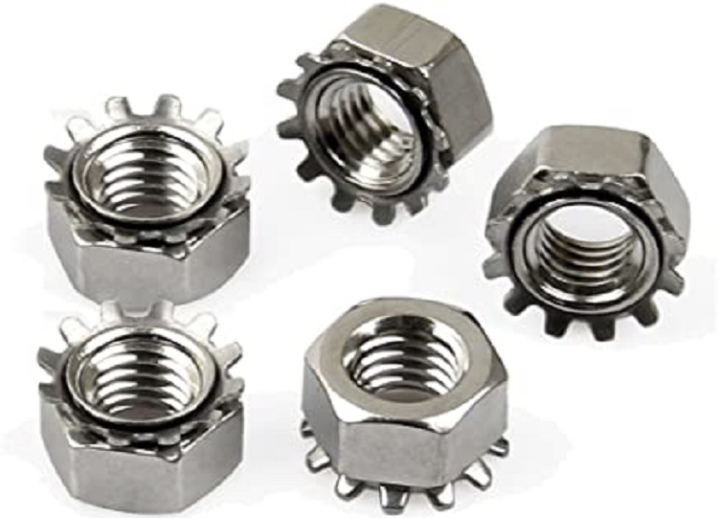

The described type, as well as fasteners with a captive toothed washer, are not reflected in any standard. Their locking properties are assessed based on the results of bench tests. In any case, you need to require a certificate of conformity ISO 2320. Of course, you need to contact only trusted companies, ideally - to direct manufacturers and their partners. The size of the fasteners is selected taking into account the problem being solved.
Lock nuts of modifications KMT (KMTA) can be used in conditions when it is important:
-
maximum accuracy;
-
ease of assembly;
-
fixation reliability;
-
adjustment (compensation) of angular deviations of mating parts.
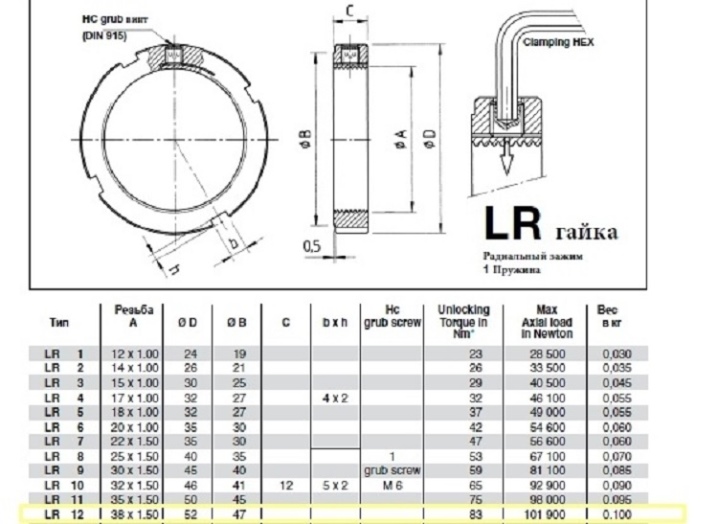
Operating tips
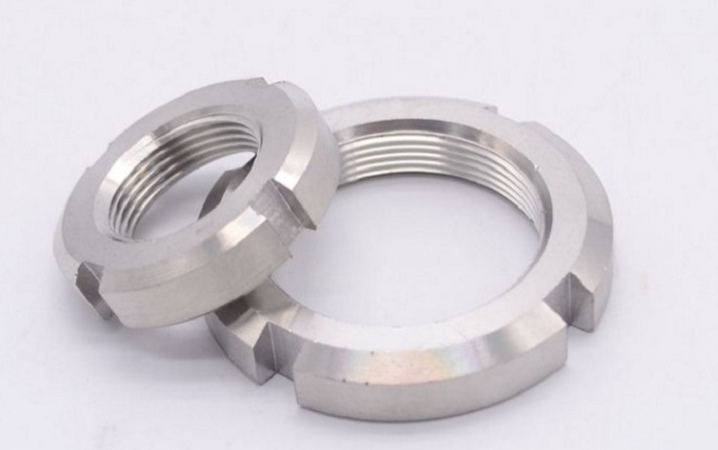
KMT (KMTA) high precision lock nuts are equipped with 3 pins, the distance between which is the same. It is these pins that must be tightened (tightened) together with the screws to fix the nut on the shaft. The end face of each pin is machined to match the shaft thread. Such nuts, however, cannot be used on shafts with grooves in the threads or on adapter sleeves.
Violation of these rules threatens deformation of the locking pins.

The tightening speed of self-locking nuts should be the same, but not more than 30 turns per minute. Remember that the design torque may not provide the required pull. The reason is the pronounced spread of the coefficient of friction force. The conclusion is obvious: critical connections should be created only with careful control of the applied force. And, of course, you should take into account the recommendations of the manufacturers.
See below for nuts and their mounting features.













The comment was sent successfully.