Driven piles: varieties and subtleties of installation

The most important element of any building is the foundation. The choice of technology for its construction depends, first of all, on the characteristics of the soil, as well as on the type of building under construction. The most actively used in modern construction is the strip and pile version of the foundation.

Peculiarities
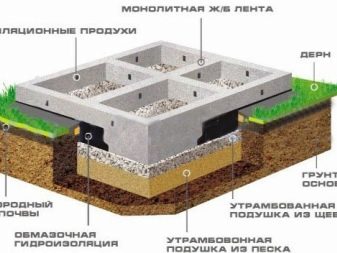
The foundation on driven piles, used in construction on unstable soils, has become widespread. For such a base, supports are used - reinforced concrete rods with a cross-section (often square) in the range of 150-500 mm and a length of 3 to 25 m.
In the lower part, they can be sharp for better penetration into the ground, and in the upper part, they are equipped with a head. The latter serves to protect the supports from deformation during the driving process, hammer blows fall on the head.

The piles are driven into the ground using special equipment - a hydraulic hammer. The length and section of the pile are calculated based on the characteristics of the soil and the object under construction. An important point - the length should be sufficient so that the support stably rests on hard ground, bypassing soft layers. Only in this case can we talk about the stability and reliability of the object, not susceptible to its influence from the heaving of the soil.
The sphere of using the foundation on driven piles is “problem” soils - first of all, organic, that is, boggy, peaty soils. This type of base is suitable for clay and loamy, fine sandy soils, as well as water-saturated soils. The pile foundation can be used on uneven areas with height differences. In other words, the use of this technology makes it possible to make almost any soil suitable for construction.


It should be noted that about 60% of objects in our country were built in this way.
The foundation on the piles can be tiled (grillage) or tape type. The first type is considered the best option for unstable soils.
Pile driving can be carried out according to one of the following options:
- a pile field, usually used for the construction of high-rise buildings on a slab base;
- in a row - piles are mounted in rows for low-rise private construction, while the supports must be installed at the intersection of the load-bearing walls, in the corners;
- single supports mounted in places prone to the greatest soil deformation.



pros
The main advantage of driven pile foundations is the ability to build on almost any, including very unstable (peat) soils - where other systems are not applicable. An exception for pile driving is only rocky and permafrost soils, on which pile foundations are also made, but using a different technology (bored method).
Piles can withstand not only vertical but also horizontal loads, which allows them to be used on "quicksands". By adjusting the height of the piles at different points of the object, it is possible to carry out construction on relief surfaces, slopes, areas with height differences.
The piles have a high bearing capacity, therefore, they are suitable for the construction of both small private housing buildings and multi-storey residential buildings, civilian, industrial, and agricultural facilities. At the same time, the supports have a long service life, which is 50-150 years.
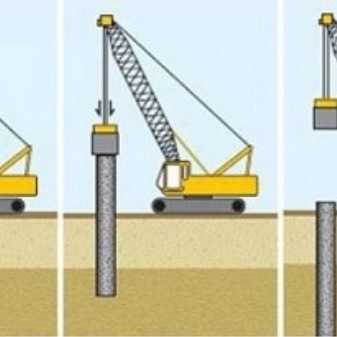
The pile driving process can be carried out all year round, assumes a minimum amount of earthwork, as well as a high driving speed - on average, one pile with a length of 4 m takes several minutes.


Minuses
Like any system, driven pile foundations have drawbacks. First of all, it is the impossibility to use this method in the conditions of factory buildings or in the event that there are erected houses nearby. This is due to the fact that when driving, soil vibrations occur, which are undesirable for the foundations of neighboring objects, as well as roads, main pipelines. In addition, the installation process is accompanied by a high level of noise, which becomes discomfort for people living in neighboring houses.
Despite the conducted research and the construction of preliminary drawings, it is extremely difficult to imagine how the soils will behave at great depths, therefore this technology does not exclude the risk of foundation settlement and violation of geometry.

The pile foundation does not allow you to get a full-fledged basement or basement roomthat can be exploited. If it is nevertheless necessary, then a pile-tape system with a dug pit is used, but this is a laborious and not always possible option. Finally, the need to attract special equipment can also be considered a disadvantage, which will also entail additional costs.
The main regulatory document governing the construction process is SNiP (Building Norms and Rules). As for the design features of foundations on piles, they are set out in SNiP 2.02.03-85 ("Pile foundations"). Direct installation of supports must comply with the requirements of SNiP 3.02.01-87 ("Earthworks, foundations and foundations").
During construction, reinforced concrete piles should be used that comply with GOST 1984-2012. Geological surveys (soil analysis, drilling of test wells) must be carried out in accordance with GOST 19912.


Views
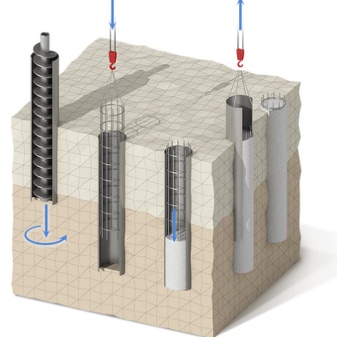
Depending on the material from which the driven piles are made, there are several types.
- Wooden. Wood piles have the smallest margin of safety, they are used in private housing construction for light log cabins or frame houses. Larch, oak, cedar and other hard species are used as raw materials, which are resistant to moisture and temperature changes. Structurally, they are supports with a diameter of 20-40 cm and a length of 3-8 m, usually equipped with a steel tip with a strapping. Depending on the climate and operating conditions, the service life of wooden piles is at least 50 years.


- Steel. They have a slightly higher bearing capacity, but they are also rarely used. As a rule, they serve as a support for temporary structures. A characteristic feature is the tapered tip. Such a tapered metal pile is similar to a screw analog, but does not have blades.
- Reinforced concrete (RC). They are the most widespread, depending on the size, they can withstand a weight of 10-60 tons, the service life reaches 150 years.

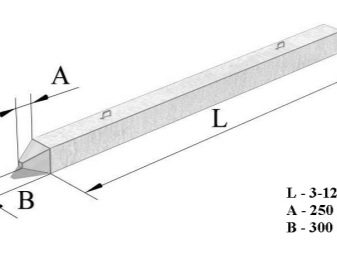
RC piles, in turn, differ according to the following criteria:
- depending on the method of reinforcement, there are prestressed longitudinal reinforcement (for sands, flowing sandy and clayey soils), prestressed transverse reinforcement (for compressible, except for clay, soils), longitudinal reinforcement without prestressing (for clayey, sandy soils), and also piles with a square section and a circular cavity inside with prestressed or non-stressed longitudinal reinforcement;


- in shape, piles are distinguished with round, square, tee and hollow sections, as well as cylindrical and prismatic;
- based on the design features, monolithic and prefabricated (composite) piles are distinguished;
- depending on the peculiarities of the heel - piles with a shackled or hollow heel and piles with a widened base that have appeared relatively recently.
In addition, piles-columns are distinguished, the above-ground part of which acts as the columns of the building on objects of one floor. The device of such structures cannot be carried out on weak (peaty, silty), as well as coarse gravel soils.


Dimensions and calculation
To ensure the reliability of the foundation, an accurate calculation of the number of piles, their cross-sectional diameter and length allows. When building a residential building, depending on the type of soil, reinforced concrete piles with a cross section of 150-250 mm and a length of 3 to 10 m are used. As you know, piles must rest on solid layers of soil - their length depends on this.
By drilling a geological well, the features of the soil are established, and the depth of the solid layers is determined. To calculate the number of supports, you need to know the mass of the house. For example, the depth of hard layers on loamy soils is on average 3.5 m, so the length of the piles will be 4 m.

To calculate the weight of a house, you need to know how much 1 cubic meter weighs. m of material from which it is built. In our case, this is larch, 1 cubic meter. m which weighs about 800 kg (this parameter allows you to find out a special table, which can be found in the public domain for different building materials). The total area of the house is 60 sq. m. The total weight of the object is calculated by the product of these indicators. The result is 50 tons.
To this weight, add the mass of the grillage, floors, finishing and other materials. Calculating by volume, we get another 80 tons. Add 10 tons for furniture and equipment used in the house during operation.

Adding up the resulting figures, we get 140 tons. About 30% of the weight is added for strength, so the total weight of the house will be equal to 182 tons.
A pile with a length of 4000 mm, depending on the type of soil, can withstand a load of 10-40 tons. If we take an average value of 20 tons, then for the construction of a wooden house with an area of 60 sq. m will require 9 piles.

In practice, their number may vary slightly, since for wooden and frame houses on the grillage, the distance between the piles is set at 2-2.5 m.
After the calculations have been made, a pile driving scheme is drawn up. They must necessarily fall on the corners of buildings, at the intersection of load-bearing elements.
The pile section also determines its strength and bearing capacity. For example, a pile with a section of 150x150 mm is recommended for seasonal buildings, baths. An analogue with a section of 200x200 mm can be used for the construction of one-story wooden or frame houses. For more impressive objects of 2-3 floors, as well as made of building blocks or bricks, supports with a section of 300x300 mm are required.

Installation
Installation of the foundation on driven piles begins with geological surveys, during which the type of soil is established. Based on the data received, project documentation is created, materials are purchased. Directly at the construction site, the installation begins with its clearing and marking, the supply of materials. When marking the site, the pile driving points are also marked, after which the level and geometry of the future foundation are checked.
Driving technology involves the use of special equipment with a pneumatic or hydraulic hammer. The pile is installed strictly vertically and driven into the ground with a hammer, sinking deeper with each blow. It is important to monitor the behavior of the support - it may stumble upon a stone or other solid formation, or literally begin to "sink" in the soil (falls into underground voids).

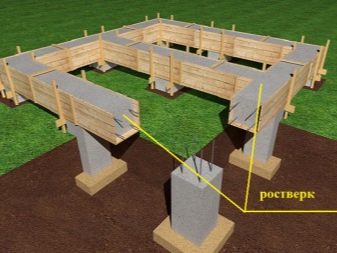
In this case, the support is lengthened or moved 0.5-1 m further. When all the piles are driven in, they begin to beat the top of the support to gain access to the reinforcement. The latter are aligned at the same height. After that, the grillage is installed, or the formwork for the strip foundation is being prepared. In the latter case, the formwork is reinforced with a reinforcing cage and poured with concrete.After it gains strength (after about 28 days), you can proceed to further work.
The grillage, which is a monolithic slab that connects all the supports together, can be metal or reinforced concrete. In the first case, these are finished metal products installed on top of the supports and welded to the reinforcement rods. As a rule, this type of grillage is used for small buildings (verandas, baths) and temporary objects.

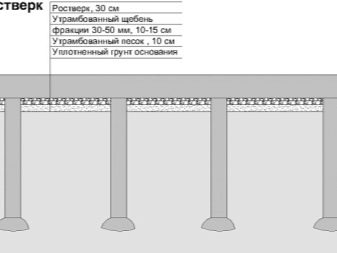
For capital residential buildings, a reinforced concrete slab is used, which is obtained by pouring a pre-installed formwork with concrete.
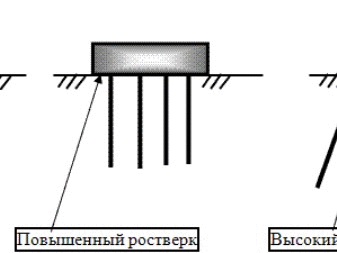
Depending on the type of construction, the grillage is of the following types:
- hanging - in this case, the slab is high above the ground, and the space under the floor is not isolated (suitable as a basis for baths, attic, seasonal dachas);
- shallow - plunges to a shallow depth into the ground, which, however, does not make it an additional support, but allows you to reduce the underground space of the building from bad weather and cold winds;
- recessed - by analogy with a strip base, it plunges into the ground, due to which, like piles, it takes on the load of the building (usually used for capital residential buildings).
Advice
After pouring the strip base or reinforced concrete grillage, the concrete must be protected with a covering material from the negative effects of the environment. In the hot season, it is important to protect the surface from drying out; in the first week, the concrete should be moistened as needed.
It is better not to pour the solution in the cold season, however, if you still have to do this, then you should add special components to the composition, and also use a heating cable at the stage of solution hardening. To mix the mortar, you should use cement, the brand strength of which is not less than M500.

During the pouring process, the formation of air bubbles in the solution should be excluded, since they reduce the strength of the surface. For this, submersible vibrators are placed in the formwork, where the composition is already located, which compact the solution.
What is a driven pile foundation, how it differs from others and how much it costs, you will learn from the video below.













The comment was sent successfully.