Types of foundations: technical characteristics and features of operation

The foundation is an indispensable part for any building, without which the structure can quickly collapse under the influence of destructive environmental factors. A correct understanding of what basis is required in a particular case allows you to find the optimal combination of price and quality.


Design features and purpose
Any type of soil is capable of supporting a specific weight without sagging. A person usually does not see this, since it weighs relatively little, but the solid structure of a one-story private house or a two-story cottage weighs at least several tens of tons. Only a solid rock can withstand such a weight, but such a terrain on a site is usually not considered a plus, therefore houses are erected on softer soil.



The foundation is just a substitute for such a rock, which allows you to make the foundation more stable. The modern SNiP includes specific norms regarding the construction of foundations. The main GOST regulating the construction of such structures is SP 22.13330.2016 "Foundations of buildings and structures." Ignoring the norms specified in this document can not only lead to the destruction of the building, but also entail liability for the damage caused.
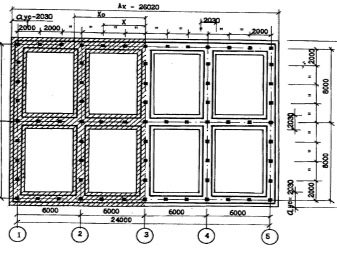

At large construction companies, specialists are engaged in the corresponding calculations, but a person who decides to build a country house with his own hands will either have to order calculations, or delve into all the details in detail.
For the construction of the foundation, materials are used that are harder than the surrounding soil. Usually it is concrete, stone or wood - depending on the weight of the future structure. In most cases, the foundation design assumes that it penetrates deep into the soil below the freezing level. This ensures that the frozen ground does not swell, so the risk of wall cracking and building nodes divergence is considered negligible. An exception may be perhaps a situation in which a light garden house is settled on top of non-porous soils.
The exact choice of the type of foundation depends on numerous factors., among which are not only the weight of the structure, but also its architectural form, the specificity of the soil, the level of seismic activity in the region, while some types of materials put forward their own requirements for the conditions of work. For example, it is possible to work with concrete only at temperatures above 5 degrees, so in the winter time an order can be fulfilled only if it is electrically heated.


Classification
Foundations are very diverse and are divided into different types depending on the design features. Most foundations are of the deep type to provide protection against swelling when the ground freezes. But there are also shallow structures, if the structure is not heavy. In general, the foundations for buildings are easiest to divide into five main types, each of which has its own characteristics that are completely different from competitors.
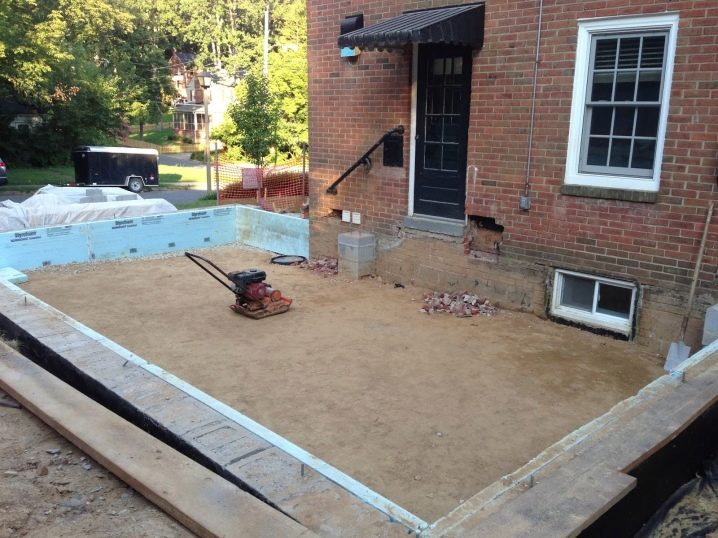

Tape
In recent decades, this type of foundation is rightly considered the main one in the field of individual construction.In fact, it is an extension of the load-bearing walls, which goes deep into the soil to a certain depth, increasing the stability of the structure. In the minimum version, such a tape completely duplicates the perimeter of the house, but it is possible to strengthen it by copying all or some of the internal walls. You can also strengthen the columns.


The tape can be either prefabricated or monolithic. The prefabricated version is good because it can be built much faster - for this, factory blocks made of concrete or reinforced concrete are used. An important point is that the block tape itself can serve as a basis for masonry.
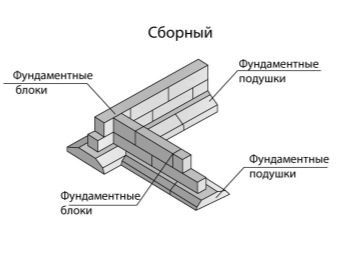

The disadvantage of this solution is the fact that the structure is not integral and is usually constructed without reinforcement, and therefore is subject to distortions and other unpleasant phenomena associated, for example, with the penetration of water into the joints.
An alternative could be a monolithic tape frame, when reinforcement is first formed, which is then poured with concrete, and sometimes diluted rubble or other stone. It is logical that such a structure turns out to be much more reliable and durable, however, its construction can take a long time.
It should be noted that such a basis is well suited for most private buildings. The strip foundation will withstand not only a fence and small structures like a garage or a bathhouse, but also residential buildings made of wood, aerated concrete, brick or stone, and sometimes even reinforced concrete. The only exception will be huge multi-storey structures, while a typical village house, even built on a certain scale, does not need more.
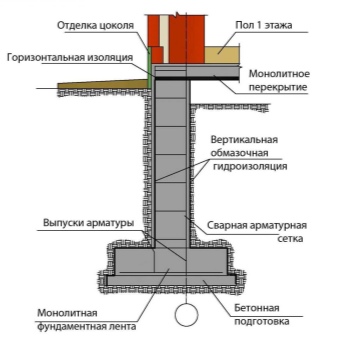

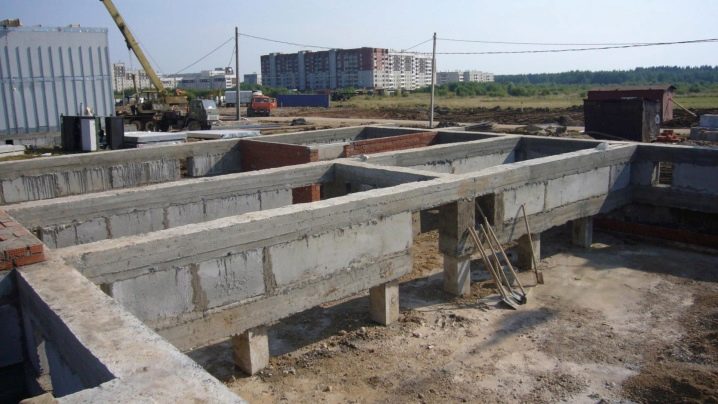
If we talk about the advantages of choosing in favor of the "tape", then they are obvious. First of all, in the foundation from the same walls, you can equip a basement or basement. This plinth is enough to support the weight of two or three upper floors.
In addition, heavy concrete slabs can be laid on top of it, which will become a reliable floor of the first floor. The comparative simplicity of the structure should also be noted - the owner, who knows how to build an even wall, will be able to build a "tape" on his own. The only drawback is the cost of the materials required, but the result is worth it.
The strip foundation is also divided into two types: shallow and buried. The first variety goes deep into the ground only 50-60 cm, so you can't equip a basement here, but you can save on materials. A shallow “tape” can be built only on sand and gravel, as well as on stony ground - such foundations do not lend themselves to heaving. However, if the groundwater is located significantly below the freezing level, then it is permissible to build a shallow strip base even on loam and clay, while the terrain must be flat, and even a one-story brick house may be too heavy for such a foundation.
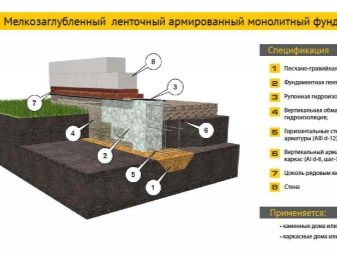
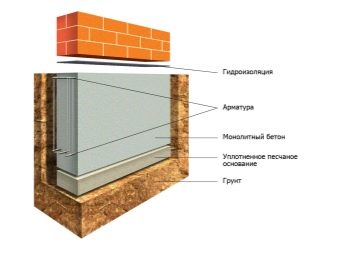
The recessed version is much more convenient, since it goes into the ground by at least 70 cm, and in the northern regions - even up to 1.5 m. The base of the foundation should be below the freezing level, but above the groundwater level.
The surface of the terrain on the site must be flat. Such a plinth is suitable for almost all buildings and any soils, the only contraindication is swampy and loose soils. It also seems inappropriate to erect a "tape" if the soil freezes too deeply, because then such a foundation for the building will cost the owner a pretty penny.


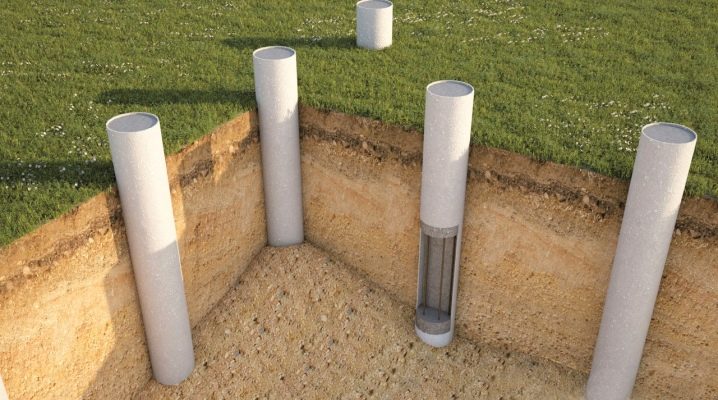
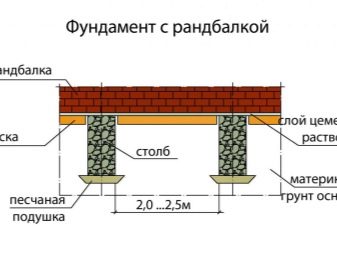
Columnar
If the weight of the building is not expected to be so large, it will be much cheaper to build a columnar foundation, which is perfect for light houses made of wood and aerated concrete, as well as for small outbuildings.

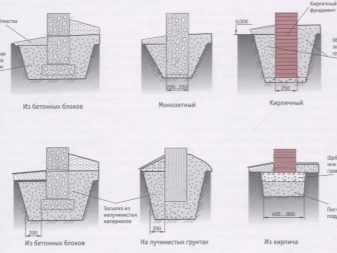
The structure consists of pillars made of concrete, rubble stone or their combination, as well as bricks or wood, located at a distance of 2.5-3 m from each other along the outer perimeter or under all walls.Such pillars are usually deepened to the depth of freezing of the soil, and if the site is uneven, then to the point where sufficient soil density is achieved. The task of the builders is to ensure a perfectly horizontal surface of all pillars so that a concrete or wooden grillage can be made on top of them, serving as the basis for the entire house.
The columnar type of foundation should not even be considered by those owners who definitely want a basement or underground garage, but this is a great option in case the slope on the site is very noticeable. In addition, the columnar base is in great demand in regions with severe winters, since it can go several meters into the ground - where frost does not reach.



It should be noted that wood is sometimes used to build pillars, but is considered the least durable of all materials.
The choice in favor of wooden pillars provides for the mandatory comprehensive processing of the material in order to protect it from moisture, decay and various pests, but it is still undesirable to use this material for serious durable structures. In fact, the wooden columnar foundation is limited only to gazebos.
Columnar-tape according to TISE technology. This kind of foundations has not yet been tested on the proper scale, since it is a relatively new invention. Nevertheless, over the years of operation, no serious complaints have been received, and in general, all the best qualities of those two types of bases that have already been described above are expected from such a foundation.

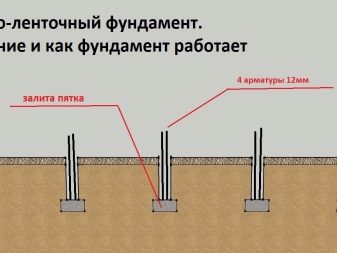
The meaning of the design is that in its lower part it looks the same as an ordinary columnar foundation. The pillars go 4-5 m underground, so they are not afraid of any features of the climate, while the supports are made exclusively by pouring reinforcement with concrete. This is done because the upper part of the structure is a typical strip foundation, which in this case rests not on bare ground, but on pillars.


The main advantage of the "tape" - the ability to withstand buildings of significant weight - remains, while the material consumption becomes much less even in the northern regions of the country, because the lower part of the foundation is relatively economical.
The main disadvantage of this solution is considered to be a relatively long period of arrangement, because in order for a lightweight structure to withstand significant loads, it has to be completely cast from concrete. The required strength is gained by this material within about four weeks, while it is advisable to choose a dry and warm weather, otherwise you will have to spend money on electric heating. Moreover, even such a universal design has certain operating restrictions: on swampy soils, it is very likely that the foundation is skewed or the pillars separate from the "tape".


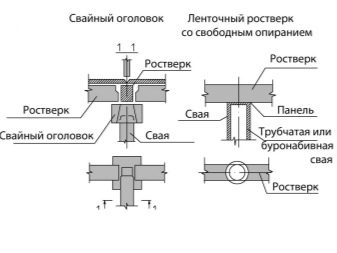
Pile
If the soil turns out to be too unreliable even for a columnar foundation, then this is not a reason to abandon the construction of a house. If the land on the site is characterized by high flowability and low density, is swampy or has a high slot coefficient, the most expedient solution is to organize the foundation using piles.

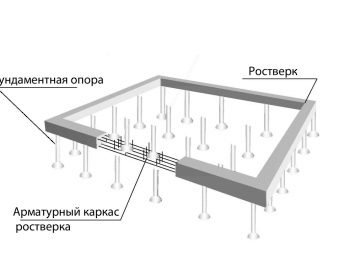
It should be noted that their use is not prohibited also on areas of solid land, if only for the customer for some reason it is more profitable.
Piles are usually prefabricated concrete or reinforced concrete, metal or timber, often with a screw end for easier entry into the ground. Most people understand by the concept of piles such a variety of them as standing piles. These supports penetrate to a depth of 4-6 meters, due to which they often pass through the entire layer of soft soil and abut against a solid foundation, ensuring the stability of the future building.
However, in some cases, even this depth is not enough to reach reliable rocks. But piles (now hanging) can be used in this case too. Although they supposedly do not have reliable support, their significant deepening under different parts of the building allows them to achieve proper balance.


There are driven and rammed piles. The first ones are supports produced at the plant, which are driven into the ground by special equipment. It also compacts the soil around the pile along the way, providing additional stability. Rammed piles are practically no different from the pillars used to create a columnar foundation - they are equipped already at the construction site.
Regardless of the type of piles, a grillage must be installed on top of them, which is the direct basis for the future house. It is necessary to choose the material for it taking into account the planned weight of the building - as a rule, a wooden grillage is made for wooden buildings, and concrete slabs are used for stone houses.


The pile foundation is one of the few types of foundation that has absolutely no restrictions on the terrain.
It is possible to build a house on piles even in a swamp or quicksand, peat bogs and subsiding soils will also not become an obstacle to driving in piles. The pile foundation is also in great demand in those areas where there is a radical level of surface slope.

Platen
This type of foundation is massively used in cities, where the foundations for heavy multi-storey buildings are created by this method, however, this technology is also used in private construction. This may be due to the extremely low quality of the soil on the site in a situation where the owner would like to have a really impressive and heavy house. It is obvious that a dried bog or peat bog will not be able to withstand such a load, as well as columnar or pile foundations, and the "tape" is likely to deform due to the instability of the surrounding soil.
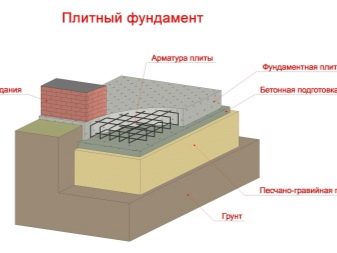

The slab foundation, as the name implies, is a solid reinforced concrete slab, which, if something happens, will move along with the entire structure of the building, but the latter is guaranteed to remain intact. Such a solution is rightly called the most reliable, strong and durable - it actually takes up solid rock, which would become an ideal foundation for a heavy house. The disadvantages, of course, directly relate to the complexity and high cost of arranging such a foundation, because it will require a huge amount of materials, special equipment and several workers.


It will not be possible to create a slab foundation even in a week - it will take at least a month to dig a pit, weld a crate of reinforcement in it, fill it with concrete and wait until it gets stronger. Arrangement of such a foundation is an urgent need, and not in any way savings.
It is not surprising that a slab foundation is almost never built on reliable solid soils. - for a private house, it usually turns out to be superfluous. However, it will come in handy on clay and subsidence soils, in swampy and peaty areas, on quicksand or heaving soils, and even then only if the estimated weight of the building does not allow the use of foundations of other types.


Materials (edit)
The types of materials used in the construction of foundations are very numerous - it all depends not only on the weight of the future structure and the specifics of the soil, but also on the chosen type of foundation and prices for various building materials in a particular region. At the beginning of the article, wood, brick and concrete were mentioned as the main materials, but you can use not only them, especially if the weight of the future building is not so significant.
A strip foundation for a lightweight building can be built from relatively lightweight materials - the same foam blocks or cinder blocks. If the soil under the construction site has good reliability, and the building itself is planned to be small and built from the same lightweight materials or expanded clay concrete blocks, it is likely that such a foundation will be sufficient.


Here you can not do without accurate calculations, for which you should contact the professionals, however, for greater reliability, you can simply strengthen the structure by adding width and depth to it or duplicating all the walls underground, and not just the outer ones.
The use of metal is likely in almost all types of foundations. The combined reinforced concrete version can be both pillars and a tape, and the latter can be integral, cast in place or assembled on site from individual blocks produced by the factory method. Reinforcing metal mesh can be used even in combination with conventional brickwork. A purely metal foundation for light buildings can be made even from pipes alone, some of them used as pillars or piles, and the other can be welded on top in the form of a grillage or a base for it.



A wooden foundation is relatively rare because it is not so reliable and relatively short-lived. This material is usually preferred for self-erection of light-type buildings: small garden houses and gazebos made of the same wood.
This material is appreciated for its availability and the possibility of simple processing even at home, because theoretically, a foundation of a columnar or pile type can be assembled even from old railway sleepers. Another thing is that such pillars or piles will have to be additionally protected, and although it is usually recommended to use special impregnations from insects, rodents or moisture, even roofing material, which could remain after roofing in the main house, will help solve the latter problem. Sheets of roofing material must be tightly wrapped around that part of the piles that goes deep into the ground. However, it should be remembered that roofing material protects only from moisture, but not from full flooding.


Criterias of choice
It is not for nothing that the types of foundations are so numerous - each has its own advantages and disadvantages, focused on different construction conditions and customer requests. A foundation praised by everyone may simply not fit the soil on a particular site, but it will be better than an overly expensive or too sophisticated option.
For example, many owners do not want to spend a lot, because they are looking for the cheapest way to build a base. In terms of the combination of price and quality, the shallow-type strip foundation seems to be the best, however, it assumes that the soil will already be quite stable, and the house itself will be relatively light. If at least one of the stated requirements is not met, it is better to forget about savings and take care of reliability, starting not from the price, but from the durability in the current conditions.
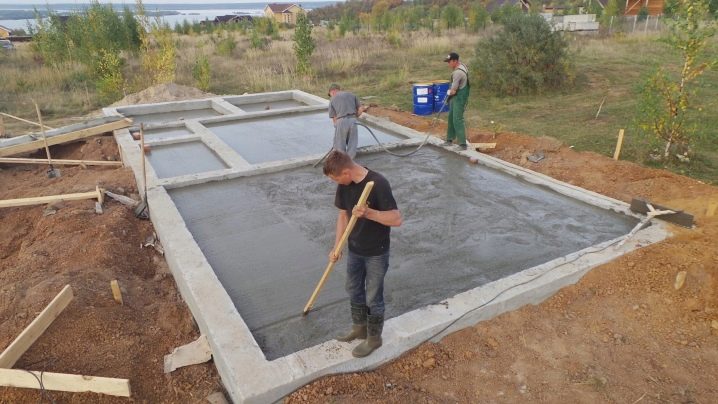

A shallow tape is almost the only correct option for a summer residence, if the groundwater is located at a high level, quite close to the surface.
Any other type of foundation will be in a losing position here, since soil moisture in the summer will erode the material, and in cold weather it will cause the soils to heave, provoking cracks in the walls. In such conditions, it will be necessary to confine oneself to the construction of a low-rise building from light SIP panels. Alternative options like piles will give approximately the same effect, but their independent construction is not possible and requires expensive equipment.
Any type of foundation can be built on bulk and sandy soil provided that the density of the soil is quite high. Such bases usually easily let water into the deeper layers of the bowels, so the area under the house is highly resistant.In this case, they are guided by the fact that the base being built simply withstands the weight of the structure at minimal cost. The requirements for those buildings whose foundations are planned to be built on clay are completely similar, but with one clarification - the level of occurrence of groundwater must be below the level of freezing of the soil in this region.


Buildings are most difficult to construct on quicksand, peat bogs, swamps and other unreliable surfaces. There are only two options here - either fast and relatively cheap piles, or a solid and reliable slab foundation. The choice depends solely on the weight of the building, since you should not expect that the piles in such conditions will withstand even a one-story, but heavy house.
If the problem of the site lies not so much in unsuccessful soils, as in too uneven terrain, then you will have to choose between poles and piles. Both options allow you to level out even a significant level skew, so you often have to choose just from what the surrounding construction companies can offer, paying attention to the requested cost.

Payment
Determining the type and exact parameters of the foundation is a rather difficult engineering task, since a lot of factors will have to be taken into account. If the house is planned to be solid and large, and the soils on the site are not stable, it is better to entrust this task to qualified professionals who can give a guarantee that, according to their figures, the structure under construction will stand for more than a dozen years.

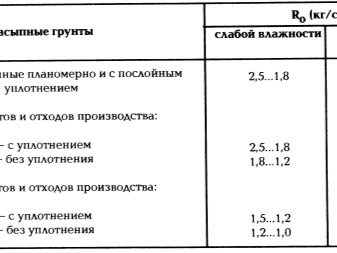
It is necessary to understand that it is not worth evaluating the density of soils or the proximity of the occurrence of groundwater "by eye" - all measurements should be made according to the formulas. An exception may be a complete copy of another building, provided that it is literally on the adjacent site.
However, in most cases, the foundation is erected by the hands of specialists, who at the same time carry out the necessary calculations. In this case, the owner can also roughly determine what foundation is needed in order to get a preliminary idea of the amount that will need to be laid out for building materials. For this purpose, you can take approximate values that are easy to find on the Internet.
For example, if we talk about a strip foundation, then its depth depends on the level of freezing of the soil: the further north the site is located, the larger it is usually. In this case, the tape will go deep into at least half a meter, so this value should be taken as the minimum. Also take into account that usually such a basement rises at least 20-30 cm above the ground. The length is determined by summing the lengths of all walls under which the foundation lies. The thickness of the future support is made about 20% greater than the thickness of the walls built above the ground.

Thanks to everything described, it is possible to determine the approximate volume of the tape, which allows you to calculate the amount of block material or concrete with which the strip foundation will be poured. In this case, the calculations should also take into account a layer of crushed stone of 30 cm and a layer of sand of 10 cm, with which the bottom of the trench is filled up along the entire length even before the erection of the main structure. The costs will not be complete if you do not take into account the cost of the lathing and reinforcement, as well as the waterproofing material that should be lined with the trench.
The calculation of the cost of a columnar foundation should start with the fact that the pillars will be located with a step of 2.5-3 meters from each other - from here their number is determined. The depth of the pillars is chosen in such a way that they reach the non-freezing layer of the earth, but at the same time they are above the groundwater level. The amount of sand, crushed stone, waterproofing and reinforcement is calculated by the number of pillars, taking into account their thickness - after all, there is no trench that runs along the entire perimeter, however, all indicators relating to the strip foundation are preserved.
Separately, you need to plan the grillage - its area is approximately equal to or slightly exceeds the area of the entire building, so it remains to decide on the material and thickness.
The pile foundation is calculated in approximately the same way as the columnar foundation. The columnar-strip type, which is a combination of columnar and strip, is calculated as two separate foundations.
The scale of the slab foundation is highly dependent on whether the basement or basement will be equipped. If not, then a slab thickness within half a meter will be sufficient, although the exact figure depends on the weight of the building, and in the case of basement equipment, the described slab size only applies to the bottom of the basement. Sand and crushed stone are scattered over the entire surface of the pit, whose dimensions should not significantly exceed the dimensions of the house, waterproofing is laid out along the bottom and walls.
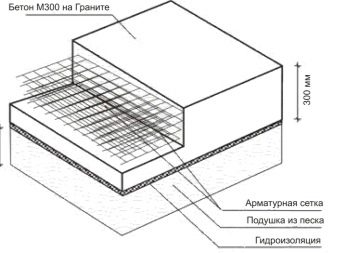
If a basement is being designed, then there should be enough concrete and reinforcement for cast walls and a ceiling. In this case, the walls can be calculated and constructed in full analogy with a strip foundation; instead of basement floors, concrete slabs or wood material can be used.
Causes of deformation
Even the most reliable structures begin to deteriorate over time, but this is not news, unless the foundation began to deform unexpectedly quickly. If this happens, it will be quite difficult to fix the problem, so it is better to investigate the possible causes in advance to avoid such a problem.
- Incorrect calculation Is the most common cause of foundation problems. The very first mistake is the incorrect determination of the weight of the building in the smaller direction, when it turns out that the base simply does not support the main part. Another option is the desire to save money, when the owner hoped that the cheaper material would be no worse than the expensive one. An incorrect determination of the level of groundwater or soil density is not excluded - in other words, the type of foundation itself was chosen incorrectly.
- Violation of technology - a reason that often turns out to be critical in the case of self-construction of the foundation. Before you engage in capital construction, you need to study in detail the properties of the building materials used.


For example, if the reinforcement is poured with concrete on a construction site, you need to know that the maximum possible density will not be achieved - you need a special technique that will mix the poured mass and ensure its proper settlement even before it dries. If this is not done, then air bubbles will remain in the hardened concrete, forming voids, and then subsidence can occur already under a completely finished house with people living in it. Even well-mixed and hardened concrete does not recognize haste - it must stand for about a month before construction work continues on top of the foundation.


Things like proper protection from moisture seem obvious, but they are not always fully observed, and after all, the seam of a prefabricated foundation can easily become deformational if water gets there. As for wood, it must additionally be protected from insects.
- Wear - the phenomenon is quite natural, and if the materials were selected and processed correctly, then this problem may already arise in front of the owner's grandchildren. However, a sudden "surprise" may come from a foundation built from recycled materials: many owners use metal pipes or wooden sleepers instead of poles or piles. If earlier these materials were used at least in some form, then they already have some kind of wear, so the period of their use will be quite insignificant. As for wood, it is not at all durable, so in most cases it turns out to be stupid to rely on its long-term exploitation.


Service
It is logical to assume that timely maintenance of the foundation can play a key role in extending its operation. For example, timely identification of defects allows you to learn about the problems faced by the design and take urgent measures to eliminate them. The appearance of cracks in a concrete structure implies their clearing and immediate repair, however, if cracking occurs too early, then you should carefully look for the reason why this happens, focusing on common causes of deformation.


It should also be understood that the foundation is functional, but usually the interior of a building. Wherever possible, it is worth using a protective type finish, because then it will take the whole brunt of the blow, and replacing it is much easier than fully repairing the entire foundation.
It is clear that a significant part of the foundation remains invisible, being located underground, but at least the visible part can be painted on the outside with a water-repellent paint to protect it from the negative effects of precipitation. A worthy alternative both outside and inside can be waterproof plaster.
For greater durability of such repairs and increased protection of the same wood from pests, the same reinforcing mesh can be used, which, during the renovation, is once again laid on the foundation and covered with a new layer of plaster. In some cases, due to general deformation of the foundation or improper attachment, the old reinforcing mesh bends and breaks away from the structure, breaking through the protective finishing layer - in this case, you should immediately cut off the protruding and protruding ends, and close the gap.


By watching the video below, you will find out what types of foundations are and their properties.













The comment was sent successfully.