Column-strip foundation: construction technology
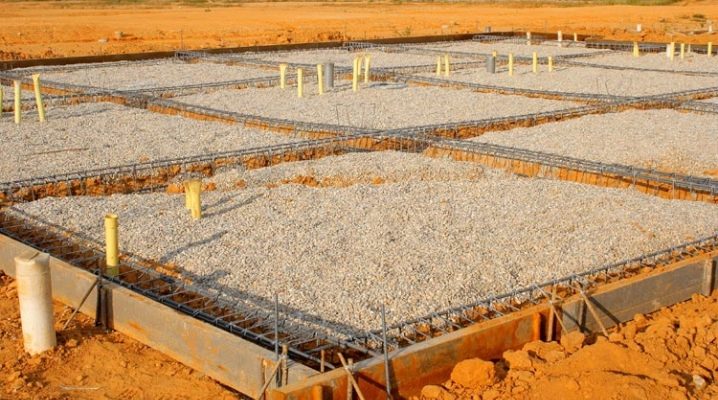

The choice of the type of foundation is determined, first of all, by the characteristics of the soil. Where, due to its instability, it is not possible to use the classical strip base, they often resort to combined systems. This option is a columnar-strip foundation.
Peculiarities
The columnar-strip foundation combines the leading features of two types of bases - columnar and strip. This combined option allows you to erect rather heavy objects on unstable soils.
The supporting elements in this system are piles, which are dug into the ground below the level of freezing of the ground and rest on hard layers of soil, bypassing the soft ones. The strip concrete base takes on the load of the object, evenly distributing it between the piles. The tape connects the pillars without exerting pressure on the ground.


These types of substrates are suitable for unstable soils prone to heaving. First of all, these are clay and fine sandy soils, organic soils (swampy, peaty), previously drained and drained. In addition, the use of piles allows construction to be carried out in areas with elevation differences. In other words, the use of a strip-pile foundation makes it possible to make almost any site suitable for construction.
A strip foundation with pillars by its principle of organization is similar to an analogue on piles, however, to install supports, you do not need to attract special equipment and drill deep wells. This allows you to do the installation yourself and reduce the size of the estimate.
The advantage of columnar foundations is the ability to carry out construction on "problem" soils, as well as in areas with elevation differences. However, the design of such a system requires accurate calculations.
In the absence of the skills of such work, it is better to entrust the matter to professionals.


The implementation of a strip base on poles does not imply a large amount of earthwork and is cheaper than pile counterparts. A gap must be maintained between the columnar-strip base and the monolithic screed in order to minimize the effect of the soil heaving process on the foundation.
The creation of a foundation based on pillars is not suitable for moisture-saturated soils (areas located in lowlands or near water bodies, soils with groundwater). For such territories, it is better to choose a pile foundation with a strip base.
From the very beginning, you should decide on the characteristics of the building - its size, number of storeys, the technologies used. The material for making the pillars, their number and diameter depends on this.


Usually, pole foundations in combination with a tape are used on unstable soils and are intended for small one-story houses with an attic or two-story objects made of lightweight materials. Suitable wall materials are foam blocks and wooden structures (log cabins), as well as "frame frames", for the construction of which Canadian and Finnish technologies are used.
Aerated concrete houses can also use a shallow foundation. But brick counterparts require deepening the pillars and increasing the strength and diameter of the pillars.
Materials (edit)
Support posts can be made of several types of materials.


Wood
It is an affordable and easy-to-install material, which, however, has the lowest load-bearing capacity and a short service life. This option can be used as a foundation for small terraces, temporary buildings, country houses.
The optimal diameter for wooden posts is 120-200 mm. Before use, the supports should be dried, covered with moisture-repellent and antiseptic impregnations. This will increase the service life of the posts. Bituminous mastics are used as a waterproofing material.


Brick
Brick pillars became widespread. Shallow-buried columnar bases of a square section with a side width of 40-50 cm are laid out of them.


Concrete
Concrete elements are monolithic or demountable concrete-based bases, reinforced with steel rods. The standard section in this case is 400 mm. This option is suitable as a basis for capital construction.


Pipes
Tubular elements are metal pipes installed in the ground and filled with concrete from the inside. Reinforcement is used as reinforcement.


Calculations
Determination of the number of piles and their length is carried out according to the calculation documentation. For areas with sufficiently stable ground, supports with a length of 2500 mm are sufficient. When erecting an object on uneven terrain, the height of the support takes into account the differences in the height of the soil. When building on highly mobile soils, the height of the support should be such that it reaches solid soil layers plus 15-20 cm.
You can calculate the number of pillars by adding up all the loads on the foundation. To do this, calculate the load (weight) of 1 m3 of wall material and multiply this indicator by the number of cubes of the entire room. This coefficient is summed up with the weight of the floor, floors, windows and doors, roofing, as well as internal equipment (furniture, finishing materials, equipment, communications).
Further, the load factor is multiplied by the safety factor (this is a constant value according to SNiP). The resulting number should be divided by the value of the bearing capacity of one support.
It should be borne in mind that it is imperative to mount the pillars in the corners, intersection points of the partitions.
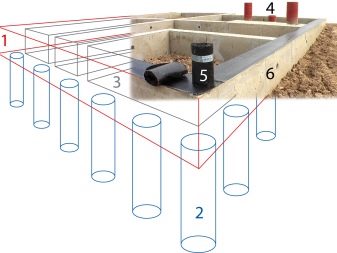
The distance between the posts is maintained within the range of 100-250 cm. The heavier the object is, the less distance is maintained between the supports. It is not recommended to increase the step by more than 250 cm, since in this case the strength of the finished building decreases.
For wooden buildings, it is recommended to put pillars with a step of 3 m, in structures made of foam and aerated concrete - 2 m.For brick houses, this figure is 1.5-1.7 m.In other words, the foundation for a house made of foam blocks measuring 9x8 m on average requires at least 16 pillars, and a wooden counterpart of the same size requires 12-14 pillars.
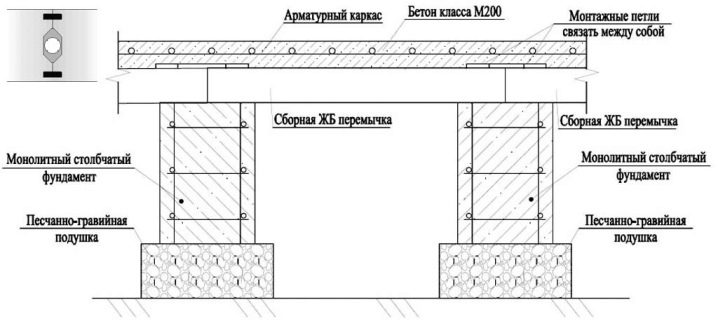
Installation steps
In general, the construction of a columnar-strip foundation is divided into 2 large stages: the creation of a system of pillars and the pouring of a shallow strip foundation.
Project creation
The construction of any type of foundation begins with the creation of design documentation. This work is preceded by geological surveys (observation and analysis of the soil to find the optimal type of foundation). The project contains information about the bearing capacity of the pillars, their size, number.
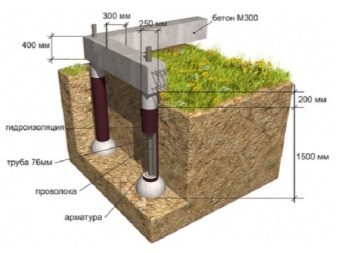
The considered type of foundation can be shallow and buried. In the first case, the pillars are immersed in the ground 40 cm, in the second - 50-70 cm below the level of soil freezing. The choice of a specific technology depends on the type of soil, the presence or absence of groundwater, and the characteristics of the facility under construction.

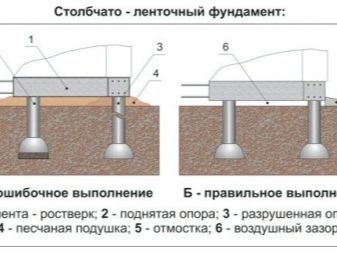
The step-by-step instructions for installing poles are not too complicated.
Site preparation
At this stage, the debris is removed from the site, the ball of the fertile layer is removed and the site is leveled.On clay soils, the top layer is removed and a layer of sand is filled in, which is compacted and leveled.


Site marking
To do this, use pegs and a skein of noticeable rope or thread. The threads should be pulled at a distance that corresponds to the width of the future foundation tape. It is important to monitor the intersection of the threads in the corners, it should be strictly perpendicular. The markings are made at the points of passage and intersection of internal partitions, in the corners, as well as in areas subject to maximum loads.


Creation of trenches and indentations for posts
At the location of the strip foundation, a trench should be dug about 400 mm deep. The width of the trench should be 70-100 mm greater than the depth.
In places of increased loads (according to the design documentation), recesses are made, where the support pillars will then go down. Their diameter is calculated based on the load on the foundation. The higher it is, the larger the diameter of the posts should be. A drill is used to create a depression. If the recess is long enough, then first it is performed with a drill, then with a screw.
When laying the pillars to a depth of more than 100 cm, it is necessary to build supports from solid boards that will prevent the soil from shattering. If the depth of the foundation is less than 100 cm, the use of props can be dispensed with.
Sand 10 cm thick is poured into the bottom of each recess. With a greater depth of laying the base, the thickness of the sand "cushion" reaches 30-40 cm.


Installation of supports
At this stage, the pillars are lowered into the prepared recesses. Most often, pipes are used that are poured with concrete. Pipes are pre-waterproofed, for example, by pasting with a double layer of roofing material. After that, the pipes are lowered all the way into the recesses, after which their vertical orientation is checked.
The next step is pipe reinforcement. For this, a frame made of reinforcing rods with a diameter of 12-14 mm and knitting wire is used. The resulting frame should protrude 12-20 cm from the pipe.
After that, a concrete solution is prepared, which is first poured into the free space between the walls of the recess and the pipes. The filling height is about 20 cm. Then the cavity inside the pipes is filled.


After the solution has gained the necessary strength, they begin to install the tape part. First, the frame of reinforcing rods and knitting wire must be welded to the reinforcement elements protruding from the pipes. Next, a formwork is mounted, consisting of boards about 150 cm wide and no more than 40 mm thick. Instead of boards, you can use plywood, chipboard or sheet metal.
The inner part of the formwork is lined with polyethylene film or a special membrane, which serve as a waterproofing layer, and also make it possible to obtain even and smooth surfaces of the strip foundation after stripping.
After that, you can start pouring concrete. Casting should be carried out in one step (maximum break in work - 2 hours) strictly in the horizontal direction. Vertical filling of the formwork will lead to the appearance of joints and cracks in the concrete even before the mortar hardens.
When pouring, it is important to exclude the appearance of air bubbles in the solution, which can negatively affect its strength. For this, vibrators are used.


After that, the concrete should be given time to gain strength, having previously protected it with a covering material. As a rule, the foundation is poured in the summer, so it is possible that it will dry out. Periodic wetting of the concrete surface for the first 1.5-2 weeks of curing will help prevent this. In the cold season, it is recommended to lay the heating cable over the entire surface of the concrete for the entire curing period.
After the specified time has elapsed, the foundation is stripped, its hydro and thermal insulation. The remaining space of the trench is filled with soil, after which you can proceed to the rest of the work.
How to calculate the columnar-strip foundation, see below.













The comment was sent successfully.