Rules and methods for calculating the foundation

It doesn't matter what kind of walls, furniture and design in the house. All this can depreciate in an instant if mistakes were made during the construction of the foundation. And the blunders concern not only its qualitative features, but also the basic quantitative parameters.



Peculiarities
When calculating the foundation, SNiP can be an invaluable assistant. But it is important to correctly understand the essence of the recommendations outlined there. The fundamental requirement will be the complete elimination of wetting and freezing of the substrate under the house.
These requirements are especially relevant if the soil has an increased tendency to heave. Having explored the exact information about the soil on the site, you can already safely refer to building codes and regulations - there are scrupulous recommendations for construction in any climatic zone and on any mineral materials existing on Earth.
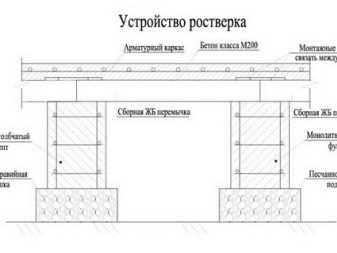
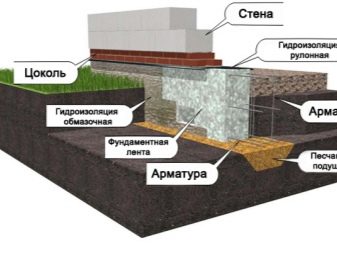
It should be understood that only professionals can make a sufficiently correct and deep idea. When the design of the foundation is carried out by amateurs trying to save on the services of architects, just a lot of problems result - warping houses, always damp and cracked walls, musty smells from below, weakening of the bearing capacity, and so on.
A professional design takes into account the properties of specific materials and financial constraints. Thanks to this, it allows you to balance the loss of funds and the results achieved.

Type of
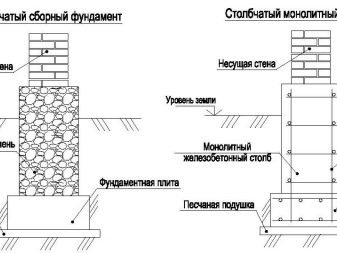
The stability of the foundation under the house directly depends on its type. There are clear minimum requirements for the performance of different types of foundations. So, under a house with dimensions of 6x9 m, ribbons 40 cm wide can be laid, this will allow you to have a two-fold safety margin compared to the recommended value. If you install bored piles, expanding at the bottom to 50 cm, the area of a single support will reach 0.2 sq. m, and 36 piles will be needed. More detailed data can be obtained only through direct acquaintance with a specific situation.
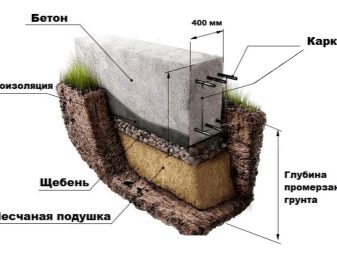
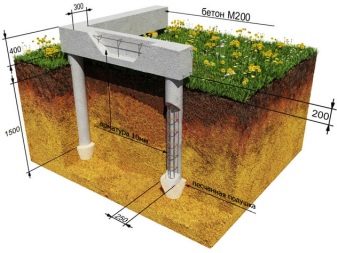
What does it depend on?
The design of foundations, even within the same type, can be quite different. The main boundary runs between shallow and deep bases.
The minimum bookmark level is determined by:
- soil properties;
- the level of the waters in them;
- arrangement of basements and basements;
- the distance to the basements of neighboring buildings;
- other factors that professionals should already consider.



When using slabs, their upper edge must not be raised more than 0.5 m to the surface of the building. If a one-story industrial facility is being built that will not be subject to dynamic loads, or a residential (public) building of 1-2 floors, there is a certain subtlety - such buildings on soils that freeze to a depth of 0.7 m are erected with the replacement of the lower part of the foundation by pillow.
To form this pillow, apply:
- gravel;
- crushed stone;
- sand of coarse or medium fraction.
Then the stone block must have a height of at least 500 mm; for the case of medium-sized sand, prepare the base so that it rises above the groundwater. The foundation for internal columns and walls in heated structures may not adapt to the water level and the amount of freezing. But for him, the minimum value will be 0.5 m. It is necessary to start a tape structure under the freezing line by 0.2 m.At the same time, it is forbidden to lower it by more than 0.5-0.7 m from the lower planning point of the structure.



Methods
General recommendations on dimensions and depth may be useful, but it will be much more correct to focus on the results of calculations of a professional level. The method of layer-by-layer summation is of great importance in their implementation. It allows you to confidently assess the settlement of a foundation resting on a natural substrate of sand or soil. Important: there are certain restrictions on the applicability of such a method, but only specialists can deeply understand this.
The required formula includes:
- dimensionless coefficient;
- the average statistical stress of an elementary soil layer under the influence of external loads;
- module of soil mass damage during initial loading;
- it is the same at secondary loading;
- the weighted average stress of the elementary soil layer under its own mass extracted during the preparation of the soil pit.


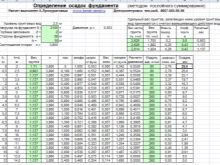
The bottom line of the compressible mass is now determined by the total stress, and not by the additional effect, as recommended by building codes. In the course of laboratory tests of soil properties, loading with a pause (temporary release) is now considered. First, the base under the foundation is conventionally divided into layers of identical thickness. Then the stress is measured at the joints of these layers (strictly under the middle of the sole).
Then you can set the stress created by the soil's own mass at the outer boundaries of the layers. The next step is to determine the bottom line of the stratum undergoing compression. And only after all this, it is possible, finally, to calculate the proper settlement of the foundation as a whole.
A different formula is used to calculate the eccentrically loaded base of a house. It proceeds from the fact that it is required to strengthen the outer border of the bearing block. After all, it is there that the main part of the load will be applied.
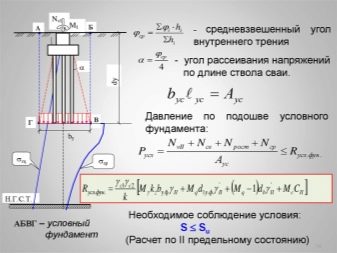
Reinforcement can compensate for the change in the force application vector, but it must be carried out in strict accordance with the design conditions. Sometimes the sole is reinforced or a column is placed. The beginning of the calculation involves the establishment of forces that act along the perimeter of the foundation. To simplify the calculations, it helps to reduce all forces to a limited set of resulting indicators, which can be used to judge the nature and intensity of the applied loads. It is very important to correctly calculate the points at which the resulting forces will be applied to the sole plane.
Next, they are engaged in the actual calculation of the characteristics of the foundation. They start by determining the area that he should have. The algorithm is approximately the same as that used for the center-loaded block. Of course, accurate and final figures can only be obtained by shifting by the required values. Professionals operate with such an indicator as a plot of soil pressure.
It is recommended to make its value equal to an integer from 1 to 9. This requirement is associated with ensuring the reliability and stability of the structure. The proportion of the smallest and largest project loads must be calculated. Consideration should be given to both the features of the building itself and the use of heavy equipment during construction. When a crane is intended to act on an off-center loaded foundation structure, the minimum stress is not allowed to be less than 25% of the maximum value. In cases where construction will be carried out without the use of heavy machinery, any positive number is acceptable.
The highest permissible ground mass resistance must be 20% greater than the most significant impact from the bottom of the sole. It is recommended to calculate the reinforcement not only of the most loaded sections, but also of the structures adjacent to them.The fact is that the applied force can shift along the vector due to wear, reconstruction, overhaul or other unfavorable factors. It is very important to take into account all those phenomena and processes that can have a harmful effect on the foundation and worsen its characteristics. Consultation from professional builders, therefore, will not be superfluous.



How to calculate?
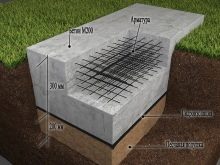
Even the most carefully calculated loads do not exhaust the numerical preparation of the project. It is also necessary to calculate the cubic capacity and width of the future foundation in order to know what kind of excavation for the pit to make and how much materials to prepare for work. It may seem that the calculation is very simple; for example, for a slab with a length of 10, a width of 8 and a thickness of 0.5 m, the total volume will be 40 cubic meters. m. But if you pour exactly this amount of concrete, significant problems may arise.
The fact is that the school formula does not take into account the space consumption for the reinforcing mesh. And let its volume be limited to 1 cubic meter. m., it rarely turns out to be more than this figure - you still need to prepare just as much material as required. Then you will not have to overpay for the unnecessary, or search feverishly where to buy the missing fittings. Calculations are made somewhat differently when using a strip foundation, which is empty inside and therefore requires less mortar.



The required variables are:
- the width of the employee for laying the pit (adjusted for the thickness of the walls and formwork to be mounted);
- the length of the bearing wall blocks and partitions located between them;
- the depth to which the base is embedded;
- a subspecies of the base itself - with monolithic concrete, from ready-made blocks, from rubble stones.
The simplest case is calculated using the formula for the volume of a parallelepiped minus the amount of internal voids. It is even easier to determine the necessary parameters for the foundation of the pillar design. You only need to calculate the values of two parallelepipeds, one of which will be the bottom point of the pillar, and the other - the bottom of the structure itself. The result must be multiplied by the number of posts that are placed under the grillage with an interval of 200 cm.
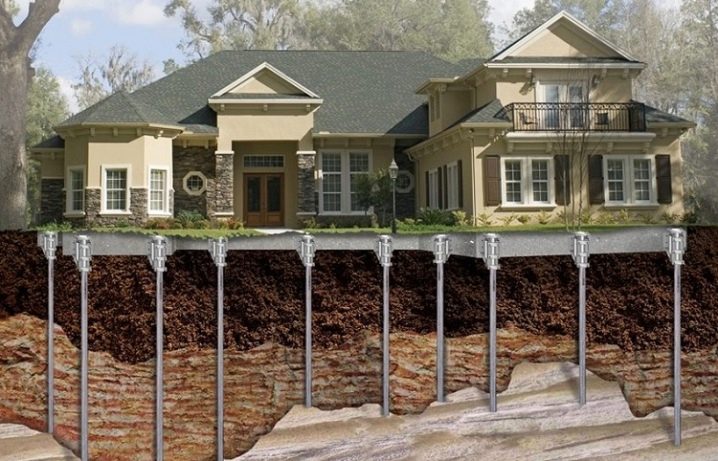
The same principle applies to screw and pile-grillage bases, where the volumes of the pillars and slab parts used are summed up.
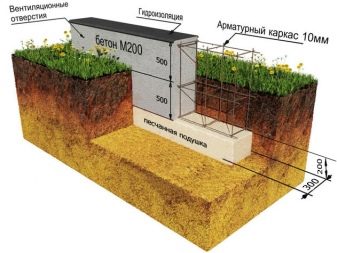

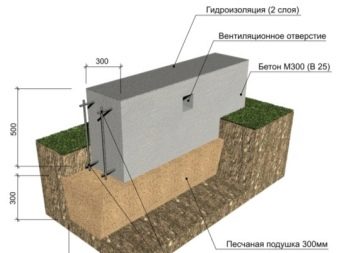
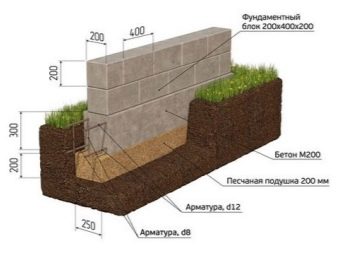
When using factory-made bored or screw-in piles, only tape segments will have to be calculated. Pillar sizes are ignored, except for the prediction of earthwork size. In addition to the volume of the foundation, the calculation of its settlement is also very important.
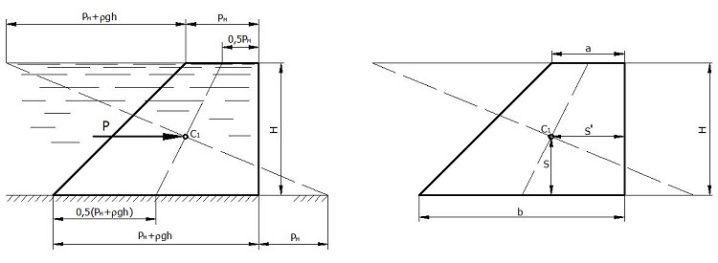
The graphical representation of the layer-by-layer stacking method shows that you need to pay attention to:
- the mark of the surface of the natural relief;
- penetration of the bottom of the foundation into the depths;
- the depth of the location of groundwater;
- the lowest line of the rock being squeezed;
- the amount of vertical stress created by the mass of the soil itself (measured in kPa);
- complementary stresses due to external influences (also measured in kPa).

The specific gravity of soils between the groundwater level and the line of the underlying aquiclude is calculated with a correction for the presence of liquid. The stress that arises in the aquiclude itself under the gravity of the soil is determined ignoring the weighing effect of water. A great danger during the operation of foundations is created by loads that can cause overturning. Calculating their size will not work without determining the total bearing capacity of the base.
When collecting data, the following can be used:
- dynamic test reports;
- static test reports;
- tabular data, theoretically calculated for a specific area.
It is recommended that you read all this information at once. If you find any inconsistency, discrepancies, it is better to immediately find and understand its cause, rather than engage in risky construction.For amateur builders and customers, the calculation of parameters affecting rollover is easiest to carry out in accordance with the provisions of SP 22.13330.2011. The previous edition of the rules came out back in 1983, and, naturally, their compilers simply could not reflect all modern technological innovations and approaches.


It is advisable to take into account all the work that will be carried out to reduce the deformations of the very future foundation and foundations under nearby buildings.
There is a set of loss of resilience situations, developed by generations of builders and architects, that need to be modeled. First of all, they calculate how the base soils can move, dragging the foundation along with them.
Additionally, calculations are carried out:
- flat shear when the sole touches the surface;
- horizontal displacement of the foundation itself;
- vertical displacement of the foundation itself.
For 63 years now, a uniform approach has been applied - the so-called limit state technique. Building rules require two such states to be calculated: for bearing capacity and for cracking. The first group includes not only complete destruction, but also, for example, a downward drawdown.


The second - all kinds of bends and partial cracks, limited settlement and other violations that complicate operation, but do not exclude it altogether. For the first category, the calculation of retaining walls and work aimed at deepening the existing basement is being carried out.
It is also used if there is another pit nearby, a steep slope on the surface or underground structures (including mines, mines). Distinguish between stable or temporarily acting loads.
Long-term or permanently influencing factors are:
- the weights of all component parts of buildings and additionally filled soils, substrates;
- hydrostatic pressure from deep and surface waters;
- prestressing in reinforced concrete.

All other impacts that can only touch the foundation are taken into account in the composition of the temporary group. A very important point is to correctly calculate the possible roll; tens and hundreds of houses collapsed prematurely only because of inattention to him. It is recommended to calculate both the roll under the momentary action and under the load applied to the center of the base.
You can assess the acceptability of the result obtained by comparing it with the instructions of SNiP or with the technical design task. In most cases, a limitation of 0.004 is sufficient, only for the most critical structures the level of permissible deviation is less.

When it turns out that the default roll level exceeds the norm, the problem is solved in one of four ways:
- a complete change of soil (most often, bulk cushions made of sand and soil mass are used);
- compaction of the existing array;
- increasing the strength characteristics by fixing (helps to cope with loose and watery substrates);
- the formation of sand piles.
Important: whichever approach you choose, you will have to re-calculate all the parameters. Otherwise, you can make another mistake and only waste money, time and materials.
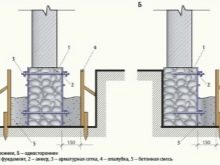
Choosing a specific option for a shallow backfill, the technological and economic parameters of the reinforced concrete base are first calculated. Then a similar calculation is carried out for the pile support. Comparing the results obtained and once again rechecking them, you can make a final conclusion about the optimal type of foundation.
When determining the number of cubes of materials per base plate, carefully evaluate the consumption of boards for formwork, as well as the length and width of the reinforcement cells, and their diameter. In some cases, the number of rows of reinforcement being laid may differ. Next, the optimal proportions of dry and mortar concrete are analyzed.The final cost of any free-flowing substances, including auxiliary fillers for concrete, is determined by their mass, and not based on their volume.
The average pressure under the sole of the foundation structure is determined taking into account the eccentricity of the resultant of various forces with respect to the center of gravity of the structure. In addition to finding out the design resistance of the soil, it is necessary to check the weak underlying layer throughout its entire area and thickness for punching. Almost always, the maximum thickness of the elementary layers in the calculations is taken to be no more than 1 m.When a strip foundation is being built, reinforcement is used no thicker than 1-1.2 cm.For a pillar base, they are guided by a binding material with a thickness of 0.6 cm.



Advice
It is very important not only to perform all calculations efficiently, but also to clearly understand what the finished foundation should be. In the case of the construction of a very small auxiliary structure, it is worthwhile to carry out calculations for the construction of an asbestos-cement pipe. Tape and pile supports are chosen mainly for houses that create a very serious load.
Accordingly, it is determined:
- cross-section of the base in diameter;
- diameter of reinforcing fittings;
- the step of laying the reinforcing lattice.
On sands, the layer of which is over 100 cm below the building, it is best to form light foundations with a depth of 40-100 cm. The same value should be adhered to if there is a pebble or a mixture of sand and stone below.
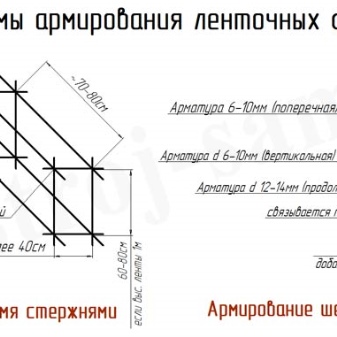
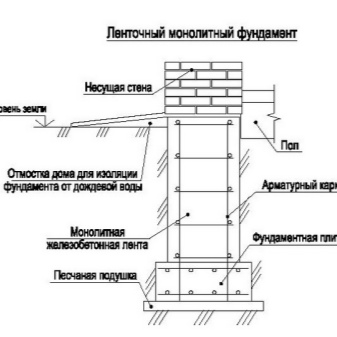
Important: these figures are only approximate and refer exclusively to light bases of a small section, obtained in the form of a tape with weak reinforcement or pillars saturated with broken stones. Approximate parameters do not excuse the need for more detailed and careful calculation of the actual requirements.
On loams, houses are most often built along a massive tape monolith pierced by reinforcing contours from below and from above. The sides should be covered with manually compacted sand, the layer of which is from 0.3 m along the entire height of the tape. Then the squeezing effect of stresses is minimized or completely suppressed. When construction takes place on soil represented by sandy loam, it is required to analyze the ratio of sand and clay, and then make a final decision. When calculating a construction on a peat space, the organic mass is usually taken out to a strong substrate under it.
When it is very difficult and the work on the construction of the tape or poles turns out to be disproportionately heavy and expensive, the piles must be calculated. They are also necessarily brought to a dense point where a stable support is created. Absolutely any type of foundation is supposed to start below the freezing line. If this is not done, the power of frosty displacement and destruction will crush any strong and solid structures. It is advisable to lay in projects such a type of excavation as digging along the perimeter of trenches 0.3 m wide.
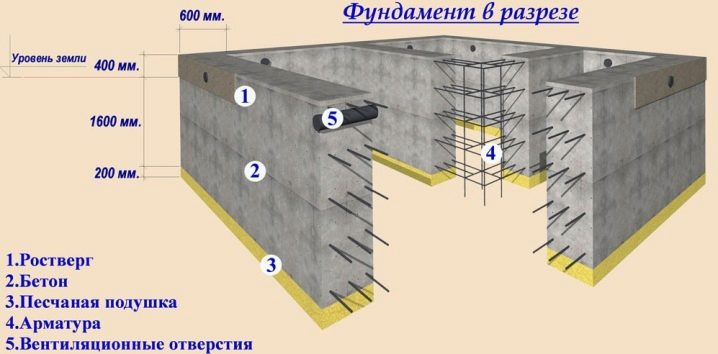
Correct information about the properties of the soil for calculations cannot be obtained simply by digging a garden or focusing on the words of neighbors, even if they are conscientious people. Experts advise drilling exploratory wells 200 cm deep. In some cases, they can be deeper if necessary for technical reasons.
It is useful to order a chemical and physical analysis of the extracted mass, otherwise it may present unexpected surprises. Ideally, you should completely abandon independent design and only check the calculations provided by the construction organization.
In the next video, you will find the calculation of the foundation of the house in terms of bearing capacity.













The comment was sent successfully.