Collecting foundation loads: the best calculation system
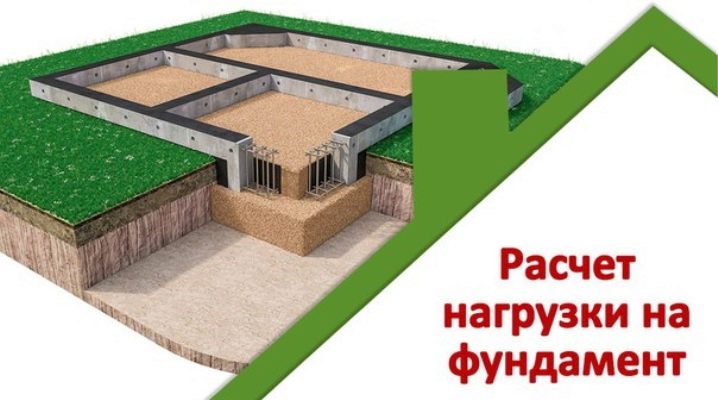

Collecting foundation loads is one of the important design stages. It will allow you to choose the best option for the foundation, taking into account the characteristics of the soil on the site, the layout of the future structure, its features, number of storeys, materials for construction and decoration. This will help increase the life of the building and avoid deformation.


Peculiarities
By themselves, the loads on the foundation differ in the duration of the impact and can be temporary or permanent. Permanent loads include walls, partitions, ceilings, and roofs. The temporary ones include furniture, equipment (belong to the subgroup of long-term loads) and weather conditions - exposure to snow, wind (short-term).
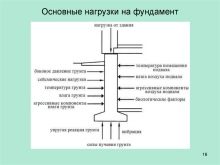


Before collecting loads, it is necessary to carry out some activities, namely:
- draw up a detailed plan for future construction, include all the piers in it;
- decide whether the house will be equipped with a basement, and if so, what its depth should be;
- clearly determine the height of the base and select the materials that will be used in its manufacture;
- decide on insulation, waterproofing, wind protection, finishing materials - both internal and external, and their thickness.

All this will help to most accurately calculate all the loads, which means to avoid skewing, bending, subsidence, bending, tilting or displacement of the building. It is not worth mentioning the increase in the service life, durability and reliability of the building - it is obvious that all these indicators will only benefit if the calculations are carried out correctly.
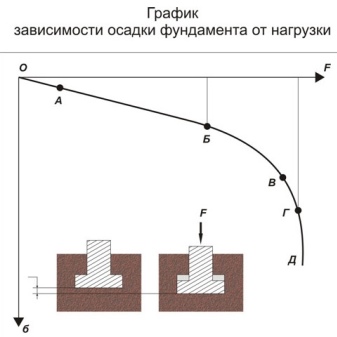
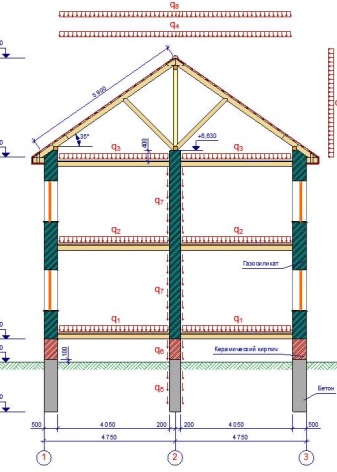
In addition, the calculation of the load will help to choose the right geometric shapes, the base of the foundation and its area.
What does it depend on?
Foundation load is a combination of a number of factors.
These include:
- in which region the construction will be carried out;
- what is the soil in the selected area;
- how deep the groundwater is;
- what materials the elements will be made of;
- what is the layout of the future building, how many floors it will have, what kind of roof there will be.

It is important to correctly determine the soil on the site of future construction, since it has a direct impact on the durability of the foundation, on which type of support structure is better to give preference to and on the depth of the laying. For example, if at the construction site there is clay, loamy soil or sandy loam, then the foundation will need to be laid to the depth to which the soil freezes in winter. If the soil is large-block or sandy, this is optional.
You can correctly determine the type of soil using the joint venture "Loads and Impacts" - a document that is required when calculating the weight of a structure. It contains detailed information about what loads the foundation is experiencing and how to determine them. Maps in SNiP "Construction climatology" will also help determine the type of soil. Despite the fact that this document has been canceled, it can be very useful in private construction as a material for acquaintance.


In addition to depth, it is important to correctly determine the required width of the supporting structure. It depends on the type of foundation. The width of the strip and columnar foundations is determined based on the width of the walls. The supporting part of the slab foundation should extend beyond the outer boundaries of the walls by ten centimeters. If the foundation is piled, the section is determined by calculation, and its upper part - the grillage - is selected based on what load will be on the foundation and what is the planned thickness of the walls.
In addition, it is necessary to take into account the own weight of the supporting structure, the calculation of which is made taking into account the depth of freezing, the level of occurrence of groundwater and the presence or absence of a basement.
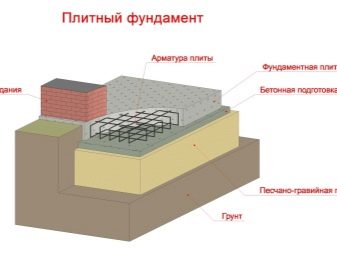

If a basement is not provided, the base of the foundation must be at least 50 centimeters above groundwater. If a basement is expected, the base should be located 30-50 centimeters below the floor.
Dynamic loads are also of great importance. This is a subgroup of temporary loads that have an immediate or periodic impact on the foundation. All kinds of machines, engines, hammers (for example, stamping hammers) are examples of dynamic loads. They have a rather complex effect both on the supporting structure itself and on the soil below it. If it is assumed that the foundation will experience such loads, they must be especially taken into account when calculating.
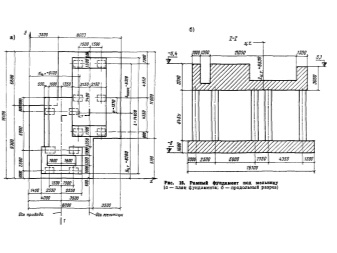
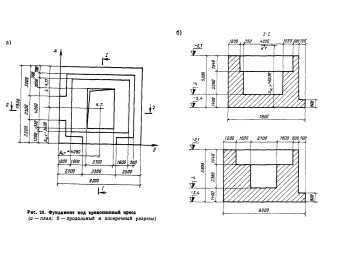
How to calculate?
The load on the foundation is determined by the totality of the loads of all the constituent elements of the building. To correctly calculate this value, you need to calculate the load of walls, roofs, ceilings, the impact of natural factors, for example, snow, add it all together and compare with the value that is considered acceptable.
Do not forget about the type of soil, which has a direct impact on which type of foundation to prefer and to what depth to lay it. For example, if the site has very mobile and unevenly compressible soils, a foundation slab can be used.
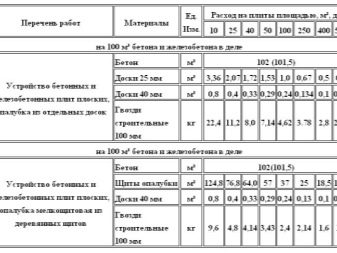
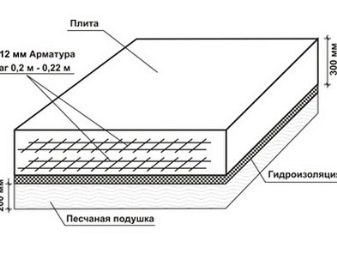
In order for the determination of the load to be as accurate as possible, it is necessary to collect the following information:
- What is the shape and size of the future home.
- What height will the basement be, what materials it is planned to make, what will be its outer finish.
- Data on the outer walls of the building. It is necessary to take into account the height, the area occupied in the walls by the gables, window and door openings, from what materials they will be folded, what materials will be used for exterior and interior decoration.
- Partitions inside the building. Determine their length, height, area that will be occupied by doorways, the material from which the partitions will be made, and how they will be finished. Data on load-bearing and non-load-bearing structures are collected separately.
- Roof. Take into account the type of roof, its length, width, height, material of manufacture.
- The location of the insulation is on the ceiling of the attic or in the space between the rafters.
- Basement overlap (floor on the ground floor). What type it will be, what kind of screed will it have.
- The overlap between the first and second floors - the same data as for the basement floor.
- Overlap between the second and third floors (if a multi-storey building is planned).
- Overlapping the attic.





All these data will help to make an accurate calculation of the loads and determine whether the obtained value meets the requirements of GOST or not.
A pre-drawn building diagram, which will indicate the dimensions of the building itself and all structures, will help in making calculations. In addition, it is necessary to take into account the specific gravity of the materials from which the walls, ceilings, partitions and finishing materials are built.
A table will help you, where the mass value for the materials most often used in construction is given.
Construction type | Her weight |
Walls | |
Ceramic or silicate solid brick 380 mm thick (1.5 pieces) | 684 kg per m2 |
510 mm (2 pcs) | 918 kg per m2 |
640 mm (2.5 pcs) | 1152 kg per m2 |
770 mm (3 pcs) | 1386 kg per m2 |
Ceramic hollow brick. Thickness - 380 mm | 532 kg per m2 |
510 mm | 714 kg per m2 |
640 mm | 896 kg per m2 |
770 mm | 1078 kg per m2 |
Silicate hollow brick. Thickness - 380 mm | 608 kg per m2 |
510 mm | 816 kg per m2 |
640 mm | 1024 kg per m2 |
770 mm | 1232 kg per m2 |
Pine bar 200 mm thick | 104 kg per m2 |
300 mm | 156 kg per m2 |
Frame with insulation 150 mm | 50 kg m2 |
Partitions and internal walls | |
Ceramic and silicate solid bricks. Thickness 120 mm (250 mm) | 216 (450) kg per m2 |
Ceramic hollow brick.Thickness 120 (250) mm | 168 (350) kg per m2 |
Drywall. Thickness 80 mm without insulation (with insulation) | 28 (34) kg per m2 |
Overlapping | |
Solid reinforced concrete. Thickness 220 m. Screed - cement-sand (30 mm) | 625 kg per m2 |
Reinforced concrete from hollow core slabs. Thickness 220 mm, screed - 30 mm | 430 kg per m2 |
Wooden. The height of the beams is 200 mm. With insulation, the density of which is not more than 100 kg per m3. The flooring is parquet, laminate, linoleum, carpet. | 160 kg per m2 |
Roof | |
Ceramic roof tiles | 120 kg per m2 |
Bituminous shingles | 70 kg per m2 |
Metal roof tiles | 60 kg per m2 |
Next, you need to calculate what load is exerted separately by one or another structural element. For example, a roof. Its weight is evenly distributed on those sides of the foundation on which the rafters rest. If the projection area of the roof is divided by the area of the sides on which the load is exerted, and multiplied by the weight of the materials used, the desired value will be obtained.
To determine what kind of load the walls have, you need to multiply their total volume by the weight of the materials and divide all this by the product of the length and thickness of the foundation.
The load exerted by the slabs is calculated taking into account the area of those opposite sides of the base on which they rest. It should be borne in mind that the floor area and the area of the building itself must be equal to each other. Here, the number of storeys of the building is also important and what material the floor is made of on the first floor - the overlap of the basement. To calculate the load, you need to multiply the area of each of the floors by the weight of the materials used (see table) and divide by the area of those parts of the foundation on which the loads are placed.


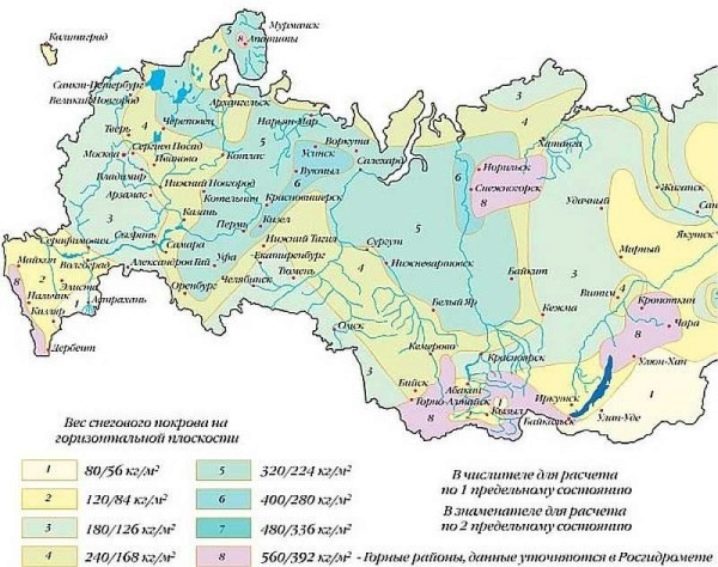
Of no less importance are the loads exerted by natural climatic factors - precipitation, wind, etc. As an example, the load from snow. Initially, it affects the roof and walls, and through them - the foundation. To calculate the snow load, you need to determine the area covered by the snow cover. A value equal to the area of the roof is taken.
This value must be divided by the area of the sides of the base under load and multiplied by the value of the specific snow load, which is determined from the map.
You also need to calculate the own load of the foundation. For this, its volume is taken, multiplied by the density of the materials used in the execution, and divided by the square meter of the base. To calculate the volume, you need to multiply the depth by the thickness, which is equal to the width of the walls.
When all the required values are calculated, they are added up. The result obtained will be the required load on the foundation. At the same time, the permissible value of this value should in no case be lower than the result that was obtained in the process of calculations. Otherwise, there is a high probability that the cargo area will not withstand the load and the building or foundation will deform.
Advice
Calculation of the load on the foundation is not a simple, but necessary measure. Therefore, you need to carefully calculate all the components, check all the values. However, in addition to building materials, floors, walls, and so on, all objects in the house will exert a load. This includes furniture, all kinds of equipment, and people in the building.
Calculating all these values is quite problematic, therefore, when determining the payload of a building, it is believed that 180 kg per square meter. To find out how much payload is on the entire building, you need to multiply the total area by this value.
In addition, each design has a characteristic such as a safety factor. It has its own for each material. So, for metal, this value is 1.05, reinforced concrete and reinforced masonry structures have a safety factor of 1.2 (if they are manufactured at the plant). If reinforced concrete is made directly at the construction site, its coefficient is 1.3.
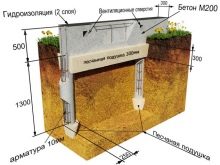


Familiarization with the necessary documents, such as JV "Loads and Impacts", SNiP "Construction climatology" (although the latter was canceled), will help to calculate the load on the foundation as accurately as possible and get all the necessary information.
You should not start construction without completing the calculations. This is a question not only of a prudent and responsible attitude to work, but also of the safety of people who will subsequently live in the house. Incorrectly performing load calculations or even refusing to carry them out can lead to deformation, destruction of both the foundation and the building itself.
See the next video about the system for calculating the load on the foundation.













The comment was sent successfully.