Subtleties of calculating the foundation slab

Modern houses are built on different foundations. The choice directly depends on the loads, the relief of the selected area, the structure and composition of the soil itself and, of course, climatic conditions. This article reveals complete information about the slab foundation, intelligibly answers the question of how to correctly make a complete calculation that will help build the required foundation.


Peculiarities
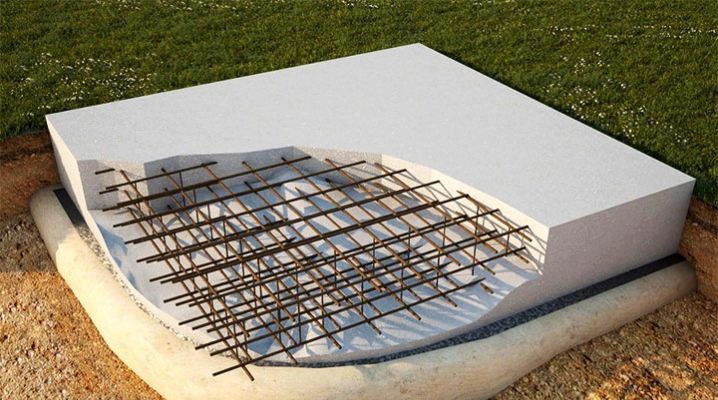
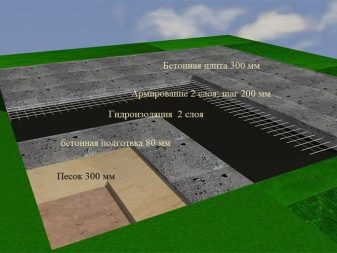
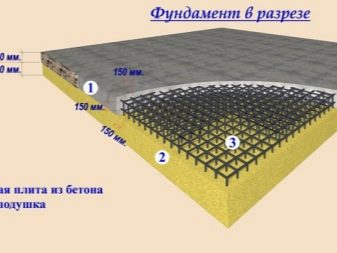
The tiled type of foundation consists of the base of the building, which is a flat or reinforced concrete slab with stiffeners. The structure of this foundation is of several types: prefabricated or monolithic.
Prefabricated foundations are prefabricated slabs made at the factory. Plates are laid with construction equipment on a previously prepared, that is, leveled and compacted, base. Airfield slabs (PAG) or road slabs (PDN, PD) can be used here. This technology has a major drawback. It is associated with the lack of integrity, and, as a consequence, with the corresponding impossibility of resisting even the smallest movements of the ground. It is for this reason that the prefabricated type of slab foundation is mainly used only on surfaces made of rocky soil or on non-porous coarse-grained soils for the construction of small structures made of wood in areas where the minimum freezing depth is.


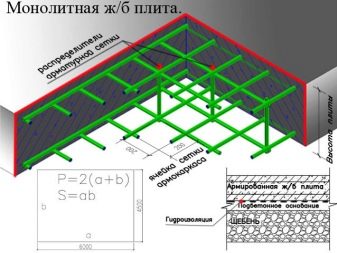
But a monolithic slab foundation is one whole rigid reinforced concrete structure that is being erected under the area of the building itself.
Geometrically, this type of foundation is of several types.
- Simple. When the underside of the foundation tile is flat and level.
- Reinforced. When the underside has stiffeners that are arranged in a specially calculated order.
- USB. This is the name of the insulated type of Swedish slabs, which belong to a variety of reinforced foundation slabs. During construction, a unique technology is used: the concrete mixture is poured into a separately developed factory type of permanent formwork, which allows further forming on an elastic foundation, or rather, in its lower part and on the surface, a mesh of reinforced and small-sized stiffeners. Also, the USHP has a heating system.
This article talks about the simplest monolithic slab foundation.



Advantages and disadvantages, selection criteria
The first advantage is almost perfect versatility. Sometimes on the net you can find articles that say that foundation tiles can be built everywhere.
Even if construction work is carried out on a swampy area, nothing terrible will happen to the tiles: during the period of severe cold weather, it will rise, and during the hot period, on the contrary, it will sink, so to speak, to swim.
It turns out a kind of "concrete ship", which has a superstructure on top of the whole house.
And yet, the following remark will be fair here: the only foundation that allows for a fairly reliable erection on planting and highly heaving soils, including a swampy soil type, is a pile foundation. This type of foundation is used when the piles have enough own length to be anchored in the lowest bearing soil layers.


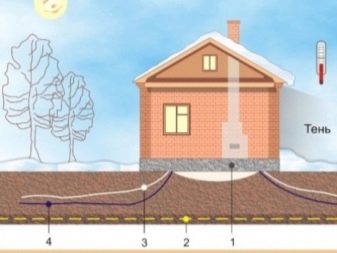
Frosty type of heaving, including subsidence, during thawing or subsidence of the foundation due to moistening of the soil surface (for example, during the rise of groundwater) cannot equally occur under the surface of the entire tile. In any case, only one of the sides will move more. A simple example would be the spring thawing of the soil surface. The thawing process will be much faster and more intense on the south side of the house than on the north. In the meantime, the tile will be subject to enormous loads, which, by the way, it does not always withstand. All this will affect the structure: the house can simply tilt. It won't be so scary if this building is made of wood. And if it was built of bricks or blocks, cracks may appear on the walls.
The slab foundation allows you to build houses even on the most difficult soils, which include the medium-porous type of soil, which has the least bearing capacity than, for example, strip soil. But you don't need to overestimate this opportunity.


Are slab foundations used when building large structures? Some argue that only the lightest and at the same time insufficiently durable structures can be built on a monolithic slab. This statement is not entirely true, because with the choice of favorable conditions and a correctly designed foundation with competent construction work, the slab foundation is able to withstand even the capital's Central Department Store. By the way, this building was built on a slab.
The price is too high. For some reason, this opinion is widespread. Almost everyone is sure that the slab type of foundation is very expensive, more expensive than the existing types of foundation. Also, for some reason, most believe that the cost will be about half of the available costs for all subsequent construction work.
At the same time, no one has ever conducted any comparative analysis. Also, for some reason, many do not take into account that during the construction of a house, for example, there is no need to make floors. Of course, this refers to a rough floor surface.

The complexity of the work itself. The following statement is often heard: "For the construction of a slab-type foundation, the experience of qualified workers is required." And yet, if you think about it, it becomes clear that such "masters" greatly overestimate the prices for their work. In fact, only ignorance of the technology usually leads to mistakes, and you can twist it with any other foundation.
So what kind of difficulties can you face when working with a slab foundation? When leveling the site? No, everything here is also no more complicated than when leveling a buried strip foundation foundation. Perhaps the difficulty with waterproofing or insulation? Here, rather, it is better to perform these operations on a flat horizontal surface than on vertical planes.


Maybe it's the knitting of the reinforcement cage? Again, you need to compare and understand which is easier, for example, you can take the reinforcement laid out on a flat site, or crawl with your hands into the strip foundation itself with its formwork. Maybe it's the pouring of the concrete mixture itself? In this option, everything depends not on the chosen foundation, but rather on the characteristics of a separate area, on whether the mixer can drive up to the construction site or whether the concrete will have to be mixed manually.
In fact, erecting foundation slabs is a physically challenging task. Due to the rather large construction area, this work can be called tedious, but it does not say that the help of qualified builders will be required. Therefore, ordinary "handy" men will be able to cope with such a case. In addition, if you correctly follow the construction technology and SNiP of a columnar, slab and other foundation, everything will definitely work out.


Calculations
Each zero cycle will require a calculation, which consists, first of all, in determining the thickness of the slab itself.This choice cannot be made approximately, since such an unprofessional solution to the issue will lead to a weak base that can crack in cold weather. They do not make too massive a deep foundation so as not to waste unnecessarily extra money.
For self-construction of houses, you can use the calculation below. And even if these calculations do not compare with engineering ones, which are carried out in design organizations, nevertheless, it is these calculations that will help in the implementation of a high-quality foundation.

Examine the ground
The soil on the selected building site should be examined.
For further calculations, you will need to select a certain thickness for the foundation slab with the appropriate mass. This will help to obtain the best specific pressure on the available soil type. When the loads are exceeded, the structure usually begins to "sink", at minimal loads, a slight frosty swelling of the soil surface will tilt the foundation. All this will cause corresponding not too pleasant consequences.
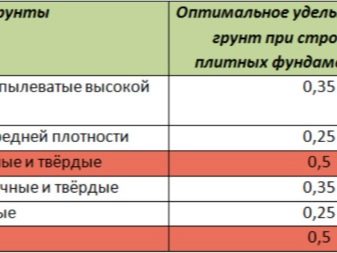
The optimal specific pressure for the soil surface on which construction is usually started:
- fine sand or dusty type of high density sand - 0.35 kg / cm³;
- fine sand with an average density of 0.25 kg / cm³;
- sandy loam in solid and plastic form - 0.5 kg / cm³;
- plastic and hard loams - 0.35 kg / cm³;
- plastic grade of clay - 0.25 kg / cm³;
- hard clay - 0.5 kg / cm³.


Total weight / weight of the house
Based on the developed project of the future structure, it is possible to determine what the total mass / weight of the house will be.
The approximate value of the specific gravity of each structural element:
- brick wall with 120 mm thickness, that is, half a brick - up to 250 kg / m²;
- aerated concrete wall or 300 mm D600 aerated concrete blocks - 180 kg / m²;
- wall of logs (diameter 240 mm) - 135 kg / m²;
- 150 mm timber wall - 120 kg / m²;
- 150 mm frame wall (insulation is required) - 50 kg / m²;
- attic made of wooden beams with mandatory insulation, density reaching 200 kg / m³, - 150 kg / m²;
- hollow concrete slab - 350 kg / m²;
- interfloor or basement made of wooden beams, insulated, density reaches 200 kg / m³ - 100 kg / m²;
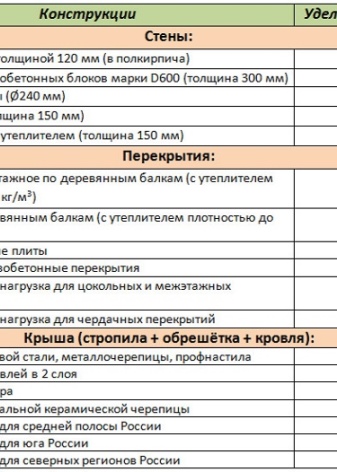
- monolithic reinforced concrete floor - 500 kg / m²;
- operating load for overlapping interfloor and basement - 210 kg / m²;
- with a roof made of sheet steel, corrugated board or metal tiles - 30 kg / m²;
- operating load for overlapping the attic - 105 kg / m²;
- with a two-layer roofing material made of roofing material - 40 kg / m²;
- with a ceramic tile roof - 80 kg / m²;
- with slate - 50 kg / m²;
- snow type of load applied to the middle zone of the Russian territory - 100 kg / m²;
- snow type of load for the northern regions - 190 kg / m²;
- snow type of load for the southern part - 50 kg / m².
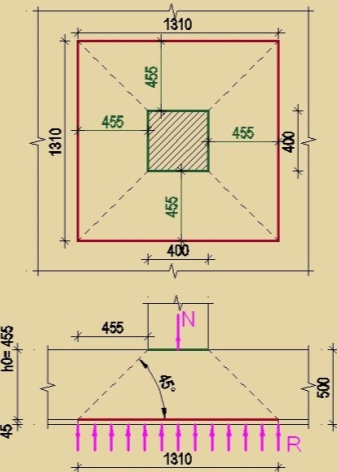
Calculating the area of the slab
The area of the entire slab must be calculated based on the engineering design. The weight of the structure should be divided by the area in order to obtain an indicator of the specific load acting on the soil surface. By the way, the result obtained does not take into account the fundamental mass. Next, you have to compare the resulting figure with the optimal concentrated load, then you can calculate the difference, that is, find out how much is not enough to obtain the optimal specific pressure. The resulting difference must be multiplied by the area of the slab itself in order to ultimately obtain the required mass of the foundation.
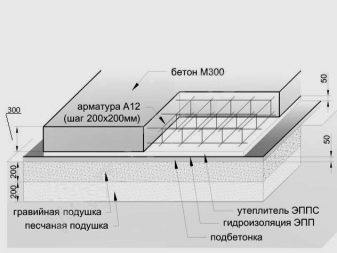
Further, the resulting result of the mass of the foundation slab is divided by the density of reinforced concrete 2500 kg / m³. Thus, the required volume of the foundation slab will be obtained. This volume must be divided by the value of the area of this slab to get its thickness.
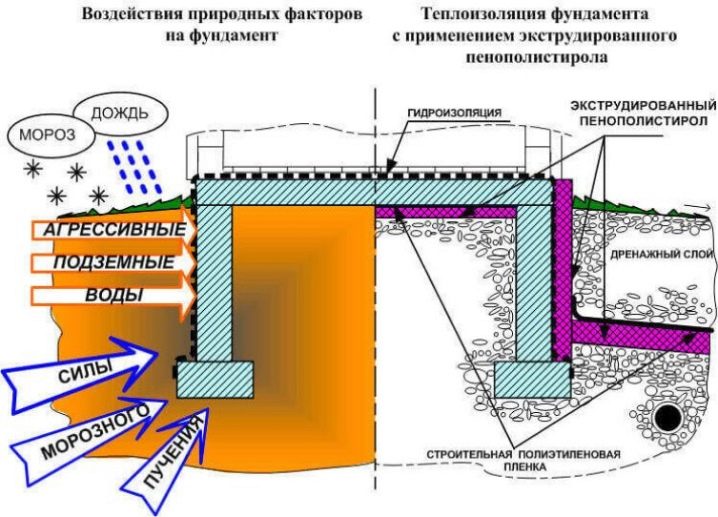
The resulting thickness must be rounded to the nearest largest or, conversely, the smallest value, which is a multiple of 5 centimeters.Based on the already rounded values, it is necessary to recalculate the weight of the foundation again, adding the number with the mass of the building to determine the calculated specific pressure acting on the soil surface. Next, you should compare the obtained result with the optimal one. It is important to remember that this difference cannot exceed ± 25%.
The specific type of load from the total weight of the building acts on the concrete below. Based on this, it is necessary to determine the optimal grade of concrete that will be used for pouring, provided that the strength of the concrete pavement remains in compression, that is, to calculate for punching. Basically, the choice is between the M300, M200 and M250 brands.
In fact, such calculations are considered simple. Here you only need the knowledge acquired at school in mathematics lessons.
For information on how to build and calculate a monolithic foundation, see the next video.













The comment was sent successfully.