Rules for calculating and erecting a slab foundation

Not a single capital structure can do without a foundation. Even if it is practically on a special place belongs to structures based on slabs of stone materials.
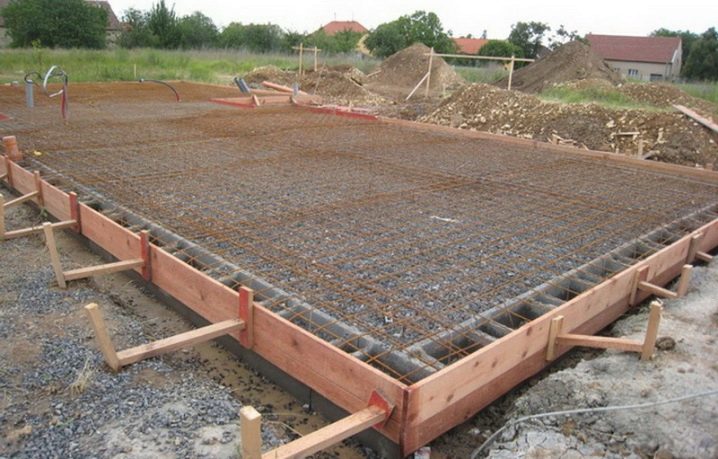

Peculiarities
No matter how much the tape and piles are praised, the slab foundation in a private house is not going to give up its positions. There are many names - many know about a solid, floating foundation, about Swedish slabs and simply slabs that come in various shapes. All this is far from accidental, because such a base for houses is used in a variety of conditions and situations. It is very important to understand correctly what is the specificity of the slab mass in general and of a specific type in particular. According to professionals, flat supports made of reinforced concrete of moderate thickness are best suited for private construction.
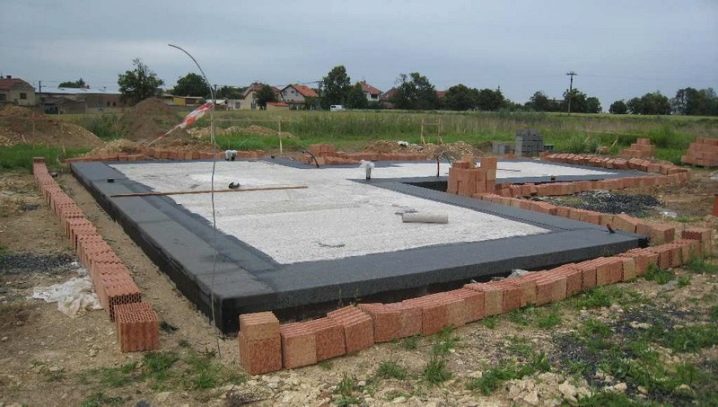

Advantages and disadvantages
The slab foundation system is authoritative for a reason, the reasons for its demand are related to both engineering and other considerations.
You can expand the slab on any basis:
- on soil with weakened bearing properties;
- on permafrost;
- in soils with high rates of horizontal movement;
- with a significant rise in groundwater;
- in areas prone to heaving.


You can find references to the fact that the slab foundation is difficult to erect on the slopes and that the pile foundation is more effective there. But it is not so. In the practice of construction in foreign countries, hybrids of slabs and high belts of monolithic design or a combination of piles with slab grillages have long been mastered. Regardless of the location, if done correctly, the bearing capacity of the slab foundation will be very high. This quality is ensured by the increased support area; suffice it to say that the Ostankino TV tower stands on a slab.


A solid level of spatial rigidity is ensured by the elimination of seams and rigid reinforcement schemes. The flip side of this decision is the inevitably increased material consumption. Architects consider slab foundations to be the optimal solution for structures with rigid walls, which should not move even in the smallest degree. Brick and cinder block houses, shell rock and aerated concrete structures feel calm and confident on such a basis. A reinforced concrete slab with little or no deepening is well suited for work even on very violently swollen soils.


It is harder for water to seep through the slab base, in addition, it is better than tape and piles in terms of thermal characteristics. Construction from scratch requires a minimum amount of earthwork, marking the structure is not difficult, as well as reinforcement and concreting. The level of requirements for the qualifications of builders is being reduced.
At the same time, it is worth considering certain weaknesses of the slab foundation:
- very poor compatibility with the organization of the basement;
- high consumption of concrete mortar and reinforcement;
- poor understanding of many people about the real characteristics of plates and their types;
- the ability to work only in good weather.


It is worth considering that the significant consumption of materials when pouring the foundation slab is fully justified at the subsequent stages of work, since the subfloor for the first floor will already be ready, there is no need to create an overlap.It will be possible to form a warm floor directly in the mass of the slab, abandoning the addition of an additional screed. To make the formwork, you will need significantly less planks or steel sheets than using tapes. Since the volume of excavated soil is reduced, the payment for its removal is also reduced.
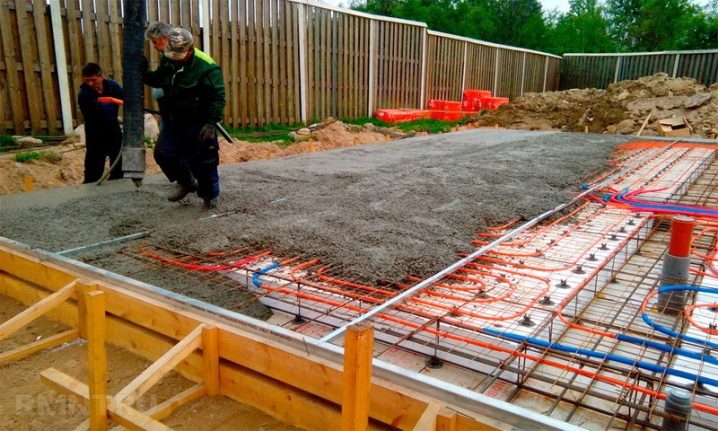

Lowering the basement reduces the height of the walls, the cost of money and labor for their decoration becomes less. There is no need for concrete pumps, lifting equipment and excavators, and drilling. All you need are mixer cars. Ideally, you can do all the work with your own hands and not depend on the skill of professionals.
Regulatory Requirements
GOST prescribes a number of standards that any slabs used to organize foundations must comply with. According to them, such structures can only be used for buildings and structures designed for seismic hazard of no more than 9 points. It is unacceptable to lay such slabs without special protection if the soils and the waters contained in them can destroy reinforced concrete. But the resistance to severe frosts (at air temperatures below -40 degrees) is quite sufficient. Before construction begins, a full set of geological surveys should be carried out.


The list of them is determined by the design organization, starting from the technical specifications for construction. Sounding in static and dynamic mode is obligatory. This is the only way to assess well the strength and mechanical parameters of the soil substrate. For load calculations, official building guidelines allow the slab to be built to ignore its own weight if it is to be placed on sand. The interaction of the base with the structures at the top should be calculated taking into account the sequence of construction work.
The choice of the design scheme is necessarily preceded by an assessment of the compressible base thickness. When the shrinkage of a future house or other structure is calculated, it is categorically unacceptable to ignore any loads, including natural ones. To eliminate misunderstandings from heterogeneity in assessing soil properties, the substrate is conventionally divided into so-called nodes. The preliminary dimensions are taken exactly such that they will guarantee to avoid punching the concrete layer under the design load. Given the many nuances that arise, it is recommended to entrust the design to specialized organizations.
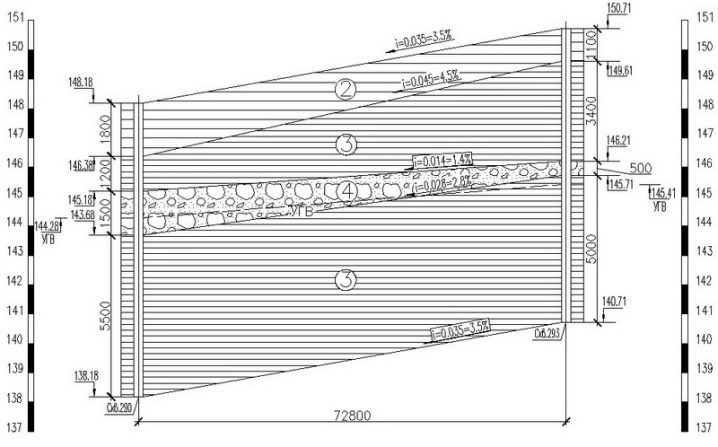
Views
When building houses, the concrete slab base is not always the same.
The monolithic schema is divided into three subtypes:
- without deepening (with pouring directly on the surface);
- with shallow penetration (0.5-0.6 m);
- with deep penetration (up to 150 cm, that is, to the greatest depth of soil freezing).



Industrial construction sometimes implies large depths of laying slabs, but they will not be required for the construction of residential buildings. A solid concrete slab is much better than a chain of prefabricated blocks connected with cement mortar. The combination of even strictly homogeneous parts is not durable enough, and the joints are the main problem. Another problem is that the RC slab can only be delivered and installed on site using expensive machines. Directly on site, you can use both plain concrete and reinforced concrete; the width of the surfaces to which the load is applied is 160 mm as standard.

The slab foundation can be poured properly only with special heavy concrete. The choice of his brand in each specific situation is strictly individual. Developers must take into account both the future operation of the structure and the climatic characteristics of the construction area. When making a final decision, you must first make sure that it guarantees resistance to getting wet and freezing.Reinforced foundation blocks are supposed to be stuffed with either steel rods or reinforcing wire of strictly defined sections.


Road concrete products are attractive for their good climatic characteristics. Suffice it to say that they are used for their intended purpose even in the Far North and in other regions with severe weather conditions. With strength, too, everything is in order - on the roads where such plates are used, it is allowed to pass heavy equipment. Previously used road blocks are not always of good quality. If you buy brand new ones, you will need to pay a noticeably larger amount.

Experience has shown that paving slabs are best placed where there is no need for a high plinth. This is a garage, an outbuilding or a summer kitchen. In the case of a country house or suburban building, the owner is limited to two floors. Some people are also interested in slab foundations made of aerated concrete.
According to the regulations in force in the Russian Federation, it is strictly forbidden to use for foundation construction:
- fired stoneware containing a void or gap;
- silicate brick and materials based on it;
- concrete blocks with cracks or voids;
- ceramic bricks produced by the semi-dry pressing method;
- all cellular concrete in any form.




Aerated concrete belongs to the last category of materials; for the same reason, the foam block is also prohibited. There are a number of reasons why the drafters of the regulations introduced such a strict ban. So, aerated concrete blocks are designed to reduce the mass of the enclosing structures, and their specific gravity is three times or even four times lower than that of heavy concrete. Therefore, the strength and bearing capacity are insufficient to solve the problem. Air filling, improving acoustic and thermal properties, reduces strength.

In terms of mechanical strength, ready-mixed concrete is ahead of aerated concrete, because crushed stone from gravel or granite acts as fillers. If there are still any doubts, it is enough to take into account that load-bearing walls made of gas blocks are not designed to support floor slabs. Given this, aerated concrete and aerated concrete are unacceptable even for above-ground parts of foundation structures. Aerated concrete blocks laid in the walls must be covered with a layer of waterproofing from the outside and a vapor barrier must be created from the inside. The statements of any teams and contractors about the construction of aerated concrete foundation testify only to their low professionalism.

Device
It is not enough just to choose the right type of slabs. It is necessary to carefully evaluate their required dimensions, and first of all, the thickness. The calculation of these parameters is based on the design loads.
The main focus is on:
- pushing loads;
- bending forces;
- the effects of frosty heaving of the soil.
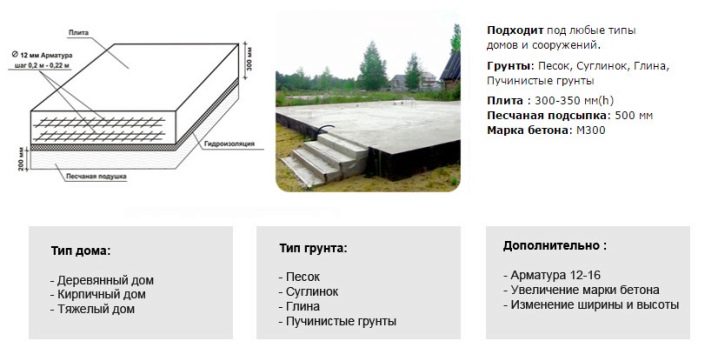
An analysis of long-term practice shows that for a frame house of two floors, the floors in which are made of reinforced concrete, it is necessary to put 200 mm thick slabs in the base. If the structure of the house is lighter, you can get by with a 150 mm slab. Important: these numbers apply only to the simplest cases with minimum load. As the weight of the house grows and its dimensions increase, the required thickness of the slab also increases. When it is known in advance that the house will be used all year round, it is recommended to carry out thermal insulation.


The thermal protection layer is formed both below the slab and above it. These materials should also be taken into account in order to make the right choice. Hydraulic protection in areas where groundwater is separated from the surface of 1 m of soil or more is performed in a simplified format. But with a high level of soil fluid, this practice is contraindicated. The reliability and strength of the slab foundation largely depends on how well the sand cushion is made under it.


There is gravel at the top.This material prevents moisture from concentrating under the sole of the base. The diverted water falls into a layer of sand, through which it passes even further. Additionally, the sand mass ensures uniform pressure distribution, dampens the effect of heaving forces. Under the garages where the car has to be repaired (and not just stored), the depth of the foundation is made deeper than usual, and the complexity of the work increases.
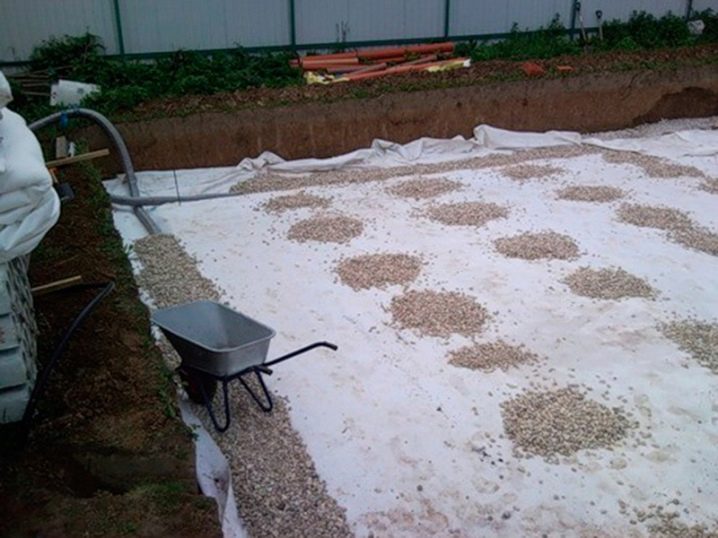

Most often, a monolithic slab is mounted under the garages according to a floating scheme. It is suitable for absolutely any soil and effectively suppresses the destruction of the garage during ground movements. As with home construction, there is no need to fill in an additional floor screed. Arrangement of underfloor heating with the rejection of classic radiator heating or in addition to it does not pose any particular problems. Attention: the secondary importance of the structure in comparison with the house does not allow it to be considered a less significant or secondary object.

How to calculate?
Accurate calculations are the builders' faithful helpers in any business. The dimensions of the building should be determined by driving the stakes in the corners. The depth of laying slab foundations under garages varies from 20 to 50 cm. In this case, as well as during the construction of houses and other utility structures, the area may increase if a blind area is equipped. It is imperative to calculate in advance the necessary gravel backfill in terms of the thickness and volume of the material.

It is recommended to obtain data for calculating soil properties empirically. To do this, they dig a hole 1.5 m deep; the soil in it is assessed by the level of moisture, by the chemical and structural composition, by the density. In addition to the properties of the substrate, the type of building material, the highest thickness of the snow cover, the intended brand of cement should be taken into account. The most reliable estimate is obtained with several holes dug in different places at the same distance from each other. Do not forget about the safety factor, which allows you to create a safety margin of the structure.
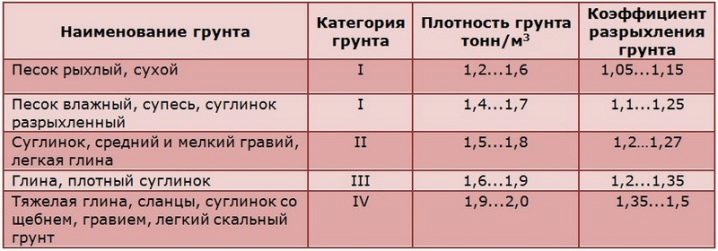
An indispensable step in the calculations is to determine the critical mass of the base, above which it is likely that the slab itself and the building will settle under the created load. When calculating the required slab thickness over 350 mm, tape or piles should be preferred, since a monolithic base will be too complex and expensive for most cases. The thickness of the filling of sand and crushed stone can vary from 0.15 to 0.6 m - everything determines the properties of the area and the typical climate. At depths of freezing over 1 m, it is advisable to make a pillow of 400-450 mm of sand and 150-200 mm of crushed stone. Heat protection even in the southern regions of the Russian Federation cannot be less than 0.1 m, and in the northern territories - from 0.15 m (with an additional increase in humidity).
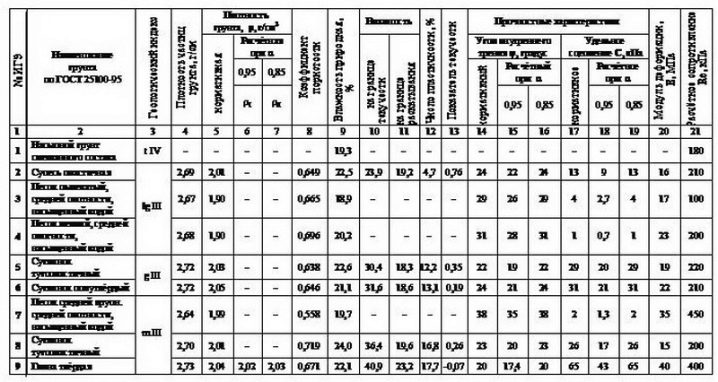
How to build?
It is advisable to pour concrete into the foundation structure continuously, therefore it is recommended to order the delivery of ready-made mortar. They usually lay it from the distant edges; when distributing the mixture, it must be compacted with a vibrator. After 24 hours after pouring, the concrete surface should be watered with water. If the air temperature is high, it is covered with a film and periodically moistened. When pouring a concrete slab foundation with your own hands, any work can be performed only when the strength of the artificial stone reaches 200% of the maximum level.

Complex and heavy structures must be supported with stiffeners. The trench encircling the foundation should have a depth of 0.5 and a width of 0.45 m. The ditch is supposed to be filled up in the same way as the foundation pit; reinforcement and tamping are required. The box is poured only after the end of these manipulations. Before the construction of aerated concrete or other lightweight house on weak or water-saturated soils, the list of surveys reaches a maximum.
The step-by-step instruction, for all its simplicity, does not guarantee a decent result if the terrain is complex and the soil structure is contradictory. In such a situation, it is advisable to start with the preparation of the project by specialists, and it is advisable to also involve at least one knowledgeable builder in the work. Self-construction is categorically unacceptable if the water approaches the surface closer than 1-1.2 m. But even in a more favorable case, it is recommended to select materials and structural elements with utmost care.


The general sequence of works according to the standard construction technology implies:
- laying out a pillow;
- installation of formwork;
- preparation of a hydraulic barrier;
- stretching communications;
- the formation of a reinforcing cage;




- pouring concrete;
- compacting the mass with vibrators;
- covering the casting with plastic wrap for about 5 days;
- dismantling of formwork structures;
- completion of waterproofing works;
- finishing the outer contour of the blind area.




Although such a solution is considered budgetary, this does not affect the quality characteristics. It is very important not only to fill the pit with high-quality cement, but also to think about the characteristics of the reinforcement. If it is poorly laid or unprofessionally tied, there is a risk that such an element simply will not accept the bending force and will not even out the resulting stress. It is for this reason, which is important, that most of the structures on a slab base fail. When the very work of forming a support for a house or other building is completed, it is worth thoroughly making drainage and a blind area.
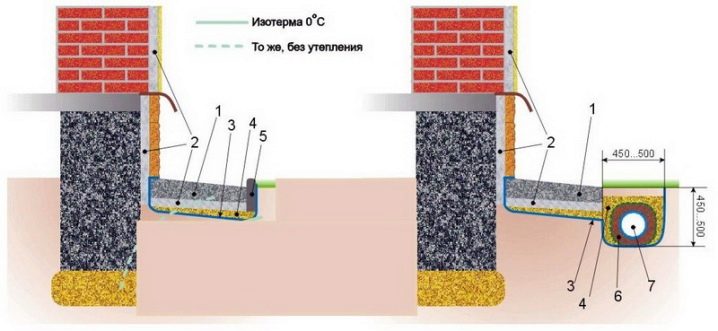
Errors in these two elements will very quickly lead to the degradation of the foundation itself. It will be useless to fill in the cracks and flaws that appear, because the cause that generates them will continue to work. The crushing power of frost and moisture, when combined, will damage the foundation slab with ease. According to professionals, it is necessary to mark the contours on the ground immediately after removing the top layer. If landmarks and points of interest are forgotten, serious mistakes will inevitably arise.

The pipe for the drainage system is discharged into a specialized drain outside the site. It is recommended to invite a roller or other heavy machine to compact the soil. Manual ramming and even the use of electrified mechanisms do not always give an acceptable result. In extremely damp areas, it is recommended to pour a thin gravel shell from a fine fraction of the stone. By imprinting it into the ground, they achieve such an implementation so that even a passage in shoes with stiletto heels does not leave visually noticeable traces.

After finishing the ramming, geological textiles are usually laid out. Instead of the road version, experts advise a denser variety of material weighing 0.15-0.2 kg per 1 sq. cm. The run of the canvases on each other is up to 200 mm. Staples inserted with a construction stapler help to avoid movements of textiles when pouring a layer of sand on top. For movement, the center of the pit is laid with a plank path.


Gravel backfill is made with pebbles, a layer of fine fraction is replaced by a larger stack. For waterproofing, glass roofing material or other roll material is used. Its canvases are wound on top of each other by about 100 mm. To prevent the seams from coming apart under the influence of "cement milk", use bitumen mastic. Reinforcement of the corners in the formwork panels is made by pinning the spacers horizontally. The outer sections of the waterproofing are slightly released onto the walls of the slabs and attached after a while.


Reinforcement of the foundation on soft soils is carried out in two layers, the second group of rods is laid along the perimeter, the distance is maintained at 3-3.5 cm. It is not recommended to bring the reinforcement closer to the upper and lower surfaces of the slabs by more than 40-50 mm. The thinner the slab, the more durable the grade of concrete you need to take for it.Experienced builders are advised to purchase all building materials directly from enterprises, since each intermediary is not only extra prices, but also the risk of quality loss. It is inappropriate to increase the thickness of the foundation beyond measure; it would be more correct to introduce plasticizers into the mixture to help avoid accelerated stratification.

To reduce the cost of operating the house and extend its service life, it is recommended to insulate the basement with mineral wool. At the same time, a number of works are being carried out that need to be known thoroughly. According to statistics, the basement part of the basement accounts for up to 15-20% of heat losses, and if the rest of the house is not thoroughly insulated, this percentage is even higher. When insulating material is selected, they are guided not only by low thermal conductivity, but also by reliable protection from getting wet. Special boards and sprayed coatings meet the requirements in the best way.


Mineral wool can also be applied, but you have to take care of additional cover for it. Insulation of the basement from the inside and outside is carried out using an identical technology. You have to choose either one or the other. When the basement part of the foundation is insulated from the outside, a steam barrier is preceded by the insulation, and if the work is done from the inside, a hydraulic protection is first created. There is also a difference in the finish - inside they use sheets of drywall, outside, only ceramic granite and moisture-resistant tiles are acceptable.

Mineral wool when insulating the basement must have a level of permeability to water vapor of at least 0.5 mg per minute. When a plaster layer is to be created over the wool, the minimum permissible density is 0.15 kg per 1 cubic meter. m. It is recommended to take only time-tested, well-known manufacturers for insulation. We must not forget about the danger to the respiratory system and the need to protect the hands. Work with wadded insulation should be done in tight, impervious clothing.


Insulating layers should be applied only on the prepared surface. It is cleaned thoroughly and even the smallest defects are removed. A height difference of 1 cm will inevitably disrupt the packing density. But even less pronounced deviations will greatly complicate the work. The alignment of the walls of the slab foundation is most often done using gypsum plaster. The need for such work will help assess the building level.


In order for the foundation to serve for a long time, attention should be paid to such a moment as the foundation. Its most important function is the elimination of leaks of a liquid solution. Also, the moisture in the poured screed will be evenly distributed, the base will definitely not crack. It will be possible to reduce the consumption of the solution, to reduce the susceptibility of the poured slab to groundwater.
Crushed stone concrete cannot be considered a reliable method. The reason is low rigidity, which does not allow the subsequent work to be carried out efficiently. This problem only manifests itself in the construction of houses. For a utility shed, street workshop, gazebo or small bath, there is no difference. The improvement in waterproofing properties is best achieved with bitumen. Roofing material and polyethylene materials protect the foundation from moisture worse.

Sand base is optimal in spring and autumn months when the soil changes.
The exact parameters of the foundation and the type of interlayer are selected taking into account:
- type of substrate;
- seismic activity in a given location;
- development of the adjacent territory.

For foundations made of slab and tape, the most reliable solution in many cases is not crushed stone or even sand, but a strong reinforcing frame made of concrete. For this purpose, low-quality varieties of the solution are usually taken. The required strength is achieved even for a layer of 100 mm, unless there is an active circulation of groundwater. When such circulation is found, moisture resistant films should be applied over the sand cushion for footing.On top of them, a reinforcing frame with a mesh size of 600x600 mm is additionally placed.

Advice
The grade of concrete for the main layer of the foundation, in contrast to the lining for it, must be very high. Extremely weak soil rocks, no matter how difficult it may be, you need to try to remove completely. If the excavator has dug somewhere deeper than required, you cannot fill the excavations with the extracted soil. For this, only the sand is suitable that will not allow the building to settle. Drainage taps for liquids are dug in advance, taking into account what kind of elevation difference is created.
For the rules for calculating and erecting a slab foundation, see the following video.













The comment was sent successfully.