What foundation to make on loam?
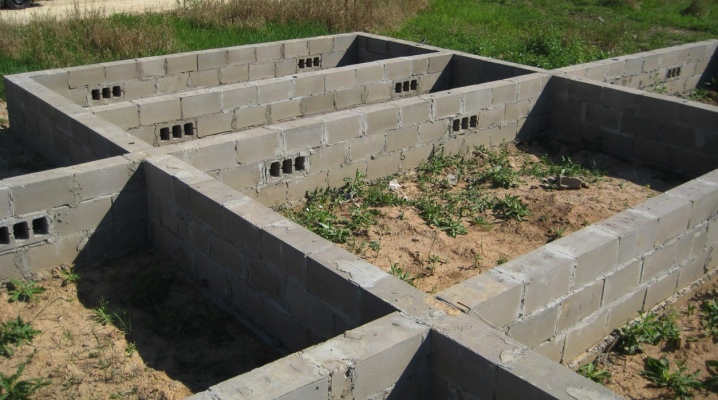

During construction, many people need to know the nuances of the foundation for loam. There you can equip a strip foundation with drainage and pile-grillage, some other types. It is useful to understand the characteristics of the soil and what type of base is best to choose for soft-plastic loam on the site.


What is special about soil?
It is worth pointing out right away that loam is not something monotonous, as is often believed. Despite the absolute dominance of clay, the specific proportion of substances may differ. The higher the sand penetration, the more pores appear and the lower the calculated soil resistance. In this case, they speak of soft-plastic loams. Such soil is moist to the touch, it is not difficult to knead it, and then the rock retains its given shape.
Dry loams are mostly crumbly. It was found that this property is associated with the entry of sand. The viscosity after wetting is due to the presence of clay. It also provokes freezing at certain temperatures and a sharp increase in volume. This combination of properties makes building on loam not so easy.
The proportion of clay, more specifically, ranges from 30 to 50%. The porosity can be from 0.5 to 1. The fewer the pores, the lower the probability of shrinkage and its severity. Water resistance is not provided; wet loam is easily washed away.


The level of bearing capacity tends to change - when wet it decreases, when it dries it increases.
Foundation types
When characterizing the base of houses, one cannot fail to mention the types of its drainage. If you do not equip drainage communications, then over time, housing or other building will be completely unusable. Although in ideal conditions storm sewers can be dispensed with, this approach is unacceptable for loam. We'll have to create full-format communications. Ring drainage helps to reduce moisture directly around the building, but a wall system on loamy soil is more effective.
Basic principles:
- processing of the entire foundation from sole to top;
- the use of storage wells (it is better not from concrete rings, but from plastic);
- covering the base from moisture using mastics or professional-grade rolls;
- preparation of revision wells.


As for the types of foundations themselves, pile-grillage foundations are often erected on loam. This is a kind of hybrid that connects pillars or concrete piles using tape or a monolithic slab. The connecting node is located above the pillars (piles). Such a solution is suitable for a very large house, for example, a full-size two-story or even a three-story mansion. But the main advantage is not carrying capacity.

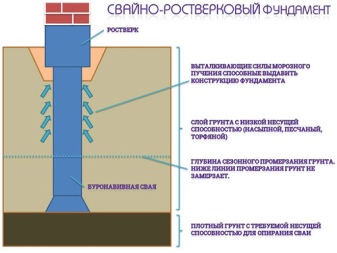
A shallow or completely devoid of deepening subtype of such a base implies the installation of pillars above the level of soil freezing. Suspended pile-grillage foundation is most suitable for medium-sized private buildings. It is not able to withstand a significant load, however, it guarantees resistance to uneven mechanical stress and winter heaving. In engineering and construction practice, such a solution received the code name TISE. If the work is done correctly, reliability is guaranteed; the characteristics of such a technology are sufficient to make it possible to almost abandon buried foundations in private construction.
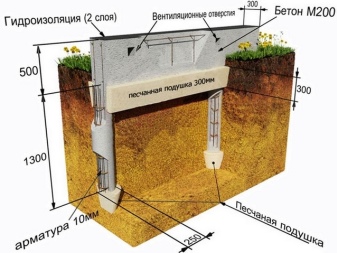

In some cases, you have to make a foundation slab. It is reliable and durable. The amount of excavation is relatively small. Despite the great complexity, the final price is not higher than that of the buried tape, especially when correcting for the arrangement of floors on the ground. A very important role is played by the correct organization of water drainage, waterproofing and blind areas.
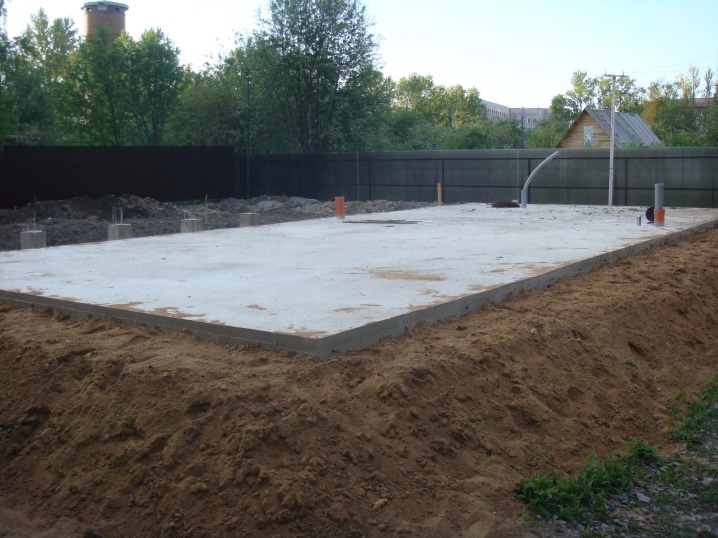

In areas with high groundwater (distance no more than 0.5 m from the surface), the only option is to use piles. It is best if these are monolithic piles that perfectly withstand the effects of frost heaving and other dangerous forces. But screw designs have been very popular lately.
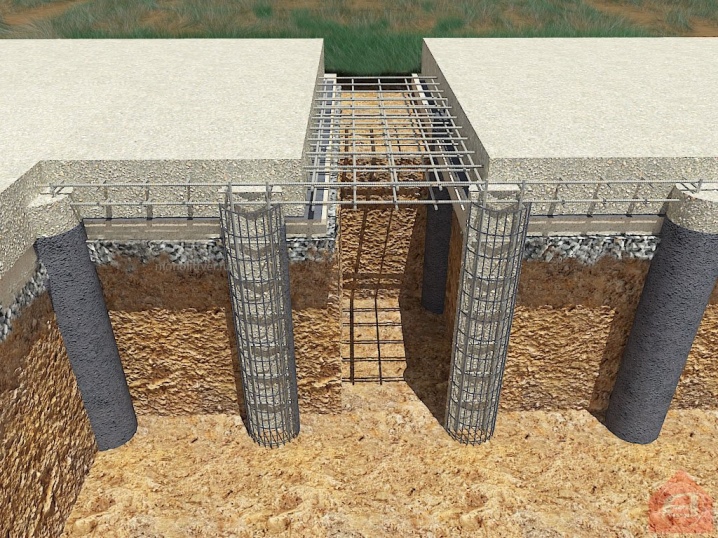

Their use is captivating in its simplicity. Importantly, such structures are not among the unequivocally recommended for loam - and therefore they can be used only after consultation with specialists.
If the groundwater is high, but still deeper than 0.5 m, you can use a traditional stove. Choosing a tape device helps to simplify things even more. It reduces the cost of preparing concrete. Almost always, it is possible to dig a recess for a shallow belt without an excavator. Important: you need a platform that is even or inclined by a maximum of 5 degrees.
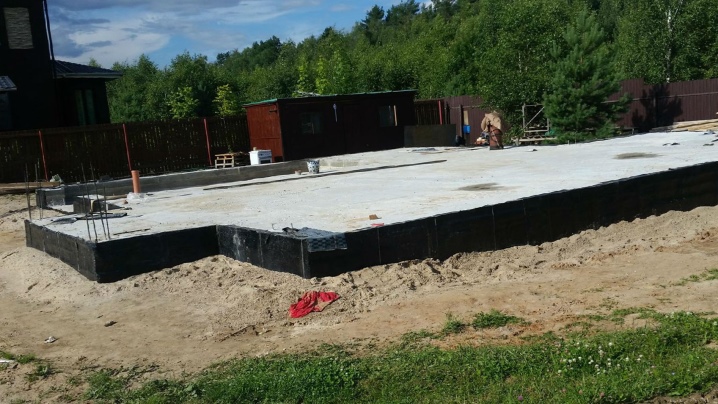

Which one is better to choose?
But nevertheless, clearer recommendations are needed on what basis to put on a site with loamy soil. Drilling wells and analyzing samples taken from different depths will provide useful information. A simpler method is to take samples from a depth of 1.5-2 m using garden drills. Samples are best done in spring or in the first half of autumn, when the soil water level is at its maximum. If the laboratory determines that this is a type of loam with special requirements, these requirements will have to be met.
In general, the approach is as follows:
- tapes laid below the freezing level are needed for heavy brick buildings;
- the slab will serve as a reliable base for different types of buildings and guarantee protection against non-uniform heaving;
- pile structures are used when you need to build reliably and quickly.


What foundation to make on loam, see the video below.













The comment was sent successfully.