Erection of a monolithic foundation: expert recommendations
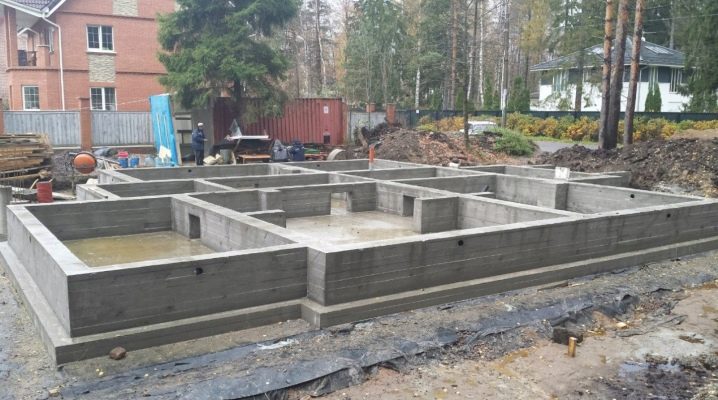

Moving, water-saturated soils, as well as relief with height differences, makes builders look for new technologies for organizing the foundation. One of these is a monolithic system, which allows construction on mobile and prone to seasonal waterlogging, swelling of soils.
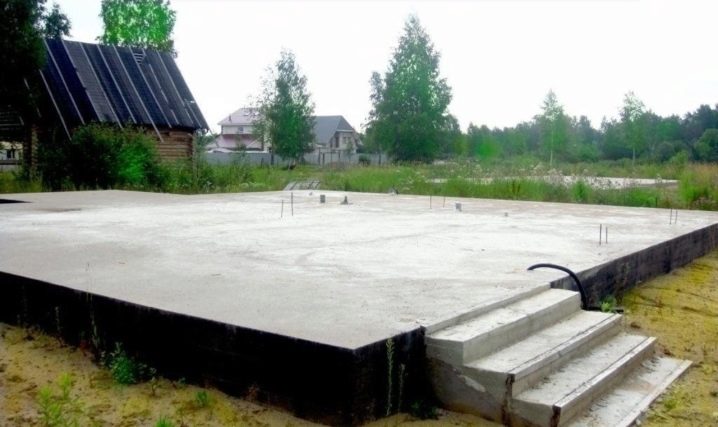

Peculiarities
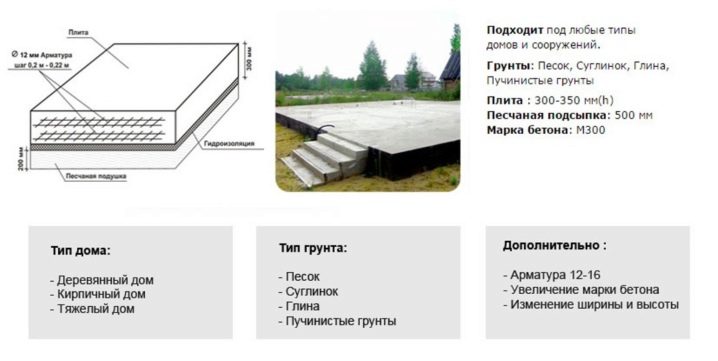
The monolithic foundation is a shallow slab, which is an inseparable structure of a reinforcing frame and concrete. Forming a single whole, reinforcement and concrete provide reliability and high load-bearing capacity.
Such a base is suitable for unstable and water-saturated soils., since it turns out to be quite mobile, but at the same time it provides an even distribution of the load. In other words, even experiencing some vibrations and vibrating with the ground, such a plate protects the house from subsidence and geometry disturbance.

This is achieved due to the unity of the structure and its shallow deepening. If the slab is lowered too far into the ground, then its side walls will be overly rigidly fixed. In this case, the soil swelling under the influence of negative temperatures will exert negative pressure on the slab.
Advantages and disadvantages
The main advantage of a monolithic foundation is the possibility of building on moving soils with a low bearing capacity. It saves if the construction of a private house on a pile or strip foundation is impossible or unprofitable on this type of soil. This can only be established when analyzing soils, including during their seasonal changes.

It is a misconception that a slab foundation is suitable for all types of soils. This is not true, although the slab is capable of leveling out some instability of the soil.
Such a foundation is not suitable for the construction of a massive cottage on very swampy soils. In this case, it is better to choose the pile option, strengthening the supports on hard ground, bypassing soft ones.

A floating slab foundation is indispensable for significant ground movements. He moves in a small amplitude (invisible to the residents of the house) with him. However, if significant changes in the movement of the soil are noticed under the slab foundation and near it, this means that the load on the soil is uneven, which is dangerous for the object. To prevent such phenomena, we repeat, only a thorough analysis of the composition and properties of soils will help.
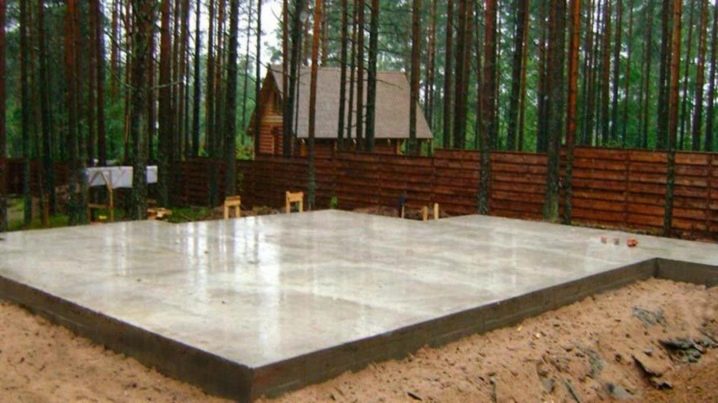

The advantage of a monolithic foundation is the ability to build rather massive, multi-storey structures on it.
However, provided that this type of soil is suitable for installing the slab, and all calculations are made with high accuracy.
The slab foundation has no seams, therefore, when the soil moves, it retains its reliability and solidity.


Often, among the advantages of a monolithic foundation system, a small amount of earthwork is indicated. A similar statement is true when it comes to a typical slab base. However, in some cases it is necessary to increase the thickness of the sand layer, therefore it is necessary to dig a deeper pit, which entails an increase in the volume of earthworks. A similar situation is observed when arranging a basement.
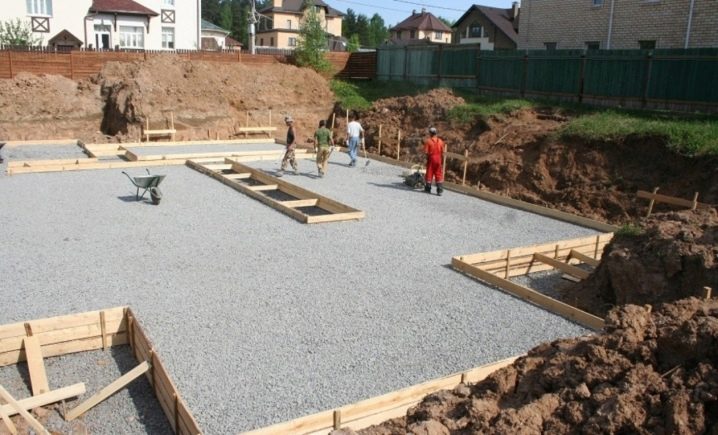

The advantage of the monolith foundation is the ease of installation of the floor, which is due to the ability to use the slab as a subfloor.If the installation is carried out according to Swedish technology, which assumes thermal insulation of the slab, then additional insulation is not required. On the one hand, this simplifies the process of installing the floor, on the other, it requires a responsible and professional approach to organizing each layer of the slab.
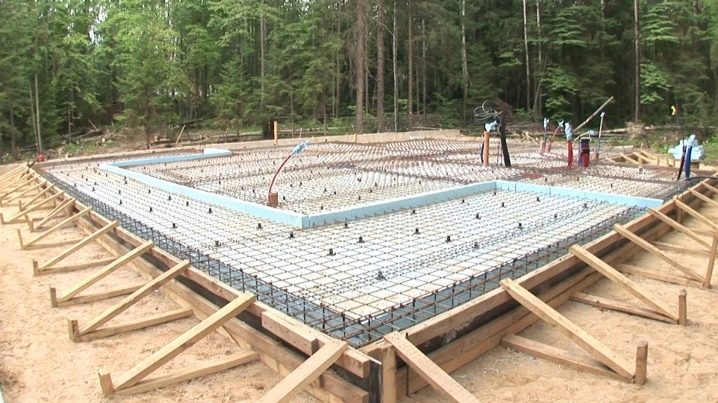

The last two factors lead to a higher speed of work. Such a foundation is, in fact, being erected quite quickly. Much time has to be devoted only to tying reinforcement.
In general, a slab foundation is suitable for all types of buildings, including unusual shapes. It is enough to dig a pit of the required size and achieve the required configuration using formwork in order to build, for example, a house with bay windows.



Among the disadvantages of this system is the need to attract special machinery and equipment, which leads to an increase in the estimate. When erecting buildings large in area, making high-quality compaction of soil with your own hands is problematic; you should get a gasoline or electric compactor.
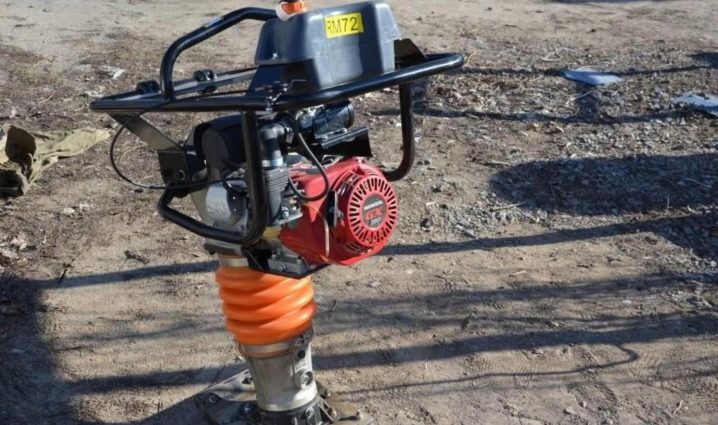

Reinforcement should be laid at a certain angle, therefore, to obtain the desired shape of the rods, it is advisable to have a special machine. Finally, the slab must be poured in one step without interruption, and the concrete must be applied evenly over the entire area. Naturally, this cannot be done without a concrete mixer or pump.


One of the disadvantages of this system is the need to level the area under the tiles. Of course, this does not mean that this type of foundation is unrealizable - the height differences need to be leveled, which in some cases may require significant financial expenses. In some cases, it is more profitable to resort to installing the base on piles.
A feature of the slab foundation is that all its parts must lie evenly on the ground. When voids appear, the reliability of such a structure is out of the question, which makes it impossible to organize basements under the monolith. However, this does not mean that you will have to completely abandon it. This problem is solved by organizing a deeper pit and arranging a basement directly on the slab.

This cannot be called a minus, rather, a feature - the need to carefully plan the ways of laying and routing communications at the planning stage. This is due to the fact that most of the communications are laid in the thickness of the slab. If an error occurs or you want to change something, it will be problematic to do it.
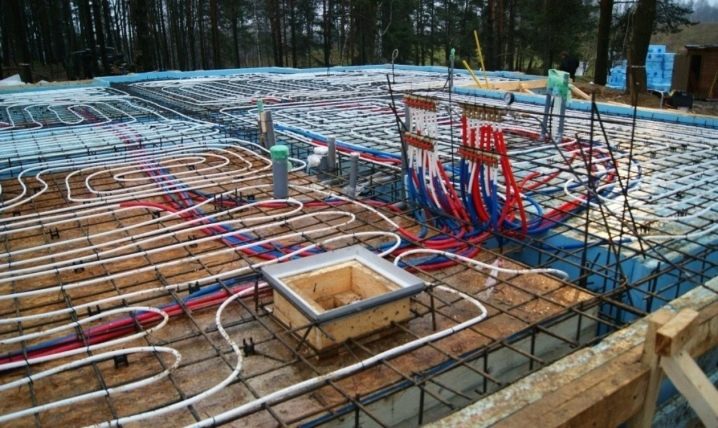

The disadvantage of this type of system is the high cost of installation. This is due to the need to fill a large area with concrete, as well as an increase in comparison with the number for a strip base, for example, the amount of required reinforcement.

Views
There are several varieties of a monolithic base.
- Tape. It is a reinforced concrete slab that is mounted around the perimeter of the building, as well as under the load-bearing wall structures of objects. This system is suitable for medium bearing capacities.

- Plate. Reinforced concrete monolith, poured under the entire surface of the house. In its classic form, it is a single slab without seams. However, there is also a collapsible version, assembled from particles. Unlike a monolith, such a structure has a lower bearing capacity, therefore it is not recommended for residential buildings. Suitable for soft soils prone to seasonal fluctuations, as well as in earthquake-prone areas.

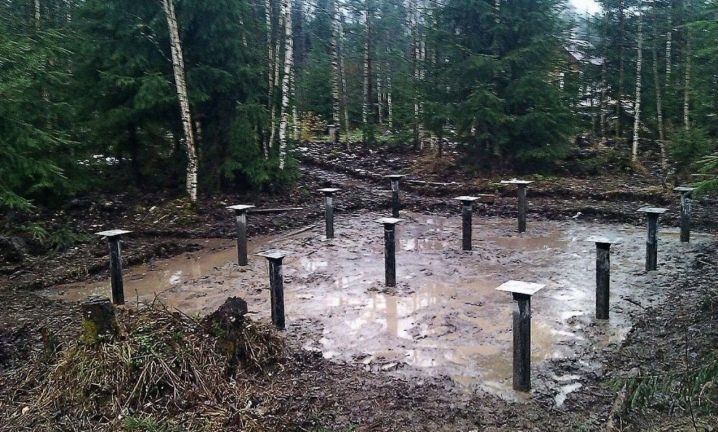
- Pile-grillage. It is a concrete base, dug into the ground and connected to each other by a single slab.

Despite the fact that all of these types of foundations have a foundation slab, a slab foundation is usually understood as monolithic (the second option in the list above).
Finally, monolithic foundations for road signs designated FM 1 are also referred to as monolithic. They are round bases made of reinforced concrete.

Depending on the type of deepening, the slab foundation is of two types.
- Shallow. It sinks into the ground by no more than 50 cm. In this case, a thick sandy "pillow" is required to level the heaving of the soil. Shallow foundations are mainly used on non-rocky soils for small buildings with walls made of wood or lightweight building blocks.


- Recessed. The depth of the slab can reach 150 cm. The exact depth is determined by the freezing point of the soil - the foundation should be 10-15 cm deeper than the freezing point and at the same time rest on solid layers.
The latter condition is paramount, that is, if the freezing level is at a depth of, for example, 1.2 m, and the solid layers are at a depth of 1.4 m, then the slab is laid at a depth of 1.4 m.
It is usually used in the construction of massive objects on a slab or structures higher than two stories.



Device
As already mentioned, the slab foundation does not require a large deepening; under it, a pit is dug at a shallow depth in size corresponding to the slab. Further, the bottom of the pit is covered with a layer of compacted soil, which is additionally crushed and leveled.


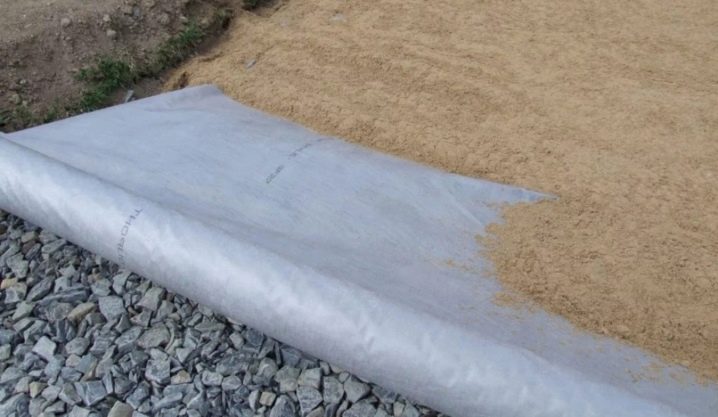
The next layer is a sand cushion, which helps to distribute the load correctly and evenly. Features of the material (small grains of sand) prevent the foundation from tilting and its subsidence, and also neutralizes the effects of soil heaving. Clean sand can also be replaced with a sand-gravel mixture or several layers of gravel of different fractions.

Geotextiles are laid on top of the sand layer, which performs a reinforcing and waterproofing function.
If you refuse to use this material, then you should be ready for the quick siltation of a layer of sand, especially when building on moisture-saturated soils. Depending on the characteristics of the soil and the object, geotextiles can be laid in several layers.
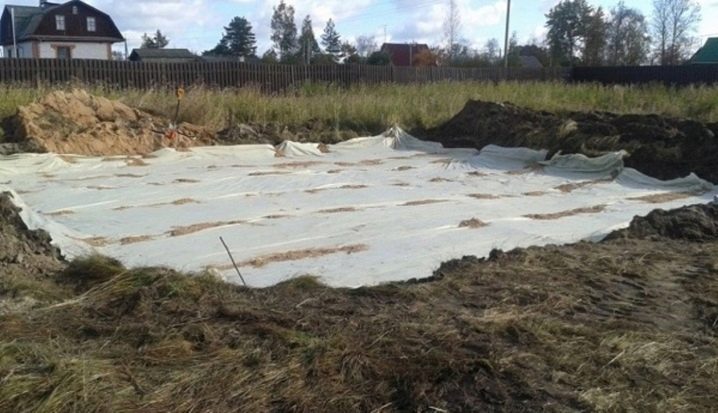

There is also a variant of preliminary waterproofing, when the installation of geotextiles is carried out immediately along the foundation pit - it is laid directly on the compacted ground. A sandy "pillow" is laid on top of it. This version of the device is relevant for unstable swampy soils. In some cases, geotextiles can be laid between sand and gravel layers. Usually crushed stone or coarse gravel is poured down, geotextile is poured on top, on which sand is poured. For the stability of the lower gravel layer, some sand can also be poured under it. This construction technology allows for better drainage of the site for the foundation.

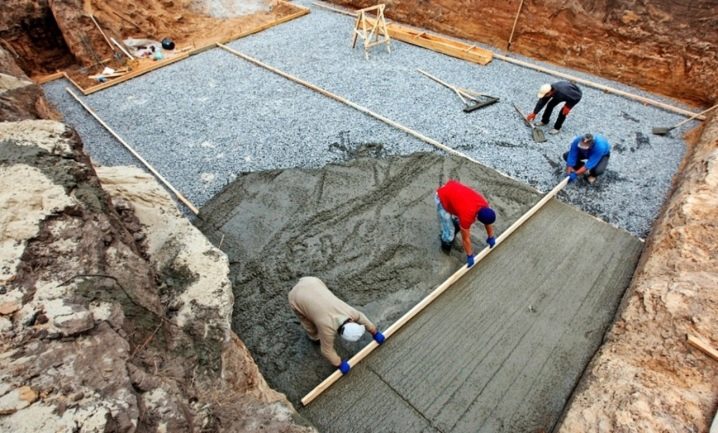
Even professional builders do not always lay the next layer due to their desire to reduce the cost estimate and speed up the installation time. However, this does not mean that this layer does not have its own functionality. We are talking about a thin concrete layer, the solution of which is poured over the lighthouses. Pre-concreting allows you to achieve the ideal level, and therefore the accuracy of the geometry of the entire structure. In addition, it is easier to insulate and waterproof the floor over the concrete layer.

The next layer is the finishing waterproofing, which is carried out using rolled bituminous materials. They are glued or fused in several layers and overlapping. Bituminous mastic can be applied under the layer of roll material.
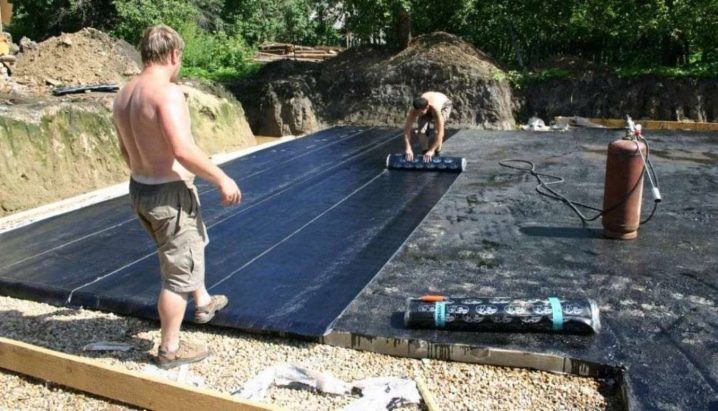

After completing the waterproofing work, a reinforced concrete monolith is mounted. Standard reinforcement is carried out in 2 levels with interlacing by means of vertical reinforcing elements.
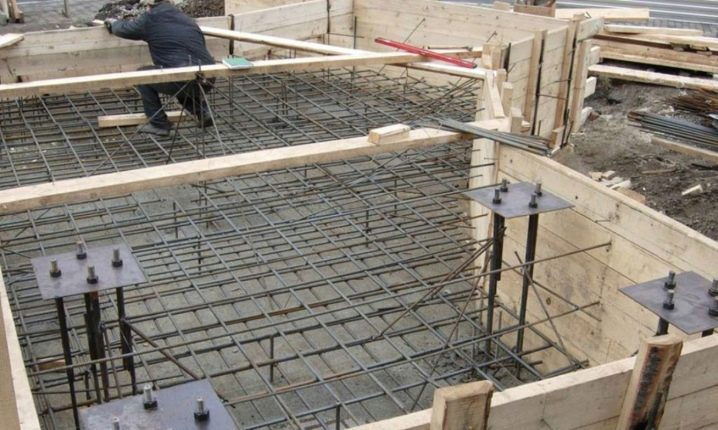

When pouring, make sure that each side of the reinforcing grid is completely covered with concrete, the width of which in these places is at least 5 cm. This will eliminate the penetration of moisture by the capillary method and protect the metal from destruction.
In some cases, the given typical scheme of a monolithic foundation may change. So, when the concrete level coincides with the soil line, they resort to increasing the thickness of the slab or using stiffeners. Both methods allow you to protect concrete from moisture, but the first will cost significantly more. In this regard, they often resort to installing stiffeners, which are poured under the load-bearing and internal walls. In addition to moisture protection, this design allows you to organize a basement room on a monolithic reinforced concrete base.
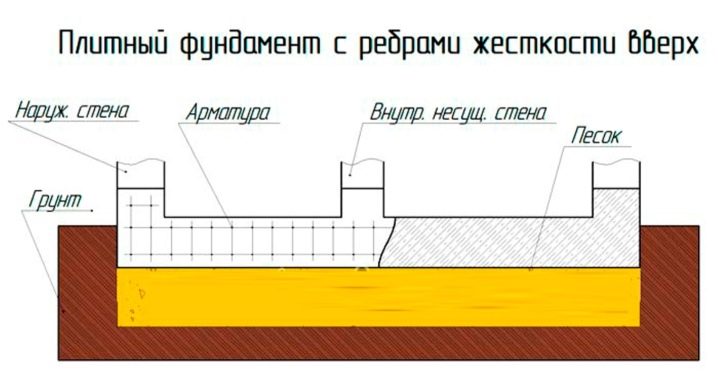
For outbuildings, you can use a slab prefabricated foundation. It is not a monolithic slab, but is assembled from "squares", which are closely placed on the prepared base. Such a design is characterized by less laboriousness of installation, however, it is inferior to a monolithic analogue in its reliability, and therefore is not recommended for residential buildings.
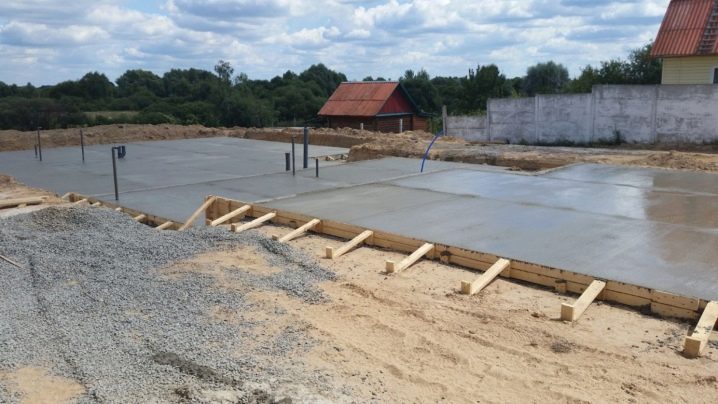

Payment
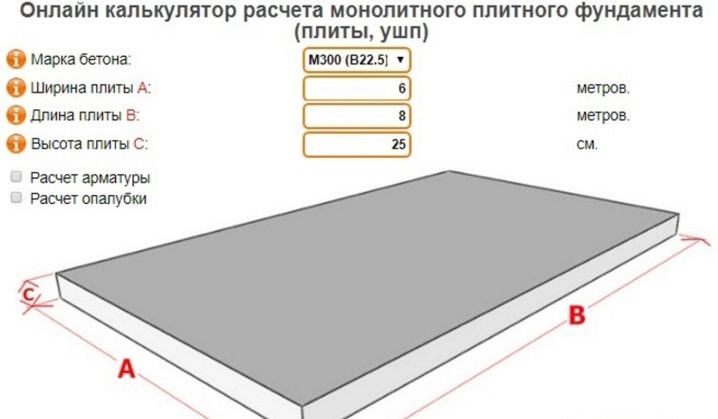
The construction of any foundation begins with preliminary calculations, which are part of the design documentation. Based on the data obtained, information about the dimensions and characteristics of each element of the base is taken, a plan of the "pie" of the slab is drawn up, the thickness of each of the layers is selected.
The most important indicator of the strength of a structure is the thickness of the monolith. If it is insufficient, then the foundation will not have the required bearing capacity. With excessive thickness, an unreasonable increase in labor intensity and financial costs occurs.
Correct calculations can only be made on the basis of geological surveys - soil analysis. For this, wells are usually made at different points of the site, from which the soil is taken. This method allows you to determine the types of soil present, as well as the proximity of groundwater.

Each type of soil is characterized by variable resistance to load, which means how much pressure (in kg) the foundation can exert on a specific unit of soil area (in cm). The unit of measurement is kPa. For example, the variable resistance of crushed stone and coarse gravel to the load is 500-600 kPa, while for clay soils this figure is 100-300 kPa.
However, calculations should be made based on the values not of the specific resistance of the soil, but of the specific pressure on a specific type of soil. This is due to the fact that with a small resistance, the foundation will sink into the soil. If the pressure turns out to be insufficient, it is impossible to avoid swelling of the soil under the foundation and its deformation.

Optimal pressure values are constant, they can be found in SNiP or freely available. The specific pressure is measured in kgf / cm kV and is individual for different types of soils. For example, plastic clays have a specific pressure of 0.25 kgf / cm kV, while the same indicator of fine sand is 0.33 kgf / cm kV.
Interestingly, if you compare the data from the resistivity table and the soil pressure, it turns out that the second table (pressure) will contain a smaller number of soil varieties. So, gravel and crushed stone will "disappear" from it. This is explained by the fact that the slab foundation is not the only possible option for construction on this type of soil. Perhaps the use of a tape analog will be more rational.
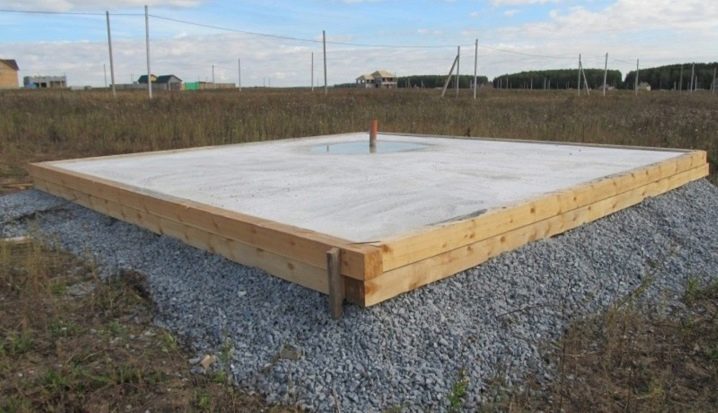

The above facts indicate the need to calculate the total load of the monolith, which acts on the soil. Knowing this indicator, it will be possible to make a decision to increase or decrease the thickness of the monolith, and also (if it is irrational to reduce the thickness of the slab) to use lighter materials for load-bearing wall structures. For example, instead of heavier bricks, use blocks, erecting walls of aerated concrete.

The optimal thickness for most buildings is a monolith thickness of 30 cm. The load-bearing capacity of the structure in this case will be sufficient, and the project will be economically viable.
If during the calculations it becomes obvious that the required base thickness exceeds 35 cm, it makes sense to consider other base technologies. Additional stiffeners can also be used to reduce material consumption while maintaining the thickness of the slab.
For brick walls, it is recommended to slightly increase the thickness of the base - it should be from 30 cm.For lighter materials, foam and gas blocks, this value can be reduced to 20-25 cm.
After the data on the required thickness of the monolith is obtained, they begin to calculate the amount of concrete solution. To do this, according to the drawing, you should calculate the height, thickness and width of the slab and make a small stock of solution of 10% to the resulting number. Cement grade must be at least M400.

Preparation
The preparatory stage can be divided into 2 parts - conducting geological surveys and creating a project, direct preparation of the site for the foundation.
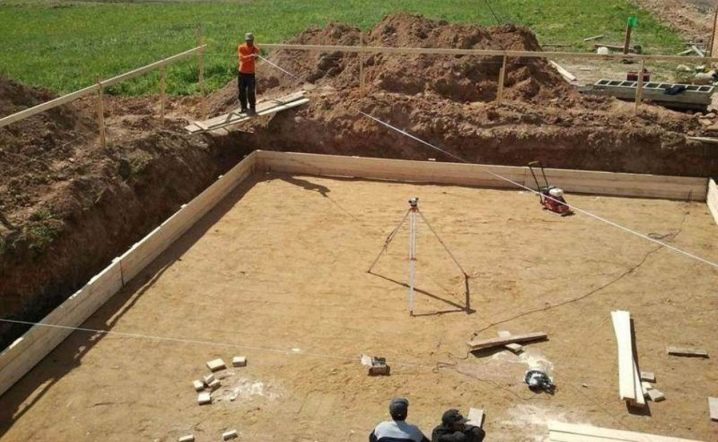
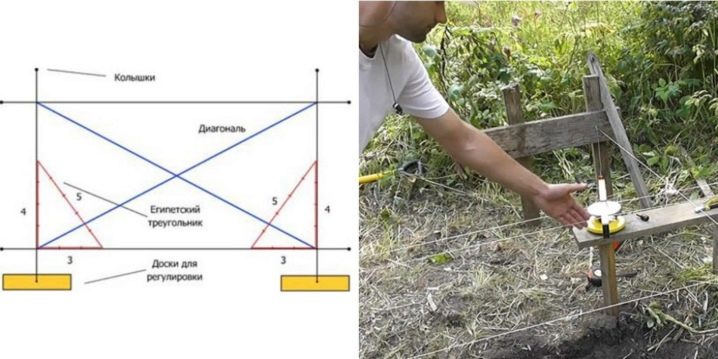
The area needs to be cleared of debris, and the entrances for special equipment should be prepared. After that, you should start marking. It is performed with pegs and a rope. It is enough to outline the outer perimeter of the future foundation.
It is important to make sure that the perpendicular lines form right angles.
After marking (or before it, as it is more convenient), the top layer of soil along with vegetation is removed under the foundation. The next step is digging a pit.


How is it being built?
Due to the small amount of earthwork and an understandable construction technology, the organization of a monolithic foundation can be done by hand. True, one cannot do without the involvement of special equipment.
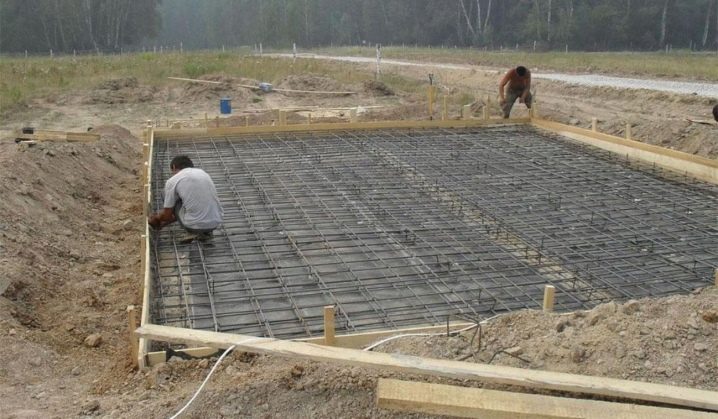

Step-by-step installation instructions are presented below.
- Site preparation, marking the location of the future foundation.
- Excavation - digging a foundation pit. It is more convenient to do this with an excavator. The depth of the pit must be sufficient to accommodate all layers of the "cushion", as well as part of the monolith. We must not forget that another part of it (10 cm is enough) should rise above the ground. In this case, the resulting walls and the bottom of the recess should be leveled mechanically.
The depth of the pit corresponds to the design one and is determined by the characteristics of the soil and the building. For example, on highly mobile soils, they resort to organizing a buried slab, therefore, the foundation pit is dug deeper. Similar actions are performed if you need a basement or semi-basement.


- The prepared foundation pit is covered with geotextiles. The material is overlapped in pieces. To avoid its creeping under the weight of the "pillow", gluing the joints with a moisture-resistant tape allows. Geotextiles are laid on the bottom and walls of the pit.
- Falling asleep in the pit of sand or crushed stone.
If sand is used, then it is immediately covered with an incomplete layer. In other words, the entire thickness of the sand is filled up in several stages, but one layer must immediately fill the entire surface of the pit. If you neglect this recommendation and fill up the entire volume of sand at once, then its weight will be unevenly distributed.


- Simultaneously with the filling of the sand layer, a drainage system is organized, thanks to which excess moisture will be removed from the monolith. A trench is dug around the perimeter of the pit, into which a plastic pipe is placed, which acts as a drainage channel. Its individual elements are collected into a single system, which is located at an angle to remove moisture to a designated place. Perforations are made in the pipe, and the space around it is filled with rubble.
- Let's return to the sandy "pillow", the thickness of which should be at least 20 cm. After backfilling, the layer is rammed, and the layer level should be checked all the time. This will help to make several pegs hammered in at different points inside the pit.
- The next layer (about 15 cm thick) is crushed stone, which will remove moisture from under the slab.It should also be tamped, keeping the layer level horizontally.



- After filling the crushed stone, they begin to create the side formwork, which should be quite strong, since significant loads will fall on it. When the slabs are insulated along the entire perimeter, the formwork is made of non-removable polystyrene foam plates of high rigidity. In other cases, removable formwork is made from boards or plywood.
- To reduce the risk of moisture penetration to the concrete layer, a polymer membrane is laid on top of the crushed stone. It also overlaps, but it is important to lay the membrane with the correct side to the rubble. The membrane is laid with an overlap and on the formwork.
- The next step is to pour the concrete screed, which is usually 5-7 cm thick.



- After the concrete sub-base gains strength, you can proceed to the final waterproofing. For this, the surface of the screed is covered with a bituminous primer, which improves the adhesion properties of the materials. Next, they proceed to fusing the first roll material for waterproofing on a bitumen basis. After the first sheet is glued, the next one is glued in the same way without gaps. Usually, waterproofing is laid in 2 layers, while it is important to lay the second one with an offset so that the joints of the first layer do not coincide with the seams between the materials of the second layer.
- After waterproofing, they begin to insulate the foundation, for which they usually use slab polystyrene foam material. As with waterproofing, the insulation is laid in several layers with an offset. Expanded polystyrene boards have different thicknesses, however, where one thick layer is enough to achieve the desired thermal efficiency, it is better to use 2 thinner boards.



- The next step is reinforcement. It cannot be laid directly on the insulation, bricks should be placed under the reinforcing frame or special legs should be used. A gap of at least 5 cm should remain between the reinforcing layer and the insulation. The lathing should not be welded, it is tied with a wire.
- Laying communications, since after pouring the floor it will be impossible to do this. If a warm floor is organized, then the pipes are attached to a metal crate. At the same time, collectors are installed that connect all pipes. Ensure that all conductors are under pressure, this will help to quickly identify a hole if damaged during pouring.
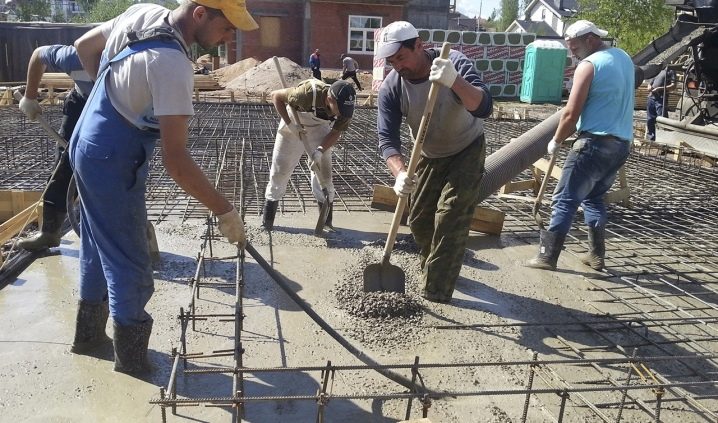
- The final stage is the pouring of the concrete mixture, before which the quality of the formwork is carefully checked again. It should not have gaps through which concrete can flow. The solution should be poured over the entire area at once. Pumps or wooden mops are used to level the layer. It is imperative to use vibrators, which will eliminate the appearance of air in the thickness of the solution. After that, the surface is equalized by the rule and left to "rest" until the strength gains.



To exclude the negative impact of the environment on hardened concrete, it is possible to protect it with a covering material. In winter, a heating cable is laid over its entire surface. In addition, during the pouring process at low temperatures, it is recommended to add special admixtures to the concrete that accelerate the setting process, as well as to use steel panels with a heating function for formwork.
In extreme heat, the concrete surface should be prevented from drying out, therefore, in the first 1.5-2 weeks after pouring, it is periodically moistened.


You will learn more about the features of the construction of a monolithic foundation by watching the following video.
Advice
One of the factors affecting the strength of the monolith is the quality of the reinforcement. The number of reinforcement levels is determined by the thickness of the slab. If a slab with a thickness of no more than 15 cm is used, then one level of reinforcement is sufficient, while the steel rods are tied with wire and placed exactly in the center of the base.
With a slab thickness of 20 cm, two-level reinforcement is used. The distance between the reinforcement elements is on average 30 cm.
In areas not subject to constant and heavy loads, you can lay rods with a large pitch. Leave 5 cm from the edge of the slab to the edge of the reinforcement cage on each side.

The strength and durability of the slab largely depends on the quality of the concrete.
It must meet the following requirements:
- density indicators - within 1850 - 2400 kg / m3;
- concrete class - not less than B-15;
- concrete grade - not less than M200;
- mobility - P3;
- frost resistance - F 200;
- water resistance - W4.
When preparing a solution on your own, first of all, you should pay attention to the brand strength of the cement. It is recommended to choose your brand for each type of soil, as well as based on the structural features of the building. So, on soft soils for heavy buildings (for example, with brick walls), cement M 400 is recommended. For aerated concrete houses, cement with a brand strength of M350 is sufficient, for wooden houses - M250, for frame houses - M200.



Finally, it is important how the concrete is fed and poured. It is not recommended to feed concrete from a height of more than 1 m, and also to move it at a distance of more than 2 m (you need to periodically move the concrete mixer around the perimeter, and also use a pump). The filling must be done in one session, it is not recommended to fill in sections, optimally in layers.
When leveling, as well as at the moment of solidification of the concrete layer, it is unacceptable to walk on it, since this violates the structure of the reinforcement and leads to uneven solidification of the concrete layer.

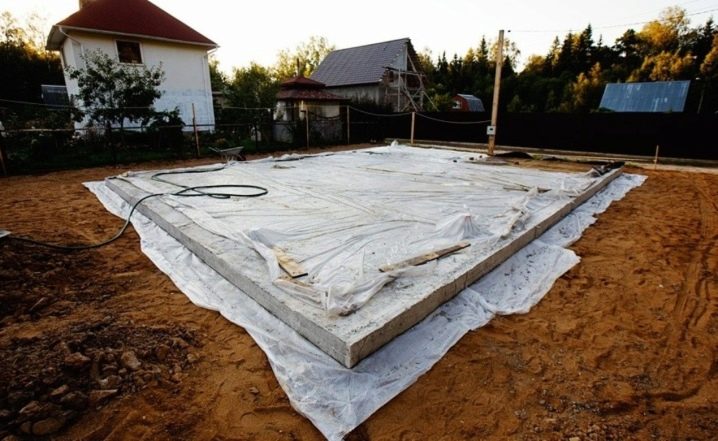
Optimal conditions for concrete curing are: temperature - not less than 5C, humidity level - not less than 90-100%. To protect the concrete at this stage, you can use regular polyethylene or tarpaulin. It is important that the covering material overlaps, and the joints are glued with tape. Otherwise, there will be no sense in such protection.
The optimal installation is considered to be such a laying of protection, in which the material covers not only the concrete layer, but also the formwork, and its edges are fixed on the ground with stones or bricks.

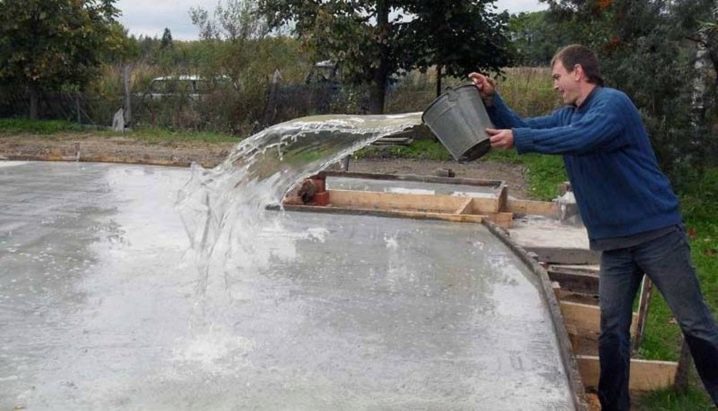
When irrigating concrete, the moisture must be distributed drip, and not poured in a stream. To prevent the formation of grooves in a fresh layer of concrete, placing sawdust or burlap on its surface, which are covered with a film, will help. In this case, water is poured onto sawdust or burlap, evenly absorbing into the concrete.














The comment was sent successfully.