Strip foundation: features and stages of construction

Everyone knows the old adage that a real man must do three things in his life: plant a tree, raise a son and build a house. With the last point, especially many questions arise - which material is better to use, choose a one- or two-story building, how many rooms to count on, with or without a veranda, how to install the foundation and many others. Among all these aspects, it is the foundation that is fundamental, and this article will be devoted to its tape type, its features, differences, construction technology.



Peculiarities
Despite the fact that there are several types of foundations for a house, preference in modern construction is given to a strip foundation. Due to its durability, reliability and strength, it occupies a leading position in the construction industry around the world.
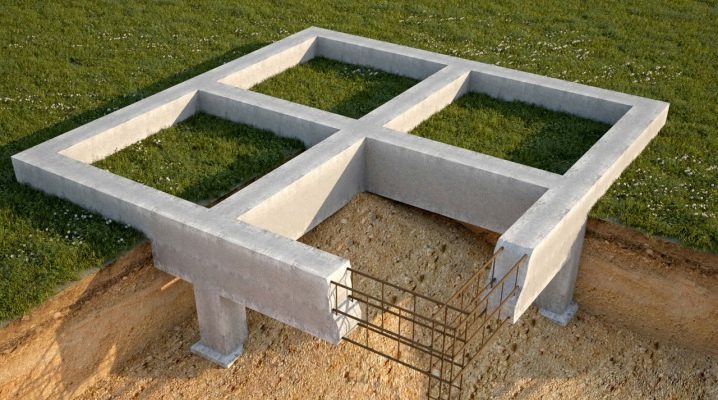
Already from the name it is clear that such a structure is a tape of a fixed width and height, laid in special trenches along the boundaries of the building under each of the outer walls, thus forming a closed loop.
This technology gives the foundation the ultimate rigidity and strength. And due to the use of reinforced concrete in the formation of the structure, maximum strength is achieved.


Among the key features of the strip type of foundation are the following:
- already mentioned above reliability and long service life;
- fast construction of the structure;
- general availability in terms of cost relative to its parameters;
- the ability to install manually without the use of heavy equipment.
According to the standards of GOST 13580-85, the strip foundation is a reinforced concrete slab, the length of which is from 78 cm to 298 cm, the width is from 60 cm to 320 cm and the height is from 30 cm to 50 cm. After the calculations, the base grade is determined with a load index of 1 up to 4, which is an indicator of the pressure of the walls on the foundation.



In comparison with the pile and slab types, the strip base, of course, wins. However, a columnar foundation overpowers the foundation with a tape due to the significant consumption of materials and an increase in labor intensity.
The estimate of the tape structure can be calculated taking into account the sum of the cost of installation and the cost of building materials. The average price for a finished running meter of a tape of a concrete foundation is from 6 to 10 thousand rubles.
This figure is influenced by:
- soil characteristics;
- the total area of the basement;
- type and quality of building materials;
- depth;
- dimensions (height and width) of the tape itself.

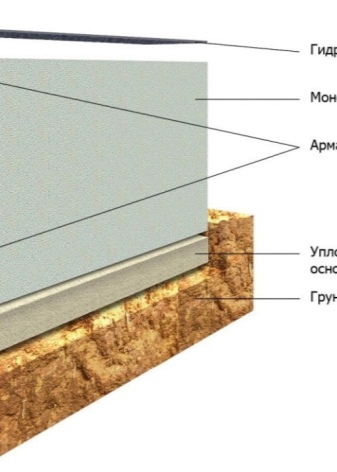
The service life of the strip foundation directly depends on the correct choice of a site for construction, compliance with all requirements and building codes. Taking into account all the rules will extend the service life for more than one decade.
An important feature in this matter is the choice of building material:
- a brick foundation will last up to 50 years;
- prefabricated structure - up to 75 years;
- rubble and monolithic concrete in the manufacture of the base will increase the operational life up to 150 years.



Purpose
It is possible to use the belt technology for the construction of the foundation:
- in the construction of a monolithic, wooden, concrete, brick, frame structure;
- for a residential building, bathhouse, utility or industrial building;
- for the construction of fences;
- if the building is located on a site with a slope;
- great if you decide to build a basement, veranda, garage or basement;
- for a house where the density of the walls is more than 1300 kg / m³;
- for both light and heavy buildings;
- in areas with heterogeneously bedded soil, which leads to uneven shrinkage of the base of the structure;
- on loamy, clayey and sandy soil.



Advantages and disadvantages
The main advantages of the tape foundation:
- a small amount of building materials, as a result of which the low cost relative to the characteristics of the foundation;
- possibly arrangement of a garage or basement room;
- high reliability;
- allows you to distribute the load of the house over the entire base area;
- the structure of the house can be made of various materials (stone, wood, brick, concrete blocks);
- does not need to take land over the entire area of the house;
- able to withstand heavy loads;
- fast erection - the main time costs are required for digging a trench and building formwork;
- simple construction;
- it is a time-tested technology.



Among all the many advantages, it is worth mentioning some of the disadvantages of the strip foundation:
- for all the simplicity of the design, the work itself is quite laborious;
- difficulties with waterproofing when installed on wet ground;
- unsuitable for soils with weak bearing properties due to the large mass of the structure;
- reliability and strength is guaranteed only when reinforcing (reinforcing the concrete base with steel reinforcement).


Views
By classifying the selected type of foundation according to the type of device, monolithic and prefabricated foundations can be distinguished.
Monolithic
The continuity of the underground walls is assumed. They are characterized by low construction costs in relation to strength. This type is in demand when building a bathhouse or a small wooden house. The disadvantage is the large weight of the monolithic structure.
The technology of a monolithic foundation assumes a reinforcing metal frame, which is installed in a trench, after which it is poured with concrete. It is due to the frame that the necessary rigidity of the foundation and resistance to loads are acquired.
Cost for 1 sq. m - about 5100 rubles (with characteristics: slab - 300 mm (h), sand cushion - 500 mm, concrete grade - M300). On average, a contractor for pouring a 10x10 foundation will take about 300-350 thousand rubles, taking into account the installation and the cost of materials.



Prefabricated
A prefabricated strip foundation differs from a monolithic one in that it consists of a complex of special reinforced concrete blocks interconnected by means of reinforcement and masonry mortar, which are mounted with a crane at the construction site. Among the main advantages is the reduction in installation time. The downside is the lack of a single design and the need to attract heavy equipment. In addition, in terms of strength, the prefabricated foundation is inferior to the monolithic one by as much as 20%.
Such a foundation is used in the construction of industrial or civil buildings, as well as for cottages and private houses.
The main costs will be spent on haulage and hourly rental of a truck crane. 1 running meter of a prefabricated foundation will cost at least 6,600 rubles. The base of the building with an area of 10x10 will have to spend about 330 thousand. Laying wall blocks and pillows with a short distance will allow you to save money.


There is also a strip-slotted subspecies of the structure, which in its parameters is similar to a monolithic strip foundation. However, this base is adapted for pouring exclusively on clay and non-porous soils. Such a foundation is cheaper due to the reduction of land work, since the installation takes place without formwork. Instead, a trench is used, which visually resembles a gap, hence the name. Slotted foundations allow you to equip a garage or utility room in low-rise, non-massive buildings.
Important! Concrete is poured into damp ground, since in a dry trench, part of the moisture goes into the ground, which may deteriorate the quality of the foundation. Therefore, it is better to use concrete of a higher grade.



Another subspecies of the prefabricated strip foundation is cross. It includes glasses for columns, base and intermediate plates. Such foundations are in demand in a row building - when a columnar foundation is located in proximity to a foundation of the same type. This arrangement is fraught with subsidence of structures. The use of cross foundations involves the contact of the lattice of the final beams of the building under construction with an already built and stable structure, thereby allowing the load to be evenly distributed. This type of construction is applicable for both residential and industrial construction. Among the shortcomings, the labor intensity of the work is noted.
Also, for a strip type of foundation, you can make a conditional division relative to the depth of the laying. In this connection, the buried and shallow buried species are distinguished by the magnitude of the load.
Deepening is carried out below the established level of soil freezing. However, within the limits of private low-rise buildings, a shallow foundation is acceptable.


The choice in this typing depends on:
- building mass;
- the presence of a basement;
- type of soil;
- height difference indicators;
- groundwater level;
- the level of soil freezing.
Determination of the listed indicators will help in the correct choice of the type of strip foundation.


The in-depth view of the foundation is intended for a house made of foam blocks, heavy buildings made of stone, brick, or multi-storey buildings. For such foundations, significant differences in height are not terrible. Perfect for buildings in which the arrangement of the basement floor is planned. It is erected 20 cm below the level of soil freezing (for Russia it is 1.1-2 m).
It is important to take into account the frost heaving buoyancy forces, which should be less than the concentrated load from the house. To confront these forces, the foundation is set in the shape of an inverted T.
The shallow tape is distinguished by the lightness of the buildings that will be located on it. In particular, these are wooden, frame or cellular structures. But it is undesirable to locate it on the ground with a high level of groundwater (up to 50-70 cm).
The key advantages of a shallow foundation are the low cost of building materials, ease of use and a short installation time, in contrast to a buried foundation. In addition, if it is possible to get by with a small cellar in the house, then such a foundation is an excellent and low-cost option.


Among the disadvantages is the inadmissibility of installation in unstable soils., and such a foundation will not work for a two-story house.
Also, one of the features of this type of base is the small area of the lateral surface of the walls, and therefore the buoyant forces of frost heaving are not afraid of light construction.
Today, developers are actively introducing the Finnish technology for installing a foundation without deepening - pile-grillage. The grillage is a slab or beams that connect the piles to each other already above the ground. The new type of zero-level device does not require the installation of boards and the installation of wooden blocks. In addition, there is no need to dismantle the hardened concrete. It is believed that such a structure is not subject to heaving force at all and the foundation is not deformed. Installed on the formwork.



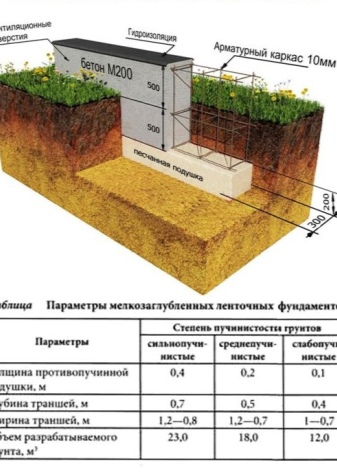
In accordance with the norms regulated by SNiP, the minimum depth of the strip foundation is calculated.
Freezing depth of conditionally non-porous soil | The depth of freezing of slightly heaving soil of solid and semi-solid consistency | Foundation laying depth |
up to 2 m | up to 1 m | 0.5 m |
up to 3 m | up to 1.5 m | 0.75 m |
more than 3 m | from 1.5 to 2.5 m | 1m |
Materials (edit)
The strip foundation is mainly assembled from bricks, reinforced concrete, rubble concrete, using reinforced concrete blocks or slabs.
Brick is suitable if the house is supposed to be built with a frame or with thin brick walls. Since the brick material is very hygroscopic and easily destroyed due to moisture and cold, such a buried foundation is not welcome in places with a high level of groundwater. In this case, it is important to provide a waterproofing coating for such a base.
The popular reinforced concrete base, despite its cheapness, is quite reliable and durable. The material contains cement, sand, crushed stone, which are reinforced with a metal mesh or reinforcement rods. Suitable for sandy soil when erecting monolithic foundations of complex configuration.


A strip foundation made of rubble concrete is a mixture of cement, sand and large stone. A fairly reliable material with length parameters - no more than 30 cm, width - from 20 to 100 cm and two parallel surfaces up to 30 kg. This option is perfect for sandy soils. In addition, a prerequisite for the construction of a rubble concrete foundation should be the presence of a gravel or sand cushion 10 cm thick, which simplifies the process of laying the mixture and allows you to level the surface.
The foundation made of reinforced concrete blocks and slabs is a finished product manufactured at the enterprise. Among the distinctive features - reliability, stability, strength, the ability to use for houses of various designs and types of soil.


The choice of material for the construction of the strip foundation depends on the type of device.
The base of the prefabricated type is made:
- from blocks or slabs of an established brand;
- concrete mortar or even brick is used to fill up the cracks;
- completed with all materials for hydro and thermal insulation.


For a monolithic foundation, it is recommended to use:
- the formwork is constructed from a wooden board or expanded polystyrene;
- concrete;
- material for hydro and thermal insulation;
- sand or crushed stone for the pillow.


Calculation and design rules
Before the project is drawn up and the parameters of the foundation of the building are determined, it is recommended to review the regulatory construction documents, which describe all the key rules for calculating the foundation and tables with established coefficients.
Among such documents:
GOST 25100-82 (95) “Soils. Classification";
GOST 27751-88 “Reliability of building structures and foundations. Basic provisions for the calculation ";
GOST R 54257 "Reliability of building structures and foundations";
SP 131.13330.2012 "Construction climatology". Updated version of SN and P 23-01-99;
SNiP 11-02-96. “Engineering surveys for construction. Basic Provisions ";
SNiP 2.02.01-83 "Foundations of buildings and structures";
Manual for SNiP 2.02.01-83 "Manual for the design of the foundations of buildings and structures";
SNiP 2.01.07-85 "Loads and Impacts";
Manual for SNiP 2.03.01; 84. "Manual for the design of foundations on a natural foundation for the columns of buildings and structures";
SP 50-101-2004 "Design and construction of foundations and foundations of buildings and structures";
SNiP 3.02.01-87 "Earthworks, foundations and foundations";
SP 45.13330.2012 "Earthworks, foundations and foundations". (Updated edition of SNiP 3.02.01-87);
SNiP 2.02.04; 88 "Bases and foundations on permafrost."


Let's consider in detail and step by step the calculation plan for the construction of the foundation.
To begin with, a total calculation of the total weight of the structure is made, including the roof, walls and floors, the maximum permissible number of residents, heating equipment and household installations, and the load from precipitation.
You need to know that the weight of the house is determined not by the material from which the foundation is made, but by the load that is created by the entire structure from various materials.This load directly depends on the mechanical properties and the amount of material used.
To calculate the pressure on the sole of the base, it is enough to summarize the following indicators:
- snow load;
- payload;
- load of structural elements.
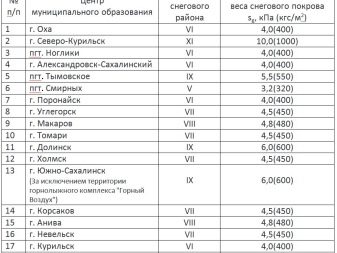
The first item is calculated using the formula snow load = roof area (from the project) x set parameter of snow cover mass (different for each region of Russia) x correction factor (which is influenced by the angle of inclination of a single or gable roof).
The established parameter of the mass of snow cover is determined according to the zoned map SN and P 2.01.07-85 “Loads and Impacts”.
The next step is to calculate the potentially acceptable payload. This category includes household appliances, temporary and permanent residents, furniture and bathroom equipment, communication systems, stoves and fireplaces (if any), additional engineering routes.
There is an established form for calculating this parameter, calculated with a margin: payload parameters = total structure area x 180 kg / m².

In the calculations of the last point (load of parts of the building), it is important to list all the elements of the building to the maximum, including:
- directly the reinforced base itself;
- ground floor of the house;
- load-bearing part of the building, window and door openings, stairs, if any;
- floor and ceiling surfaces, basement and attic floors;
- roof covering with all the resulting elements;
- floor insulation, waterproofing, ventilation;
- surface finishing and decorative items;
- all the set of fasteners and hardware.
Moreover, to calculate the sum of all the above elements, two methods are used - mathematical and the results of a marketing calculation in the building materials market.
Of course, there is also the option of using a combination of both methods.

The plan for the first method is:
- breaking complex structures into parts in the project, determine the linear dimensions of the elements (length, width, height);
- multiply the obtained data to measure the volume;
- with the help of all-Union norms of technological design or in the documents of the manufacturer, establish the specific weight of the used building material;
- having established the parameters of the volume and specific gravity, calculate the mass of each of the building elements using the formula: mass of a part of the building = volume of this part x parameter of the specific gravity of the material from which it is made;
- calculate the total mass allowed under the foundation by summing up the results of the parts of the structure.
The method of marketing calculation is guided by data from the Internet, mass media and professional reviews. The indicated specific gravity is also added up.

The design and sales departments of enterprises have accurate data, where possible, by calling them, clarify the nomenclature or use the manufacturer's website.
The general parameter of the load on the foundation is determined by summing all the calculated values - the load of the parts of the structure, useful and snow.
Next, the approximate specific pressure of the structure on the soil surface under the sole of the designed foundation is calculated. For the calculation, the formula is used:
approximate specific pressure = weight of the entire structure / dimensions of the foot area of the base.
Having determined these parameters, an approximate calculation of the geometric parameters of the strip foundation is permissible. This process occurs according to a certain algorithm established during the research by specialists from the scientific and engineering department. The calculation scheme for the size of the foundation depends not only on the expected load on it, but also on the construction documented norms for deepening the foundation, which, in turn, are determined by the type and structure of the soil, the level of groundwater, and the depth of freezing.
Based on the experience gained, the developer recommends the following parameters:
Soil type | Soil within the calculated freezing depth | The interval from the planned mark to the groundwater level during the freezing period | Foundation installation depth |
Non-porous | Coarse, gravelly sands, coarse and medium size | Not standardized | Any, regardless of the border of freezing, but not less than 0.5 meters |
Puffy | The sand is fine and silty | Exceeds the freezing depth of more than 2 m | The same indicator |
Sandy loam | Exceeds the freezing depth by at least 2 m | Not less than ¾ of the calculated freezing level, but not less than 0.7 m. | |
Loam, clay | Less estimated freezing depth | Not less than the calculated level of freezing |
The width parameter of the strip foundation should not be less than the width of the walls. The depth of the pit, which determines the base height parameter, should be designed for a 10-15 centimeter sand or gravel cushion. These indicators allow in further calculations to determine with: The minimum width of the base of the foundation is calculated depending on the pressure of the building on the foundation. This size, in turn, determines the width of the foundation itself, pressing on the soil.
That is why it is so important to make an examination of the soil before starting the design of the structure.
- the amount of concrete for pouring;
- volume of reinforcing elements;
- the amount of material for the formwork.



Recommended sole width parameters for strip foundations, depending on the selected material:
Rubble stone:
- basement depth - 2 m:
- basement wall length - up to 3 m: wall thickness - 600, basement base width - 800;
- basement wall length 3-4 m: wall thickness - 750, basement base width - 900.
- basement depth - 2.5m:
- basement wall length - up to 3 m: wall thickness - 600, basement base width - 900;
- basement wall length 3-4 m: wall thickness - 750, basement base width - 1050.
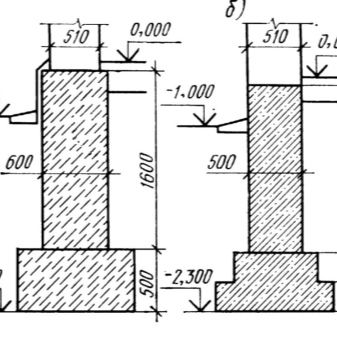

Rubble concrete:
- basement depth - 2 m:
- basement wall length - up to 3 m: wall thickness - 400, basement base width - 500;
- basement wall length - 3-4 m: wall thickness - 500, basement base width - 600.
- basement depth - 2.5m:
- basement wall length up to 3 m: wall thickness - 400, basement base width - 600;
- basement wall length 3-4 m: wall thickness - 500, basement base width - 800.
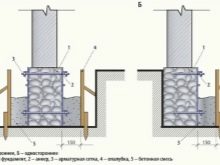


Clay brick (ordinary):
- basement depth - 2 m:
- basement wall length up to 3 m: wall thickness - 380, basement base width - 640;
- basement wall length 3-4 m: wall thickness - 510, basement base width - 770.
- basement depth - 2.5m:
- basement wall length up to 3 m: wall thickness - 380, basement base width - 770;
- basement wall length 3-4 m: wall thickness - 510, basement base width - 900.

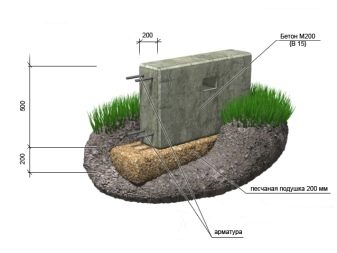
Concrete (monolith):
- basement depth - 2 m:
- basement wall length up to 3 m: wall thickness - 200, basement base width - 300;
- basement wall length 3-4 m: wall thickness - 250, basement base width - 400.
- basement depth - 2.5m;
- basement wall length up to 3 m: wall thickness - 200, basement base width - 400;
- basement wall length 3-4 m: wall thickness - 250, basement base width - 500.
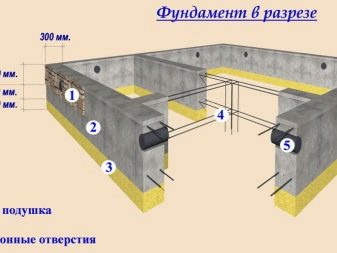
Concrete (blocks):
- basement depth - 2 m:
- basement wall length up to 3 m: wall thickness - 250, basement base width - 400;
- basement wall length 3-4 m: wall thickness - 300, basement base width - 500.
- basement depth - 2.5m:
- basement wall length up to 3 m: wall thickness - 250, basement base width - 500;
- basement wall length 3-4 m: wall thickness - 300, basement base width - 600.
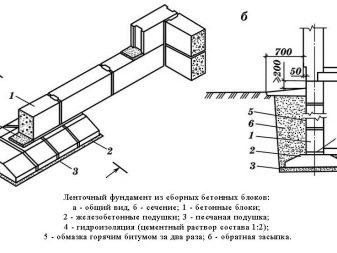

Further, it is important to optimally adjust the parameters by adjusting the norms of specific pressure on the soil of the sole in accordance with the calculated resistance of the soil - the ability to withstand a certain load of the entire structure without settling it.
The design soil resistance should be greater than the parameters of the specific load from the building. This point is a weighty requirement in the process of designing the base of a house, according to which, in order to obtain linear dimensions, it is necessary to elementarily solve an arithmetic inequality.
When drawing up the drawing, it is essential that this difference be 15-20% of the specific load of the structure in favor of the value of the soil's ability to withstand the pressure from the building.
In accordance with the types of soil, the following design resistances are displayed:
- Coarse soil, crushed stone, gravel - 500-600 kPa.
- Sand:
- gravelly and large - 350-450 kPa;
- medium size - 250-350 kPa;
- fine and dusty dense - 200-300 kPa;
- medium density - 100-200 kPa;
- Hard and plastic sandy loam - 200-300 kPa;
- Loam hard and plastic - 100-300 kPa;
- Clay:
- solid - 300-600 kPa;
- plastic - 100-300 kPa;
100 kPa = 1kg / cm²
Having corrected the results obtained, we obtain the approximate geometric parameters of the foundation of the structure.
In addition, today's technology can significantly simplify calculations using special calculators on developers' websites. By specifying the dimensions of the base and the building material used, you can calculate the total cost of building the foundation.

Mounting
To install the strip foundation with your own hands you will need:
- round and grooved reinforcement elements;
- galvanized steel wire;
- sand;
- edged boards;
- wooden bars;
- a set of nails, self-tapping screws;
- waterproofing material for the foundation and formwork walls;
- concrete (predominantly factory-made) and appropriate materials for it.
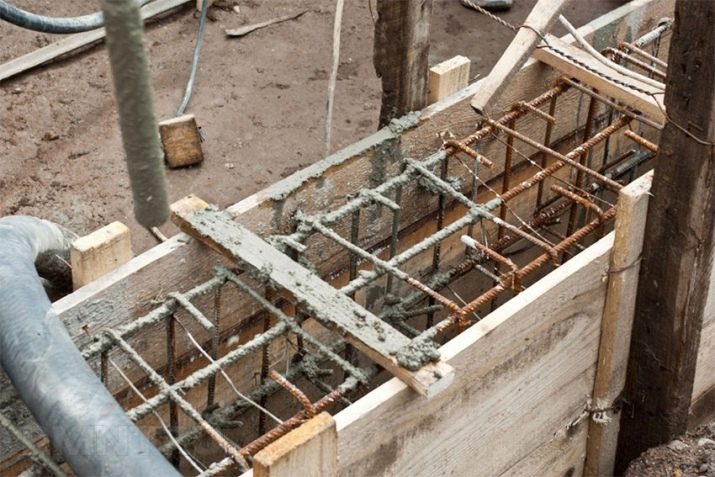






Markup
Having planned to build a structure on the site, it is worthwhile to first investigate the place where the construction is planned.
There are some rules for choosing a place for a foundation:
- Immediately after the snow melts, it is important to pay attention to the presence of cracks (indicate the heterogeneity of the soil - freezing will lead to a rise) or failures (indicate the presence of water veins).
- The presence of other buildings on the site makes it possible to assess the quality of the soil. You can make sure that the soil is uniform by digging a trench at an angle at the house. The imperfection of the soil indicates the unfavorableness of the place for construction. And if cracks are noticed on the foundation, then it is better to postpone the construction.
- As mentioned above, carry out a hydrogeological assessment of the soil.
Having decided that the selected site meets all the standards, you should start marking the site. First of all, it needs to be leveled and rid of weeds and debris.


For marking work you will need:
- marking cord or fishing line;
- roulette;
- wooden pegs;
- level;
- pencil and paper;
- hammer.
The first line of the marking is defining - it is from it that all other boundaries will be measured. In this case, it is important to establish an object that will serve as a reference point. It could be another structure, a road, or a fence.
The first peg is the right corner of the building. The second is installed at a distance equal to the length or width of the structure. The pegs are connected to each other with a special marking cord or tape. The rest are clogged in the same way.
Having defined the external boundaries, you can go to the internal ones. For this, temporary pegs are used, which are installed at a distance of the width of the strip foundation on both sides of the corner markings. Opposite marks are also connected with a cord.
Lines of load-bearing walls and partitions are installed in a similar way. The intended windows and doors are highlighted with pegs.


Excavation
When the marking phase is completed, the cords are temporarily removed and trenches are dug out along the marks on the ground under the external load-bearing walls of the structure along the entire perimeter of the marking. The interior space is pulled out only if it is supposed to arrange a basement or basement room.
The established requirements for earthworks are specified in SNiP 3.02.01-87 on earthworks, foundations and foundations.
The depth of the trenches should be greater than the design depth of the foundation. Do not forget about the obligatory preparatory layer of concrete or bulk material. If the excavated excavation significantly exceeds the depth, taking into account the reserve, you can replenish this volume with the same soil or rubble, sand. However, if the overkill exceeds more than 50 cm, you should contact the designers.
It is important to take into account the safety of workers - the excessive depth of the pit requires strengthening the walls of the trench.
In accordance with the regulations, fasteners are not required if the depth is:
- for bulk, sandy and coarse-grained soils - 1 m;
- for sandy loam - 1.25 m;
- for loam and clay - 1.5 m.


Typically, for the construction of a small building, the average trench depth is 400 mm.
The width of the excavation must correspond to the plan, which already takes into account the thickness of the formwork, the parameters of the underlying preparation, the protrusion of which beyond the lateral boundaries of the base is allowed at least 100 mm.
The usual parameters are considered to be the width of the trench, equal to the width of the tape plus 600-800 mm.
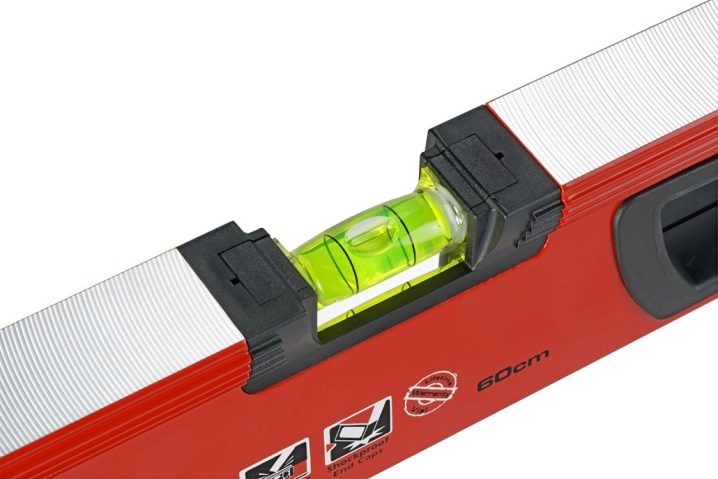
Important! In order for the bottom of the pit to be a perfectly flat surface, a water level should be used.

Formwork
This element represents the shape for the intended foundation. The material for the formwork is most often wood due to its availability in terms of cost and ease of implementation. Removable or non-removable metal formwork is also actively used.
In addition, depending on the material, the following types differ:
- aluminum;
- steel;
- plastic;
- combined.
Classifying the formwork depending on the type of construction, there are:
- large-board;
- small-shield;
- volumetric adjustable;
- block;
- sliding;
- horizontally movable;
- lifting and adjustable.


Grouping the types of formwork by thermal conductivity, they differ:
- insulated;
- not insulated.
The structure of the formwork is:
- deck with shields;
- fasteners (screws, corners, nails);
- props, struts and frames for support.


You will need the following materials for installation:
- lighthouse board;
- board for shields;
- fight from longitudinal boards;
- tension hook;
- spring bracket;
- ladder;
- shovel;
- concreting area.
The number of the listed materials depends on the parameters of the strip foundation.



The installation itself provides for strict adherence to the established requirements:
- the installation of the formwork is preceded by a thorough cleaning of the site from debris, stumps, plant roots, and the elimination of any irregularities;
- the side of the formwork in contact with the concrete is ideally cleaned and leveled;
- the reattachment occurs in such a way as to prevent shrinkage during concreting - such deformation can adversely affect the entire structure as a whole;
- formwork panels are connected to each other as tightly as possible;
- all formwork fastenings are carefully checked - the compliance of the actual dimensions with the design ones is checked with a barometer, a level is used to control the horizontal position, the verticality - a plumb line;
- if the type of formwork allows you to remove it, then for reuse it is important to clean the fasteners and shields from debris and traces of concrete.


Step-by-step instructions for arranging continuous formwork for a strip base:
- To level the surface, the lighthouse boards are installed.
- With an interval of 4 m, formwork panels are attached on both sides, which are fastened with struts for rigidity and spacers that provide a fixed thickness of the base strip.
- The foundation will turn out to be even only if the number of shields between the beacon boards is the same.
- The grapples, which are longitudinal boards, are nailed to the sides of the backboards for horizontal alignment and stability.
- The contractions are stabilized by inclined struts that allow the backboards to be vertically aligned.
- Shields are fixed with tensioning hooks or spring clips.
- Solid formwork is usually obtained with a height of more than a meter, which requires the installation of stairs and platforms for concreting.
- If necessary, the analysis of the structure is carried out in the reverse order.


Installation of a stepped structure goes through several stages. Each next tier of formwork is preceded by another of the same tier:
- the first stage of the formwork;
- concreting;
- second stage of formwork;
- concreting;
- the installation of the required parameters is carried out according to the same scheme.
The installation of stepped formwork is also possible at once, like the assembly mechanism for a solid structure. In this case, it is important to adhere to the horizontal and vertical arrangement of the parts.
During the formwork construction phase, the planning of the ventilation holes is an essential issue. Air vents should be located at least 20 cm above the ground. However, it is worth considering seasonal flooding and varying the location depending on this factor.
The best material for the ventilation opening is a round plastic or asbestos-cement pipe with a diameter of 110-130 mm. Wooden beams have a tendency to stick to the concrete base, which makes them difficult to remove afterwards.
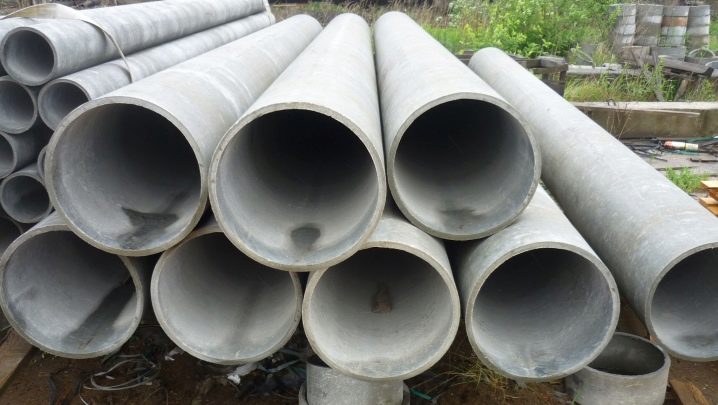

The diameter of the vents is determined depending on the size of the building and can reach from 100 to 150 cm.These ventilation holes in the walls are located strictly parallel to each other at a distance of 2.5-3 m.
With all the need for airflows, there are cases when the presence of holes is not required without fail:
- the room already has ventilation vents in the floor of the building;
- between the pillars of the foundation, a material with sufficient vapor permeability is used;
- a powerful and stable ventilation system is available;
- The vapor-proof material covers sand or soil compacted in the basement.
Understanding the variety of material classifications contributes to the correct selection of fittings.
Depending on the manufacturing technology, the fittings may differ:
- wire or cold rolled;
- rod or hot rolled.


Depending on the type of surface, the rods:
- with a periodic profile (corrugations), providing maximum connection with concrete;
- smooth.
By destination:
- rods used in conventional reinforced concrete structures;
- prestressing rods.
Most often, reinforcement in accordance with GOST 5781 is used for strip foundations - a hot-rolled element applicable for conventional and pre-stressing reinforced structures.
In addition, in accordance with the grades of steel, and therefore the physical and mechanical properties, the reinforcement rods differ from A-I to A-VI. For the manufacture of elements of the initial class, low-carbon steel is used, in high classes - properties close to alloy steel.
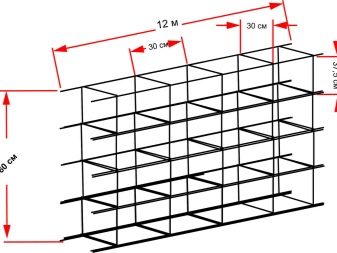
It is recommended to arrange the foundation with a tape using reinforcement rods of class A-III or A-II, which are at least 10 mm in diameter.


In the planned areas with the highest load, installation fittings are installed in the direction of the expected additional pressure. Such places are the corners of the structure, the areas with the highest walls, the base under the balcony or terrace.
When installing a structure from reinforcement, intersections, abutments and corners are formed. Such an incompletely assembled unit can lead to a crack or subsidence of the foundation.
That is why, for reliability, they are used:
- legs - L-shaped bend (inner and outer), attached to the outer working part of the frame made of reinforcement;
- cross clamp;
- gain.
It is important to remember that each class of reinforcement has its own specific parameters of the permissible bending angle and curvature.
In a one-piece frame, the parts are connected in two ways:
- Welding, involving special equipment, the availability of electricity and a specialist who will do it all.
- Knitting possible with a simple screw hook, mounting wire (30 cm per intersection). It is considered the most reliable method, albeit time consuming. Its convenience lies in the fact that, if necessary (bending load), the rod can be slightly shifted, thereby relieving the pressure on the concrete layer and protecting it from damage.


You can make a hook if you take a thick and durable metal rod. A handle is made from one edge for more convenient use, the other is bent in the form of a hook. Having folded the mounting wire in half, form a loop at one of the ends. After that, it should be wrapped around the reinforced knot, putting the hook into the loop so that it rests against one of the "tails", and the second "tail" is wrapped with a mounting wire, carefully tightening around the reinforcing bar.
All metal parts are carefully protected with a layer of concrete (at least 10 mm) to prevent acid corrosion.
Calculations of the amount of reinforcement that will be needed for the construction of a strip foundation require the determination of the following parameters:
- dimensions of the total length of the foundation tape (external and, if available, internal lintels);
- the number of elements for longitudinal reinforcement (you can use the calculator on the manufacturers website);
- the number of reinforcement points (the number of corners and junctions of the foundation strips);
- the parameters of the overlap of the reinforcement elements.
SNiP standards indicate the parameters of the total cross-sectional area of longitudinal reinforcement elements, which will be at least 0.1% of the cross-sectional area.

Fill
It is recommended to pour a monolithic foundation with concrete in layers 20 cm thick, after which the tier is compacted with a concrete vibrator to avoid voids. If concrete is poured in winter, which is undesirable, then it is necessary to insulate it with the help of materials at hand. In the dry season, it is recommended to use water to create a damp effect, otherwise it may affect its strength.
The consistency of the concrete must be the same for each layer, and the pouring must be done on the same day., since a low level of adhesion (a way of adhesion of surfaces of dissimilar solid or liquid consistencies) can lead to cracking. In the event that it is impossible to fill it in one day, it is important to at least pour water over the concrete surface abundantly and, in order to maintain dampness, cover it with plastic wrap on top.
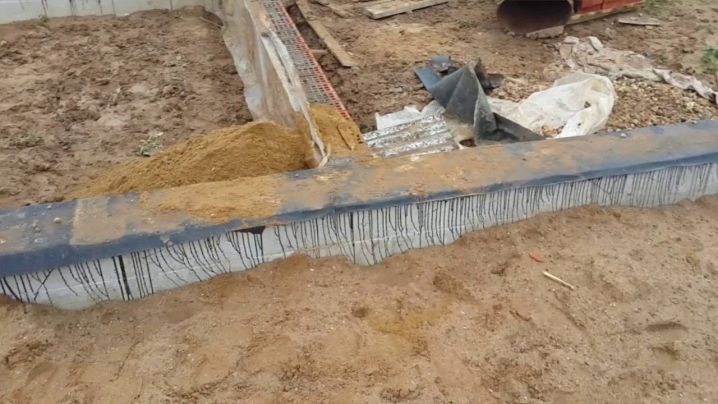
The concrete must settle. After 10 days, the walls of the base are treated outside with bitumen mastic and a waterproofing material (most often roofing material) is glued to protect against water penetration.
The next stage is backfilling the cavities of the strip foundation with sand, which is also laid in layers, while carefully tamping each tier. Before laying the next layer, the sand is watered.

Useful Tips
A correctly installed strip foundation is a guarantee of long years of operation of the building.
It is important to clearly maintain a constant foundation depth throughout the entire area of the construction site, since minor deviations lead to a difference in soil density, moisture saturation, which jeopardizes the reliability and durability of the foundation.
Among the frequently encountered omissions in the construction of the foundation of a building are mainly inexperience, inattention and frivolity in installation, as well as:
- insufficiently thorough study of hydrogeological properties and ground level;
- the use of cheap and low-quality building materials;
- the unprofessionalism of the builders is demonstrated by damage to the waterproofing layer, curved markings, unevenly laid pillow, violation of the angle value;
- failure to comply with the deadlines for removing the formwork, drying the concrete layer and other time stages.
In order to avoid such errors, it is fundamentally important to contact only specialists who are engaged in the installation of the foundations of structures, and try to follow the stages of construction. If, nevertheless, the installation of the base is planned independently, it would be preferable to consult with specialists in this field before starting work.
An important topic when building a foundation is the question of the recommended time of year for such work.As mentioned above, winter and late autumn are considered undesirable times, since frozen and soggy soil leads to inconveniences, slowing down of construction work, and, importantly, shrinkage of the foundation and the appearance of cracks on the finished structure. Professionals point out that the optimal time for construction is warm and dry periods (depending on the region, these intervals fall on different months).


Sometimes, after the construction of the foundation and the operation of the building, the idea of expanding the living space of the house comes up. This issue requires a close analysis of the condition of the foundation. With insufficient strength, construction can lead to the fact that the foundation will burst, sag or cracks appear on the walls. Such an outcome can lead to the complete destruction of the building.
However, if the condition of the foundation does not allow the completion of the building, you should not be upset. In this case, there are some tricks in the form of strengthening the foundation of the structure.
This process can be carried out in several ways:
- in case of minor damage to the foundation, it is sufficient to restore the hydro- and heat-insulating layer;
- more expensive is the expansion of the foundation;
- often use the method of replacing soil under the base of the house;
- using various types of piles;
- by creating a reinforced concrete jacket that prevents collapse when cracks appear on the walls;
- reinforcement with monolithic clips strengthens the base throughout its entire thickness. This method involves the use of a double-sided reinforced concrete frame or tubes that inject a solution that freely fills all the voids in the masonry.
The most important thing when building any type of foundation is to correctly determine the required type, carry out a thorough calculation of all parameters, follow the instructions step by step to perform all the actions, adhere to the rules and advice of specialists and, of course, enlist the support of assistants.
The technology of the strip foundation is in the next video.













Nice site.
The comment was sent successfully.