How to calculate the required number of screw piles?

The foundation is the basis of the building, and its correct calculation is the basis for the longevity of the entire structure. In order to calculate the required number of screw piles, their width and other parameters required for the construction of the foundation, you need to adhere to a verified standardized method. It includes a set of formulas in which it is necessary to substitute geodetic data about the specifics of a particular area and tabular values corresponding to the required parameters of the foundation. In order to calculate the number of screw piles for a foundation in a private house, it is necessary to delve into all the features and subtleties of calculations.



Appointment
The foundation on screw piles is an excellent solution for areas with difficult terrain, which, moreover, has a reasonable price. The specificity of this technology allows the installation of supports within 3 days and at the same time guarantees the reliability of the foundation for at least 100 years. To obtain a high-quality result, it is necessary to take into account all the factors inherent in the technical process: uniform distribution of the load, soil characteristics, depth of soil freezing, the presence and specifics of groundwater, etc.
As a result of all calculations, data appears that gives answers to questions such as:
- required height of screw piles;
- screw pile diameter;
- the depth of their installation;
- the required number of screw piles;
- total cost of materials.
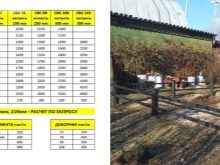
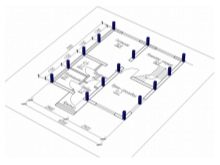

Calculation order
Design is always the first step in any job.
For calculations, you can use the standardized method for screw piles described in SNiP 2.02.03–85. It is based on geodetic survey data for a specific piece of land.
They include the following information:
- description of the relief of the site;
- composition and density of the soil;
- groundwater level;
- depth of soil freezing;
- seasonal rainfall in the development region.


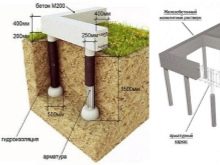
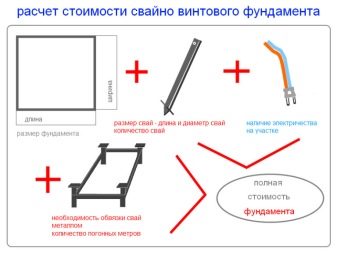
Using this data, the number of screw piles for the foundation (K) is calculated.
For calculations, you need the following indicators:
- the total load on the foundation (P), which is the sum of the masses of all materials used;
- safety factor (k), which is a corrective indicator for the value of the total load on the piles;
- bearing capacity of soil - tabular value;
- the area of the pile heel, which is in direct proportion to its diameter, is a tabular value;
- the maximum permissible load (S), the indicator for one pile is a tabular value.
This is followed by the substitution of values in the formula of the following form: K = P * k / S.
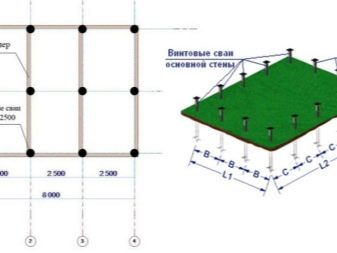
The reliability factor (k) correlates with the total number of piles and has the corresponding values:
- k = 1.4 if piles are from 11 to 22 pieces;
- k = 1.65 - from 5 to 10 pieces;
- k = 1.75 - from 1 to 5 pieces.
Each pile is loaded with a load equal to the total load divided by the number of supports. The fewer there are, the stronger the load on one pile and the faster it becomes unusable, and with them the entire foundation and the house.
The correct calculation consists in the selection of such a number of piles, which will be enough for the entire period of operation of the structure, but without excessive surplus, which is a waste of funds.



Using the above formula, the coefficient for screw piles, the calculation of loads and further construction is not associated with special difficulties.
In the final calculations, it is necessary to distribute the loads under the supporting structures and critical points with excessive pressure on the foundation, taking into account:
- type of piles (hanging or racks);
- masses;
- roll force values.
Options
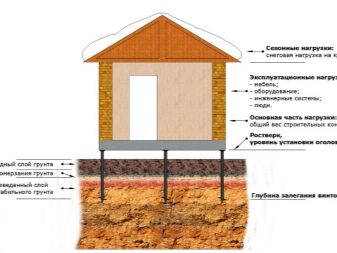
When calculating the screw foundation and the loads exerted on it, the following indicators must be taken into account:
- the total mass of the structure (constant), measured in kilograms, is the sum of the masses of such elements:
- walls and partitions;
- overlappings;
- roofs;
- additional loads (temporary, variable):
- the mass of snow on the roof;
- the mass of all items in the house: furniture, equipment, finishing materials and residents (average value 350 kg / sq. m);
- dynamic loads of a short-term nature arise from the effects of:
- gusts of wind;
- sedimentary processes;
- temperature fluctuations.

Varieties
Depending on the structure (shape) of the screw pile, the specificity of its application differs.
There are such common types:
- shirokoplastny with a cast tip - used for small buildings with simple soil;
- multi-layer with several blades at different levels - used with increased load on difficult ground;
- with a variable perimeter - a narrow-profile product for specific conditions;
- narrow-plastic with a cast toothed tip - used in permafrost and stony soil.

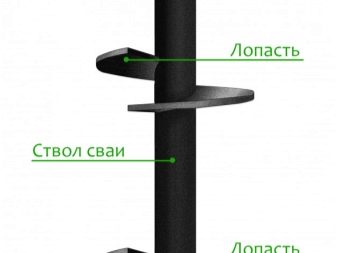


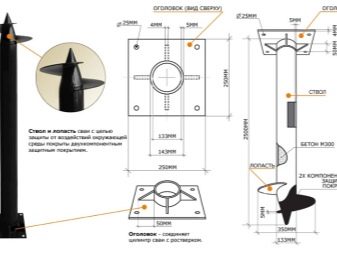
Specifications
There are several main technical characteristics of screw piles.
These include:
- barrel length and material of manufacture;
- pile diameter;
- a variety of blades and their method of attachment to the barrel.


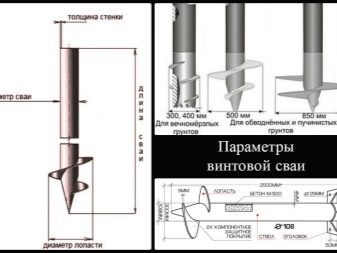
Diameter
Piles are manufactured with standardized dimensions for the performance of the corresponding tasks:
- 89 mm (blade diameter 250 mm) - with a design load on one support no more than 5 tons, these are mainly single-storey frame houses;
- 108 mm (blade diameter 300 mm) - with a design load on one support no more than 7 tons: frame one- and two-story houses, timber buildings and foam block structures;
- 133 mm (blade diameter 350 mm) - with a design load on one support no more than 10 tons: brick and aerated concrete houses using metal elements.
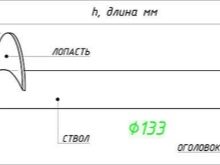
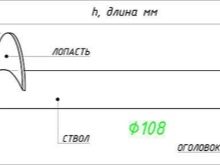
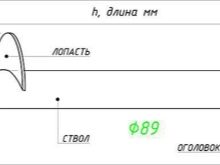
Length
The choice of pile length is based on an indicator of soil density: the pile should only be supported on solid soils.
Also, their length depends on the available height differences on the site:
- the depth of the loam is less than 1 meter - the length of the piles is 2.5 meters;
- with loose soils or quicksand, the length of the pile is determined by the depth of immersion of the drill to hard layers;
- in case of unevenness of the site, the difference in the length of the piles can vary from 0.5 meters or more, depending on the specific case.
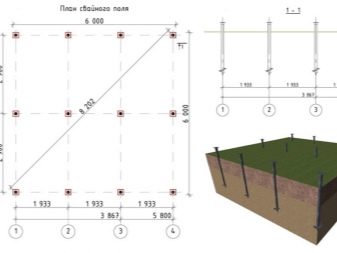
The number of supports and the interval of their location
The tabular values of the location of the supports relative to each other include the following values:
- from 2 to 2.5 meters - for timber-framed houses and block buildings;
- 3 meters - for buildings made of timber or logs.
When placing the foundation piles for an even distribution of loads, the following rules for their placement should be taken into account:
- at every corner of the house;
- at the point of intersection of the load-bearing wall and the internal partition;
- near the entrance portal;
- inside the building perimeter at intervals of 2 meters;
- at least 2 piles under the fireplace;
- under a load-bearing wall, at the location of a balcony, mezzanine or similar structure.

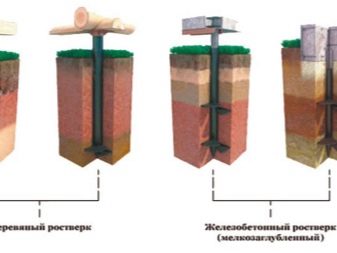
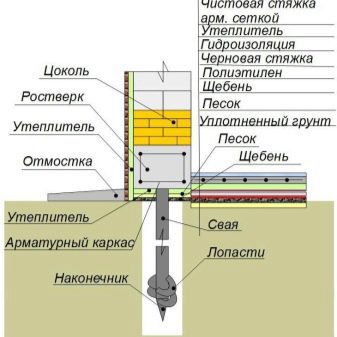
Grillage
A grillage is a foundation element required to evenly distribute the load exerted by the structure on the foundation. To ensure the reliability of the grillage, it is necessary to calculate a number of parameters, while the type of grillage does not matter.
The calculations include:
- punching force of the foundation;
- punching force acting on each corner separately;
- bending force.
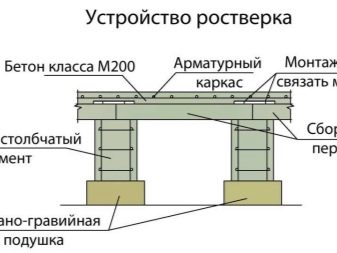
If a high grillage is used, the entire load is applied to the piles. The vertical load acts from below, the deforming load acts from the side. Such calculations are very complex and require professional knowledge. For calculations, you must use the standards of individual construction.
They define the following norms:
- supports can be connected to the grillage in two ways: rigid and free;
- the depth of entry of the pile head into the grillage is at least 10 cm;
- the distance between the ground and the grillage is at least 20 cm;
- the thickness of the grillage cannot be less than the thickness of the walls and is at least 40 cm;
- the grillage must have a height of more than 30 cm;
- the grillage is reinforced with longitudinal and transverse reinforcement with a rod section from 10 to 12 mm.
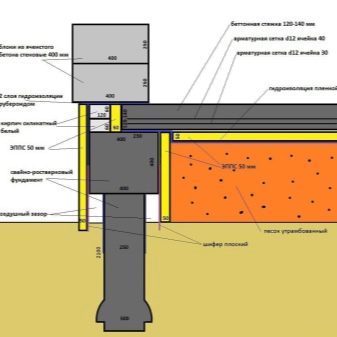
Counting example
This example serves to show in detail the application of formulas in the calculation of the pile-screw foundation.
The initial data for a house with a 10x10 perimeter are:
- a house built using frame technology, the roof is covered with slate, there is a porch;
- foundation dimensions - 10x10, building height - 3 meters;
- two partitions are installed inside, which, crossing, divide the room into 3 rooms;
- roof slope - 60 degrees;
- the frame is made of a bar with a section of 150x150;
- the grillage is made of a bar with a section of 200x200;
- the walls are made of SIP panels.
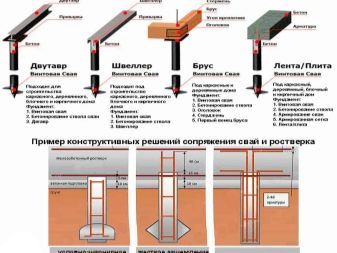

Next, the calculations of the following structural elements are carried out:
- wall area:
- carriers: 10 * 3 * 4 = 120 sq. m;
- partitions: 10 * 3 + 5 * 3 = 45 sq. m;
- mass of walls (the mass of 1 sq. m of a wall from a bar and a partition is taken from the table of average values):
- load-bearing: 50 kg * 120 = 6000 kg;
- partitions: 30 kg * 45 = 1350 kg;
- total: 6000 + 1350 = 7350 kg;
- the mass of floors per 100 sq. m .:
- basement: 150 kg * 100 = 15000 kg;
- attic: 100 kg * 100 = 10,000 kg;
- roof: 50 kg * 100 = 5000 kg;
- total: 15000 * 10000 + 5000 = 30,000 kg;
- the mass of additional elements (the internal content of the house, the type of household appliances, finishes, the number of residents, etc.), a tabular average value for 1 square meter is taken. m in 350 kg:
- 350 * 100 = 35000 kg.;
- total mass of the building:
- 35000 + 30,000 + 7350 = 72,350 kg;
- for example, a safety factor of 1.4 is taken;
- the maximum load on the heel of a pile with a diameter of 300 mm is 2600 kg, provided that the soil resistance is 3 kg / cu. cm (soil with medium density, deep water occurrence and a freezing level of no more than 1 meter);
- we calculate the number of piles according to the formula K = P * k / S: K = 72350 * 1.4 / 2600 = 39 piles.
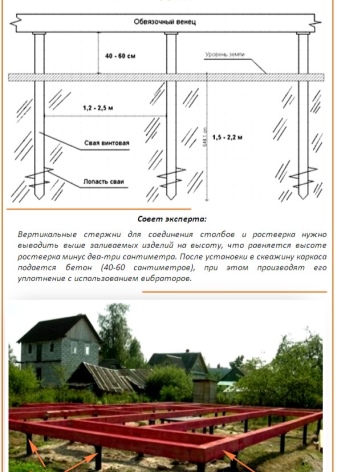

Additional recommendations
In the process of calculating the number of piles and their distribution over the entire area of the foundation, there are many small features, each of which in one way or another affects the improvement of the final result:
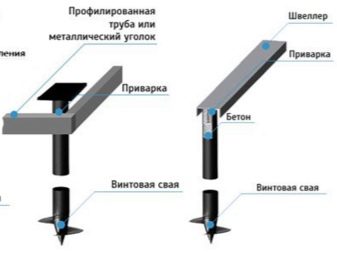
- when installing a foundation made of screw piles on complex unstable soil, to strengthen the support structure, a strapping is used using a metal angle or channel at the basement level;
- in the absence of geodetic data for calculations, it is better to use the parameters corresponding to the minimum design load, that is, create a maximum safety factor;
- to improve the quality of calculations, in addition to formulas and tabular data, it is worth using a design program: it will recalculate all the parameters and refute or confirm the manual calculation;
- the least durable piles have seam pipe trunks with welded blades;
- according to the standards, the basement should not rise more than 60 cm above the ground, while the pile's length margin should be from 20 to 30 cm.


The estimated number of piles is not always optimal: there may be additional circumstances that require the use of a larger number of piles. In addition, a small margin of safety has a beneficial effect on the durability of the foundation.
When installing piles on an uneven area, it is advisable to leave a margin in length in the region of 20-50 cm. In the future, the excess can be cut off or pulled out. But if there is a shortage, you will have to drive in a new pile.
For information on how to calculate the number of screw piles, see the video below.













The comment was sent successfully.