Foundation for a house made of expanded clay concrete blocks

The foundation for a house made of expanded clay concrete blocks has important features and nuances. Before building, you need to weigh all the pros and cons of such a building material. And you should also decide on the optimal depth of laying for a bath and other technological subtleties.

Features and calculation
It is necessary to use expanded clay concrete for the arrangement of foundation structures very thoughtful. The density of the material can vary from 500 to 1800 kg per 1 m3. That's why its application does not cause any significant problems. Reducing the amount of expanded clay increases the density and hardness of the base. But at the same time, the level of load that it will apply to the soil and continental layers of the earth's crust increases. Therefore, you will always have to look for the optimal balance.
The larger the fraction of expanded clay, the stronger the foundation becomes. However, this tempting circumstance is overshadowed by the simultaneous increase in thermal conductivity, which cannot be avoided. The water absorption rate is approximately 15%. This is a pretty decent figure compared to other building materials. The level of vapor permeability depends on the specific type of expanded clay.
The width and thickness of the foundation for a building built of expanded clay concrete blocks is quite simple to determine. If reinforced concrete beams are placed under the house, then they should not be narrower than 15 cm. The width of the foundation tape should be at least the same as the size of the walls. Ideally, some reserve should be made, abandoning it only in the case when it is fundamentally impossible and unattainable.
The total load from the structure, transmitted through the foundation, must be maximum 70% of the allowable impact on the load-receiving site.


The calculation of the minimum permissible width can be performed independently according to the formula 1.3 * (M + P + C + B) / Tape length / Soil resistance, in which the variables are as follows:
-
M - the so-called dead weight of the building (that is, the total weight of all the main structural parts);
-
WITH - the indicator of the additional snow mass, which in unfavorable conditions can even significantly exceed the dead mass;
-
NS - payload (occupants, furniture, their property and so on, usually 195 kg per 1 m3);
-
V - wind impact (you can always find out the required figure from the building recommendations for the region).


An important aspect in many cases is the depth for a bath or a barn. The total height of the structure is determined taking into account:
-
the level of distribution of soil waters;
-
properties of the materials used;
-
bearing capacity of the land plot;
-
a number of other parameters.


Only full-fledged geological research. Only with the correct clarification of these properties can we guarantee the absence of any cracks, skewed and sagging areas. On finely structured and dusty soil, foundations can sink heavily. Gravels and coarse sands are mechanically more reliable. However, whenever possible, it is still advised to place all buildings on a rocky foundation, which is characterized by maximum stability and stability.

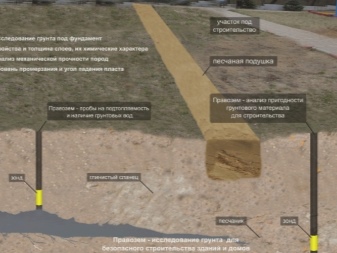
What are they?
The columnar foundation is used for relatively simple and light structures.A summer garden house, a bathhouse or a workshop on the site can be installed without any problems. But a full-fledged dwelling, especially one with at least 2 floors, will have to be placed on more solid supports. The maximum permissible depth is 1.5 m. However, in practice, it is extremely rare for pole supports to go into the ground by more than 50–70 cm.
Important nuances:
-
support points are placed at all corners of the structures;
-
the optimal gap between them is from 1.5 to 3 m;
-
it is possible to increase the capital structure of the structure due to the additional calculation of the reinforced concrete slab.

The pile-grillage foundation is considered by specialists to be a more reliable solution than the use of simple piles. The slab is located mainly at the level of the soil, sometimes rises slightly above it. If the work is done correctly, the stable use of the structure can be guaranteed for several decades. The grillage is divided into:
-
national team;
-
monolithic reinforced concrete;
-
prefabricated monolithic group.


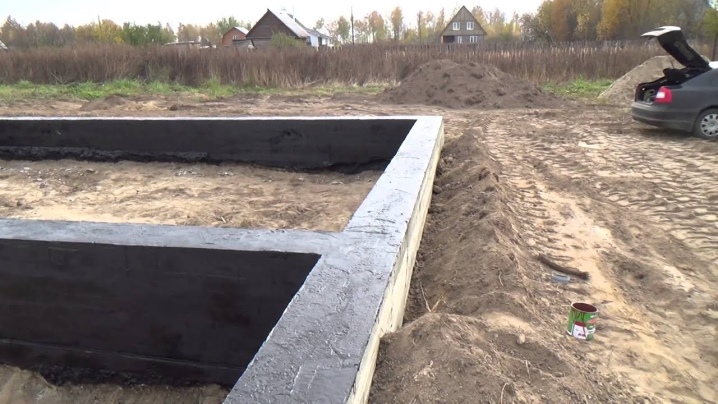
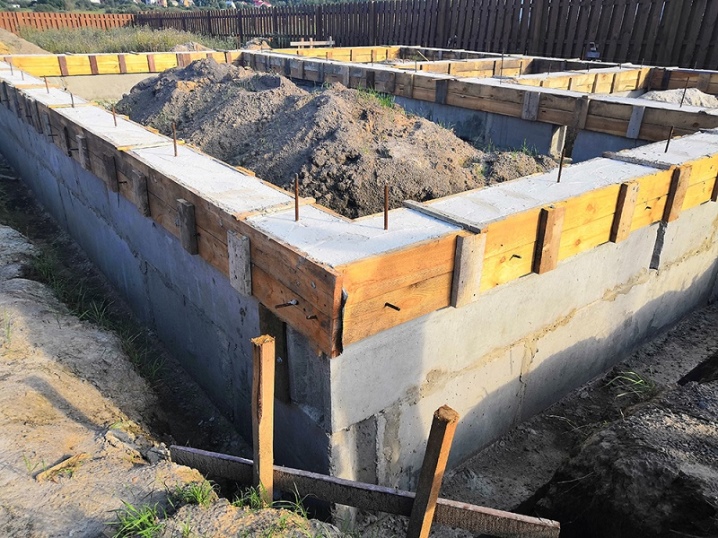
Construction of a strip foundation
Shallow strip foundations are very popular in low-rise private buildings. Even great technical difficulties and lengthy work do not scare off knowledgeable people. If you use high-quality powerful technology, the operating time is reduced many times... True, the cost increases further. It is not enough just to dig trenches - you will have to take care of strengthening their walls.
Auxiliary fasteners in clay soil are required from a depth of 1.2 m.In loose sand - from 0.8 m. But zealous owners usually take care of such a moment in any situation. In addition, the shallow tape allows almost no fear of the effects of frost heaving forces.


Important: you will need to strictly adhere to the technology, and those blunders that, with other options, can still be minimally tolerated, will cause a lot of problems here.
If groundwater is removed 2 m or more from the freezing horizon, it is possible to get by by deepening the monolith by 0.6-0.7 m. At a higher standing, the trench is immersed about 20 cm below the seasonal freezing line. For the formation of the formwork, dismantled wooden and steel panels are used, and both options have advantages and disadvantages. In theory, hollow concrete formwork or extruded polystyrene foam panels are acceptable.


This solution allows you to leave the formwork later as part of the overall structure. The foundation will be stronger and will retain heat better. But only professional engineers will help to work out all the solutions correctly. Therefore, the reduction in the cost of private construction is usually achieved by choosing an inexpensive, time-tested method. Strip cast foundation:
-
serves for a long time;
-
is the only acceptable method for a two-story expanded clay concrete house;
-
makes it possible to equip underground garages;
-
suitable for places with strong freezing;
-
not inclined to squeeze out;
-
is relatively expensive;
-
settles for a long time;
-
requires a huge amount of earthwork.

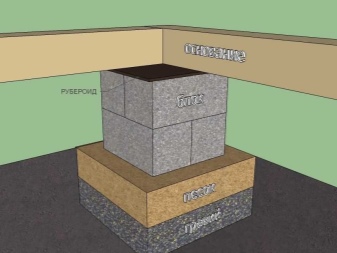
Block base device
If it is decided to build a house from expanded clay concrete blocks, then it is quite possible to use the same blocks for the base. The complete identity of thermal expansion is a rather serious advantage. A good expanded clay concrete block absorbs no more than 3% of water in relation to its weight.
For understanding: for high-quality bricks, this figure is from 6%, and for concrete it reaches 15%.


The conclusion is obvious: you can confidently create a prefabricated base. But here you need to immediately weigh all the pros and cons of this option:
-
good level of thermal insulation;
-
acceleration of installation work;
-
long period of service;
-
the need to use special equipment;
-
unsuitability for use in places with a high level of soil water;
-
comparative high cost (the use of a solid monolith is up to 30% more economical).


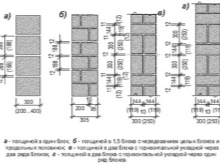
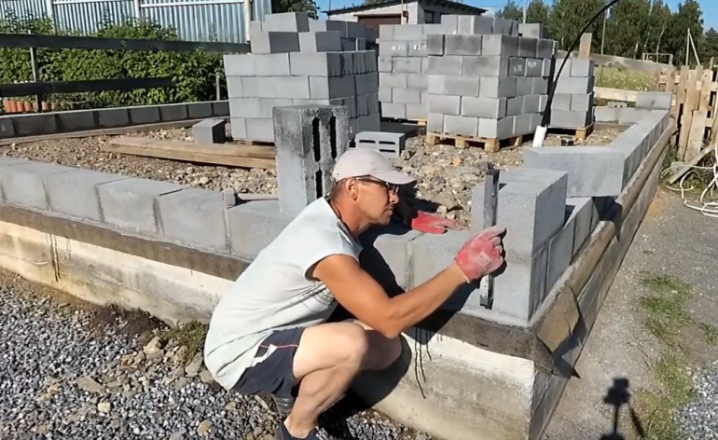
Often, the foundation is insulated with foam and bricked. It is possible to do the initial preparatory work (geological referencing, excavation of soil and arrangement of a cushion of sand and gravel) according to the same scheme as when working under a monolithic structure. On sandy terrain, a simple bottom seal can be dispensed with. Blocks should be laid in the foundation in exactly the same order as when forming the main walls. For work, a classic cement mortar is used; dressings are applied at 0.5 heights, but the base cannot be made more than 5 rows high.
Despite the shortcomings of the expanded clay concrete foundation, it is quite acceptable for a one-story house made of the same material. It is even allowed to equip such a house with an attic - the bearing capacity of the base will be large enough. In most cases, modules with a size of 200x200x400 mm are chosen, because their do-it-yourself laying is quite convenient. In addition, such designs are extremely widespread and are sold at affordable prices.
The solution must be thoroughly mixed, avoiding delamination.


Dry glue is often used, which is diluted with water according to the recipe. However, this is already a more expensive solution than using a cement-sand mixture. But the plasticity of the adhesive mass allows you to make thin seams. The laying of the first row is carried out only after scrupulous leveling of the support platform. After installing the beacons, the cord is stretched, which will ensure maximum evenness.
They start working from a higher angle - and nothing else... Only this method guarantees the strength of the masonry. It is these knots that reinforce and tie up. Only in some cases, the most experienced builders choose a scheme with ligation of internal partitions.
The seams should be approximately 12 mm thick.

Finishing works
The installation of the foundation made of expanded clay concrete blocks is completed by the finishing work on the arrangement of waterproofing, thermal insulation and, if necessary, an armored belt.
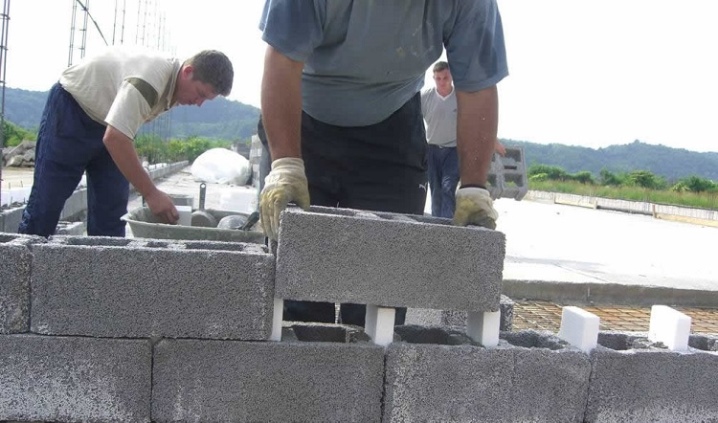

Waterproofing and thermal insulation
Protection against excessive water ingress is essential. It is provided using hydrophobic mixtures. They are processed both internally and externally. There are 4 main options:
-
mineral mastic;
-
bituminous mastic;
-
roofing material;
-
special adhesive film.



It is worth taking seriously the organization of thermal protection.... So, ideally, they seek to create not only a monolithic foundation, but also a floor with an insulating heat layer. The horizontal waterproofing layer plays an important role in this entire assembly. It is placed on a sand and gravel cushion prior to pouring. Such a layer itself is created from roofing material, 2 levels of which are connected using bituminous mastic.
Further, sand and gravel backfill is provided. However, on quick-flowing ground, it is much more correct to use a concrete pillow. A heat-insulating plate is also required. It can be made of expanded polystyrene or polyurethane foam. Its function is not limited to retaining heat: no less important is the prevention of rupture of the waterproofing film during pouring; additionally, vertical waterproofing is carried out.



According to another scheme, thermal protection includes (not counting the foundation blocks):
-
main wall and floor;
-
a groove for which hydrophobic cement is used;
-
waterproofing horizontally inside and vertically outside;
-
sand filling;
-
drip channel through which condensate is removed;
-
the actual heat retention system based on EPS or mineral wool;
-
insulation for the floor - under the lower plane of the basement.



Armopoyas
It is necessary to create reinforced belts when building on unstable soil or on pronounced relief. This prevents shrinkage and associated deformation. The maximum thickness of a high-quality armopoyas is the same as that of the wall. It has a square section. It is recommended to use a mortar based on cement M200 and higher grades.
Between the block rows, it is strongly advised to introduce reinforcing bars.They are complemented with a special masonry mesh. The optimal section of the rod is 0.8-1 cm. The external reinforcing belt is usually created on the basis of concrete or solid bricks. The width of the reinforcing shell can vary from 100 to 200 mm.
The formwork is made equal in height to the future protective structure. The shuttering boards knocked out of the boards are attached on both sides to self-tapping screws. Ladder frames are available in most common areas. But if there is a reliable seismic risk, choose the "parallelepiped" shape.
Important: the metal base is supposed to be poured with concrete 100%.


Advice:
-
prepare or buy concrete with the expectation of filling at a time;
-
drive nails into the walls or twist wire for better adhesion;
-
solid brick should be laid out on top when preparing the floor on wooden beams;
-
thoroughly insulate the armopoyas;
-
tamp the mixture to avoid air pockets.














The comment was sent successfully.