Foundation depth: standards and norms

A properly designed and reliable foundation is one of the key elements of the construction and a guarantee of the safety of the building during its operation. It performs both the function of distributing the load and pressure from the building, and the function of a support base on soil. An important step for every developer when installing a foundation is to determine the depth of the foundation, based on the required standards and norms.

Peculiarities
Determining the depth of the foundation is a kind of stumbling block for many inexperienced builders. It was believed that for the reliable construction of any building, the greatest possible depth should be used. Often, when building country houses, baths or other structures of a medium and small type, you can find hollows or pile holes with a depth of more than 2.5 m.
In some situations, this technique works, but to be unequivocally sure that the greater the depth, the more reliable the structure, is unacceptable for the developer.
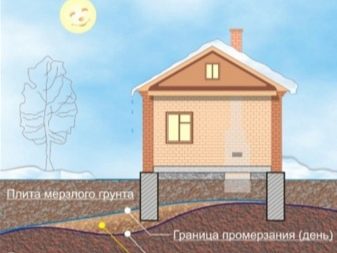
It should be understood: a large depth of the foundation does not guarantee 100% reliability of the building (it does not protect against possible freezing of the soil, landslides). What it really guarantees is additional financial and time costs.


Another erroneous opinion in the calculation of the foundation is the confidence of the technician in the proportional dependence of the depth of the laying on the level of freezing of the soil.
To some extent, this conclusion is logical, excessive heaving of the soil (or the property of a rock to change its characteristics depending on the temperature of the external environment) threatens with displacement or deformation of the soil. This can lead, at best, to a subsidence of the foundation and an increase in the load from the structure to its other part, and at worst - to landslides, overhanging parts of the building, cracks and destruction of the material (if the building is based on stone, brick or reinforced concrete).
It is worth remembering that determining the depth of the foundation depends on a number of other factors:
- Variety and composite characteristics of the soil. There are three types of soil - sandy loam, clay and loam. Each of the types needs a special foundation layout. Installation in sandy loam, for example, may require additional waterproofing with roofing felt and bitumen due to the significant moisture permeability of the soil.



- Estimated load on the base of the foundation. This nuance is in many ways fundamental. Each building, regardless of size and height, has its own specific gravity. It depends on the material used in the construction of the building and the design of additional reinforcement parts, the possible cladding of the building and the installation of auxiliary elements. Do not forget about such a factor as the weight of equipment, household items, structures and other objects that will be inside the building after its construction. Separately, these objects do not exert much pressure on the foundation, however, an incorrect calculation of their total load can lead to disastrous consequences.


- The depth of soil freezing. The heaving of the soil is usually determined by the technician only during the warmest or coldest seasons. This has its own logic - it is much easier to carry out measurements during these periods.You can calculate soil parameters under extreme temperature conditions, but this does not give complete confidence, since the depth of soil freezing is not always a constant value, and its indicator may vary slightly from year to year. As a result, after another winter with unexpectedly high temperatures, you may find a significant subsidence of the building.
- Individual features of the building itself. Each building has its own characteristics, if one developer has this ordinary one-story building (bathhouse, small store, covered gazebo), then the other has a two-story and even higher building with a basement, an attic or attic, a veranda or an underground garage. Each of the superstructures carries its own load on the foundation of the building, therefore, the calculation of the total pressure must take them into account. In doing so, pay attention to the pressure in individual parts of the structure on the foundation. Try not to place several large and heavy elements / objects at once on one section of the foundation. Each of the types of foundation assumes a large load on certain areas, but it is better to additionally secure your structure.


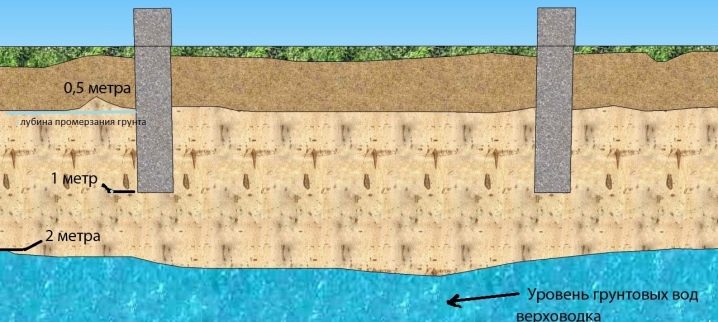
- Ground water level - a very important point in the construction of even the smallest objects. Accurate measurements of this indicator will help you find out: whether waterproofing of foundation elements is necessary; whether an additional layer of compaction with crushed stone or sand is needed; the need to install drainage - pipe / trench systems to remove moisture from the soil. You should understand that the level of groundwater is a relatively fixed value, but if you want to ensure greater safety of your building and can afford additional financial costs, the installation of the above additional systems is necessary.



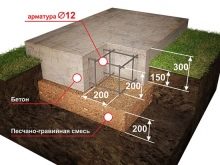
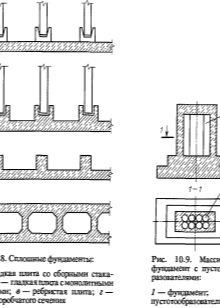
- Type of foundation used. Only a few types of foundations are common in the construction market, the use of which again differs depending on the factors described above. There are the following types of foundations: pile, slab, tape. Also, depending on the depth, they distinguish a buried, not buried and shallow foundation. When using a monolithic foundation, pay attention to the safety of its soles (lower parts in contact with the ground), they may need additional waterproofing.


- The presence of other communications near the building. Needless to say, construction is often carried out on an already equipped territory. In an urban environment with a large number of above-ground structures, these are sewerage, underground power lines, gas and water pipelines. Make sure that the elements of your building do not interfere with other economic or cultural objects.
Also, the construction of new buildings in such places requires a separate permission from the authorities. In the conditions of private estates outside the city, these requirements are not so strict, however, do not forget here that actions to install the foundation in one place can damage the supporting structures in nearby buildings.

There is no need to worry about these factors. Always remember that these tips have already been tested by many technicians and are designed for your own safety. In addition, compliance with these factors is a mandatory measure when building public buildings. If you - the owner of a private territory - decide to independently lay the foundation without taking into account these factors and the advice of a qualified specialist, then the responsibility for this decision rests entirely with you.
Sometimes even the strongest and most reliable foundation, with incorrect calculations, is not able to withstand the entire load of the building. Therefore, claims against the manufacturer of cement or reinforcement parts in this case will be completely inappropriate.


Regulatory Requirements
As you may have noticed from the above, the installation of the foundation is a complex process that requires accurate measurements and taking into account a large number of external factors on the territory of the building.
Since the installation of the foundation has long been a mandatory process in the construction of most buildings, it is natural that special provisions and standards have been developed for its safe use.


These norms mean the requirements of the normative documentation of the joint venture 22.13330.2011, namely, SNiP under the number 2.02.01-83. Some of these norms have already been indicated in the text, as they represent common and proven information over the years. So, the depth of the foundation is calculated based on:
- the actual purpose and design features of the building or structure being erected, loads and impact on the base of the foundation (1, 2-storey or higher building);
- the depth of the installation of foundations for buildings located in the immediate vicinity of the new building, the depth of the laying of third-party communications (pipes, cables and other elements);
- features of the relief of the territory (the presence of elevations, lowlands);
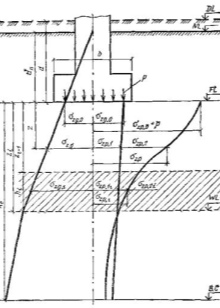
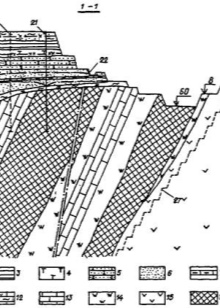
- geological parameters of the building site (varieties of rock and its properties, features of bedding, the presence of such elements as weathering pockets or karst-type cavities);
- the conditions of the site of the hydrogeological type and the proposed modernization of the development area during the construction of the facility;
- site features, taking into account such phenomena as: soil erosion, landslides (such phenomena are often found at the sites of bridges and underground pipe laying);
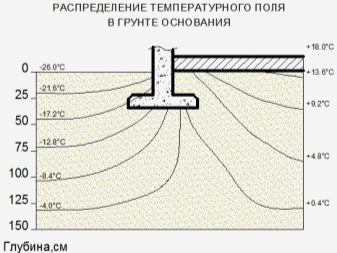
- freezing of the soil at different times of the year and the depth of this freezing.
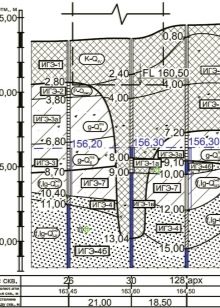
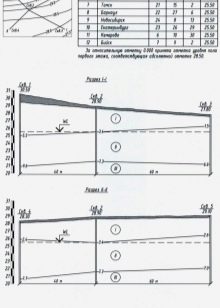
The calculation of the last point should be taken into account based on the calculation of the average annual maximum depths of soil freezing in the seasonal time. The observation period in this case is at least 10 years. At the same time, the site should be open, without stagnation of moisture and snow, and the groundwater level should be located below the level of soil freezing in a certain season.
If there are no observation data for the specified period, the reference depth should be determined based on the thermal engineering studies of the soil, which will be described below.

How to calculate?
Of course, in order to avoid additional costs for professional specialists in calculating the recommended depth for a particular territory, developers are looking for information to independently determine these factors. And this is understandable. These services are expensive and require significant budget increases.
There are separate documents with maps and actual data on the normative depth of soil freezing: in some areas it ranges from 50 to 80 cm, in others the distance varies from 170 to 260.
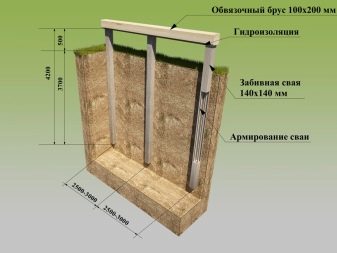
To calculate and clarify this value, a separate technical formula has been developed: dfn = d0 * Mt, df = kh * dfn
- dfn in this case, it is the standard depth of soil freezing, its calculation is necessary to calculate the estimated depth.
- df - estimated depth of rock freezing.
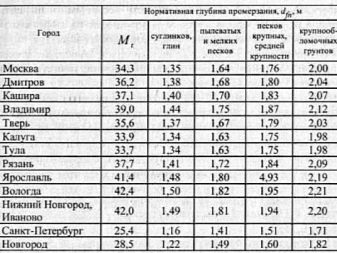
- Mt is the total coefficient of minimum temperatures depending on SNiP 2.01.1-82. Using the information specifically for your territory, you can calculate the average monthly summed value. Calculate this parameter without taking into account the minus in the values.
- d0 - a factor calculated based on the individual characteristics of your soil. For loam, it is 0.23 m, for sandy loam - 0.28 m, for loamy rocks of a larger type - 0.30 m, for some rocks of dispersed soil (soil obtained in the process of weathering of rocky soils) - 0.34 m ...
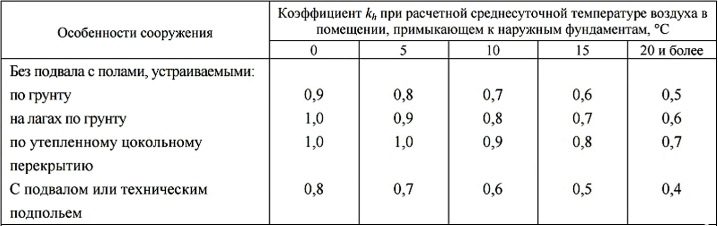
- kh - thermal coefficient, which depends on the temperature characteristics of the building construction.For example, if you are not going to heat the building, the value of 1.1 is taken, however, in the presence of constant heating, it is worth choosing a value suitable for your territory, based on the tables in SNiP 2.02.01-83
In addition, do not forget that data on soil freezing should be present at the geological service of your area, and some information on average climatic conditions should be at the meteorological service.
The use of all the presented characteristics is useful, however, as we have already found out, the freezing depth is far from the only factor affecting the depth of the foundation. One of the uniquely important factors in calculating the depth of the foundation is its type, which is determined based on the design and the elements used and the occurrence above ground level.
The current standards for the installation of strip-type foundations suggest: at least 450 mm on low-heaving rock and at least 750 on loam and heaving-type soils.
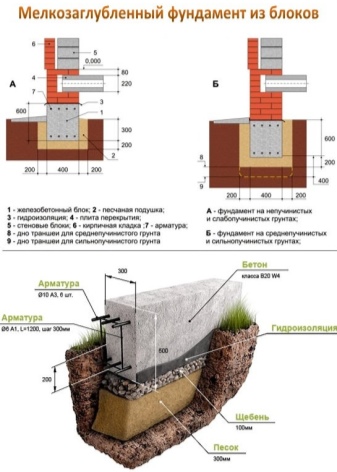

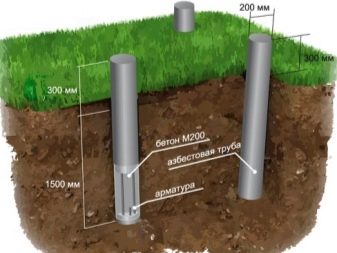
The foundation of the columnar type is most susceptible to the negative influence of the processes of heaving of the soil. Digging in this case is at least 200-300 mm below the freezing level on heaving type soils, non-heaving type rocks are less demanding, and here the depth is calculated based on the type of soil. The width and diameter of the pillar supports are calculated based on the weight categories of the structure.
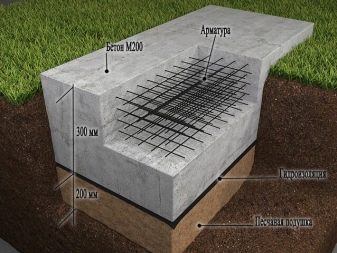
Tile-type foundations are rarely buried to the level of freezing, however, they are often subject to waterproofing, and the non-buried type, as the name implies, is installed no lower than the ground level.
Advice
Unfortunately, many developers neglect the above calculations due to time and financial costs, and, as a result, make the wrong choice. Before installing the foundation, it will not be superfluous to consult with people who have already gone through this process. But remember that the installation of a large building is a long-term matter, and many problems (which can appear just due to non-compliance with the rules) often become noticeable more than a dozen years later. In any case, it is worth protecting yourself and your property now, so as not to deal with unpleasant consequences in the future.
For information on what mistakes are when laying the foundation, see the next video.













The comment was sent successfully.