Bored piles: device and subtleties of construction work

Any building of a modern type needs a reliable foundation or foundation, which ensures the safety, stability and reliability of the entire structure. Most often, developers use a strip type of foundation - it is easy to install, does not require large physical or financial costs, but it can not be used in all areas of the soil. Hard ground rocks are sometimes located at great depths, which several times increases the volume of earthworks and increases all types of costs. Here it is advisable to use a foundation on bored piles, the device and subtleties of construction work on the installation of which we will consider in this article

Peculiarities
The pile type of foundation installation is known even to beginners in the construction industry. It is quite popularized, and it can be found in the construction of absolutely any buildings - be it entire shopping centers or private houses. This is, of course, explained by the reliability of the installation (since the piles evenly distribute the load from the building on hard soil) and lower financial costs, since a monolithic foundation foundation, and especially a good quality foundation, costs much more money.


The installation of any type of foundation assumes the presence of both positive and negative aspects, this is explained by environmental conditions, soil characteristics, and individual characteristics of the foundation. Very often, in order to avoid one "ailment" in the building, you have to sacrifice something else. So, let's look at the main pros and cons of bored piles.
Let's start with the positives:
- As already mentioned, the work of installing any pile structures is much cheaper than monolithic or tape analogs, while they have the same high bearing capacity due to the uniform distribution of the load;
- The design of bored piles allows you to install the foundation of a building on almost any soil areas, meaning sandy loam and rocks with a high level of groundwater;
- The service life or service life of bored piles with proper planning and installation can reach 50 years or more;
- Unlike the installation of a strip foundation with driven piles, which need more or less soft surface soil for reliable driving, bored piles are placed in the ground after drilling the hole, and cannot be damaged as a result of mechanical or automatic driving;
- The installation of bored piles, in fact, does not exert any pressure on soil rocks, as in the case of driven piles, so they can be used in areas even with high ground congestion, when there are already many buildings next to the future construction, which is typical for large cities;
- The placement of foundations of many types presupposes the presence of special equipment, which, as a rule, is quite dimensional and can harm the landscape integrity of your territory, in contrast to bored piles, the installation of which can be done by hand and rarely requires any equipment;
- Some types of reinforced concrete are very unstable to processes such as corrosion, it destroys their internal structure, which leads to a decrease in the reliability and stability of the entire structure, at the same time, high-quality bored piles are devoid of this drawback and can work properly without inspection work for a large amount of time;
- As for large cities with a developed sewerage system or a large number of underground engineering structures, bored piles do not pose a potential danger to these communications, since they can be placed in absolutely any place and, if desired, moved;
- An insignificant, but important plus - unlike other types, the foundation on bored piles is installed quickly and almost silently.


Despite such a number of positive aspects, this type of pile structures also has disadvantages.
- At the first stages of installing this type of pile, the technician is faced with the problem of high concrete costs for a separate pile. In addition, depending on the type of soil and its characteristics, it is in this area that it is difficult to calculate the exact volume of the required concrete - this is due to the fact that the soil around the installed pile is usually not compacted.
- The second significant drawback is the large volume of manual earthworks. Carrying out manual works is cheaper and less resource-intensive only in those cases when you yourself are an experienced developer and understand all the subtleties of a competent work organization. In another case, without the help of paid workers, the independent installation of bored piles can lead to disastrous results, which is already more expensive for oneself.


- The next drawback is common for each type of foundation and pile structures - exceptional accuracy in calculations. Remember that factors such as the level of freezing of the soil, heaving of the soil, the level of groundwater, the influence of external climatic factors may not bother you at the stage of installing the piles, but they will certainly remind you of themselves in the future, since these factors for the most part can change.
- An important drawback is the complexity, or rather, the impossibility of placing a basement or basement room under the building. With a competent layout, you can place a small cellar for vegetables and food under the foundation of the building, but even in this case, you should be careful - the uneven distribution of piles under the building leads to an increase in loads on their individual sections. And these are already breakdowns, cracks and chips.


Having studied all the pros and cons described above, it is worth formulating a clear definition of bored piles. Bored piles (some call this type "bored") are those piles, for the installation of which holes of the required depth and diameter are pre-dug or drilled in the soil. Then a reinforcing frame is placed there, which is subsequently filled with cement (some developers first fill the pile with cement, and then reinforce it under a certain pressure). After passing through these stages of work and hardening of concrete, the piles are interconnected with a reinforced concrete base, and as a result, the same strip foundation is obtained, but already on bored piles.

Regulatory Requirements
At the moment, there is no separate GOST standard for the installation of bored piles, but there is a separate list of rules and regulations that a technician must adhere to when installing any type of pile-type foundation. These are SNiP 02.03, 02.01 and 03.01. Each of these rules was introduced into production at the end of the 20th century, however, their general provisions, due to minor changes in the processes of installing piles, have not changed to the present day.
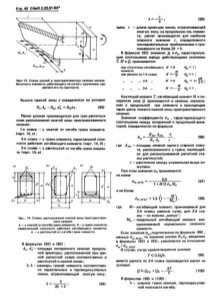
If you adhere to the requirements of SNiPs, before the installation of bored piles, it is necessary to make calculations of a geological, hydrometeorological and geodetic nature. After carrying out accurate calculations, it is worth choosing: the appropriate type of bored piles specifically for your territory, the size of the piles or supports themselves. You can calculate some of the geological and hydrometeorological data yourself, with the help of an expert technician, or contact the nearest hydrometeorological centers for factual information.
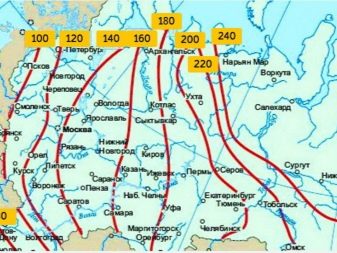
The SP standards assume the influence of climatic factors on the installation process itself. Here the technician is advised:
- to carry out the placement of bored piles in moist soils under thermal conditions of the external environment not lower than -10 Hz;
- carry out the whole range of measures to prevent freezing of the concrete composition before the process of pouring into the well;
- to ensure the proper operation of equipment in certain environmental conditions.


To a greater extent, these requirements relate, of course, to environmental conditions at low temperature values, since most problems arise due to the processes of heaving of the soil (to minimize these processes, you should use data on soil freezing in your territory). At high temperatures, as a rule, there are no problems with the performance of the equipment and the pouring of the solution.
In addition to the described recommendations, a certain set of measures should be taken to prepare the territory for the installation of bored piles.
This complex assumes:
- installation of barriers and warning signs at the boundaries of the work;
- liberation of the territory from all elements restricting movement or construction - they will slow down both the construction process and have an unnecessary effect and load on the ground (if the objects are oversized);
- removal of grass cover and all kinds of shrubs from the construction site - individual plant elements can interfere with the work;
- providing the site with drainage structures - this is both useful for the future operation of an already built house, and it will be useful in the development process itself due to not always favorable weather conditions or too high groundwater levels;
- organize the construction area in such a way that all the equipment necessary for drilling and pouring can freely enter the object and move around it.




Specifications
Manufacturing a high-quality foundation on bored piles has some characteristic features. This applies, as a rule, to the characteristics of the used fastening elements, fixing and sealing of both the well and the pile structures. Consider the characteristics of the elements of the foundation of the bored type. The first important element is the formwork, their structure and characteristics. They have already been mentioned just above in the material as a fixing element for reinforcement parts.


Perhaps many of you are used to understanding formwork as a wood or iron element for shaping concrete or reinforced concrete structures.
In part, this technology also applies to the construction of piles, but in this case, the following can act as formwork:
- cylindrical rolled roofing material (it is advisable if the hole diameter does not exceed 50-60 centimeters) - this element will provide additional waterproofing of the reinforcement parts during the pouring process;
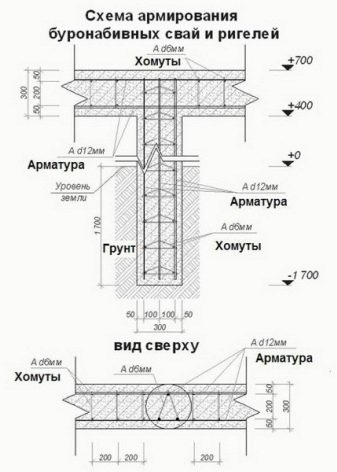
- asbestos-cement pipe - it is stronger than other analogues, strengthens the entire structure and protects from unintentional mechanical damage;
- PVC, PP pipes or pipes made of other polymers (this type is applicable for small, oversized and light buildings, an example of this is a small house, a bathhouse, a building of no more than 2-3 floors).


Formwork can be both removable and non-removable, even after pouring concrete. Technicians most often use the first type, the second type provides additional fixation and waterproofing of the reinforced concrete foundation, but the first is more economical. Please note that when using some types of polymer formwork, it is worth considering the vulnerability of some species to direct sunlight. When mentioning the formwork, it is worth mentioning the method of fastening the walls of the hole by using a casing - it performs a somewhat similar function, but most often it is not removed from the pipe, although thrifty developers and developers with limited finances may do differently.


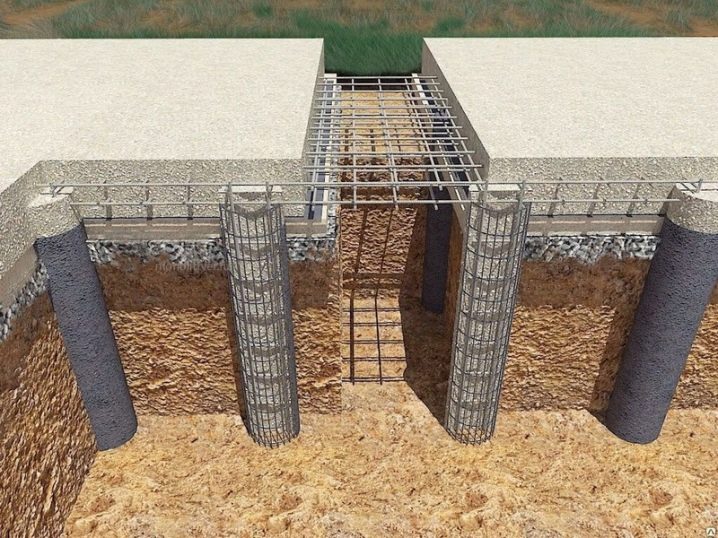
The second no less significant element is the reinforced frame and its properties / characteristics.
Many inexperienced builders do not pay attention to such an important parameter as the quality and correct installation of reinforced elements in a bored foundation. A common mistake in defining the role of reinforcement parts for piles is simply their presence or absence. In other words, if they exist, then it's already good. This is fundamentally the wrong approach, and it can be applied to small private buildings, but if you ignore this factor when building large buildings, you risk the reliability of the entire building.


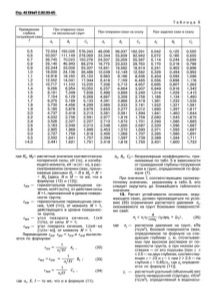
Based on the norms of SNiPa, the reinforcing cage is a structure of 4 or more vertical rods with a diameter of at least 10 mm. The structure of the reinforcing cage itself, in fact, is a cylinder - the fastening of the rods with special horizontal clamps (metal, as a rule). It is worth noting that when the reinforcement cage is immersed in a prepared well, the tops of the rods should be released by 20-40 centimeters from the highest design point of the well (or from the point of the casing, formwork) - this is necessary for the subsequent fastening of the reinforced concrete foundation.

It should be noted that the placement of a reinforced frame in case of rubble-concrete laying (using crushed stone or rubble stone, which are driven into concrete by applying vibrator pressure) can be problematic. In this case, the reinforced elements are not placed over the entire height of the structure, but only in the upper part of the pile. This method is used in two cases: when the developer wants to strengthen the piles in a natural way; if desired, save on concrete mix.


Whether this method is expedient or not - many experts think differently.
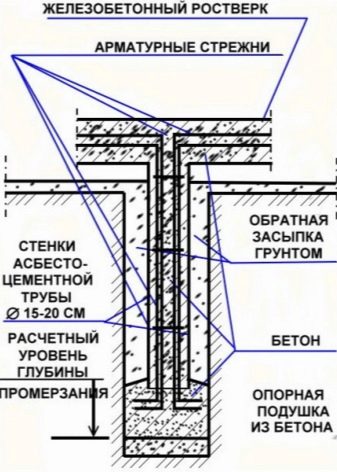
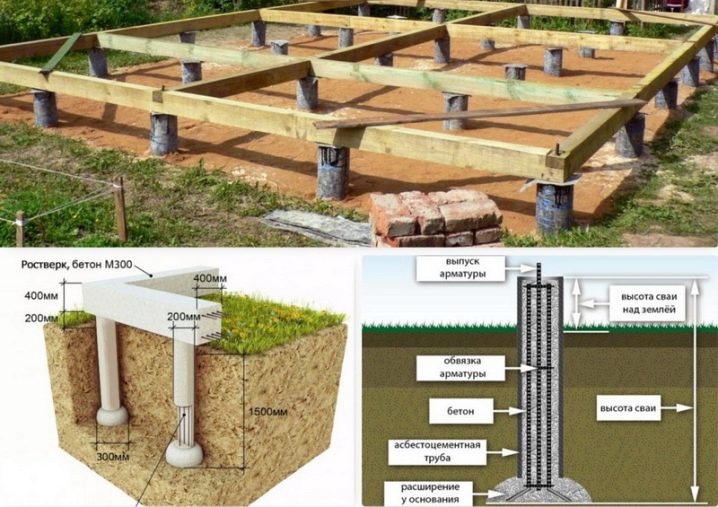
Another important point in the installation of a bored foundation is the correct placement of the grillage and the correspondence of its functions to the required characteristics. Whether the correct installation of the grillage is important, or is it enough to simply place it on the piles - the question is rather rhetorical. The grillage performs the main function in the work of the foundation - it distributes the applied pressure and load from the building to the piles or soil. The difference between the grillage of the bored foundation and the grillage of the usual tape type is that it rests not on soil rocks in prepared trenches, but on the ends of reinforced rods that grow above the pile.
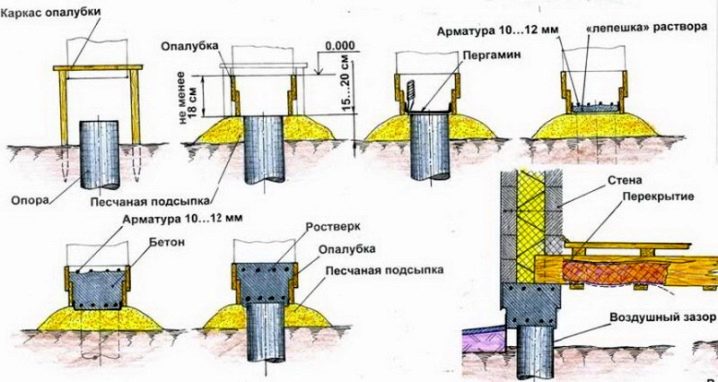
Remember, in winter there is a high risk of soil deformation due to heaving processes - for a pile-type foundation, this is a common problem, therefore, in order to avoid damage to the foundation itself, it is worth leaving a gap of 15-20 centimeters between its base and the ground. If you have already installed the grillage and the height from the ground is lower than the one given, we recommend placing a 5-cm layer of foam plastic under the grillage, it will prevent swelling and usually restores its shape in a warmer period.


The grillage is installed after the formwork is poured with concrete and after it has completely dried out. In the future, for waterproofing the foundation, it is recommended to cover the grillage with two layers of roofing material.
Mounting
It is worth giving step-by-step instructions, when using which, and after carrying out the precautions and measures described above, the technician will be able to build a high-quality bored foundation with his own hands.
So, the builder should adhere to the following steps:
- performance of measuring and marking work - for their competent implementation, technicians prepare or order special drawings, taking into account both the territorial and technical features of the building;
- determination of the type of piles - hanging piles (which do not reach dense soil) and pile-piles (pile structures based on solid rocks), the first type is more applicable on controversial soil areas - with a high level of groundwater, with possible ground shifts and with high heaving soils in winter;
- installation of a drilling rig at the drilling point;


- drilling a well with the depth and diameter values necessary for the technician (these two parameters are selected in advance of the start of construction, depending on the dimensions of the building and the type of soil);
- the introduction of a clay solution - this is necessary to prevent the processes of shedding the walls of the hole, and then - the clay surface does not allow moisture from the groundwater and becomes a kind of natural internal strengthening of the hole;
- cuttings (or the same drilling products - all kinds of rocks, impurities, strata obtained during drilling) must be removed to the surface with drilling fluid or mechanically (it all depends on the type of drilling);

- if the object is large and dimensional, and the future pile elements require exceptional reinforcement, the developer uses specialized equipment to immerse the reinforcement elements to the entire depth of an already dug well (depending on the depth, this process can take place under pressure);
- after being placed in the hole, the reinforcing elements are fixed with stops, such stops can be formwork, the varieties of which we will consider below;
- after the above procedures, the hole is filled with concrete (depending on the depth of the pile structure, concrete can be delivered by special equipment or manually, however, concreting in any case should not last longer than 3 hours - this is the SNiP norm);
- further actions involve drilling and filling the wells already at a different point according to the described scheme, further measuring actions and fastening all the piles with a reinforced concrete strip foundation.

Payment
The installation process of any foundation is based on clear and dry numbers. No matter how much you would like to think otherwise, the slightest mistake in installing the foundation - and you can provide yourself and your structure with constant repairs with earthworks and a lot of financial costs. Avoiding this is simple - just take into account the widest possible range of factors that can affect the reliability of your foundation. This, of course, also applies to the foundation on bored piles.


Here is a complete list of parameters that, in one way or another, affect the safety of installing a bored foundation:
- the area and length of the foundation / grillage, as well as its height, the area of the lateral surface and the foot - this way you can calculate the average pressure from the building on a separate part of the foundation and the pile (do not forget to take into account the parameters of the internal partitions);
- average costs of concrete or rubble elements - this will allow you to calculate the possibilities of rigidity and strength of an individual pile - here it is worth taking into account the presence or absence of siege pipes, formwork, waterproofing elements (do not forget that the initial planned costs of concrete are almost 100% slightly lower than the volume spent in the result);


- load and pressure on an individual pile, and load on rock from the weight of the building and foundation;
- the requirements and recommendations for the reinforced frame must be observed - this is a diameter of 1 cm, the number, length and weight of reinforcing bars, the diameter and pitch of the fastening clamps according to SNiP for your building;
- the characteristics of the formwork (depending on the material used for the formwork, these values according to GOST vary greatly);
- in addition to all this, take into account the external climatic conditions, which have already been mentioned above.


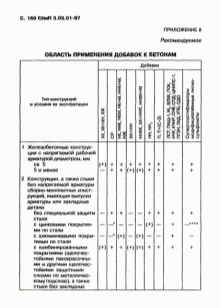
It often happens that some of the types of calculations cannot be applied to buildings erected by private developers., this can be justified by such factors as the installation of additional structures and elements on the territory (to which precise design operations cannot be applied before construction), the use of an individual type of foundation (foreign, not so popular or not so widely known types of foundation) and some others.This is a common situation today, as the number of individual projects is increasing, and there are more and more bold design solutions in the construction of buildings. In this case, the developer must use the norms, rules and tables with data in SNiP 2.02.03-85, SNiP 3.03.01-87, SNiP 52-01-2003 and GOST R 52086-2003. Studying these documents will allow you to determine the optimal number of pile elements, calculate the depth of piling, the load on the soil and foundation in your area, and will certainly be useful for novice builders.

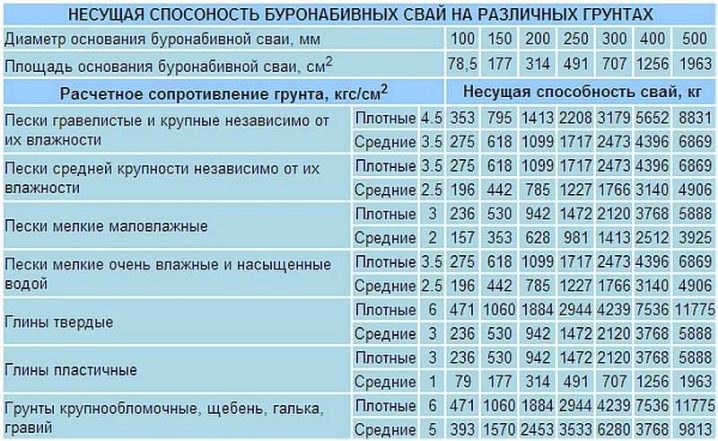
The process of calculating a bored foundation is simple. First, you need to calculate the weight of all foundation structures, take into account the approximate weight of furniture, people, wall barriers, stairs, superstructures, loads from snow or rain. The next step will be to determine the bearing capacity of an individual pile, it will depend on such parameters as the diameter and length of the pile, the characteristics of the reinforcement cage, the loads of soil rocks and their properties. You can calculate the bearing capacity of the piles from the data obtained from the die tests
After the calculated measures, the builder carries out corrective work, which includes optimization of the number of piles (if the number is odd, it is usually rounded to an even number) and checking the entire structure for damage and cracks. The number of piles, as well as the distance between them, is determined by the weight of the building and the diameter of the piles themselves. When placing piles, keep in mind that their installation at the corners and at the junction of the walls near the building is required. Otherwise, the load and pressure on certain sections of the foundation may be close to the critical value.

Advice
After reading the recommendations of experts, you can understand that you should not neglect the rules for installing bored piles. Any foundation is the foundation of a building, its "core". A fundamental inaccuracy in miscalculations - and consider that instead of the prescribed 100 years, your house will only stand for 30-40. Consider this fact if you want to save on the quality of concrete or on the number of reinforced rods, do not forget to use the norms of SNiPs and GOSTs, they are not created to limit your activities and not to restrain actions at the facility, but only for your safety and the safety of other people.
And the advice and advice of professionals will help you build a durable and reliable building.
For information on how to make bored piles with your own hands, see the next video.













The comment was sent successfully.