Drilling for piles: construction technology
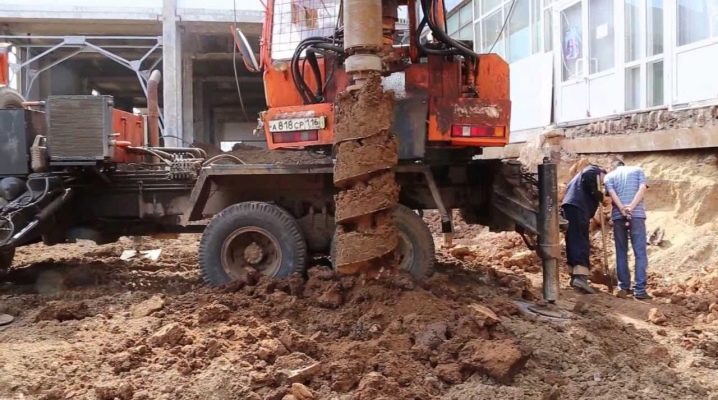

Pile foundations under houses and other structures are in many cases the best solution. But in order for such a structure to last long enough and not malfunction, it is required to carefully drill the excavations. This work has many subtleties and nuances, which will be discussed in detail in this article.

Peculiarities
Drilling for piles allows:
- build something in a shorter time frame;
- reduce the cost of work;
- guarantee the real stability and strength of the building.
Driving wells under piles is really necessarywhen it is required to build a house in places with an increased risk of earthquakes or on an area with low-density soil. Such drilling can be done in any season, the type of climate does not matter. These advantages have allowed construction drilling to become one of the leading methods of excavation preparation.
Drillers are hired in cases where it is required to strengthen the foundation without affecting the characteristics of previously delivered buildings. Drilling can also keep the slopes stationary.



Instruments
Pile drilling techniques can be very diverse. In most cases, vehicles with a wheeled, auger or caterpillar drive are used for this purpose.
To arrange a well for a pile, use:
- universal drilling rigs for wells;
- piling drilling units;
- drilling and crane complexes.
The differences between them in general and between individual models in particular are determined, first of all, by the level of productivity, the specifics of the control bodies and the size of the wells created. In terms of the cost of work and the availability for non-professionals, it is difficult to find analogues of a hand drill.



Low productivity is justified by the fact that expensive equipment and trained specialists are not needed. But in those situations where speed is important or the soil is very difficult, it is worth using a yamobur. Fastening of such devices is carried out on wheeled and tracked platforms. If the conditions are not easy, even highly specialized equipment has to be involved.
A drill helps to make it easier to work alone. The reinforced construction of the popular TISE version allows for an enlarged heel at the lowest point. As a result, the base goes below the freezing zone, and with the same bearing characteristic, the solution consumption is reduced by 3-4 times compared to alternative technologies. In addition, for a foundation identical in properties, it will be necessary to install fewer piles than usual, and their diameter will be reduced.


Process steps
To drill a hole with your own hands or with the help of specialists to the required depth, you must strictly adhere to the technology.
A typical work algorithm is as follows:
- installation of drilling equipment and its fixation;
- penetration to the design depth and diameter;
- conservation work using clay solution or casing insertion;
- saturation of the formed cavity with concrete solution.
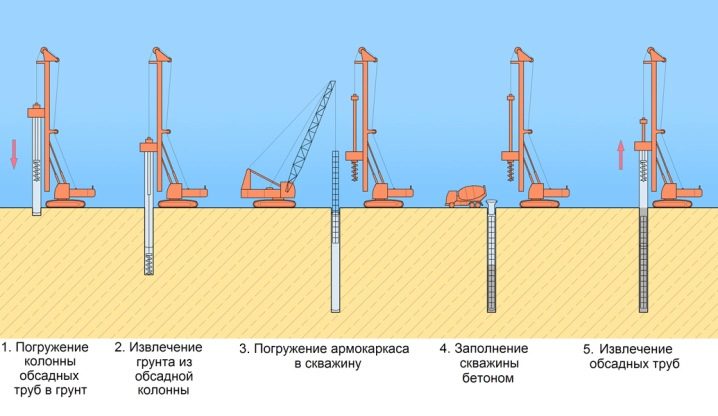
Experts pay special attention to the fact that both the prepared pit and the concrete poured into it have a short shelf life. According to the generally accepted standard, a maximum of 8 hours should elapse from raising the drill to pouring in the last drop of concrete.
Their requirements are also imposed on preparatory work, which look as follows:
- Fertile soil is harvested (up to 150 mm over the entire area).
- A pile field is planned at a selected elevation.
- A fence from strangers is mounted.
- The site is formatted, and then the flatness of the surface is checked again.

- The pillows for the work itself and the passage of cars are filled up.
- Route lines for drilling systems using reinforced concrete slabs are being prepared.
- Drainage channels are being organized.
- Lighting fixtures are connected (only if it is required to drill around the clock or with reduced daylight hours).
- The arrangement of drilling systems and the required materials and products is carried out.


Methods
Rotary drilling of wells consists in the fact that initially they pass the leader part equal to the length of the casing section. This method has shown itself very well in a variety of geological conditions, with unequal water saturation of soils.
The use of a typical auger auger (an elongated rod with a tip of increased strength and helical blades) allows the crushed soil to be lifted up as quickly as possible. The hole rate can be up to 120 cm per minute. The drilling complex periodically pulls out and raises the working part, freeing it from the adhered soil.


High-quality adherence to technological principles will allow for a working cycle, from one lifting of the drill to another, to form holes up to 10 m in length. Another option for penetration involves covering the walls of the hole with an inventory pipe formed by single steel sections. Each piece can be up to 6 m in length. At the bottom is a carbide-tipped cutting part. When the drill moves down, the pile is pressed in at the same time, it blocks the seepage of water from the soil and prevents the walls from collapsing.
Having reached the zero level, determined by the foundation project and SNiP for a specific area, the auger drill is lifted up. Water seeping from the soil into the prepared cavity is removed. But a reinforcing frame is immersed there. The final step is to saturate the empty space with concrete.


Another type of drilling is the use of a core auger, which feeds the solution through the cavity in the rod itself. This approach ensures the formation of 400 linear meters. m of channels for a standard 8 hours. In this case, the channels can be large in diameter (from 50 cm) and reach 30 m in depth each. This is due to the systematic increase in the length of the auger until it reaches a predetermined mark. The saturation of the cavity with the solution is combined in time with the lifting of the mast, this helps to make an array for rammed piles. Remember that concrete is injected under pressure and therefore harder than usual.
If the introduction of a reinforcing frame is provided, it is simply pressed mechanically into small wells, and it is introduced into large wells using a vibrating submersible machine. A typical auger works well in dry or nearly dry soil. There is no need to prepare and strengthen the internal cavities of the wells.
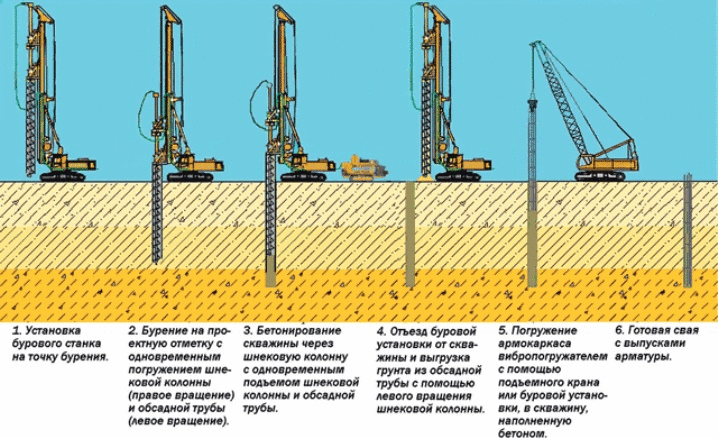
The inventory tube approach also has its merits. Only it can form channels with a diameter of 1500 mm in very wet soil and quicksand. Wet drilling helps to strengthen the borehole through medium-gravity clay or sand.
It is the wet technique that is considered the least noisy, and it also does not destroy the layers of the soil as a whole. In some places, the canal can be widened up to 350 cm, which guarantees the highest stability of the base.
Leader drilling is designed to solve such a problem as the vertical installation of supports in dense ground. It is used in the winter months, when the soil density is greatest. It is also important that the volume and vibration level are relatively small.

The lack of "leaders" is the obligatory preparation for drilling. It is also worth considering that the well will be 30-50 mm smaller than the reinforced concrete structure, the depth reduction will be approximately 1 m.
Leader drilling is recommended if:
- A layer of sand of increased density was found.
- The top layer of the soil is hard.
- The site is located on permafrost.
- The construction site is abundantly filled with rocky soil.
- The piles are to be driven to a great depth.
- The territory is filled with dispersed soil with a very low density.
Test drilling for piling allows us to once again weigh all the subtleties and nuances. In some cases, an error can be very expensive, and it is revealed after the completion of all construction work in general. The properties of the soil vary widely in space, and if it is completely solid at 10 - 15 m, this does not mean that there will be no unexpected phenomena in a particular place. They also turn out to be voids, aquifers, loose particles and the departure of a really strong layer to an unusually great depth. Quite often there is such a problem as fluctuations in freezing lines.


Advice
A hand drill is unacceptable if the pile penetration depth must exceed 7 m. Simplifying the work with the help of gasoline or special equipment, one should strive to reduce the overall operation time to a minimum. Even a slight rain or the beginning of snow melting can bring down a well that has just been prepared at the expense of great efforts.
It will not be possible to extract the soil and reanimate the site; you can only re-drill the hole. The fastest option (although not always acceptable) is screw piles, which simultaneously serve as a drill and support.
It is recommended to carefully select the propeller configuration and blade angles, this will allow the most effective penetration of a particular rock.
Screw piles can even be inserted manually, although there are specialized devices for this purpose. There is no need to level the area, the total running time is reduced by 1/5 compared to installing concrete props. Drilling with solid augers provides a passage up to 50 m in depth, the diameter of the channel can be from 10 to 80 cm.


When it is required to install bored piles with an extended heel, auger drills with expanding knives are in demand. From the position parallel to the rod, they move out when the hinge block is started, and at the moment of torsion they cut a cylinder into the soil.
The cutting ends of the casing pipes are adapted to the situation on the construction site. They go through gravel, clay and sand with ordinary tips, no welding is needed. Strong clay requires hard metal to be applied to the cutting fragments. Only clamshell drilling can be advised where rocky layers alternate with rocky and hard sand.
To keep the bottom of a well drilled through wet dusty sands clean, use drilling valves and bucket-type drills. More detailed information on a specific object can only be given by specialists.


The process of drilling and concreting a bored pile with the BAUER BG24H drilling rig is shown in the video below.













The comment was sent successfully.