What is late blight on tomatoes in a greenhouse and how to deal with it?

Late blight often affects tomato bushes, especially if they are grown not outdoors, but in greenhouse conditions. How this fungal disease looks like and how to deal with it during flowering, during fruiting and in other periods, we will describe in detail in this article.
Description
Late blight is a disease of fungal origin. Pathogens are able to live in the ground for a long time and are activated at any time, affecting tomato bushes. This disease is especially typical for glazed greenhouses or polycarbonate greenhouses, where, as a rule, there are all the necessary conditions for the activation and further development of the fungus. You can infect a plant in other ways: the fungus can be carried by the wind, on clothes, animals and more. Moreover, late blight tends to mutate, which may complicate the situation somewhat.
However, most often the reasons for the appearance and further spread of the fungus are increased temperature and humidity in a greenhouse.
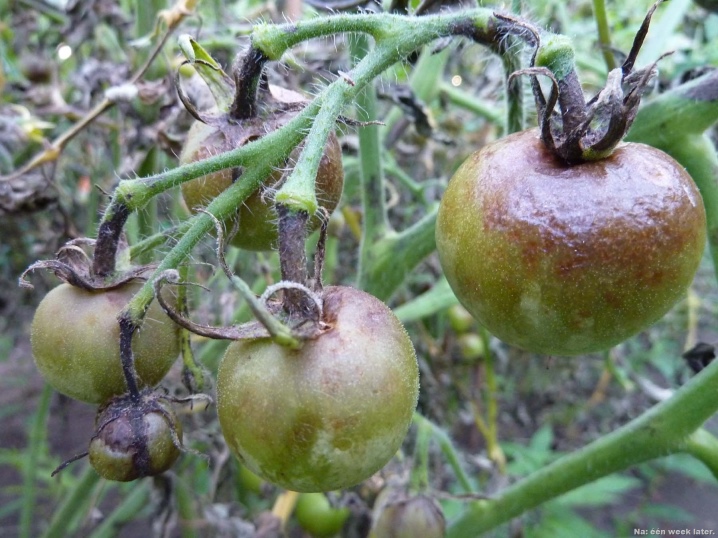

The first symptoms of the manifestation of the disease can be noticed by a number of signs. So, necrosis begins to form on the leaves and stems of tomato bushes, which look like brown spots with a light border. Turning over the affected leaf plate, you can see serous plaque - this is the mycelium of the fungus, which reproduces very actively. Further, the foliage curls, the process of photosynthesis is disrupted in it, which negatively affects the growth, development and number of fruits. Subsequently, the diseased areas of the plant change color to brown, become soft.
The symptomatology of the disease is also manifested on the fruits of the tomato bush: they become covered with brown specks, and then rot. The whole bush as a whole begins to dry, sinks to the ground. It is worth considering that diseased fruits change not only their appearance, but also their taste: they are distorted, noticeably give off rot, it is not recommended to eat them. However, it is allowed to eat fruits that are not too affected if they are cooked.


What can be processed?
It is possible to process tomatoes in a greenhouse from late blight in different ways.
Chemicals
Many summer residents dislike chemicals, despite their high performance. This can be explained quite simply: drugs of this kind, as a rule, are highly toxic, they cannot be used for fruiting or flowering, and if used incorrectly, they can harm both humans and plants and the environment. Therefore, they are used mainly in advanced cases, when other means cannot help get rid of late blight and are less effective.
At the present time, many chemicals have appeared on the market for combating fungus. Among them, copper sulfate, Bordeaux mixture, "Hom" and copper oxychloride are especially distinguished. Before using the listed products, you must carefully read the instructions, which are usually located on the packaging of the product. Only with the correct dosage of the drug can you remove late blight without harming sick tomatoes.
When using poisonous chemicals, you must follow the safety rules and use personal protective equipment (mask and gloves) to protect yourself from the chemical coming into contact with your skin.
At the same time, it is best to spray the plants with a spray bottle, which helps to evenly distribute the product.


Biological agents
Biological preparations are also suitable for the treatment of late blight, and their advantages are relatively high efficiency, safety and environmental friendliness. They are among the best after chemicals in terms of effectiveness.
The first places in the list of the most effective biological drugs are occupied by the following products: "Fitosporin-M", "Gamair", "Baktofit" and "Alirin-B". Some summer residents also resort to treating the plant with drugs: Trichopolom, Metronidazole and Furacilin. Any of these can be purchased at the pharmacy.
In order for the treatment with the above means to be more effective, they need to be mixed not only with water, but also with laundry soap: this will make the medicinal mixture more effective, which will protect both healthy plants and those that are already sick.

Folk ways of fighting
Solutions prepared according to folk recipes have a lot of advantages: they are quite economical, and they can be prepared from improvised means right at home. However, it should be borne in mind that they are effective only in non-started cases, when late blight has not yet developed. Otherwise, it will not be possible to stop the disease with such simple means, only more effective drugs can defeat it. Below we present the recipes for the most popular solutions that are used to combat late blight on tomatoes.

Lactic
For a milk solution, you will need a liter of low-fat milk or kefir and a bucket of water. All this must be mixed, after which a couple of drops of iodine, potassium permanganate or nine percent vinegar are added to the solution. Next, the resulting mixture can be used to process tomatoes. Primary processing can be carried out with a similar product: it is carried out when the seedlings completely take root in greenhouse conditions.
If necessary, the treatment can be repeated, but this should be done no more than once every two weeks.

Serum
Whey solution is also an effective control method that allows you to treat the plant from phytophthora. To prepare the solution, fresh milk whey with a fat content of 1% is required. If necessary, it can be diluted in water. The mixture can be watered or sprayed on plants.
It is recommended to do this for a week, after which you need to take a break of 14 days and, if necessary, repeat the procedure.

Garlic tincture
This solution can also help save the plant from such a fungal disease as late blight. To make the solution, you need a bucket of boiled water and 0.2 kilograms of garlic. It does not have to be cloves: it is also allowed to use stems, leaves and arrows for the mixture. All this is thoroughly mixed, after which the solution is sent to infuse in a dark place for 48 hours. After the required time has elapsed, the tincture must be filtered, after which you can start spraying the tomatoes. If necessary, the treatment can be repeated after 10 days.
It is recommended to start it when the process of ovary formation starts in the tomato.

Wood ash
This is another component that is required to create an effective solution against late blight. It is prepared as follows: 0.25 kg of ash is added to a bucket of boiled water. All this is stirred and sent to a dark place for seven days for full infusion. After a week, you can add shavings of laundry soap to the solution so that it better adheres to the foliage of the tomatoes. Ready! The resulting infusion can be used in a greenhouse. As a rule, treatment with this tool is carried out several times: when planting seedlings, during flowering and during the period of fruit formation.
It should be noted that wood ash is an effective remedy on its own, without any solutions. When planting, it is often poured into the holes, which helps the plant to maintain health.
By the way, wood ash is also a good top dressing for tomatoes, which also has a positive effect on their health.

On the green
A solution against phytophthora can also be prepared on the basis of ordinary pharmacy greenery, because it also has antiseptic properties, that is, it can fight the fungus.
So, the solution is prepared as follows: 40 drops of the product must be poured into a bucket of boiled water. After mixing all the components, the solution can be used to spray the plants. This should be done several times per season. Note that this mixture is only suitable if the plant is already sick. If your goal is to protect tomato bushes, then a prophylactic solution (a liter of boiled water per drop of green stuff) is suitable.

On table salt
Salt also helps fight fungal infections that are actively precipitating in greenhouse tomato bushes. A solution is prepared based on this component as follows: 0.2 kg of salt is dissolved in a bucket of boiled water, if desired, you can add shavings of laundry soap to the mixture. After that, you can start processing the plant. Before that, you need to eliminate the affected tomato foliage. If necessary, this procedure can be repeated after a month.


Straw infusion
This product is prepared from the following components: 0.2 kilograms of urea, a kilogram of rotting straw and a bucket of boiled water. The mixture should be properly infused in a dark place for four days. After that, the solution can be used to spray tomatoes, and they need to process the plantings all week.

Mustard
Mustard also helps protect tomatoes from late blight. This plant secretes special substances that help prevent the formation and development of fungi, mold and bacteria. So, in order to provide protection to the plantings, mustard is planted between tomato bushes.
It is worth considering that this remedy helps to avoid the occurrence of late blight. For treatment, it is best to use other methods.

Prevention measures
Preventive measures help maintain plant health, as well as prevent the development of diseases in the early stages of their occurrence. So, first you need to regularly inspect greenhouse plantings for problems. If symptoms of the disease are detected, the affected areas of the tomato bush must be immediately eliminated, after which the plants should be urgently processed.
Do not forget about proper care of greenhouse plants. Ventilate the greenhouse regularly, because warmth and high humidity are the best conditions for the active development of phytophthora. Do not forget about watering. It must be carried out in a timely manner and in moderation, while avoiding excess moisture.
Feed the plants. This significantly strengthens their immunity, which makes it easier for them to resist infectious diseases and parasites, and also has a positive effect on their entire appearance and taste of the fruit. Carry out regular preventive treatments: this will help prevent the onset of the disease. At the same time, the culture must be processed carefully, not forgetting about the undersized bushes and the back of the leaf plate.
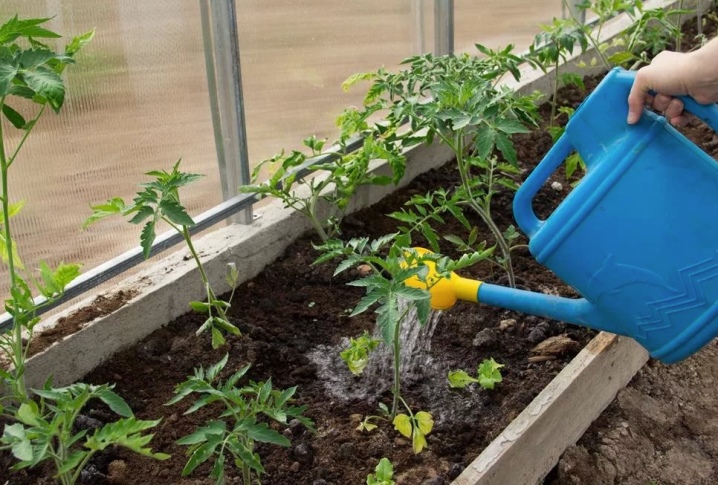

Eliminate pests that are the main carriers of the infection. They often start in a greenhouse because they feel comfortable there. Do not forget about the elimination of weeds, because this is where parasites most often live. It is worth remembering about the disinfection of garden tools: it is with its help that the fungus is transferred from diseased plants to healthy ones.
It is also worth paying attention to the collection of plant residues after the final harvest. It is under parts of old plants that parasitic insects, their larvae, and also a fungus can winter: there they can easily survive frosts and become active closer to May, when it becomes warm.
Do not forget about the planting material: it must be checked and undamaged, otherwise there is a risk of being left without a crop.

Resistant varieties
By using resistant varieties of tomatoes for planting, you can avoid many of the problems associated with late blight and not only. So, there are many varieties of tomatoes that are resistant to late blight.
Among the yellow varieties, the following are distinguished: "Indira", "Golden Canary", "Apriori", "Yellow Empire" and "Kaspar striped". Among the undersized, you can choose such species as "Vidal", "Zapovedny", "Antyufei" and "Vereisky Early". Among the fleshy varieties, the most popular are "Zapovedny", "Fig pink", "Green honey" and "Zateynik".












The comment was sent successfully.