Phytophthora on potatoes: what does it look like and how to deal with it?

Why everyone's favorite potatoes are not sick. And pests do not bypass him - everyone likes it. But the most common and dangerous disease, which significantly reduces the yield of potatoes, is late blight.
Description
The disease and its causative agent were first described by the botanist from Germany de Bary. He also gave the name to it - late blight, which means plant eater.
This disease damages not only potatoes, but also all nightshades - tomatoes, peppers, eggplants, some other crops, in particular, there are varieties that even affect strawberries.
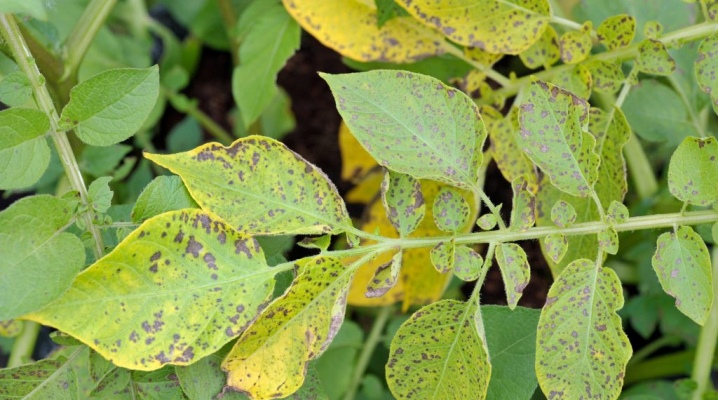
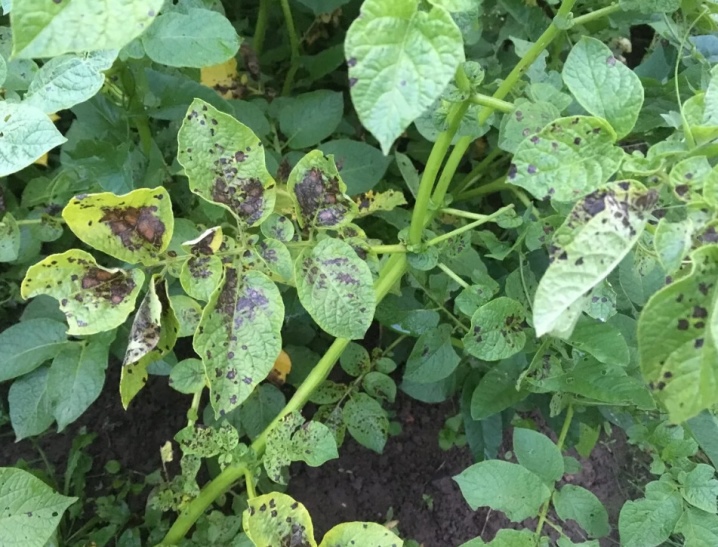
Phytophthora on potatoes damages all parts of the plant - not only leaves, but also tubers, stems, flowers. For an outbreak of the disease, certain conditions are necessary - a low temperature with high humidity and a number of other conditions, which will be discussed below. The disease begins with the lower leaves that are in contact with the ground. On the edge of the leaf plate, brown spots appear on top, and on the bottom, along the border of healthy and diseased tissues, a white bloom - this begins to sporulate the fungus.
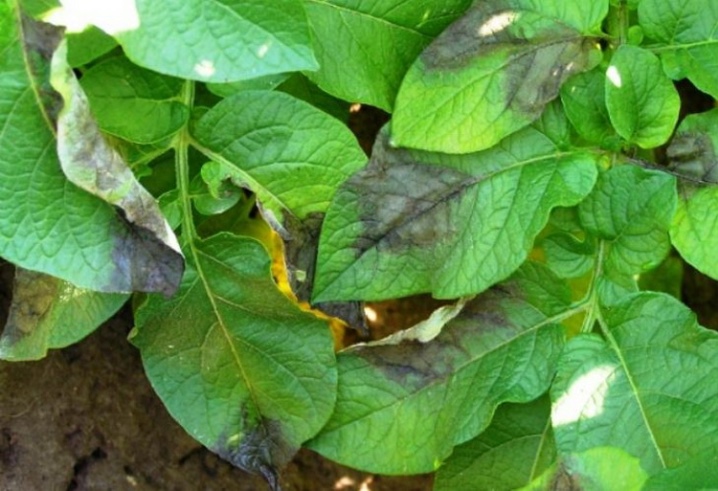

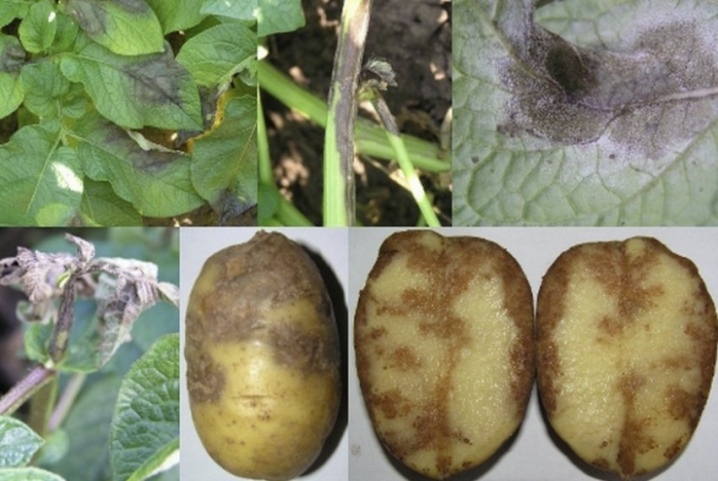
With the onset of dry weather, the growth of spots stops, the leaves become dry and brittle. Wet, rainy weather causes rapid growth of spots, and the whole plant is affected by late blight. Diseased plants infect healthy ones, and if the rainy weather lasts for several days, the infection will cover the entire potato field. It looks very deplorable: brown bare stems stick out from the ground, the plant almost completely dies. Tubers remain in the ground, but they are also already affected by the disease. They appear depressed dark or brown spots, which penetrate into the thickness of the pulp.
Such potatoes are stored very poorly, various rot develops on the spots, and it completely decomposes. In addition, if it is not removed from the common heap, the infection spreads to other tubers.

Causes and symptoms of defeat
Potato infestation is caused by Phytophthora infestans. Strictly speaking, the fungi that cause late blight, in their physiology, are located between fungi and plants. Because they reproduce by spores, and their cell wall does not consist of chitin, as in fungi, but of cellulose, as in plants, and they are closer to plants. Therefore, they are classified as a separate group of organisms.
These organisms reproduce by zoospores, which have an unusually high resistance to adverse external conditions. They easily overwinter in the soil even at very low temperatures, and not only in the soil, but also on the surface of the leaves left after harvesting, in last year's tops that were not harvested from the field, in bags and boxes where infected potatoes lay, on shovels and hoes with which they were processed potato.
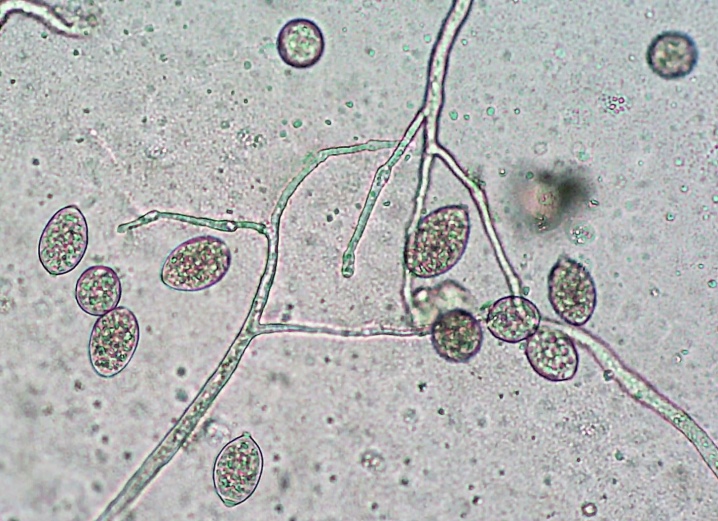
When in spring the air temperature exceeds + 10 ° С, and the humidity is 75% and higher, zoospores wake up and begin to move along the stem from top to bottom, penetrating into the stem along the way. After a week, if the weather remains wet, the entire plant becomes infected. It should be noted that in the southern regions, where spring and summer are hot, the first signs of late blight usually appear in the second half of summer, when the heat is replaced by lower temperatures, and the nights become noticeably colder.
If late blight appears on several bushes, the entire field can soon become infected, because spores can not only be carried out of the ground, but also spread through the air with the help of the wind.
The symptoms of the disease can be seen from afar. It all starts with the lower leaves - they turn yellow, giving the potato bushes an unhealthy look.
Unfortunately, this symptom suggests that the fungus has spread throughout the plant, and preventive spraying will no longer help here.


The leaves are first covered with gray spots, wet to the touch, then the color turns brown. The spots do not have clear boundaries and regular shape, they usually appear at the edge of the leaf, then gradually spreading to the entire leaf blade. The stems become wet in the affected areas, the elongated spots join and form large areas, which soon cover the entire stem.
With early spread, phytophthora begin to hurt and the inflorescences along with the peduncles. The resulting fruits (more correctly called berries) are a "shelter" for the fungus if the weather turns hot and dry. Such berries are first covered with hard spots, then the spot covers the entire surface, under the skin the flesh has areas that are colored brown.

How to process?
Pre-planting soil treatment will be an excellent prophylactic agent, since overwintered plant residues containing phytophthora spores may be on it. To disinfect them, you can spill the ground with such effective antifungal drugs as Bordeaux liquid or copper sulfate, prepared strictly according to the instructions.
The fight against late blight on potatoes should begin even before the seed is planted in the ground, even earlier - when storing it in the fall. To do this, you need to spray the tubers with a disinfectant material. Both chemical and biological drugs can help to successfully fight the disease.
At the stage of laying seeds for storage, it is better to use biological products; there are a large number of them on sale now. They will help get rid of fungal spores that remain on the surface of the tubers. It is difficult to say how to choose the most effective biological products, because everything must be tested in practice. Hay stick preparations are very popular.
It is not necessary to treat already diseased bushes with them, because the effectiveness is low. But for prevention, you need to use it as often as possible, preferably every 10-15 days during the entire growing season.


If the potato bushes are already sick, then in this case, you can save the crop with the help of chemical fungicides. They are subdivided according to the nature of the impact and distribution within plant tissues, there are contact action and systemic.
Contact fungicides destroy the causative agent of the disease by direct contact with it, that is, by contact. Some of them can penetrate shallowly into plant tissues. The effectiveness of such drugs strongly depends on many reasons - for example, on the weather and the duration of exposure to the tops, since rains can wash them off the surface, as well as on the amount of fungicide and how well it can hold on to the plant (in this case, an additive will help various adhesives).
It is very important to take into account the fact that contact drugs cannot treat plants that show clear signs of infection, especially at later stages. Their peculiarity is the ability to protect against infection, but this ability persists until the first heavy rain. Then you need to repeat the treatment, and this should be done every time after rain.

The main advantage of contact drugs is that they are not addictive, and they can be used several times per season - up to 6 treatments.Such funds act only in those places on which they are directly located, therefore, you need to carefully process the entire surface of the plant, including the underside of the leaves.
Systemic fungicides have the ability to be distributed not only over the surface of the plant, but also with the help of the vascular system within all tissues. Their effectiveness does not depend on weather conditions and lasts for several weeks.
But pathogens are capable of developing resistance and addiction to systemic fungicides, and they must be constantly changed to new ones so as not to be used more than 2 times per season.

Chemicals
When working with chemical fungicides, a number of rules must be followed.
- Wear a face shield or respirator and gloves. This rule must be observed without fail, since fungicides penetrate quite well into the human body through the skin and respiratory tract.
- Processing must be carried out at a certain time: either in the morning at dawn, or in the evening after sunset, and also if the weather is calm, cloudy, when the sun is not visible.
- The preparations must be diluted strictly according to the instructions and consumed at the rate indicated in it. It is necessary, if possible, to alternate them so as not to cause persistent addiction in plants.

Now let's take a closer look at chemical fungicides, and how to use them.
Contact ones are copper sulfate, Antracol, Tsineb, Polycarbacin, copper oxychloride, colloidal sulfur, Mancozeb, Bordeaux liquid, Cuprolux and others.
- Copper sulfate in its pure form is rarely used for plant protection. It must be diluted in a solution of quicklime to obtain Bordeaux liquid. This is an old, proven method with more than a century of experience in application. It has not lost its relevance to this day.
- "Antracol" - highly effective contact fungicide against late blight on potatoes. Not addictive to plants.
- "Tsineb" - contact, but can also exhibit the properties of a systemic fungicide. The duration of action is up to 2 weeks, in warm weather the drug decomposes faster, the duration of action decreases.
- "Polycarbacin" - fungicide of protective action, used for vegetable crops and very effectively fights late blight.
- "Hom" and "Oxyhom" - copper-containing preparations, without which the fight against some fungal diseases is impossible. Both products contain copper oxychloride. They differ in composition: “Hom” has only a contact effect, “Oxyhom” has a contact-systemic effect.
- "Cuprolux" - also contains copper oxychloride, can stop the development of the disease one day after infection. Compared to conventional fungicides, it has an increased interval between treatments. It also has a local systemic effect.
- Colloidal sulfur - one of the oldest pesticides used to protect vegetable crops. The period of protective action is 12 days, the speed of action is after 3-4 hours.
- "Mancozeb" - contains zinc, manganese, ethylene. Can be used instead of Bordeaux liquid. In order for the protection to be as effective and long-lasting as possible, it is necessary to treat the plants with "Mancoceb" quite often, because it has a short exposure period.



Systemic - Topaz, Skor, Revus, Quadris, Fundazol, Previkur, Ridomil and others.
- "Topaz" - one of the few powerful drugs approved for use in personal subsidiary plots and in an apartment.
- "Speed" - provides a long-term protective effect of the sheet apparatus.
- "Revus" - when applied, the death of phytophthora is ensured even on the surface of the leaf. The development of zoospores, its growth and infection of new tissues are prevented, the development of the pathogen of phytophthora inside the leaf is stopped.
- "Consento" - is used for both prevention and treatment of the disease. Effective at different stages of the development of the disease, as well as at all stages of plant growth, the effect is quick and long-lasting.
- Infinito - a systemic fungicide, the protective effect of which lasts up to 2 weeks, depending on weather conditions and the degree of plant infection. Non-toxic to birds, bees and earthworms.
- "Quadris" Is a very efficient means of production in Switzerland. Safe for beneficial soil microflora. Part of the drug remains after treatment in the form of an indelible film, that is, it is both a contact and a systemic drug.
- Fundazol - systemic and contact action. It has a healing effect that lasts for the first 3 days, and for the next 7 days, the protective function remains.
- "Previkur" - the period of protective action is 2 weeks. Does not cause resistance. The recommended consumption rate and number of treatments must not be exceeded.
- "Ridomil" - helps plants even in conditions of severe disease damage. Provides protection for the entire plant - leaves, fruits, tubers.
Biological fungicides are now very popular, the most famous among them is "Fitosporin". Their fundamental difference from chemical ones is that they contain a set of specific bacteria that cause the death of a certain type of pathogenic fungi, including late blight pathogens.



Biological agents
Biological fungicides are characterized by low toxicity and, at the same time, high efficiency in the prevention of late blight. They are nutrient solutions containing bacteria, fungi or metabolic products of these organisms. Currently, many types of biological products are produced, the most popular of them are:
- Fitosporin;
- "Gamair";
- "Barrier";
- "Glyocladin";
- "Barrier";
- "MaxImmun";
- "Fitop";
- "Integral";
- "Baktofit";
- "Baktogen";
- "Agate";
- "Planzir";
- Trichodermin.



Although they do not have "lethal" characteristics in comparison with chemical ones, they have a number of advantages, such as:
- do not accumulate in plants;
- do not create an addictive effect with prolonged use;
- do not harm nature;
- strengthen the immunity of plants.
They are used as prophylactic ones, so they need to be used often - every 10-12 days during the growing season of potatoes.

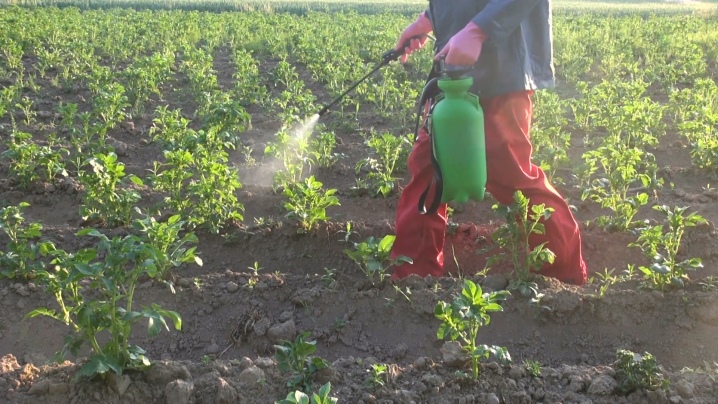
Traditional methods of treatment
Not everyone likes potatoes stuffed with "chemistry". Therefore, such gardeners have learned to use completely harmless methods of protection against diseases on their plots. Various means are used.
- Garlic. To prepare the composition, pour 150 grams of arrows, green leaves or cloves of garlic, chopped in any way, with 1 glass of water, insist for a day. Strain this infusion, add it to 10 liters of water - and spray the potato beds 1 time in 2 weeks.
- Milk serum. It is diluted halfway with warm water, and potatoes are sprayed to prevent disease.
- A tree tinder fungus, on the surface of which fungi parasitize, suppressing the pathogen of phytophthora. It is necessary to prepare a healing infusion: chopped tinder fungus (100 g) is poured with hot water, but not boiling water. After the liquid has cooled completely, it must be filtered and poured into a bucket (10 l). Use for spraying.
- Ash solutions. To prepare the ash solution, you need to take a 10-liter bucket, pour about 1/3 of the sifted ash into it. Pour water to the top, stir well and let it brew for several days, stirring the contents at least once a day. Now you need to dilute the infusion by half with water and add some kind of adhesive, for example, dissolved laundry soap. The solution is ready, you can use it every day.


Basic rules and terms of processing
As for the processing time, there can be no specific and clear recommendations here. You need to focus on the growing season of potatoes.
- Biological products are used starting from the first shoots. They are regularly treated with bushes every 10 days during the entire period of their growth.
- Chemical contact preparations are first applied before the potato blooms, but the buds should already be formed. Further - as needed after heavy rains.
- Systemic drugs can be sprayed no more than 2 times per season - before late blight appears during budding and after flowering.
- When using chemical methods, precautions and means of protection against the harmful effects of chemistry must be used.

Prevention measures
It is almost impossible to save potatoes from late blight without taking preventive measures; the disease has spread too widely. Here are a few rules to follow when working on a potato plot.
- Compliance with crop rotation. This will help reduce the incidence by 10-15%. Although in many household plots potatoes are planted after potatoes for many years, because the size of the plots does not allow doing otherwise, you can find a way out of this situation - sow siderates in the land where the potatoes grew in the fall, which have the ability to heal the soil.
- Potato plantings do not need to be thickened - they should be well ventilated. For this, the distance between the beds is made at least 60-70 cm.
- In the fall, after harvesting the potatoes, you need to collect and burn all the remains of the tops., on which phytophthora spores can overwinter and start multiplying again next year
- A very good protection for potatoes in the open field can be mulching potato plantings. But this method has a drawback - if a lot of potatoes are planted, mulch, accordingly, also needs a lot, and this is sometimes beyond the power of gardeners.
- Preventive treatments with biological products. They need to be done regularly and often, avoiding long interruptions in work. Only then will it be successful.


Which varieties are resistant to the disease?
Breeders are constantly working on developing new varieties of potatoes that have good resistance to late blight. To date, there are a number of such varieties.
- "Luck" - the variety is resistant to late blight of tubers, but weakly resistant to late blight in the tops.
- "The sorcerer" - known since 2000, very tasty, white pulp, rind
- yellow. Stores very well. Has a high resistance to late blight.
- Loshitskiy.
- "Fairy tale" - withdrawn in 2004. Has a very high degree of resistance to late blight. The starch content is 14-17%.
- "The Riddle of Peter" - withdrawn in 2005. Highly resistant to late blight.
- Nikulinsky - very tasty potatoes, with white flesh and light beige skin. The variety is resistant to late blight, excellent storage.
- "Purple Haze" - relatively resistant to late blight.
- "Belousovsky" - tasty, fruitful potatoes, but has an increased requirement for soil fertility. Does not tolerate drought, has resistance to late blight, loves feeding and watering very much.
And you can also name a few more relatively new varieties: "Naiad", "Lugovskoy", "Red Scarlet", "Vestnik".


Late blight is an insidious and dangerous disease. This can be judged at least because it has not been completely defeated for more than 100 years. It ruins about a quarter of the potato crop every year.
So far, the disease can only be suspended, muted, provided that all agrotechnical methods are observed, including regularly and on time to carry out both preventive and therapeutic measures.











The comment was sent successfully.