How to treat tomatoes from phytophthora?
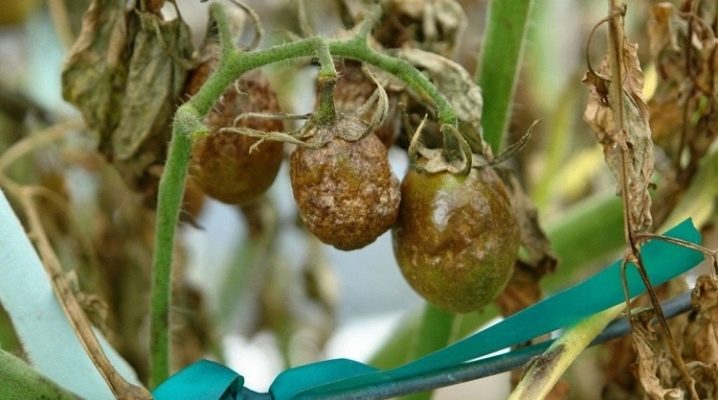

Late blight (popular name - late blight) has long become one of the most common tomato diseases. There are several methods of treatment, professional and folk, there is a clear line of prevention, and there is still the same gloomy statistics on the incidence of plants. A good fight is information preparation and a scheme according to which you need to care for tomatoes. Then they are not afraid of any late blight.
Description of the disease
Late blight is a fungal disease caused by a parasitic filamentous fungus. By the way, not only tomatoes are affected by the disease. They are also sick with potatoes and eggplants, peppers and raspberries, strawberries and cabbage. Orchids, peonies and gladioli are ill with it, and even some trees are affected by late blight. The fact is that fungal spores and mycelium quietly hibernate in the soil, survive even on garden tools. That is, they can easily be transferred from season to season.
Another name for the disease is brown rot, because its main symptom is the browning of the leaves, and then the fruits.


How late blight manifests itself:
- first, brown spots form at the bottom of some leaves, while on top the leaves are covered with an oily film, after getting wet it is visible immediately;
- spots will grow, blur, and tomato inflorescences will turn yellow and fall off;
- the developing disease leads to the fact that gray-brown spots pass to tomato bushes, appear already on the fruits;
- leaves begin to dry out en masse, tomatoes begin to rot, and this is all accompanied by an unpleasant odor;
- the spots become even darker, even the formation of a black plaque is possible.
This is not to say that late blight attacks tomatoes every year. We need (and this is important) suitable conditions for the tomatoes to get sick. If, for example, the summer is cold, without noticeable hot intervals, this is a big risk. If it rains for a long time, it is also very likely that phytophthora is expected. And it is also "helped" by dew loss, very thickened plantings, the presence of pests, proximity to potatoes, excessive soil liming.
If late blight has already appeared, you will not have to look closely at how the changes look on tomatoes for a long time. The disease develops quickly: in a few days, the disease easily manifests itself on all fruits. Therefore, one must not hesitate, one must quickly take matters into one's own hands.


What drugs should be treated?
The first spraying should start as soon as the first symptoms are found. Chemicals, of course, are the fastest and most reliable way to get rid of late blight, but far from the most environmentally friendly.
Chemical
Fungicides - this is what chemistry is called, which radically solves the problem of late blight. Let's see what remedies help get rid of the disease.
- Hom. This agent acts exclusively on the surface of fruits and leaves, does not penetrate inside. It is not for nothing that it is considered a preventive product. He will not be able to save the plant in the terminal stage. But if there is no mass infection yet, everything is quite solvable. If the preventive task is relevant, a five-time treatment is carried out, the procedures are repeated every 2 weeks. It must be borne in mind that the product is washed off by rain. The last processing should be carried out no later than 3 weeks before harvest.
- "Tattu". And this is also a popular fungicide, which is used if it is necessary to fight against a mass attack. First, it destroys the pathogen in the tissues of the bush, fruits.He also builds a system for further plant protection. It is also considered a stimulant for the growth of new shoots. That is, the replacement of the infected occurs. The fruits that had to be sprayed with this effective remedy can only be eaten after 2 weeks.
- Ordan. And this is a well-known complex fungicide that penetrates into tissues and destroys the fungus. Part of it remains on plant surfaces, it acts as a protection. That is, the plant is sprayed, and "Ordan" is active for 3 days for sure, possibly 4. It will protect the plant for 2 weeks. Tomatoes cannot be eaten for a week after processing.
- Ridomil Gold. A very powerful remedy that is used to treat seedlings on the third or fourth day after disembarkation. The procedure is repeated after 2 weeks. In total, you need to carry out 4 treatments.
A better known remedy is probably Bordeaux liquid. Quite an interesting composition that helps in the treatment of many diseases, and phytophthora too. But it is usually used to prevent ailment, as they cultivate the land before planting tomatoes. Another popular product is Furacilin, an antimicrobial and antifungal drug. Tomatoes will be processed with it during flowering, at the time of the appearance of ovaries and when the first fruits ripen.
Boric acid also helps tomatoes, which is also additionally fed by bushes.


Biological
If you don't want to touch chemistry at all, but there is phytophthora, and you need to do something with it, the option of using biological products is possible. These are good means for growing organic products. The most effective product today is Fitosporin. It has a valuable composition with beneficial microorganisms capable of destroying pathogens. It is both a preventive product and a remedy for treatment.
How Fitosporin works:
- you need to take only 2 teaspoons (you can with a slide) for 10 liters of water (preferably settled rainwater);
- the water temperature should be no higher than 35 degrees;
- the solution cannot be prepared in an aluminum or iron container;
- the solution must be left in the sun for 3 hours, so beneficial bacteria will be activated and multiplied in it;
- It is time to start processing within a couple of weeks after planting the seedlings, and it is carried out according to the schedule (every 10 days).
Even after harvesting, it makes sense to treat the soil with Fitosporin solution. Before the onset of frost, beneficial microorganisms will do their job. An alternative to this product is Trichopol. It is also included in the list of the most effective remedies in the fight against late blight. You can also use "Shining", "Baktofit", "Arilin".


Folk methods of struggle
A huge number of gardeners and gardeners do not use drugs at all, but prefer the so-called folk methods to them. Take saline, for example. One hundred grams of salt is stirred in 1 liter of water, and the affected plants are sprayed with this solution. Very simple, but certainly less effective than drugs.
Here are 8 popular recipes in the fight against late blight.
- Infusion of horsetail. It contains a lot of potassium, phosphorus, manganese and iron, and it also contains a lot of silicic acid. This acid prevents the plant from being attacked by the fungus. Or it no longer leaves the fungus a chance. Such spraying of tomatoes can be considered ecological. You can take a pound of fresh green horsetail leaves (or replace them with 100 g of a dried plant), pour 5 liters of water, wait for the end of fermentation. Dilution with water is in proportions 1: 5.
- Nettle decoction. Another very effective herb. Take a pound of fresh plant, 5 liters of water. The broth is boiled for about 30 minutes. After cooling, it is diluted with water in a ratio of 1: 5. It is precisely the problematic crop brushes that need to be sprayed. This spraying is usually done in early spring.
- Yeast. One cube of regular baker's yeast (it usually weighs 100 g) requires 10 liters of water. Sometimes another 0.5 liters of milk is sent there. Spraying with this composition is carried out once a week.
- Milk spraying. Milk in a ratio of 1: 5 is diluted with water, and the plants are also treated with this composition once a week. This is not to say that such a recipe is very effective, but still better than nothing.
- Garlic. Even the smell of garlic repels pests. Garlic arrows will be an excellent bactericidal and fungicidal agent. To make a garlic extract, you need to take 200 g of cloves, grind them, pour 10 liters of water for a day, strain through a strainer, pour the finished composition into a sprayer. But you can use it only immediately, then it will not be effective. But if you make a decoction, then in a dark place it can be stored for more than one week. But its use is a little less effective.
- Baking soda. Spraying soda is a fairly well-known move against late blight. It changes the pH of the leaves, creating an environment that is unattractive to the fungus. Spraying should be done every 2 weeks after rain. This can be done only in the morning, and it is good if the day is cloudy.
- Copper wire. The stem is pierced with a five-centimeter wire, the ends are bent at a distance of 10 cm from the ground. Copper scares off the pathogen, prevents it from attacking the plant.
- Ash and soap. Add 2 glasses of ash to 5 liters of water. And all this has been insisted for about 3 days. Then about half a piece of grated laundry soap is poured into this mixture. Once every two weeks, it is necessary to sprinkle tomatoes with this composition. It is completely safe to treat plants in this way.
But there are still recipes with brilliant green, fermented milk products (kefir and other liquids), tinder fungus. All of these compounds are used to water the culture from late blight.



Prevention measures
To protect a plant from a fungal disease, a whole complex of actions is needed. Let's see how you can effectively protect plants from massive disease.
- Organize the correct watering for the plant - with warm water and without the formation of subsequent stagnation. You will have to moisten the ground a couple of times a week. And it is better to do it early in the morning or late in the evening. Or in cloudy weather. Watering the plant is at the root. It is not necessary for the water to fall on the leaves.
- After watering or rain, the soil must be thoroughly loosened. This treatment promotes good root air exchange and does not allow moisture to stagnate.
- Mulching will also be an effective prevention: the beds can be covered with a layer of straw, hay, burlap. This will build a kind of barrier against infection, and not only late blight infection.
- During frosts, the beds are covered with foil overnight. Cold dew is another threat to the plant, therefore such a measure is absolutely necessary.
- Crop rotation is an important part of agricultural technology. Tomatoes should not be planted where nightshades grew last season. It is also better not to plant potatoes next to tomatoes.
- Garden soil must be disinfected in the spring. It must be treated with antifungal agents. Prevention should be started with just such a protection.
- When cold rains start, tomatoes become vulnerable. This means that after them, it is necessary to carry out treatment with antifungal drugs.
- Potassium and phosphorus should be added to the soil regularly.
- If you plant basil, rye, wheat near the tomatoes, then another powerful weapon will act against phytophthora.
- It is good if the sunniest place in the garden is given for the tomatoes. It will be harder for them in blackout.
- For the prevention of late blight, you can lay onion peels in the holes when planting seedlings.
- In the fall, it is imperative to dig deep into the soil. All tops are certainly removed and burned. True, this still does not promise one hundred percent death of the dispute. The best option is to bring new soil into the greenhouse.
Everything does not always work out the first time, but it is still better to learn from someone else's experience. And he suggests that you can also focus on those varieties of tomatoes that are not so vulnerable to late blight.



Resistant varieties
There are no completely resistant varieties yet, there are only relatively resistant ones. But this is already a lot.There are varieties of an early type of ripening, and they manage to give a crop without waiting for a massive outbreak of late blight.
The following varieties will be resistant: "Etual", "White filling", "Metelitsa", "Cameo", "Dubok", "Ballada", "Dubrava", "Pink dwarf", "Ephemer", "Yablonka Rossii", "Urozhainy "," Solnechny "," Siberian early ripening "and others.













The comment was sent successfully.